Professional Documents
Culture Documents
?estrogens and Androgens
Uploaded by
Karma iiiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
?estrogens and Androgens
Uploaded by
Karma iiiCopyright:
Available Formats
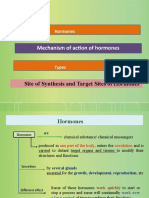
Estrogen receptors (ERs) act by regulating
transcriptional processes. The classical
mechanism of ER action involves estrogen
binding to receptors in the nucleus, after
Estrogens and Androgens which the receptors dimerize and bind to
specific response elements known as
Dr.Raghad abdulsalam estrogen response elements (EREs)
located in the promoters of target genes.
Physiology Uses : HRT – Effects of Treatment
Reproductive Tissues
Growth of
Ovarian
Estrogen, or oestrogen, is the primary female sex hormone. Vaginal Mammary
Epithelium follilcle Gland
It is responsible for the development and regulation of the Growth of
female reproductive system. There are three major endometrium Sperm
transport
endogenous estrogens in females that have estrogenic
hormonal activity: estrone, estradiol, and estriol. The estrane Lowers
steroid estradiol is the most potent and prevalent of these. Plasma cholesterol Decreases
rate of bone (Increased risk of MI and stroke, especially in the
ESTROGENS resorption first year)
Behavioral effects Reduces
Bowel motility
Liver synthesis of
Transport Proteins Maintains normal
Increases blood coagulability
skin structure
Non-reproductive Tissues
Overview: Endocrine Physiology
Hypothalamus (GnRH)
& Pitutary
Luteinizing Hormone &
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Ovaries & Testes
Reproduction
SERMs: Other
Raloxifene (EVISTA):
- High affinity for both ER-α and ER-β
-Treatment of osteoporosis in post-menopausal women.
-Does not cause proliferation of the endometrium or breast tumor cells
Selective estrogen receptor Side effects: 2-3 fold ↑ risk of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
modulators, called SERMs Interactions: Ampicillin ↓ absorption
Raloxifene ↓ warfarin efficacy
SERMs (Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators)
There are three SERMs:
tamoxifen in pill form (also called tamoxifen citrate; brand name:
Nolvadex) and in liquid form (brand name: Soltamox)
Evista (chemical name: raloxifene)
Fareston (chemical name: toremifene)
Each is a pill, usually taken once a day, except for tamoxifen in liquid
form. Tamoxifen is the oldest, most well-known, and most-prescribed
SERM.
SERMs can be used to treat women both before and after menopause.
• Selectivity is possible because
• ER-α and/or ER-β show differential tissue expression.
• Conformation dependent binding to DNA and transcription factors
• Tissue dependent responses ranging between pro-estrogenic, partially
estrogenic and anti-estrogenic effects
SERMs: Tamoxifen continued Anti-Estrogens
- Most effective in treatment of tumors that are ER-positive (50% response) or ER • Clomiphene Weak agonist and strong antagonist for
+ PR positive (70-80% response rates). Responses of ER-negative tumors is < ER-α or ER-β.
10%. -Oppose the negative feedback effects of endogenous
estrogen. ↑amplitude of the LH and FSH pulses
- Adjuvant therapy with chemo or radiation in treatment
- Major use: induction of ovulation in women with an
- Preventative agent for women at high risk for breast cancer. intact hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis
-Adverse effects: multiple births, ovarian cysts
-Resistance is usually developed in 5 years, which may, in part, reflect alterations
in the ER receptors in the tumors.
• ICI 182,870 Fulvestrant (FASLODEX)
- pure estrogen antogonist
- effective in treating tamoxifen-resistant tumors
Progestins: anti-Progesterones
Mifepristone (RU 486) (mifeprex): PR antagonist
Used in first trimester to terminate pregnancy (along with prostaglandins to increase
uterine contractions)
Post-coital contraceptive (prevent implantation)
Investigational: induction of labor after fetal death and treatment of endometriosis.
Adverse Effects: vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain and cramping
Contraindicated in patients with vaginal bleeding, adrenal dysfunction or asthma
(due to anti-glucocorticoid actions)
Interactions:
Decreases efficacy of anticoagulants.
Inhibits hepatic metabolism by CYP3A4 (eg.anti-retroviral protease inhibitors,
calcium-channel blockers, carbamazepine)
Progestins – Therapeutic Progesterone Outline
• Naturally occurring progesterone (low oral bioavailability)
- Micronized particles suspended in oil and packaged in gelatin capsules • Contraception
(PROMETRIUM)
- Vaginal gel (CRINONE) • Therapeutic Estrogens & Progesterones
- Slow-release intrauterine device (PROGESTASERT)
• Oral Contraceptive Formulations
• 17-α-hydroxy-progesterone derivatives have substitutions at C17 that slow hepatic
metabolism : medroxyprogesterone (MPA) (PROVERA) • Emergency Contraception
• 19-nor testosterone derivatives display primarily progestational rather than • Extended-Regimen Contraception
androgenic activity : norethindrone
• Replacement of the 13-methyl group of norethindrone with a 13-ethyl substituent are • Mechanism of Action
more potent progestins and less androgenic: norgestrel, nomegestrol
• Effects
Progestins continued Contraception
Hypothalamus
Mechanism of Action: Interacts with PR to mimic the stimulatory affects of
progesterone GnRH
Oral Contraceptives
GnRH analogs Pituitary
Physiological Target: Reproductive Tract
- Decreases estrogen-driven endometrial proliferation LH FSH
- Establishment and maintenance of pregnancy
Ovary
Common Uses:
ovum Estradiol
- Oral contraceptives Progesterone
- HRT to limit estrogen’s effects on the endometrium Fallopian Tube
Tubal Ligation
- Uterine Bleeding disorders
Ovum transport
- Premature labor (decrease uterine contractions) IUD Uterus
Progestin only contraceptive
- Stimulate Appetite in AIDS or cancer patients Implantation
Barrier Methods Sperm transport
Natural family planning Cervix and Vagina
Effects: Drug Interactions
Drugs that disrupt liver metabolism and increase oral contraceptive
metabolism
- anti-seizure medications, St. John’s wort
- antibiotics tetracycline and ampicillin
- HIV protease inhibitors
- Anti-tuberculosis drugs such as rifampin
Oral contraceptives effect the activity of other drugs
a. anticoagulants
b. benzodiazepines,
c. beta-blockers
d. corticosteroids, and tricyclic antidepressants
Emergency Contraceptives
• Drugs used for the prevention of pregnancy following unprotected
intercourse or a known or suspected contraceptive failure.
• Emergency hormone contraceptive regimens are highly effective and
decrease the risk of pregnancy by 75 percent
• To be effective these must be taken within 72 hours of intercourse
• May also inhibit ovulation or fertilization depending on timing of
administration Alteration of the endometrium, sperm penetration, and
tubal motility are also affected . ESTABLISHED PREGNANCIES ARE NOT
HARMED.
• Two products are available:
– Plan B: 0.75 mg levonorgestrel
– Preven: 0.25 mg levonorgestrel and 0.05 mg ethinyl estradiol (this
product includes a pregnancy test kit)
Contraceptives: MOA
↓LH/FSH release
An androgen (from Greek andr-, the stem of the word meaning Androgens are used for several reasons, such as:
↓ Follicular "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the To replace the hormone when the body is unable to
development & development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates produce enough on its own.
ovulation by binding to androgen receptors. This includes the embryological To stimulate the beginning of puberty in certain boys
development of the primary male sex organs, and the development who are late starting puberty naturally.
of male secondary sex characteristics at puberty. Androgens are
synthesized in the testes, the ovaries, and the adrenal glands. To treat certain types of breast cancer in females.
Thank you
You might also like
- Gonadal Hormones and Their Pharmacological InhibitorsDocument7 pagesGonadal Hormones and Their Pharmacological InhibitorsHydieNo ratings yet
- Biochem Research On Steroids and Fat SubstitutesDocument8 pagesBiochem Research On Steroids and Fat SubstitutesIvann John RoxasNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - FinalDocument7 pagesBiochemistry - FinalAditiNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Estrogen Receptor Signaling MechanismsDocument30 pagesHHS Public Access: Estrogen Receptor Signaling MechanismsFannyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System 1: Overview of The Endocrine System and HormonesDocument5 pagesEndocrine System 1: Overview of The Endocrine System and HormonesDance RangersNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Anabolic Steroids: by Michael J Evans-Brown BSC (Hons) and Jim Mcveigh MSC, RGNDocument7 pagesAn Introduction To Anabolic Steroids: by Michael J Evans-Brown BSC (Hons) and Jim Mcveigh MSC, RGNDanijel DamnjanovicNo ratings yet
- Sex HormonesDocument11 pagesSex Hormonesharishmore596No ratings yet
- q3 Module Edited w1-7Document21 pagesq3 Module Edited w1-7Regine DigamonNo ratings yet
- Steroid Hormones in Food Producing Animals: Regulatory Situation in EuropeDocument19 pagesSteroid Hormones in Food Producing Animals: Regulatory Situation in Europekj185No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemChristine Joanne CelendroNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in HumanDocument2 pagesThe Role of Hormones in HumandebbycleyNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology 12e (1)-1048-1067Document20 pagesCampbell Biology 12e (1)-1048-1067Lâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- Hormone Functions and Gland SourcesDocument3 pagesHormone Functions and Gland SourcesLaisa RarugalNo ratings yet
- Gonadal Hormones, Their Inhibitors and Fertility and Antifertility AgentsDocument29 pagesGonadal Hormones, Their Inhibitors and Fertility and Antifertility AgentsGopal Prasad DahalNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Hormonal Fluctuations On FemaleDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Hormonal Fluctuations On FemalehalynakrutNo ratings yet
- Wierman 07Document10 pagesWierman 07RIYANI BUDHI ANTARINo ratings yet
- Identification and Quantification of Estrogen Receptor Agonists in Wastewater EffluentsDocument6 pagesIdentification and Quantification of Estrogen Receptor Agonists in Wastewater EffluentsYago Quiñones TrianaNo ratings yet
- Total Estradiol LectureDocument68 pagesTotal Estradiol LectureLucas ElyNo ratings yet
- Skenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4Document12 pagesSkenario 1 Blok 4 Tutorial 4ulfahNo ratings yet
- Signal Molecule TrackerDocument4 pagesSignal Molecule Trackerarman_azad_2No ratings yet
- P4 Fisiologia, AccionDocument9 pagesP4 Fisiologia, AccionCinthia DarceNo ratings yet
- Estrogen in Male Reproduction FunctionDocument6 pagesEstrogen in Male Reproduction FunctionWanly SyahrizalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Exocrine Glands: Hormones Bloodstream Target Tissues/effec TorsDocument2 pagesEndocrine System Exocrine Glands: Hormones Bloodstream Target Tissues/effec TorsY HNo ratings yet
- Block 1Document46 pagesBlock 1Yash YadavNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument21 pagesEndocrine SystemNo Name100% (1)
- Hormone use and effects in animal husbandryDocument7 pagesHormone use and effects in animal husbandryAzuin MustafaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Endocrine SystempengxnNo ratings yet
- Biology Worksheets on Homeostasis, Excretory System, and Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesBiology Worksheets on Homeostasis, Excretory System, and Endocrine SystemMaria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Module 1Document13 pages3rd Quarter Science Module 1Vincq100% (2)
- 2015 - Physiology Production and Action of ProgesteroneDocument9 pages2015 - Physiology Production and Action of ProgesteroneCinantya Meyta SariNo ratings yet
- HarmonesDocument6 pagesHarmonesbaskarNo ratings yet
- Sas S11Document9 pagesSas S11Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- Biology Extra QuestionDocument19 pagesBiology Extra QuestionA 26 VISHAL RAUTONo ratings yet
- The Rejuvenation of Testosterone) (10.1177 - 2042018810385052)Document4 pagesThe Rejuvenation of Testosterone) (10.1177 - 2042018810385052)FuckyaNo ratings yet
- The endocrine and reproductive systemsDocument1 pageThe endocrine and reproductive systemsMegan WolvesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument5 pagesChapter 10 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Document4 pagesMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Jaycee Anne AregloNo ratings yet
- Bp503t Pcol Unit-VDocument46 pagesBp503t Pcol Unit-VAakkkNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action of Hormones: Site of Synthesis and Target Sites of HormonesDocument26 pagesMechanism of Action of Hormones: Site of Synthesis and Target Sites of HormonesAbdul MoqeetNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System ChartDocument2 pagesEndocrine System ChartValeria Guadalupe Ramírez Moctezuma100% (2)
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemjakevcabauatanNo ratings yet
- Steroids Discussion Points: 1. Examine The Diagram Below. Dicuss About SteroidsDocument7 pagesSteroids Discussion Points: 1. Examine The Diagram Below. Dicuss About SteroidsDinu YTBNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture 9 Gonadal Hormones and Drugs (Pod Pharm DR Thatcher 2022)Document46 pages01 Lecture 9 Gonadal Hormones and Drugs (Pod Pharm DR Thatcher 2022)sahilaminNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hormones in HumanDocument2 pagesThe Role of Hormones in HumansitaracommercialcomplexNo ratings yet
- Chemical Classification of Hormones & Their Role in the Endocrine SystemDocument22 pagesChemical Classification of Hormones & Their Role in the Endocrine SystemHarini BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- estrDocument2 pagesestraviraaworldNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecture Activity 10 Endocrine SystemJohnNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Biochemistry: FSH, LH, Estrogen, Progesterone and AndrogensDocument9 pagesReproductive Biochemistry: FSH, LH, Estrogen, Progesterone and AndrogensReshma BaralNo ratings yet
- Human Body: Identifying Endocrine TissuesDocument3 pagesHuman Body: Identifying Endocrine TissuesDiana VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- How Estrogen Protects BonesDocument7 pagesHow Estrogen Protects BonesAndreas Pratama NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- Bio 100 Human Systems AssignmentDocument3 pagesBio 100 Human Systems AssignmentTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Estrogen and Signaling in The Cells of Immune System: Advances in Neuroimmune Biology January 2012Document22 pagesEstrogen and Signaling in The Cells of Immune System: Advances in Neuroimmune Biology January 2012Christian David Hernandez SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology For Nurses: Drugs For Disorders and Conditions of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument54 pagesPharmacology For Nurses: Drugs For Disorders and Conditions of The Male Reproductive Systemsteinway007100% (2)
- SLM Q3 Week 1 1Document8 pagesSLM Q3 Week 1 1robilynestacionesherreraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine ReviewerDocument5 pagesEndocrine ReviewerAshley MalolotNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Sex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDocument7 pagesSex Hormone Synthesis, Regulation, and Function - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewWahyu W'cas PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Efectos de La Perdida de Estrogenos en MenopausiaDocument14 pagesEfectos de La Perdida de Estrogenos en MenopausiaDaniel J Alejos CNo ratings yet
- Testosterone: A Complete Guide to Male Hormonal Balance (How to Boost Your Testosterone, Gain the Muscle You've Always Wanted)From EverandTestosterone: A Complete Guide to Male Hormonal Balance (How to Boost Your Testosterone, Gain the Muscle You've Always Wanted)No ratings yet
- Neurotransmission and synaptic potentialsDocument2 pagesNeurotransmission and synaptic potentialsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- ? AnxiolyticsDocument2 pages? AnxiolyticsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- ?antidepressantsDocument1 page?antidepressantsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- ?? MCQ - PharmacologyDocument9 pages?? MCQ - PharmacologyKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- Buy Adderall OnlineDocument12 pagesBuy Adderall OnlineDany JamesNo ratings yet
- Ketamine's Medical Uses and EffectsDocument23 pagesKetamine's Medical Uses and EffectsDimas Gatra DiantoroNo ratings yet
- SDCEP Drug Prescribing Ed 3 Update June 2021Document4 pagesSDCEP Drug Prescribing Ed 3 Update June 2021ABNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris A Review of Causes and Treatment.6Document10 pagesAcne Vulgaris A Review of Causes and Treatment.6Nuwaira BalochNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Rev.2 / DEC.2021Document6 pagesRev.2 / DEC.2021Linh PhạmNo ratings yet
- Compartment ModellingDocument46 pagesCompartment ModellingBio DataNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Anadrol Cycles For Huge Muscle GainsDocument1 pageTop 5 Anadrol Cycles For Huge Muscle GainsKinan KholandiNo ratings yet
- AMRI API ProductCatalog WebDocument16 pagesAMRI API ProductCatalog Webমোঃ এমদাদুল হকNo ratings yet
- BetahistinDocument2 pagesBetahistinThuc TranNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument56 pagesAnalgesicMuhammad hilmiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee Policies and ProceduresDocument5 pagesPharmacy and Therapeutics Committee Policies and ProceduresPHARMACY OLMCMCNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology II - Exam 3 Review (Katzung) Flashcards - QuizletDocument16 pagesPharmacology II - Exam 3 Review (Katzung) Flashcards - Quizletyeshuavelando13No ratings yet
- Journal ClubDocument28 pagesJournal Clubapi-355090691No ratings yet
- Venlafaxine and Chronic PainDocument2 pagesVenlafaxine and Chronic PainteddypolNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics: Mary C. Brucker Tekoa L. KingDocument26 pagesPharmacotherapeutics: Mary C. Brucker Tekoa L. KingVishal KotiaNo ratings yet
- IV PO ConversionsDocument1 pageIV PO Conversionsdamondouglas100% (1)
- Please Note: Slower Titration May Be Appropriate For Some PatientsDocument1 pagePlease Note: Slower Titration May Be Appropriate For Some PatientsSholehuddin MunajjidNo ratings yet
- Vanco & Ag PK 2018Document35 pagesVanco & Ag PK 2018Nguyen GeenNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Medimart - Diciembre 2016Document16 pagesCatalogo Medimart - Diciembre 2016arturo ayalaNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassificationDocument14 pagesDrug ClassificationQueenie Anne ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: PsychopharmacologyDocument37 pagesChapter 4: PsychopharmacologyGummyCola100% (2)
- Stok Tanggal 10 November 2023Document3 pagesStok Tanggal 10 November 2023Nita FitriNo ratings yet
- Penggolongan Obat 1Document27 pagesPenggolongan Obat 1Dias Angga PerdanaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics: A Refresher: Curtis L. Smith, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSDocument36 pagesPharmacokinetics: A Refresher: Curtis L. Smith, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSSyahrul Tuba Al Fatih100% (1)
- DiphenhydramineDocument3 pagesDiphenhydramineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- FiberCon (Polycarbophil)Document1 pageFiberCon (Polycarbophil)ENo ratings yet
- DTRDocument6 pagesDTRThessa Lonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1a Antiinfective DrugsDocument4 pages1a Antiinfective DrugsMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Summary For Antibiotic For USMLE Exam - USMLE MaterialsDocument6 pagesSummary For Antibiotic For USMLE Exam - USMLE MaterialsAshik ThapaNo ratings yet