Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SBA 11 Discussion-Biology
Uploaded by
Nisha JodhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SBA 11 Discussion-Biology
Uploaded by
Nisha JodhanCopyright:
Available Formats
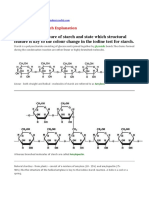
Benedict's reagent (often called Benedict's qualitative solution or Benedict's solution) is a
chemical reagent and complex mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate, and copper(II)
sulfate pentahydrate. When Benedict's solution and simple carbohydrates are heated, the
solution changes to orange red/ brick red. This reaction is caused by the reducing property
of simple carbohydrates. The copper (II) ions in the Benedict's solution are reduced to
Copper (I) ions, which causes the color change.
So, when the Benedict's test gives a negative result, add dilute hydrochloric acid and put this
in a water bath; this will hydrolise the bonds between the disaccharides (any of a class of
sugars whose molecules contain two monosaccharide residues) . Hydrogen carbonate is then
added to neutralise the solution as Benedick's reagent doesn't work under acidic conditions.
Why was sodium hydrogen carbonate added to the mixture?
Neutralization. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is necessary for neutrallization as the reduction
of the copper(II) ions will not take place in acidic conditions - of excess acid is present.
With diabetes, your body either doesn't make enough insulin or can't use it as well as it
should. Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body
turns food into energy.
Some complications/effects of diabetes are:
- Eye problems (retinopathy)
- Heart attack and stroke
- Kidney Problems (neuropathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
Some fruits which were recommended to diabetic patients are:
- Tangerine
- Lime
- Cucumber
- Gooseberry
These fruit were recommended because when tested there were very low sugar present in the
fruits, making it health enough for diabetic patients to intake.
You might also like
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Benedict's Test For Non-Reducing SugarsDocument2 pagesBenedict's Test For Non-Reducing SugarsSamer Ehab75% (4)
- Biology Paper 3 Guide (As-Level)Document17 pagesBiology Paper 3 Guide (As-Level)XEDGER0986% (7)
- Final ProjectDocument22 pagesFinal ProjectDevil KingNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Quantitative Reagent Contains Potassium Thiocyanate and Is Used To Determine How MuchDocument2 pagesBenedict's Quantitative Reagent Contains Potassium Thiocyanate and Is Used To Determine How MuchHOly makaroniNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing SugarDocument2 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing SugarMohammed Parfals100% (2)
- Describe The Structure of Starch and State Which Structural Feature Is Key To The Colour Change in The Iodine Test For StarchDocument9 pagesDescribe The Structure of Starch and State Which Structural Feature Is Key To The Colour Change in The Iodine Test For StarchFelix AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Molisch Test and Benedict TestDocument6 pagesMolisch Test and Benedict Testعلاوي البرشلونيNo ratings yet
- Reducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyDocument36 pagesReducing and Non-Reducing Sugars Test: Lab Activity in Preparation For Practical Exam AS Level BiologyAmisha JuraiNo ratings yet
- G03bio PDFDocument12 pagesG03bio PDFyasaman dahmardeNo ratings yet
- Benedict'S Test: Procedure Results && Discussion ApplicationsDocument20 pagesBenedict'S Test: Procedure Results && Discussion ApplicationsImmanuel Lashley33% (3)
- Benedict 2Document7 pagesBenedict 2Ronamae DelmarNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1JustineNo ratings yet
- Benedict's TestDocument7 pagesBenedict's TestRejie Mae Medrano100% (1)
- Dietary Fruit SbaDocument2 pagesDietary Fruit SbaannmarieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Qualitative Analysis of Simple Carbohydrates Using Benedict's TestDocument2 pagesExperiment 4: Qualitative Analysis of Simple Carbohydrates Using Benedict's TestSaif Khan100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectHuzaifa LokhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestion HandoutDocument3 pagesPhysiology of Digestion Handoutrolandroly93No ratings yet
- CarbohyratesDocument47 pagesCarbohyratesEdward SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesCarbohydratesChristine Ala67% (6)
- Biochemical TestsDocument2 pagesBiochemical TestsJacqueline DavisNo ratings yet
- Benedict's TestDocument2 pagesBenedict's TestArun PatelNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests: by Cheryl KentDocument7 pagesBiochemical Tests: by Cheryl KentNahusenay TewodrosNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument7 pagesFood TestsDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- Reducing SugarDocument2 pagesReducing SugarKiroz ChianNo ratings yet
- Iodimetry & IodometryDocument27 pagesIodimetry & IodometryAnjana Ponmili100% (2)
- Document 21Document1 pageDocument 21Mary Jane M. MorenoNo ratings yet
- English RPSDocument3 pagesEnglish RPSChichiFauziyahNo ratings yet
- Practical 2: Food TestDocument13 pagesPractical 2: Food TestNur Amirah HamzahNo ratings yet
- Occurence, Properties, Preparation, and Applications of Inorganic CompoundsDocument8 pagesOccurence, Properties, Preparation, and Applications of Inorganic CompoundsMuhammad Mustafa Ijaz100% (3)
- Biochemical Tests - Reducing Sugars & StarchDocument4 pagesBiochemical Tests - Reducing Sugars & StarchPrashasti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sodium Citrate ReviewerDocument3 pagesSodium Citrate ReviewerKeiffer Ann LopezNo ratings yet
- Discussion About Reducing SugarDocument3 pagesDiscussion About Reducing SugarAin NurfatihahNo ratings yet
- BenedictDocument10 pagesBenedictJose Ian Pagarigan BautistaNo ratings yet
- PrinatbleDocument13 pagesPrinatblethunder boltNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument27 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectMEGHA GOPENo ratings yet
- Lab 3 BfidDocument3 pagesLab 3 BfidAbdul Rafey NawazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Holiday HomeworkDocument25 pagesChemistry Holiday HomeworkManisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reducing and Non-Reducing Sugars LectureDocument13 pagesReducing and Non-Reducing Sugars LecturesamNo ratings yet
- Discussion (Food Tests)Document1 pageDiscussion (Food Tests)jaydon thomas (newband4)No ratings yet
- Action of Antacids: Chemistry Investiga Tory ProjectDocument16 pagesAction of Antacids: Chemistry Investiga Tory ProjectSairamRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chem Project Class 12 With Investigatory Project On ' Antacids'Document15 pagesChem Project Class 12 With Investigatory Project On ' Antacids'SHAHBAN55550% (1)
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- Acids and AlkalisDocument34 pagesAcids and AlkalisMoh AmedNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate TestsDocument3 pagesCarbohydrate TestsTomNaccaratoNo ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument7 pagesFood TestsborntolearnNo ratings yet
- Chem Group Project ManitDocument13 pagesChem Group Project Manitzahir khanNo ratings yet
- Project On Antacids Cbse ChemDocument15 pagesProject On Antacids Cbse ChemSairamRamakrishnan33% (3)
- Brandy To Water: Volumetric Chemical Analysis Redox Titration IodineDocument2 pagesBrandy To Water: Volumetric Chemical Analysis Redox Titration IodineSharla Jay Samaniego TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Determination of Total Chlorine ResidualDocument4 pagesDetermination of Total Chlorine ResidualJoseph PelaeloNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - POST LAB DISCUSSIONDocument6 pagesExperiment 2 - POST LAB DISCUSSIONMina BiancaNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY Project For Class 12Document19 pagesCHEMISTRY Project For Class 12Naveen Doss100% (1)
- REDOX TitrationsDocument132 pagesREDOX TitrationsAnis SayyedNo ratings yet
- Project ChemDocument13 pagesProject ChemAARYA PATHANIANo ratings yet
- HYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsDocument14 pagesHYP E R ACI D I T Y Cause FOR Intake OF AntacidsamuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Formula SheetDocument3 pagesCsec Physics Formula Sheetroneisha samuels100% (1)
- Ionic EquationsDocument3 pagesIonic EquationsNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chem Sba 4 and 5Document3 pagesChem Sba 4 and 5Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Vectors and ScalarsDocument6 pagesWeek 5 Vectors and ScalarsNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Changes in The States of MatterDocument8 pagesChanges in The States of MatterNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument1 pageChemistry AssignmentNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab-13 MarkchemeDocument1 pageChemistry Lab-13 MarkchemeNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- HSB Endocrine System and EyeDocument15 pagesHSB Endocrine System and EyeNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Handout On Digestion, Respiration, Circulation and TransportDocument47 pagesHandout On Digestion, Respiration, Circulation and TransportNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- SBA Reproduction in PlantsDocument1 pageSBA Reproduction in PlantsNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document3 pagesChapter 3Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sba 6Document2 pagesChemistry Sba 6Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- SBA Mark, Release and Recapture Technique (AI)Document3 pagesSBA Mark, Release and Recapture Technique (AI)Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Cells and Movement Across Cell MembraneDocument10 pagesCells and Movement Across Cell MembraneNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Exretion and HomeostasisDocument12 pagesExretion and HomeostasisNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Discussion # 11Document1 pageBio Lab Discussion # 11Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Biology SBADocument2 pagesBiology SBANisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Circulation, Lymphatic and Skeletal SystemDocument29 pagesCirculation, Lymphatic and Skeletal SystemNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment ResearchDocument1 pageBiology Assignment ResearchNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Excretion Homeostasis Skeletal System IrritabilityDocument37 pagesExcretion Homeostasis Skeletal System IrritabilityNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language UsesDocument12 pagesFigurative Language UsesNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Discussion # 9Document1 pageBio Lab Discussion # 9Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Passes in Business Studies SubjectsDocument2 pagesPasses in Business Studies SubjectsNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- 2020 It SyllabusDocument118 pages2020 It SyllabusNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- SVN SS SBA Guidelines (Aug 2021)Document54 pagesSVN SS SBA Guidelines (Aug 2021)Nisha JodhanNo ratings yet