Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Renal Failre Chronic Kidney Disease: Definition
Uploaded by
Ahmed almahdiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic Renal Failre Chronic Kidney Disease: Definition
Uploaded by
Ahmed almahdiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic renal failre
Chronic kidney disease
Definition:
Irreversile permanent kidney damage with ddecreased glomerular filtration rate.
It occurs over months or years. May be nort diagnosed for long time.
Stages of chronic kidney disease:
Stage 1 2 3 4 5
N GFR Mild GFR Moderate GFR Severe GFR Kidney failure
GFR(ml/min/ 1.73 m2) < 90 60-89 30-59 15-29 < 15
Causes:
< 5 years old > 5 years old
Congenital anomalies: Glomerular disease:
Hypoplastic kidney Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Vesicouretral reflux Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Obstructive uropathy Chronic glomerulonephritis
Genetic disorders: Alport’s syndrome
Congenital nephrotic syndrome Tubular disease:
Polycystic kidney disease Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis
Wilm’s tumor Nephrotoxic drugs
Oxalate Cystinosis
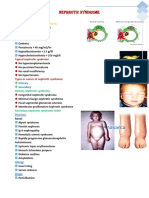
Clinical picture:
It is vague& needs high index of suspicion:
System Symptoms
General Weakness, fatigue& failure to thrive
CVS Hypertension, pericarditis, cardiomyopathy& heart failure
RS Shortness of breath
GIT Anorexia, nausea, vomiting& gastritis
GUS Polyuria, polydipsia& nocturia
CNS Drowsiness& polyneuropathy
MSS Renal osteodystrophy
Blood Anemia, bleeding tendency& infection
Endocrine Growth failure& delayed puberty
Metabolic Hyperuremia, hyperlipidemia, hyperkalemia& hyponatremia
Investigations:
Hematology: CBC: anemia of chronic illness +/- infection
Biochemistry: urea, creatinine, K, Ph, Na, Ca, PTH, Cholesterol
Head of P.W. Dr. Noura Noraddeen
Urine exam: protein, RBCs
Radiology: CXR: cardiomegaly
Bone X-ray: renal osteodystrophy
Abdominal U/S: atrophic kidneys or enlarge due to tumor or cysts
Others: ABG analysis, Echo& DMSA
Management:
Stage 1: diagnosis& management of the cause.
Stage 2&3: improve prognosis& treat complications
Stage 4: prepare for renal replacement therapy
Stage 5: renal replacement
Regular OPD visits for:
1- Vital signs& growth parameters
2- Investigations: GUE, CBC, S. electrolytes, KFT, lipid profile
OPD management:
System Treatment
Proteinuria Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor captopril or enalapril or lisinopril
Angiotensin receptor blocker: losartan.
HTN Control HTN by: diuretics, ACEI, Ca. channel blockers and/or beta blockers.
GIT Ranitidine, balanced diet, high calories, low salt& special formula
GUT Control edema by: fluid& electrolyte balance.
Osteodystrophy Ph binders, calcium carbonate& vitamin D1.
Blood Erythropoietin, iron& MVT. RBCs if needed.
Metabolic Control hyperlipidemia by: statin group.
Endocrine Growth hormone.
Immunity Vaccination.
Others Avoid NSAID.
Renal replacement therapy:
Indications of dialysis as mentioned in AKI
Types of dialysis:
Hemodialysis
Peritoneal dialysis that is preferred in children
Renal transplantation:
Is the preferred method in children that gives good outcome& near normal life.
Head of P.W. Dr. Noura Noraddeen
Head of P.W. Dr. Noura Noraddeen
You might also like
- CKD AweDocument25 pagesCKD AweMunawwar AweNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument49 pagesChronic Kidney Diseasesarguss1471% (7)
- Renal Failure: SMF Urologi FK-Unpar / RSUD Dr. Doris SylvanusDocument53 pagesRenal Failure: SMF Urologi FK-Unpar / RSUD Dr. Doris SylvanusClarissa SuheryNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure-Clinical CaseDocument35 pagesRenal Failure-Clinical Caseyaser773arfat2025No ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney InjuryDocument13 pagesChronic Kidney InjuryMaryam MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- Diagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi TPG RRTDocument56 pagesDiagnosa Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi TPG RRTASIS ADRINo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Children: DR Saiel Al Sarhan MD, PHDDocument48 pagesChronic Kidney Disease (CKD) in Children: DR Saiel Al Sarhan MD, PHDMAYSAA HamarnehNo ratings yet
- Renal and Urinary DisordersDocument11 pagesRenal and Urinary DisordersChristian Espanilla100% (4)
- Common Genitourinary Disease: Acute and Chronic Renal FailureDocument15 pagesCommon Genitourinary Disease: Acute and Chronic Renal Failureayhab abinaNo ratings yet
- Renal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityDocument36 pagesRenal Support in Hepatic Patient: by Mohammed Dabbour Lecturer of Anesthesia Ain Shams UniversityTrishenth FonsekaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease - UnhaluDocument57 pagesChronic Kidney Disease - UnhaluRahmawati HamudiNo ratings yet
- 00 NephrologyDocument98 pages00 Nephrologyeryxsp0% (1)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument28 pagesChronic Renal FailuremarshmalouNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseTamzid Rabby TanmoyNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Oleh: Ns - Edy Suryadi Amin, M.KepDocument23 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Oleh: Ns - Edy Suryadi Amin, M.KepWulandaryNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Kidney - ARFDocument14 pagesDisorder of Kidney - ARFLaxman KannaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument29 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseEsayas KebedeNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Urogenital TractDocument170 pagesDiseases of Urogenital TractMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Dr. Des Riyadi Anas, Sp. PD M. HashemyDocument43 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Dr. Des Riyadi Anas, Sp. PD M. HashemyAris DaooNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument20 pagesAcute and Chronic Kidney DiseaseCabdi WaliNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NDocument41 pagesRenal Disorders, Renal Failure, & Renal Dialysis: Remerose C. Ragasa, R.NremeroseNo ratings yet
- CKD SheetDocument4 pagesCKD SheetMomy SutanNo ratings yet
- Nephrology Notes Review - Passmedicine 2012Document33 pagesNephrology Notes Review - Passmedicine 2012adiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease DR Moses KazevuDocument29 pagesChronic Kidney Disease DR Moses KazevuMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan Dokter Hari - CKDDocument24 pagesBimbingan Dokter Hari - CKDVicky LumalessilNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument47 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseSaowda HussainNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Diseases of The Kidney and Urinary Tract FINALDocument9 pagesApproach To Patient With Diseases of The Kidney and Urinary Tract FINALgelskNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument40 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseEsayas KebedeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal Failure 4-9-18Document27 pagesChronic Renal Failure 4-9-18Muhammad MakkiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument39 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseAgatha RogerNo ratings yet
- AkiDocument42 pagesAkimarauder_popNo ratings yet
- Approach To Acute Renal FailureDocument40 pagesApproach To Acute Renal FailureMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Failure Transplant 2Document22 pagesChronic Kidney Failure Transplant 2Gail Leslie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaNo ratings yet
- Gagal Ginjal AkutDocument29 pagesGagal Ginjal AkutHafiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease - 2023Document51 pagesChronic Kidney Disease - 2023ramadhanadlansyah7100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Bobby Laksana D Putri Priela Pembimbing: Dr. Nursamsu, SPPDDocument30 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: Bobby Laksana D Putri Priela Pembimbing: Dr. Nursamsu, SPPDfrostedsurgeonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease in ChildrenDocument29 pagesChronic Kidney Disease in ChildrenAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- Post Your Experience See Others: Chronic Kidney Disease and Its ManagementDocument6 pagesPost Your Experience See Others: Chronic Kidney Disease and Its ManagementLuvita RonteltapNo ratings yet
- Final CC EdemaDocument31 pagesFinal CC EdematabatchNo ratings yet
- Noel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNDocument62 pagesNoel A. Villanueva, MD, FPCP, FPSNagilNo ratings yet
- Case Pres-CkdDocument21 pagesCase Pres-CkdKathleenNo ratings yet
- Feroven For Kidney InstituteDocument49 pagesFeroven For Kidney Institutetanvir09No ratings yet
- Lec 2Document10 pagesLec 2fbbqbcht6yNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument17 pagesRenal FailureNursidar Pascual MukattilNo ratings yet
- MHD Exam 5 MaterialDocument122 pagesMHD Exam 5 Materialnaexuis5467100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument34 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseVina ZulfianiNo ratings yet
- Renal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFDocument89 pagesRenal - Pathophysiology 2020 PDFHardian HardianNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 pagesChronic Renal FailureyazzzNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease (Chronic Renal Failure)Document38 pagesChronic Kidney Disease (Chronic Renal Failure)Mustafa AdelNo ratings yet
- L25 CLD-2Document55 pagesL25 CLD-2S sNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanDocument24 pagesPatofisiologi Sistem PerkemihanMasna Arisah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Alternative NamesDocument67 pagesAlternative NamespashaNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome Vs Nephritic SyndromeDocument46 pagesNephrotic Syndrome Vs Nephritic SyndromelilisNo ratings yet
- Kidney: Disorders of TheDocument52 pagesKidney: Disorders of ThejuliusromatolentinoNo ratings yet
- DR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiDocument39 pagesDR Aida Lombok 3 Mei 2017 - HisfarsiBasri BaslamNo ratings yet
- Gagal Ginjal Akut Pada AnakDocument37 pagesGagal Ginjal Akut Pada AnakNycoNo ratings yet
- Title Student Name ID Group InstructorDocument3 pagesTitle Student Name ID Group InstructorAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Acute Diarrhea: MicroorganismDocument5 pagesAcute Diarrhea: MicroorganismAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Persistent DiarrheaDocument1 pagePersistent DiarrheaAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Persistent DiarrheaDocument1 pagePersistent DiarrheaAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- CommonDocument2 pagesCommonAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Title Student Name ID Group InstructorDocument3 pagesTitle Student Name ID Group InstructorAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- MindmapDocument1 pageMindmapAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Title:Muscle of Facial Expression Student Name:Sultanah Mohammed Majrashi ID:444003226 Group:2 Instructor:Mustafa JanDocument3 pagesTitle:Muscle of Facial Expression Student Name:Sultanah Mohammed Majrashi ID:444003226 Group:2 Instructor:Mustafa JanAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome PathogenesisDocument3 pagesNephrotic Syndrome PathogenesisAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- AplasticDocument2 pagesAplasticAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: Micro-OrganismDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Micro-OrganismAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: Rbcs Wbcs Platelets Plasma or Serum Coagulation FactorsDocument3 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia: Rbcs Wbcs Platelets Plasma or Serum Coagulation FactorsAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Urine Analysis:: InterpretationDocument2 pagesUrine Analysis:: InterpretationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Portal Hypertension: PrehepaticDocument1 pagePortal Hypertension: PrehepaticAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Ascites: DefinitionDocument2 pagesAscites: DefinitionAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Causes: CITTTAN: Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesCauses: CITTTAN: Liver CirrhosisAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation StationDocument1 pageData Interpretation StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision StationDocument1 pageClinical Decision StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- E/R StationDocument1 pageE/R StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4Ahmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Etiology:: Viral HepatitisDocument3 pagesEtiology:: Viral HepatitisAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Neurology StationDocument1 pageNeurology StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Clinical StationDocument1 pageClinical StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- 13 PediatricDocument1 page13 PediatricAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- 18pediatric MCQDocument1 page18pediatric MCQAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- 19 PediatricDocument1 page19 PediatricAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Face StationDocument1 pageFace StationAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Development Station: What Is The Starting Age of Sitting Without Support? A. 1 Month B. 3 Months C. 6 Months D. 9 MonthsDocument1 pageDevelopment Station: What Is The Starting Age of Sitting Without Support? A. 1 Month B. 3 Months C. 6 Months D. 9 MonthsAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- Diagram Station: Low HB High MCV 95 Normal Reticulocytes High ReticulocytesDocument1 pageDiagram Station: Low HB High MCV 95 Normal Reticulocytes High ReticulocytesAhmed almahdiNo ratings yet
- 2023 AAN Myositis Autoantibodies FINALDocument53 pages2023 AAN Myositis Autoantibodies FINALEvelina ȘabanovNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Digital Age Group 4Document23 pagesIntroduction To Digital Age Group 4Mary Jane Anarna100% (1)
- BarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesBarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentBarry KueblerNo ratings yet
- Black Book Project 3Document69 pagesBlack Book Project 3Pragya SinghNo ratings yet
- Emergency ManagementDocument78 pagesEmergency ManagementHuey Calabines50% (2)
- Megan Haky: M.M.Haky@eagle - Clarion.eduDocument2 pagesMegan Haky: M.M.Haky@eagle - Clarion.eduapi-285540869No ratings yet
- Anosognosia FSDocument2 pagesAnosognosia FSraquel perezNo ratings yet
- Retirement Planning Mistakes Undermining The Post Retirement Adjustment and Well BeingDocument17 pagesRetirement Planning Mistakes Undermining The Post Retirement Adjustment and Well BeingMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Detection Using Deep LearningDocument3 pagesBreast Cancer Detection Using Deep LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Doing Work in A Certain Area .Especially in A Laboratory or in Any Work Place or Room ..Hazard and Risk Should Always Be ConsideredDocument36 pagesDoing Work in A Certain Area .Especially in A Laboratory or in Any Work Place or Room ..Hazard and Risk Should Always Be ConsideredJENA MAE FATAGANINo ratings yet
- Capillary Blood Glucose Performance Checklist: Numerical Rating Adjectival Description DescriptionDocument2 pagesCapillary Blood Glucose Performance Checklist: Numerical Rating Adjectival Description DescriptionAngeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- Hospital Annual Work Plan Format FinalDocument28 pagesHospital Annual Work Plan Format FinalSila Ontita100% (9)
- Republic of The Philippines 9173Document2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines 9173jansestacioNo ratings yet
- People's Vision For MumbaiDocument86 pagesPeople's Vision For MumbaiAravind UnniNo ratings yet
- Trichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTCDocument27 pagesTrichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Renal Disease in PregnancyDocument28 pagesRenal Disease in PregnancysuperjaxxxonNo ratings yet
- Developmental Tasks of AdolescenceDocument1 pageDevelopmental Tasks of AdolescenceAteh HashimNo ratings yet
- STSDocument2 pagesSTSNeslie CabangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Did You Know FactsDocument1 pageNursing Did You Know FactsmikErlhNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technology ScienceDocument2 pagesMedical Lab Technology Sciencecnc_program_pagesNo ratings yet
- PE UNIT 1 Active Recreation (Lifestyle and Weight Management)Document26 pagesPE UNIT 1 Active Recreation (Lifestyle and Weight Management)Charmaine RamosNo ratings yet
- 2021 ESMO Essentials For Clinicians Gastrointestinal Tract Tumours PDFDocument133 pages2021 ESMO Essentials For Clinicians Gastrointestinal Tract Tumours PDFCynthia LopezNo ratings yet
- Hajj A Bio Mechanical JourneyDocument7 pagesHajj A Bio Mechanical Journeyrizla67No ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-451436482No ratings yet
- Practical Exercise 3 Pareto Diagram: DR Yousef Amer - School of Engineering University of South Australia Page 1 of 3Document6 pagesPractical Exercise 3 Pareto Diagram: DR Yousef Amer - School of Engineering University of South Australia Page 1 of 3HarisNo ratings yet
- Mono - African Wild Mango Irvingia Gabonensis - EnglishDocument5 pagesMono - African Wild Mango Irvingia Gabonensis - EnglishTom DelongeNo ratings yet
- b2 ExamDocument6 pagesb2 ExamMaria MontesNo ratings yet
- Blood and Marrow Transplant:: Resident Education Lecture SeriesDocument30 pagesBlood and Marrow Transplant:: Resident Education Lecture SeriesAparna KinginiNo ratings yet
- Banking - Diksha Book On Effective Study Techniques PDFDocument66 pagesBanking - Diksha Book On Effective Study Techniques PDFHemrajSainiNo ratings yet