Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PCOG
Uploaded by
Chester John SotomilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PCOG
Uploaded by
Chester John SotomilCopyright:
Available Formats
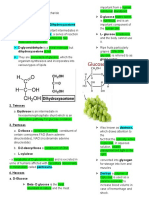
GLYCOSIDES − Aldehyde group
− Phenol group
− compounds that yield one or more sugars among the product
of hydrolysis CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES
− A glycoside is any molecule in which a sugar group is bonded − Related to steroids, CPPP nucleus
through its anomeric carbon to another group via glycosidic − Sugar component is attached on the 3 position of the CPPP
bond. nucleus
o Cyclo, pentano, perhydro, phenanthrene
In aqueous solution hexoses and pentoses will cyclize, forming − 2 aglycone
alpha (a) and beta (B) forms o (1) cardenolides
o (2) bufadienolides (discovered from BUFALIN
− Trivial names have an “in” ending and the names indicate the isolated from the skin of toad)
source of glycosides
− Examples: 1.LEIBERMANN-BURCHARD TEST
o digitoxin — from Digitalis − Tests the cardenolides/ bufadienolides
o Salicin from Salix
o Prunasin from Prunus 2.KEDDE REACTION
− Tests the presence of the lactone ring
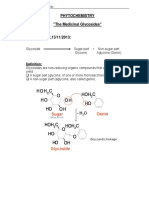
− Systematic Names are usually formed by replacing the “ose” − Detect the presence of cardiac glycosides
suffix of the parent sugar with “oside”. The anomeric prefix (a-
or b- )and the configurational prefix (D or L) immediately 3.KELLER-KILIANI
precede the sugar stem name, and the chemical name of the − 2-deoxy sugars
aglycone precedes the name of sugar.
− Example: Salicin – o – hydroxy – methylphenol B-D-
glycopyranoside CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES: ACTION
− The most frequently occurring sugar is B-D- glucose, although − Inotropic effect – the ability to increase the force of systolic
rhamnose, digitoxose, cymarose and other sugars are contraction
o Can increase bp
component of glycosides
− Depletion of Potassium ions increases Digoxin Toxicity
− Glucoside – when the sugar formed is glucose
− Glycoside – when other sugar other than glucose is produced.
1.DIGITALIS (without arrythmia)
− AN ARRYTHMOGENIC
GLYCOSIDES: COMPONENTS
− SOURCES
− Aglycone, aglycon, or genin — non sugar component of
o Foxglove (D. Purpurea)
glycosides
o Grecian foxglove (D. lanata)
− Glycone — sugar component
SCROPHULARIACEAE (Active Glycosides)
GLYCOSIDES: IMPORTANCE
DIGITALIS PURPUREA DIGITALIS LANATA
− Involved in its regulatory, protective and sanitary functions of
Digitoxin Digoxin
plants
Gitaloxin Desacetyl Lanatoside
− Therapeutic agents Gitoxin (deslanoside)
*Digitoxin past DOC for CHF but now is Digoxin
GLYCOSIDES: OCCURRENCE
*Shorter Half life, shorter duration of action
− Widely distributed in the plant kingdom
o fruits, Seeds, Barks, Leaves *Digoxin and Digitoxin: has narrow therapeutic index/window
− Animals (relatively rare) *0.5-1.5 ng/mL
*Digoxin – less protein binding
CLASSIFICATION OF GLYCOSIDES BASED ON GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES: DIGOXIN
1. O-glycosides — phenol or OH group
2. N-glycoside — N of amino group (NH) − More commonly used
3. S-glycosides — S of thiol group (SH) − It is polar because of the —OH group in the structure
4. C-glycosides—on C atom − Easily eliminated therefore, short acting.
o Pigeon — used in the bioassay (potency)
o Antidote: Digoxin Immune fab
CLASSIFICATION OF GLYCOSIDES BASED ON THE CHEMICAL − Inotropic agent
NATURE OF THE AGLYCONE GROUP
CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES: DIGITOXIN
− Cardioactive Steroid group − Lipophilic
− Anthraquinone group − Longer half life
− Saponin group − Before it is the drug of choice for CHF but now, it used in the
− Cyanophore group management of arrhythmia, atrial fibrillations
− Glucosinolate or Isothiocyanate group − Deslanoside — It is used for rapid digitalization
− Flavonol group
− Alcohol group
2.CONVALLARIA ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDES
− AKA: Lily of the Valley − related to anthracene
− Liliaceae − Upon hydrolysis yield syne that are di-, tri-, or
− From Convallaria Majalis tetrahydroxyanthraquinones or modification of these
− Liliaceae compounds.
− CONVALLOTOXIN o Example. Frangulin A, which hydrolyze to emodin(1,6,8-
o active component trihydroxy3- methylanthraguinone) and rhamnose.
o Not recommended o Penicillium islandicum — species that produce several
anthraquinone glycosides.
3.APOCYNUM
− AKA: Black Indian hemp, Dog Bane − anthranols are converted upon oxidation into anthraquinones.
− From Apocynum cannabinum − Schonteten’s test → is often used for anthranols
− CYMARIN – active cardiac glycoside − Anthranolsand anthrones are the main constituents of
APOCYANACEAE chrysarobin, a mixture of substances
4. ADONIS ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDES: USE
− Stimulant cathartics
− AKA: Pheasant’s Eye
− exert their action by increasing the tone of the smooth muscle
− From Adonis Vernalis
in the wall of the colon and stimulate the secretion of water
− Ranunculaceae
and electrolytes into the large Intestine.
− Constituent: ADONITOXIN, CYMARIN, K-STROPHANTIN
− Detected by Borntrager test
− (+) red or pink coloration at the lower ammoniacal region
5.CACTUS GRANDIFLORUS
− Occur in plants as hydroxylated, methylated or carboxylated
− CACTUS GRANDIFLORUS
− AKA: Night Blooming Cereus
− From Selenicereus grandifloras 1.Cascara Sagrada
− CACTACEAE − Rhamnuss purshiana; Sacred bark
− Causes positive inotropic effect
Source/s:
6.BLACK HELLEBORE − Rhamnus purshiana (Rhamnaceae)
− AKA: Christmas Rose − Rhamnus- ancient classical name of buckthorn
− From Helleborus niger − Purshiana — given in honor of the German botanist, Friedrich
− RANUNCULACEAE Pursh
− HELLEBRIN — constituent − Use: Cathartic
3 variety 2 Types of Anthracene compounds
− Black — glycosidal, cardiac stimulant (inotropic) − normal O- glycosides(based on emodin) — about 10 —
− Green and White — alkaloidal, cardiac depressant 20%
− aloinlike C- glycosides- about 80 — 90%
7.STROPHANTHUS − Ex. Barbaloin and deoxybarbaloin( chrysaloin)
− From S. kombe and S. hispidus
− Component: K. strophantoside
− G. strophantin (ouabain) - 3rd most important glycoside Main active principals:
available in the market − Cascarosides A → based on optical isomers of barbaloin
− Use in hunting − Cascarosides B
− Apocynaceae − Cascarosides C → based on optical isomers of chrysaloin
− Cascarosides D
8.SQUILL OR SQUILL BULB
− From Urginea maritima
2.Frangula
− HYACINTHACEAE
− Rhamnus frangula Linne; BUCKS aes - Component of OTC
− Component: SCILLAREN- A, convert to scillarenin which is
product MOVICOL- also contains karaya
more active
− Laxative effect
− (made up of scillarenin, glucose and rhamnose)
− Due to presence of frangulins A and B and related
− Use: expectorant
glucofrangulins
− Red variety: rodenticide (used for rats)
3.Aloes
9.ADELFA
− It yields not less than 50% of the water soluble extractive
− From Nerium oleander
− Aloes occur on the market as opaque masses that range from
− APOCYNACEAE
reddish black to brownish brown in color
− Genocide in Sri lank
− The taste of each variety of aloe is nauseating and bitter
− Component: Oleandrin, Digitalinum verum
− The characteristic odor 5 disagreeable Aloes are typical
− Oral ingestion — can cause poisoning
xerophytic plants.
− Mimics digoxin − types
o Curacao aloe
o Cape aloe
a. Curacao aloe − -1,6-dihydroxyanthraquinone is the natural constituent, but it
− Aloe barbadensis, Aloe vera is difficult to isolate.
− pharmaceutic aid for Compound Benzoin Tincture . − prepared synthetically from 1, 8-anthraquinone potassium
disulfonate.
b.Cape aloe
− Aloe ferox, Aloe africana, Aloe spicata USES: Cathartic → Is an important intermediate in the manufacture
of anthralin and of alizarin and indanthrene dyestuffs
Cathartic → elicits drastic cathartic action
Aloe Vera gel
− Fresh mucilaginous gel contained in the parenchymatous
tissue in the center of the leaves of A. barbadensis
− for the treatment of burns, abrasions and other skin irritations.
− Moisturizing and emollient properties
− (taken from the mucilage of the leaf)
Principal anthraquinone glycosides
− Aloin A — barbaloin
− Aloin B — isobarbaloin
Inactive ingredients including large amounts of ( 16 to 63%) of
a resinous material plus volatile oil
4.Rhubarb
− Rheum officinale; Rheum
− R. palmatum; Chinese rhubarb
− R. emodi; Himalayan Rhubarb
− R. webbianum; Indian Rhubarb
− Use: Drastic cathartic
5.Senna
− Cassia acutifolia; Alexandria senna
− Cassia angustifolia; Tinnevelly senna ( Fam. Fabaceae)
− Use: - Cathartic
− Senna is graded according to the size of the leaf and the color
of the leaflets:
− Dimeric glycosides- principal active constituents of senna
whose aglycones are composed of aloe-emodin and/or rhein
− Sennosides A and B pair of stereoisomers whose aglycones are
rhein dianthrone (sennidin A and B) Sennosides C and D are
minor constituents having dimeric aglycone Senna pods also
contain useful, active glycosides; some of the primary
glycosides in the pods have as many as 10 sugar molecules
attached to a rhein dianthrone nucleus
− Blue green —best grade, yellowish — poorest
− Cultivated on wet lands resembling rice paddies
CHRYSAROBIN
− Is a mixture of neutral principles obtained from Goa powder
− Obtained in the lysogenous cavities in the wood of Andira
araroba
− Hot benzene is used to extract chrysarobin ( 50-70%) yields
from Goa powder
− A representative sample contains approximately 30- 40% of
chrysophenolanthrone or chrysophenolanthranol, 20%
emodinanthrone-monomethyl ether, and 30% of dehydro-
emodinanthrone- monomethyl ether
USE:
− Keratolytic - psoriasis, trichophytosis and chronic eczema.
− Itis very irritating to mucous membranes and should not be
used on the face or scalp.
DANTHRON or CHRYSARIN
− -1,8- DIHYDROXYANTHRAQUINONE
You might also like
- Pharmacognosy Notes For D. Pharm # 1Document15 pagesPharmacognosy Notes For D. Pharm # 1Amol Raut83% (315)
- CABALIDA - Herbal PlantsDocument29 pagesCABALIDA - Herbal PlantsJeralyn CABALIDANo ratings yet
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseFrom EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of IndiaDocument238 pagesMedicinal and Aromatic Plants of Indiashreya bhardwaj100% (1)
- GlycosidesDocument52 pagesGlycosidesAhmed Kamran Abbasi50% (4)
- GLYCOSIDESDocument31 pagesGLYCOSIDESasma nizamNo ratings yet
- GlycosidesDocument9 pagesGlycosidesnilumpharmNo ratings yet
- CatalogDocument126 pagesCatalogHerbs For Life100% (1)
- Glycosides 1Document11 pagesGlycosides 1thetmaroothetmaroo42No ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Glycosides Intro, ClassificationDocument6 pagesLecture 17 - Glycosides Intro, Classificationahsanonweb1983No ratings yet
- PHR 113 GlycosidesDocument20 pagesPHR 113 GlycosidesRahul Banik888No ratings yet
- Glycoside Hand OutsDocument4 pagesGlycoside Hand OutsAlmabella GecoleNo ratings yet
- Glycosides 1Document78 pagesGlycosides 1Jessa LatorreNo ratings yet
- Glycosides 1Document19 pagesGlycosides 1Bismah SaeedNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- Prelims Reviewer Biochem LecDocument6 pagesPrelims Reviewer Biochem LecRiah Mae MertoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Glycosides ShortenedDocument114 pagesLecture 6 - Glycosides ShortenedToukir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glycosides: Next SlideDocument4 pagesGlycosides: Next SlideJonafe JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Glycosides: Classification of Glycosides On The Basis of Aglycone MoietyDocument3 pagesGlycosides: Classification of Glycosides On The Basis of Aglycone MoietyAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Glycosides - Part4Document23 pagesGlycosides - Part4Fuad RimawiNo ratings yet
- GlycosidesintroductionDocument41 pagesGlycosidesintroductionvershaparchaNo ratings yet
- Glycosides May Be Defined As The Organic Compounds From PlantsDocument16 pagesGlycosides May Be Defined As The Organic Compounds From Plantsratheeshkumar100% (2)
- Glycosides and Tannins NotesDocument3 pagesGlycosides and Tannins NotesGift Summer DinoNo ratings yet
- GlycosidesDocument67 pagesGlycosidesdiptishona143100% (1)
- Carbs 2Document6 pagesCarbs 2Biang AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Glycosides SAE ADDocument47 pagesGlycosides SAE ADAsif SaleemNo ratings yet
- 06-08 - Carbohydrates - Complex Carbohydrates (1) - 1Document31 pages06-08 - Carbohydrates - Complex Carbohydrates (1) - 1Frankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Ii: Grape SugarDocument31 pagesCarbohydrates Ii: Grape SugarVivien IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24Document25 pagesLecture 6-Carbohydrates Spring 24ziadwageh74No ratings yet
- Lec.1 Glycosides Hala 2014 Pharos PDFDocument9 pagesLec.1 Glycosides Hala 2014 Pharos PDFRamling PatrakarNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument25 pagesBiochem MidtermsYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- PharmacognosyDocument101 pagesPharmacognosyimam mahdi tv officialNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 GlycosidesDocument66 pagesChap 6 GlycosidesUkash sukarmanNo ratings yet
- Non Energy Role of CarbohydratesDocument34 pagesNon Energy Role of CarbohydratesDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Glycosides - Part 2Document29 pagesGlycosides - Part 2Fuad RimawiNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - CarbohydrateDocument5 pagesFood Chemistry - CarbohydrateElisa AngelNo ratings yet
- Wk. 1 - GlucoseDocument5 pagesWk. 1 - GlucoseChie HisuganNo ratings yet
- K2 - Tanin, Glikosida, KumarinDocument41 pagesK2 - Tanin, Glikosida, KumarinSafira Wahyu UtariNo ratings yet
- GlycosidesDocument124 pagesGlycosidesMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- 2B BiochemistryDocument53 pages2B BiochemistryYashNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8. Monosaccharide DerivativesDocument8 pagesLesson 8. Monosaccharide DerivativesPrincess-Nadeera Sangkula PungutanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Carbohydrates 2018Document109 pagesUnit 2 Carbohydrates 2018Christine Annmarie TapawanNo ratings yet
- Gain of Electrons Gain of Hydrogen Loss of Oxygen Loss of Electrons Loss of Hydrogen Gain of OxygenDocument30 pagesGain of Electrons Gain of Hydrogen Loss of Oxygen Loss of Electrons Loss of Hydrogen Gain of OxygenA-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieNo ratings yet
- Glycosides and TanninsDocument73 pagesGlycosides and Tanninshermella tegegneNo ratings yet
- Farmakognosi 7Document29 pagesFarmakognosi 7Randi RasyidNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Polysaccharides ActivityDocument3 pagesBiochemistry - Polysaccharides ActivityAllen Paul CoveroNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument64 pagesCarbohydratesErwin CredoNo ratings yet
- SugarDocument30 pagesSugarmamuuramadanNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument6 pagesBio ReviewerMr. DADANo ratings yet
- To Their Function.: Description and Function of Common PolysaccharidesDocument5 pagesTo Their Function.: Description and Function of Common PolysaccharidesJeyan BoncavilNo ratings yet
- (CN 112) 1st Exam ReviewerDocument6 pages(CN 112) 1st Exam Reviewermariyvonne01No ratings yet
- Glyc o SidesDocument151 pagesGlyc o Sidesbakhtawar shaikhNo ratings yet
- 251120190carbohydrates (2) 2019Document26 pages251120190carbohydrates (2) 2019slmen1269No ratings yet
- Glyc o Side TanninDocument69 pagesGlyc o Side TanninRamayda juza AbedinNo ratings yet
- Bio Bnu Carb - PrintDocument12 pagesBio Bnu Carb - Printmuhammadnewhuss2No ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY FinalDocument21 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY FinalJoliem Phya E. IdongNo ratings yet
- By Glycone/presence of Sugar: Functions of The Products of Reactions of Monosaccharides ClassificationDocument5 pagesBy Glycone/presence of Sugar: Functions of The Products of Reactions of Monosaccharides ClassificationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- SaccharidesDocument4 pagesSaccharidesmachdellangeloramziNo ratings yet
- Biographic of YogiDocument22 pagesBiographic of YogiKaveen VijayNo ratings yet
- Content Will Be Covered:: Fructose Metabolism Galactose Metabolism Uronic Acid PathwayDocument21 pagesContent Will Be Covered:: Fructose Metabolism Galactose Metabolism Uronic Acid PathwaygaasheNo ratings yet
- Xi Chapter 9 BiomoleculesDocument18 pagesXi Chapter 9 BiomoleculesStudy BoiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Naturally Occurring Nitrogen Heterocycles from CarbohydratesFrom EverandSynthesis of Naturally Occurring Nitrogen Heterocycles from CarbohydratesNo ratings yet
- Document 9Document8 pagesDocument 9sapphireNo ratings yet
- Formular de ComandaDocument31 pagesFormular de ComandaCampean IoachimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER I BOS CONCEPTUAL 3 MarchDocument29 pagesCHAPTER I BOS CONCEPTUAL 3 MarchCharity CotejoNo ratings yet
- Boards Garden Ph-2Document32 pagesBoards Garden Ph-2Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Role of Herbs in CosmeticsDocument78 pagesUnit - IV: Role of Herbs in CosmeticsPuneet WasanNo ratings yet
- New PRDocument23 pagesNew PRjelosaliva2No ratings yet
- 40 Ways To Use Aloe VeraDocument2 pages40 Ways To Use Aloe VeraMark Anthony Seballa TubioNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera BatteryDocument5 pagesAloe Vera BatterySeenivasagam SeenuNo ratings yet
- Herbs Ni TatayDocument39 pagesHerbs Ni TatayI-Reen FrancisquiteNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Aloe Vera StudyDocument5 pagesA Comprehensive Aloe Vera StudyVladianu DanNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Its BackgroundDocument5 pagesIntroduction and Its BackgroundalexaflarepetalcorinNo ratings yet
- A Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantDocument4 pagesA Review On Biological Properties of Aloe Vera PlantIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaDocument17 pagesMedicinal Plant (Rahul Sharma) ChambaRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Honest Products CG List & CombosDocument9 pagesHonest Products CG List & CombosAthira SomanNo ratings yet
- 431 417 1 PBDocument6 pages431 417 1 PBHanif KrisnajatiNo ratings yet
- Basundi : Patel and Upadhyay (2003) ConcludedDocument7 pagesBasundi : Patel and Upadhyay (2003) ConcludedAshutosh MasihNo ratings yet
- Discover Limu PlusDocument12 pagesDiscover Limu PlusmscaramelleNo ratings yet
- Aloe VeraDocument22 pagesAloe VeraNazatul Firdaus ZainonNo ratings yet
- Natural Aloe Vera Concentrate 10X MSDSDocument3 pagesNatural Aloe Vera Concentrate 10X MSDSThida WinNo ratings yet
- Babaria English Company InformationDocument22 pagesBabaria English Company InformationSera Hernandez PuenteNo ratings yet
- Forever Living Products Catalogue 2019Document44 pagesForever Living Products Catalogue 2019Ayush MittalNo ratings yet
- 01 Aloe VeraDocument6 pages01 Aloe VeraPatrisia HallaNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument10 pagesResearch PaperEllah Franzien Dutillos EderNo ratings yet
- Medicinalplantsmaster 1Document490 pagesMedicinalplantsmaster 1Tehuti byNatureNo ratings yet
- Aloe Vera For Human Nutrition Health and Cosmetic Usea Review PDFDocument9 pagesAloe Vera For Human Nutrition Health and Cosmetic Usea Review PDFNatalia MenottiNo ratings yet
- Sip Aloe Vera Plant As Termiticide Final1Document7 pagesSip Aloe Vera Plant As Termiticide Final1Brendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet