Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FINAL Diabetes Medication Summary SS
Uploaded by
ronique reidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FINAL Diabetes Medication Summary SS
Uploaded by
ronique reidCopyright:
Available Formats
For educational purposes only.
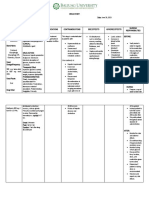
Diabetes Medication Summary
Metformin Gliptins eg alogliptin, sitagliptin, linagliptin
Mechanism of action: decreases gluconeogenesis and increases peripheral glucose Mechanism of action: Inhibit dipeptidylpeptidase-4 to increase insulin
doses, interaction, contraindications and side effects in the BNF and seek professional clinical advice before making any interventions. We do not accept any
liability for loss of any type caused by reliance on the information within this document. Please only work within your clinical competency and ensure your
utilisation secretion and lower glucagon secretion
judgement or replace your local clinical guidelines. The information included in this document is meant for educational purposes only. Please check drug
Every effort has been made to ensure the information within this document is accurate and correct, however this should not replace your own clinical
Metformin Advantages: Low hypoglycaemia risk, potential for weight loss, offers some Advantages: Low risk of hypoglyaemia (relative), overall weight neutral
Gliptins
cardiovascular protection, relatively cheap medication, offers reasonable Disadvantages: Relatively average glycaemia control compared to other
glycaemic control agents, severe and/or disabling joint pain, potential risk for acute
Disadvantages: Should be used with caution in renal impairment - if eGFR drops pancreatitis, potential increased risk of heart/kidney disease
<45 consider dose reduction. If eGFR drops <30 stop the medication. Risk of lactic Warnings: treatment should only be continued if there is a reduction of
acidosis is rare but symptoms include thirst, anorexia, abdominal pain, confusion. >5.5mmol/mol in hba1c over 6 months. avoidance of treatment in hepatic
Dehydration or tissue hypoxia can be potential triggers. impairment. Dose reduction may be needed in renal impairment
Warnings: GI disturbances such as nausea and vomiting occur at the initiation Usual dose: Alogliptin (green 1st line - check local formulary) 25mg once
stages. Taste disturbances, skin reactions. Vitamin b12 deficiency - more likely to daily. can be used as monotherapy, dual therapy or triple therapy
occur with higher doses.
Usual dose: Take with meals, start low and go slow. 500mg OD for at least 1 week,
then increase in 500mg steps at weekly intervals until highest tolerated or max
dose. (check local guidelines)
Pioglitazone
professional indemnity covers your scope of practice.
Sulphonylureas eg gliclazide Mechanism of action: Reduces peripheral insulin resistance causing lower
Pioglitazone
blood glucose concentration
Sulphonylurea
Mechanism of action: Augments insulin secretion
Advantages: Relatively cheap medication, can achieve good glycaemic control, has Advantages: Relatively good glycaemic control, low risk of hypoglycaemia
good long term safety data (rare), relatively safe in renal impairment, relatively cheap medication
Warnings: High potential risk of hypoglycaemia which can be further aggravated Disadvantages: potential for weight gain, increased risk of developing heart
with poor renal function, possibility of weight gain of a few Kg failure, fractures and bladder cancer
Disadvantages: Patients should be wary of hypoglycaemmia in terms of impacting Warnings: significant oedema can occur in some patients. Cardiac failure can
driving. Refer patients to view the fitness to drive document. Patients who drive occur when pioglitazone is used in combination with insulin. observe the
cars should monitor glucose concentration at times relevant to driving to detect patient for signs of heart failure and weight gain.
hypoglycaemia. Lorry drivers are required to monitor blood glucose twice daily Usual dose: initially 15mg to 30mg daily adjusted according to response to
and at times relevant to driving. 45mg once daily. In elderly patients use the lowest possible dose. dose
Usual dose: initially 40-80mg daily, adjusted according to response upto 160mg as should be reviewed every 3-6 months.
a single dose with breakfast. max 320mg daily. increase the dose approximately
every 4-6 weeks
GLP1 eg liraglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide
SGLT2 inhibitors eg empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin
SGLT2 inhibitor
Mechanism of action: Increases insulin secretion, suppresses glucagon
Mechanism of action: Inhibits the sodium glucose co-transporter-2 in the renal proximal secretion, slows gastric emptying and reduces appetite
convoluted tubule to reduce glucose absorption and increase urinary glucose excretion
Advantages: Very effective glycaemic control, low risk of hypoglycaemia,
Advantages: Can achieve good glycaemia control, relativey low risk of hypoglycaemia,
possible weight loss, potential cardiovascular and renal benefits
GLP-1
potential for weight loss, can have potential cardiovascular and renal benefits
Disadvantages: Increased risk of infections eg UTIs, diabetic ketacidosis (signs include nausea, Disadvantages: Relatively expensive medication, risk of necrotising and
vomiting, abdominal pain, thirst, breathing problems, confusion), rare but risk of amputation, haemorrhagic pancreatitis
use with caution in renal impairment, gangrene
Warnings: to continue therapy, patients must have achieved weight
Warnings: increased risk of hypoglycaemia when used with insulin or sulphonylureas. Ketones reduction >3% in those with high BMI and a significant reduction in hba1c
should be monitored during treatment interruption for surgical procedures or acute serious with stable renal function. Routine monitoring of blood glucose is
medicall ilnesses
recommended if GLP1 is given with another agent likely to cause
Usual dose: Empagliflozin (green 1st line - check local formulary) starting dose 10mg once hypoglycaemia such as sulphonylureas. This could impact driving status.
daily, can be increased to 25mg once daily if tighter glycaemic control is needed and renal
function is satisfactory. Usual dose: Liraglutide (green 1st line - check local formulary) 0.6mg once
daily for at least 7 days, then increase to 1.2mg once daily for at least 7 days
by s/c injection (check BNF or local guidelines).
Instagram: Pharmasinghs TikTok: Pharmasinghs Youtube: Pharmasinghs
You might also like
- 4A Drug SheetDocument14 pages4A Drug SheetTherese PagayNo ratings yet
- Small Animal/ExoticsDocument3 pagesSmall Animal/Exoticstaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- DiabetesAlgorithm Stanford2018Document7 pagesDiabetesAlgorithm Stanford2018Rogelio MoscosoNo ratings yet
- T2D PharmacologyDocument2 pagesT2D PharmacologyTan Thay HuiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes in CKDDocument20 pagesDiabetes in CKDdr_iswahyudhiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Pills How To Take How They Work Side Effects of NoteDocument2 pagesDiabetes Pills How To Take How They Work Side Effects of NoteLaurensia Erlina NataliaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Treatment: PancreatitisDocument2 pagesDiabetes Treatment: PancreatitisSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Emilio Aguinaldo College: School of NursingDocument3 pagesEmilio Aguinaldo College: School of Nursingbryan.zabala.mnlNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProglinDocument2 pagesDrug Study ProglinChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin (Jardiance) : National Drug MonographDocument16 pagesEmpagliflozin (Jardiance) : National Drug MonographSunil Murkikar (GM - PMI Quality Operations)No ratings yet
- GLYBURIDEDocument3 pagesGLYBURIDEJohn Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Leveraging GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Options To Advance Glycemic and Extraglycemic Goals in Type 2 DiabetesDocument34 pagesLeveraging GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Options To Advance Glycemic and Extraglycemic Goals in Type 2 DiabetesMagdy GabrNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MedicationDocument3 pagesDiabetes MedicationRuben Gutierrez-ArizacaNo ratings yet
- NCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCMH Drug StudyHeartlee NapuranNo ratings yet
- ADA 2023.-154-159 - OrganizedDocument6 pagesADA 2023.-154-159 - OrganizedEfren BalsecaNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesBryan BosqueNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesDocument27 pagesInsulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesSayan ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyhsiriaNo ratings yet
- Hes 005 Session 16 SasDocument7 pagesHes 005 Session 16 SasJose Melmar Autida AutenticoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyAilah Mae Dela Cruz0% (1)
- IJAMSCR-17-223 - 426-433 Review On Adverse Drug Reaction of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument8 pagesIJAMSCR-17-223 - 426-433 Review On Adverse Drug Reaction of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFtrupetiNo ratings yet
- Glyburide (Glibenclamide) : Drug Information: Brand Names: USDocument17 pagesGlyburide (Glibenclamide) : Drug Information: Brand Names: USAnonymous wmF9p2ejNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Type 2 DMDocument18 pagesDrugs in Type 2 DMhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Compare Gliflozin GliptinDocument3 pagesCompare Gliflozin GliptinRudren Eswaran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Blood Glucose Control Pathway in Type 2 Diabetes Apr 2013Document2 pagesBlood Glucose Control Pathway in Type 2 Diabetes Apr 2013J WongNo ratings yet
- Topic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesDocument8 pagesTopic: DM Section: 4 Group NamesTurkish DizilerNo ratings yet
- Type 2 DiabetesDocument2 pagesType 2 DiabetessaroshNo ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Janumet-Xr MakassarDocument49 pagesJanumet-Xr MakassarSuardy CiayadiNo ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. (Types of Anesthesia Used in Cesarean Section)Document22 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. (Types of Anesthesia Used in Cesarean Section)Vincent Maralit MaterialNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NameDocument4 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Reponsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Metformin in 2019Document2 pagesMetformin in 2019Juaan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology LectureDocument5 pagesPharmacology LectureAbdullahayad farouqNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Exercise No. 7 Case Study On Diabetes MellitusDocument9 pagesWorksheet On Exercise No. 7 Case Study On Diabetes Mellitusjameela sapiandanteNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- GliclazideDocument2 pagesGliclazideNicholas Tagle100% (1)
- Name Accession Number Type Groups Description: Show EntriesDocument14 pagesName Accession Number Type Groups Description: Show EntriesIndrayansah SiahaanNo ratings yet
- GlipizideDocument2 pagesGlipizideFeliciaDorghamNo ratings yet
- DM TYPE 2 by THEADocument29 pagesDM TYPE 2 by THEAThea SelinaNo ratings yet
- Gliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameDocument8 pagesGliclazide Diamicron: Generic Name Trade NameIsabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityDocument8 pagesDrug Study: West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo CityChristine Claire CaguimbayNo ratings yet
- 9+10. Oral Antidabetic DrugsDocument3 pages9+10. Oral Antidabetic Drugsmohammed alrubaiaanNo ratings yet
- Updates On Metformin JDM2019 DTDocument37 pagesUpdates On Metformin JDM2019 DTLaurentius JohanNo ratings yet
- More : Drug Class How It Works Generic Name Brand Name Cost Type 2 Oral Medications BiguanideDocument4 pagesMore : Drug Class How It Works Generic Name Brand Name Cost Type 2 Oral Medications BiguanideJoshua LewisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TemplateDocument2 pagesDrug Study TemplateMary hope DomalaonNo ratings yet
- Danuglipron (2023) : Activate GLP-1 ReceptorsDocument2 pagesDanuglipron (2023) : Activate GLP-1 Receptorseslambasuony98No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- CCO Diabetes South Downloadable 2Document43 pagesCCO Diabetes South Downloadable 2Carlos VásquezNo ratings yet
- PamarylDocument9 pagesPamarylPharmacist ipsNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin, Norgesic ForteDocument4 pagesLinagliptin, Norgesic FortehahahaNo ratings yet
- Metrormin (Glugophage)Document2 pagesMetrormin (Glugophage)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SitagliptinDocument3 pagesDrug Study SitagliptinEzron Kendrick Duran50% (2)
- Pharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Diabetes Mellitus: Glucose RegulationAbdullah RawashdehNo ratings yet
- BNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 PhenobarbtalDocument2 pagesBNF - 76 - British - National - Formulary - Septem-357-358 Phenobarbtalnur aisahNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Type 2 HassanDocument26 pagesDiabetes Type 2 Hassanyash_acharya007100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyErika Nena Castillo AlamoNo ratings yet
- IBD CrohnsandUlcerativeColitisDocument3 pagesIBD CrohnsandUlcerativeColitisronique reidNo ratings yet
- Facione - Critical-Thinking-What It Is and Why It CountsDocument28 pagesFacione - Critical-Thinking-What It Is and Why It Countsronique reidNo ratings yet
- Revised - Needs Identification TemplateDocument5 pagesRevised - Needs Identification Templateronique reidNo ratings yet
- Wound Cleansing Solution OptionsDocument2 pagesWound Cleansing Solution Optionsronique reidNo ratings yet
- FINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSDocument1 pageFINAL Hypertension Medication Summary SSronique reidNo ratings yet
- Nursingbundleson - Compressed 4 15Document12 pagesNursingbundleson - Compressed 4 15ronique reidNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Abbreviations and MeasurementDocument3 pagesPharmacology Abbreviations and Measurementronique reidNo ratings yet
- Medication InformationDocument12 pagesMedication Informationronique reidNo ratings yet
- ENN PHARMACOLOGY BUNDLE PrintDocument142 pagesENN PHARMACOLOGY BUNDLE Printronique reid83% (6)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- Kertas Kerja PinjamanDocument18 pagesKertas Kerja PinjamanWan AzmanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of NicotineDocument1 pageThe Impact of NicotineSanwana MoosaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 ExcretionDocument19 pagesLesson 3 ExcretionNUMAIRA UROOJNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure: A. DefinitionsDocument28 pagesChronic Renal Failure: A. Definitionssharu4291No ratings yet
- Comparison of Dopamine and NorepinephrineDocument16 pagesComparison of Dopamine and Norepinephrineyulanda fitrianaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics and Cardiology 2019 PDFDocument594 pagesHemodynamics and Cardiology 2019 PDFStollery SandboxNo ratings yet
- Stone DiseaseDocument64 pagesStone DiseaseAmmad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Management Algorithm For Adult With HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageManagement Algorithm For Adult With HyperkalemiaAnjiNo ratings yet
- Oncologic Emergencies and Urgencies A Comprehensive ReviewDocument24 pagesOncologic Emergencies and Urgencies A Comprehensive ReviewMarco Antonio Morales GonzálezNo ratings yet
- SAS #16 NUR 151: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormDocument7 pagesSAS #16 NUR 151: Your Email Will Be Recorded When You Submit This FormA.No ratings yet
- ARDS Concept MapDocument1 pageARDS Concept Mapchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Anti Anginal DrugsDocument44 pagesAnti Anginal DrugssimonjosanNo ratings yet
- 1013 Vasoactive Agents in ShockDocument20 pages1013 Vasoactive Agents in Shockrogelio cruzNo ratings yet
- ECG Brief NotesDocument5 pagesECG Brief NotesKalpani Malsha UdawelagedaraNo ratings yet
- Moderate Sedation PowerpointDocument68 pagesModerate Sedation PowerpointJames GarnerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Nicolaos Madias, MD ObjectivesDocument12 pagesRespiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Nicolaos Madias, MD Objectivesyayastoyz100% (1)
- Perinatal Asphyxia: Berhane G/her (MD, Ped.Y3R) Lecture Slides For C1 Medical Students of Adigrat UniversityDocument80 pagesPerinatal Asphyxia: Berhane G/her (MD, Ped.Y3R) Lecture Slides For C1 Medical Students of Adigrat UniversityAlemuNo ratings yet
- 1.assignment On CPRDocument7 pages1.assignment On CPRsantosh kumarNo ratings yet
- RS McqsDocument6 pagesRS McqsMuhammad Farrukh ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post Operative CareDocument87 pagesPre and Post Operative CareMeraol Hussein100% (1)
- 8.3 Acute Kidney Injury - March 16 - Dr. Austria.Document6 pages8.3 Acute Kidney Injury - March 16 - Dr. Austria.Jess PeltraNo ratings yet
- Syllab BSC Dialtech1819-22102018Document22 pagesSyllab BSC Dialtech1819-22102018Salem Polyclinic KNo ratings yet
- Effect of PIH On Mothers and Babies PDFDocument3 pagesEffect of PIH On Mothers and Babies PDFAbdifatah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine - Therapeutic Use For The Termination of Reentrant Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument9 pagesDexmedetomidine - Therapeutic Use For The Termination of Reentrant Supraventricular TachycardiaGading AuroraNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceDocument49 pagesFluid and Electrolytes ImbalanceMohamed Na3eemNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument59 pagesMedical Surgical NursingChey Dianne Seriña100% (11)
- Dr. Najeeb NephrologyDocument53 pagesDr. Najeeb NephrologyTrajce100% (4)
- Accepted Manuscript: Journal of The Neurological SciencesDocument31 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Journal of The Neurological SciencesZelNo ratings yet
- HypomagnesemiaDocument3 pagesHypomagnesemiaapi-3712326No ratings yet