Professional Documents
Culture Documents
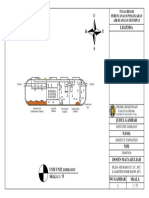
1.3.1.1 Representations
1.3.1.1 Representations
Uploaded by
fernando_falcon_9Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
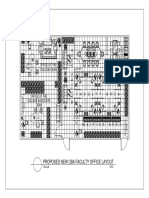
1.3.1.1 Representations
1.3.1.1 Representations
Uploaded by
fernando_falcon_9Copyright:
Available Formats
TYPES OF EXPLANATIONS
pecifies the CONSTITUENTS OR
S
COMPONENTS of the phenomenon
OT YET A DEFINITION because NOT
N
CONSTITUTIVE EXPLANATION SUFFICIENT FOR DEMARCATION
he phenomenon is linked to an
T
ANTECEDENT CAUSE
he nature of these three types of
T
CAUSAL EXPLANATION explanation, best understood if placed in a
LEVELS-OF-ANALYSIS FRAMEWORK
pecifies the detailed steps that MEDIATES
S
BETWEEN THE CAUSE & THE
EXPLANANDUM
ETIOLOGICAL
MECHANISTIC EXPLANATION
he explanandum is NOT AN ENTITY but a
T
CONSTITUTIVE
CAUSAL RELATION between entities
evel A is LOWER than level B if the entities
L
an be distinguished on the basis of
C
at level A ARE PARTS OF THE ENTITIES AT
MEREOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS
LEVEL B
he explanantia ARE CAUSAL FACTORS
T
CAUSAL EXPLANATION SITUATED AT THE SAME LEVEL of analysis
as the explanandum
ONSTITUTIVE EXPLANATIONS specifies
C
LEVELS OF ANALYSIS the PARTS OF THE EXPLANANDUM
tart from and BUILD ON CAUSAL
S
EXPLANATIONS in that they specify the
mechanisms at a lower level of analysis
that mediate between the causal entities
and the explanandum
ONSTITUTIVE & MECHANISTIC
C
The explanantia ARE PARTS I n addition, specifies THE WAY IN WHICH
EXPLANATION
different parts and activities are
1 .3 TYPES OF ORGANIZED
EXPLANATION AND ARTS have a LOCATION, SHAPE, &
P
LEVELS OF ANALYSIS ORIENTATION
ECHANISTIC EXPLANATIONS specifies
M
the PARTS OF THE MECHANISM that ARTS are the STRUCTURAL ASPECT of the
P
mediates between the cause and the explanation
explanandum and the ACTIVITIES that
spell out the causal relations between parts re FUNCTIONAL in that they are
A
SPECIFIED IN TERMS OF WHAT THEY DO
OR ACCOMPLISH
CTIVITIES are the FUNCTIONAL ASPECT of
A
the explanation
I n MECHANISTICS EXPLANATION &
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS the OUTPUT of the
activities IS THE EXPLANANDUM
xplanations that specify activities but
E
leave out structural details are dubbed
FUNCTIONAL ANALYSES I f the CONSEQUENCES of an
explanandum are ENVISAGED we speak of
a FUNCTIONAL (TELEOLOGICAL)
EXPLANATION
he OBSERVABLE INPUT is called the
T
SYSTEM produces an OBSERVABLE
A
STIMULUS, and the OBSERVABLE OUTPUT
OUTPUT (effect) IN RESPONSE TO AN
At this level, a PROCESS is described in is a BEHAVIORAL or PHYSIOLOGICAL
OBSERVABLE INPUT
terms of its OBSERVABLE INPUT, its RESPONSE
OBSERVABLE SUPER-LEVEL
OBSERVABLE OUTPUT, and the RELATION
he TRANSITION FROM INPUT to OUTPUT
T between the two he mechanism between input and
T
can be called a PROCESS and is mediated
output is treated as a BLACK BOX
by the mechanism as a whole
he mechanism is DECOMPOSED into
T
SUBMECHANISMS, which can themselves t the final stage of decomposition, they
A
be described in terms of their input, correspond to BRAIN PROCESSES situated
outputs and interrelations at the BRAIN SUPER-LEVEL
Each of the submechanisms at the mental
MENTAL SUPER-LEVEL super-level may be decomposed further
he intermediate inputs and outputs,
T into finer-grained submechanisms I n SOCIAL SCIENCES a SOCIAL SUPER-
which are NOT OBSERVABLE, are called he BIG BLACK BOX is recursively
T
HE THREE LEVELS ARE SITUATED IN THE
T LEVEL can be proposed, where regular
MENTAL REPRESENTATIONS and their DECOMPOSED INTO LITTLE BLACK BOXES
INDIVIDUAL patterns of interactions between
RELATIONS or ACTIVITIES among them are all the way down
individuals are specified
called MENTAL OPERATIONS
THREE SUPER-LEVELS
BRAIN SUPER-LEVEL
ONTOLOGICAL QUESTION
echanistic philosophers see inter-levels
M I s CAUSES should be SEPARATED FROM &
hat is the relation between
W
relations as CONSTITUTIVE and therefore PRECEDE THEIR EFFECTS, then CAUSAL
MEREOLOGICAL LEVELS
IDENTITY RELATIONS RELATIONS are STRICTLY INTRA-LEVEL
IGHER LEVEL THEORIES are EXPLAINED
H
CLASSIC REDUCTIONISM
AWAY by LOW LEVEL THEORIES
EPISTEMOLOGICAL QUESTION IGHER & LOWER LEVEL THEORIES
H
NEW-WAVE REDUCTIONISM
INSPIRE AND CONSTRAIN EACH OTHER
hat is the relation between the
W
SCIENTIFIC THEORIES the four super-levels ACH SCIENCE CONTRIBUTES in a NON-
E
"MOSAIC" UNITY OF THE SCIENCES REDUCTIVE but still INTERDEPENDENT
WAY
RANT EACH LEVEL FULL EXPLANATORY
G
EXPLANATORY PLURALISM
AUTONOMY
You might also like
- Csypra3 Assignment 2 2020Document15 pagesCsypra3 Assignment 2 2020Tshepo Moloto100% (1)
- Powerade PerformanceDocument8 pagesPowerade Performancemarco jansenNo ratings yet
- AMBERLYST BD20 Brochure - FINAL - 31102007Document6 pagesAMBERLYST BD20 Brochure - FINAL - 31102007Lim Chee SiangNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P3 Feb-March 2010 Eng MemoDocument8 pagesMathematics P3 Feb-March 2010 Eng MemoBonnie Mathula100% (1)
- Definición General 412a 1-29Document1 pageDefinición General 412a 1-29fernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Theory Development and Concepts: 1.1 Demarcation-Explanation CycleDocument1 pageCh. 1: Theory Development and Concepts: 1.1 Demarcation-Explanation Cyclefernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- The Final Cause IDocument1 pageThe Final Cause Ifernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Four-Causal Account of Explanatory AdequacyDocument1 pageFour-Causal Account of Explanatory Adequacyfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Piri Reis Maritime University - Literature Study - 1Document1 pagePiri Reis Maritime University - Literature Study - 1bhanu prakash palletiNo ratings yet
- Structur E Present Tense: Opening Pharagrap HDocument1 pageStructur E Present Tense: Opening Pharagrap HWilliam DeliNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Aug-2021Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07-Aug-2021Mohammad TaushifNo ratings yet
- Descarga Eléctrica - Agua - HungríaDocument1 pageDescarga Eléctrica - Agua - HungríaVanessa QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Concept Map QCTDocument1 pageConcept Map QCTarlene bobadillaNo ratings yet
- E Is An ADECUATE Explanation Iff E Correctly Cites Each of The Four CausesDocument1 pageE Is An ADECUATE Explanation Iff E Correctly Cites Each of The Four Causesfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- (Stats) InfographyDocument1 page(Stats) InfographyRIYA RIYANo ratings yet
- 3rd and 4th Quarter TosDocument2 pages3rd and 4th Quarter TosMary Seal Cabrales-PejoNo ratings yet
- Powerade SpeedDocument8 pagesPowerade Speedmarco jansenNo ratings yet
- Denah JohkasouDocument1 pageDenah JohkasouAngely JaitNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument1 pageTable of SpecificationAple RigorNo ratings yet
- Oral Com TosDocument4 pagesOral Com TosApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- Tos Pe 12 2022-2023Document1 pageTos Pe 12 2022-2023MAE ANN TOLENTINONo ratings yet
- Nicole PDFDocument1 pageNicole PDFAnn Jeannette PerezNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Types of Explanation and Levels of AnalysisDocument1 page1.3 Types of Explanation and Levels of Analysisfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- 1.3 Types of Explanation and Levels of Analysis - 2Document1 page1.3 Types of Explanation and Levels of Analysis - 2fernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Ch. 1: Theory Development and Concepts: 1.1 Demarcation-Explanation CycleDocument1 pageCh. 1: Theory Development and Concepts: 1.1 Demarcation-Explanation Cyclefernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- The Efficient CauseDocument1 pageThe Efficient Causefernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- The Final Cause IDocument1 pageThe Final Cause Ifernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- E Is An ADECUATE Explanation Iff E Correctly Cites Each of The Four CausesDocument1 pageE Is An ADECUATE Explanation Iff E Correctly Cites Each of The Four Causesfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Four-Causal Account of Explanatory AdequacyDocument1 pageFour-Causal Account of Explanatory Adequacyfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Primary Orientation of These Arguments - Without Matter and Form We Cannot Solve A Significant Puzzle About CHANGE & GENERATIONDocument1 pagePrimary Orientation of These Arguments - Without Matter and Form We Cannot Solve A Significant Puzzle About CHANGE & GENERATIONfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Definición General 412a 1-29Document1 pageDefinición General 412a 1-29fernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Bill Frisell - Girl Ask Boy, pt.1Document1 pageBill Frisell - Girl Ask Boy, pt.1fernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- CAGED - Major PentatonicDocument1 pageCAGED - Major Pentatonicfernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Cassia Eller - Partido AltoDocument2 pagesCassia Eller - Partido Altofernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Sting - La Belle DameDocument3 pagesSting - La Belle Damefernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Ch. II - of The State of NatureDocument1 pageCh. II - of The State of Naturefernando_falcon_9No ratings yet
- Telling Time PPT For KidsDocument23 pagesTelling Time PPT For KidsKLeb VillalozNo ratings yet
- Royal Roads University GCSPCC Program Guide PDFDocument26 pagesRoyal Roads University GCSPCC Program Guide PDFGarvit ChopraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17: From Rates To Ratios: Student OutcomesDocument6 pagesLesson 17: From Rates To Ratios: Student Outcomesdrecosh-1No ratings yet
- Hahnemannian Proving and Clinical Verification of Caesalpinia SappanDocument74 pagesHahnemannian Proving and Clinical Verification of Caesalpinia SappanJames WatsonNo ratings yet
- Assignment (ENG 413)Document2 pagesAssignment (ENG 413)Mohammad Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Research Papers Are Written in What TenseDocument4 pagesResearch Papers Are Written in What Tensej0lemetalim2100% (1)
- Iucn 2014 014Document108 pagesIucn 2014 014aebrachoNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: Lecture 8: What Is Human Nature ?Document32 pagesCritical Thinking: Lecture 8: What Is Human Nature ?Alishba KhanNo ratings yet
- 11 GR AspectDocument3 pages11 GR AspectAizhamal SakhNo ratings yet
- Markov Decision Processes and Dynamic Programming: A. Lazaric (Sequel Team @Inria-Lille)Document79 pagesMarkov Decision Processes and Dynamic Programming: A. Lazaric (Sequel Team @Inria-Lille)ZelvatoreNo ratings yet
- Storytelling Score SheetDocument2 pagesStorytelling Score SheetZykehNo ratings yet
- Lectures On CFD Multiphase Flow PDFDocument62 pagesLectures On CFD Multiphase Flow PDFPhilippe LAVOISIERNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument21 pagesDatasheetziya tutuNo ratings yet
- Maternal Occupational Exposure To Chemicals in The Textile Factory During Pregnancy Is Associated With A Higher Risk of Polydactyly in The OffspringDocument14 pagesMaternal Occupational Exposure To Chemicals in The Textile Factory During Pregnancy Is Associated With A Higher Risk of Polydactyly in The Offspringmahrani_adrinNo ratings yet
- Roult's LawDocument14 pagesRoult's LawDrMamshad AhmadNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Lithium Concentration in Drinking Water and Suicide Mortality A Systematic ReviewDocument6 pagesThe Relationship Between Lithium Concentration in Drinking Water and Suicide Mortality A Systematic ReviewGuntur YohanesNo ratings yet
- Jensen Shoes: Jane Kravitz Story: Study Group D5Document8 pagesJensen Shoes: Jane Kravitz Story: Study Group D5deadNo ratings yet
- Health10 Q3 Module2 V2 (Bedico)Document11 pagesHealth10 Q3 Module2 V2 (Bedico)Bea LegaspiNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument3 pagesAcknowledgementNadaanParindaNo ratings yet
- OECD 201 Freshwater Algae Cyanobacteria Growth Inhibition TestDocument25 pagesOECD 201 Freshwater Algae Cyanobacteria Growth Inhibition TestEllóra Diniz GomesNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics ScriptDocument1,316 pagesQuantum Mechanics ScriptsalmanNo ratings yet
- ComplexometricDocument3 pagesComplexometricSneha MunjewarNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam P2Document13 pagesMock Exam P2Abin LalNo ratings yet
- Bpse 141 (E) 2023-24Document3 pagesBpse 141 (E) 2023-24pdiksha694No ratings yet
- Boiling ReportDocument5 pagesBoiling ReportVAIBHAV MISHRANo ratings yet
- Sleeve Bearings Vs Antifriction BearingsDocument14 pagesSleeve Bearings Vs Antifriction BearingsHieuNo ratings yet
- Airport Waste Data PDFDocument617 pagesAirport Waste Data PDFDevNo ratings yet