Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodic Table and Chemical Bonding Guide
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie Cordero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesOriginal Title
periodic table(chemical bonding)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesPeriodic Table and Chemical Bonding Guide
Uploaded by
Teresa Marie CorderoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Periodic Table of Elements-the
arrangement of elements in increasing
atomic number.
Elements-the simplest form of substance.
Metals-the elements found at the left side
of the periodic table.
-they are good conductors of electricity.
Nonmetals-the elements found at the
right side of the periodic table.
-they are poor conductors of electricity.
Metalloids-these are sometimes called as
semimetals.
-they possess properties of both metals
and non-metals.
-Boron, Silicon, Germanium, Arsenic,
Antimony, Tellurium, and Polonium
Compounds-these are made up of two or
more elements chemically bound together.
-example: NaCl (Sodium Chloride)
-Ionic compound(formed from metal and
nonmetal), and Covalent compound(formed
from two non-metals or a metalloid and
nonmetal).
CHEMICAL BONDING
-a lasting attraction between atoms, ions or
molecules that enables the formation of
chemical compounds.
Types of Chemical Bonds:
1.Ionic Bond-a bond formed through
complete transfer of electrons from one
atom to another atom.
-it exists between metals and non-metals.
-it is formed after a metal atom transfer its
VALENCE ELECTRON to non-metal atom.
Ions-these are charged atoms.
Cation-a positive ion.
-it loses electrons.
Anion-a negative ion.
-it gains electrons.
Valence Electron-is the electron found in
the outermost shell of the atom.
-it is also the group/family number of an
element in the periodic table.
2. Covalent Bond-also called as Molecular
Bond.
-it is a bond that involves sharing of
electrons between atoms.
-it commonly occurs when two non-metals
bond together or a metalloid and a non-
metal.
Two types of Covalent Bonds:
Nonpolar Covalent Bond-equal sharing
of electrons.
-if the difference of their electronegativity
is 0.
-example: H2, I2
Polar Covalent bond-unequal sharing of
electrons.
-the difference of their electronegativity is
greater than 0 but less than 2.0.
-examples: HF, ICl, NO
*Electronegativity-the ability of an atom
to gain electron when it is part of a
molecule.
-the greater the pull of electrons, the higher
the electronegativity.
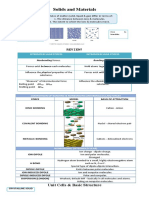
PROPERTIES OF IONIC AND COVALENT
COMPOUNDS:
Properties Ionic Covalent
Existence Exist in the Exist as
Solid state solid, liquid,
only and gas
Conductivity Low Very low
conductivity conductivity
Hardness Very Not
Hard/Brittle hard/More
flexible
Melting and High Low
Boiling Points
Malleability Non- Non-
malleable malleable
Ductility Non-ductile Non-ductile
Volatility Low High
Solubility Soluble in Insoluble in
water but water but
insoluble in soluble in
organic organic
solvent solvent
You might also like
- Classification of Matter and its PropertiesDocument4 pagesClassification of Matter and its PropertiesAriane Caranto100% (2)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelDocument34 pagesChemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelAhmed KhalilNo ratings yet
- 02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingDocument10 pages02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingShreyash ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid Systems: © 2004 Baker Hughes Incorporated All Rights ReservedDocument33 pagesDrilling Fluid Systems: © 2004 Baker Hughes Incorporated All Rights ReservedKaleem UllahNo ratings yet
- Asme - Stress Classification Lines Straight Through SingularitiesDocument10 pagesAsme - Stress Classification Lines Straight Through SingularitiesRay FaiersNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Work On Hooke's Law and Stress-Strain RelationshipDocument17 pagesPhysics Project Work On Hooke's Law and Stress-Strain RelationshipAbhisek Adhikari100% (2)
- WRAS Materials Guidance v4.4 Issued 21st November 2016Document56 pagesWRAS Materials Guidance v4.4 Issued 21st November 2016Premji FufalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Radiography Test & Liquid Penetrant Test ProcedureDocument7 pagesRadiography Test & Liquid Penetrant Test ProcedurePrashant MalveNo ratings yet
- Covalent Network MoleculesDocument1 pageCovalent Network MoleculesGill CraigNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 5 Study GuideDocument3 pagesChemistry Test 5 Study GuideLeanne RoseNo ratings yet
- X Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24Document35 pagesX Chem Master Key Differences 23 - 24zilkag47No ratings yet
- MELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1Document32 pagesMELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1A Dee YoungNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding IIDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding IIdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quarter 2Document12 pagesScience 9 Quarter 2Catherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document12 pagesScience 9Catherine Yorong PedranoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Bonding Models: Ionic BondsmartinNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Ionic, Covalent and Metallic BondsDocument7 pagesDifferences Between Ionic, Covalent and Metallic BondstriviaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument50 pagesChemical BondingLeila BonNo ratings yet
- Specialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoDocument5 pagesSpecialization: Physical Science: Environment: By: Prof. Crisanta A. OcampoApril Joyce Ricamora NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and Lewis StructuresDocument5 pagesChemical Bonds and Lewis Structuresnicole MenesNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonding PropertiesDocument11 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonding PropertiesKamran TajbakhshNo ratings yet
- Atomic bondsDocument21 pagesAtomic bondsDr-Amr HesseinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Chemistry ChapDocument22 pagesNursing Chemistry ChapJ.K HomerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Igcses Chemistry SummaryDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Igcses Chemistry Summarytaliaamjad771No ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazad832393No ratings yet
- 02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingDocument9 pages02 CHEM X ICSE SUMMARY Chemical BondingNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- Bonds ActivityDocument6 pagesBonds ActivityAna MtzNo ratings yet
- The Name's Bonds, Breaking BondsDocument6 pagesThe Name's Bonds, Breaking Bondsapi-348321624No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds GuideDocument10 pagesChemical Bonds GuideDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- Comparison On BondsDocument7 pagesComparison On Bondseliastadele7No ratings yet
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 5Document8 pagesChemistry Form 4 Chapter 5ManiArasiChandranNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of MatterDocument18 pagesBuilding Blocks of MatterPaul AckermannNo ratings yet
- Midterm Chem86 NotesDocument9 pagesMidterm Chem86 NotessujzNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bond Cont., Metallic BondDocument28 pagesCovalent Bond Cont., Metallic BondKim Bryan A. GaliasNo ratings yet
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Ionization and Electronegativity TrendsDocument4 pagesIonization and Electronegativity Trendsur momNo ratings yet
- Covalent, Ionic and Metallic BondsDocument3 pagesCovalent, Ionic and Metallic BondsJudy SherifNo ratings yet
- Bonding Summary NotesDocument17 pagesBonding Summary NotesaleenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds ExplainedDocument17 pagesIonic and Covalent Bonds ExplainedMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyDocument17 pagesBonding and Structure: Chemistry Notes GCE Study BuddyKhemou DjvickzNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesPhysical Science 2nd QuarterAngelica C. BramajeNo ratings yet
- First Topic - Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesFirst Topic - Chemical BondingSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- PH 1203 NoteDocument16 pagesPH 1203 NoteTA MI MNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Repaso Test 1 Periodo 3 10 GradoDocument7 pagesChemistry Repaso Test 1 Periodo 3 10 GradoRebeca BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 1 Periodo 3 10 GradeDocument7 pagesChemistry Test 1 Periodo 3 10 GradeRebeca BenavidesNo ratings yet
- IMFA and Chemical BondingDocument137 pagesIMFA and Chemical BondingEnna SertNo ratings yet
- Xture of SolidsDocument12 pagesXture of Solidsmuonekechibukeleonard52No ratings yet
- Inquiry Into Bonding Lab - Intro TestDocument5 pagesInquiry Into Bonding Lab - Intro Testapi-491531529No ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- C2: Structure, Bonding and The Properties of Matter: Key ConceptsDocument9 pagesC2: Structure, Bonding and The Properties of Matter: Key ConceptsMrs S Baker100% (1)
- Formation and Types of Covalent BondsDocument55 pagesFormation and Types of Covalent Bonds陈凯雯No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding ExplainedDocument94 pagesChemical Bonding ExplainedChelleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 1 Periodo 3 10 Grade ...Document7 pagesChemistry Test 1 Periodo 3 10 Grade ...Rebeca BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Bonding and FormulaDocument8 pagesBonding and FormulaJosephat MugumbaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Integrated Science (Chemistry) NotesDocument14 pagesGrade 9 Integrated Science (Chemistry) NotesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- Definitions PDFDocument9 pagesDefinitions PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Chemical BondDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Chemical Bondمسنيزواتي محمد نورNo ratings yet
- Revierwer For 2ND Quarter ScienceDocument6 pagesRevierwer For 2ND Quarter ScienceKyle OxfordNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic ChemistryDocument50 pagesChemical Bonds: Lecturer: Dr. Yayooo Course Title: Organic Chemistryyayooo200450% (2)
- Chapter 4 - Chemical BondingDocument17 pagesChapter 4 - Chemical Bondingthur.libraNo ratings yet
- Oral RecitationDocument1 pageOral RecitationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Naming CompoundsDocument2 pagesNaming CompoundsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesScience Exam QuestionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam in Chem 1Document2 pagesFinal Exam in Chem 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 SCIENCE EXAMDocument8 pagesGRADE 7 SCIENCE EXAMTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesScience Exam QuestionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Examination in Science 9Document2 pagesSecond Quarter Examination in Science 9Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Exam Review in Earth ScienceDocument2 pagesQuarterly Exam Review in Earth ScienceTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Exam in Science 7Document2 pagesFirst Quarterly Exam in Science 7Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Pretest in Physical Science 12 covers Big Bang Theory, atomic structure, hydrocarbonsDocument3 pagesPretest in Physical Science 12 covers Big Bang Theory, atomic structure, hydrocarbonsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Activity 1Document2 pagesEndocrine Activity 1Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Long Test in Science 7Document1 pageLong Test in Science 7Teresa Marie Cordero100% (1)
- 2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Document2 pages2nd Quarter Examination in Physical Science 12 (2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument5 pagesMICROSCOPETeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CARBONDocument1 pageCARBONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- TOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Document3 pagesTOS Grade 10 (1st Quarter 2019-2020)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesREPRODUCTIONTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument6 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- CELL OrganellesDocument5 pagesCELL OrganellesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity in MicroscopeDocument2 pagesActivity in MicroscopeTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- WHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Document1 pageWHLP Activity Sheet 1 (Circulatory)Teresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Ways of Separating MixturesDocument23 pagesWays of Separating MixturesTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of SolutionsDocument30 pagesConcentration of SolutionsTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Activity in MicroscopeDocument2 pagesActivity in MicroscopeTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesAtomic StructureTeresa Marie CorderoNo ratings yet
- E Cospace: AE Aterial SpecificationDocument5 pagesE Cospace: AE Aterial SpecificationAsraff Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- HOMEWORK Polymers and SynthesisDocument21 pagesHOMEWORK Polymers and SynthesisRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Industry ProfileDocument17 pagesIndustry ProfileSreelal P M LalNo ratings yet
- Hydrochloric Acid Regeneration in Hydrometallurgical ProcessesDocument13 pagesHydrochloric Acid Regeneration in Hydrometallurgical ProcessesmacNo ratings yet
- Sequentially Linear Continuum Model For Concrete FractureDocument9 pagesSequentially Linear Continuum Model For Concrete FractureStajic MilanNo ratings yet
- Plastiment P 121 R Pds enDocument2 pagesPlastiment P 121 R Pds enArdy YulisetiantoNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Simulation of Mini Pyrolysis Reactor For Conversion ofDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Simulation of Mini Pyrolysis Reactor For Conversion ofDidit Setyo PamujiNo ratings yet
- Asme b18!8!4m Pin Materials and HardnessDocument2 pagesAsme b18!8!4m Pin Materials and Hardnessjaskaran singhNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter Liquids and Solids McqsDocument6 pages4 Chapter Liquids and Solids McqsAáwáíź Jútt0% (1)
- NUST SMME Advanced Manufacturing Processes Fall 2022Document5 pagesNUST SMME Advanced Manufacturing Processes Fall 2022Abuzar AliNo ratings yet
- Celtra Press Lab BrochureDocument28 pagesCeltra Press Lab BrochureMark Saul Pérez TorresNo ratings yet
- A New Approach - MuslimMahardikaDocument15 pagesA New Approach - MuslimMahardikaheri suhud kustoyo100% (1)
- Heavy Hex Nuts PDFDocument2 pagesHeavy Hex Nuts PDFIPI100% (1)
- Welding Procedure - A - PDFDocument60 pagesWelding Procedure - A - PDFMade Agus BudiarthaNo ratings yet
- Unfolding The CausticumDocument78 pagesUnfolding The CausticumSk Saklin MustakNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet 5Document4 pagesChemistry Worksheet 5Deandra AliciaNo ratings yet
- Saeco Incanto Deluxe Parts DiagramDocument5 pagesSaeco Incanto Deluxe Parts DiagramAlain HOAREAU100% (1)
- Wedge Belts Veco 200 Dynam System: ST - API - ISO 4184 - DIN 7753 - BS 3790Document2 pagesWedge Belts Veco 200 Dynam System: ST - API - ISO 4184 - DIN 7753 - BS 3790Alexandre GelsiNo ratings yet
- Page 37 From API-1104-2016Document1 pagePage 37 From API-1104-2016Riaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 7 DIAGRAMSDocument9 pagesChemistry Notes 7 DIAGRAMSvravisankarNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Mechanism of "Smart WaterDocument28 pagesUnderstanding the Mechanism of "Smart WaterLulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- ZYTDGeDocument62 pagesZYTDGeAnonymous JIRIzeiJ6ONo ratings yet
- Hydrogen ProductionDocument3 pagesHydrogen ProductionKhairul Anwar Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Sunon Dp203at 2122LBT - GN.155 (A12003480g-00) - 1Document9 pagesSunon Dp203at 2122LBT - GN.155 (A12003480g-00) - 1German DANo ratings yet
- ISO - Doc Master List External-ProductionDocument8 pagesISO - Doc Master List External-ProductionhanujaNo ratings yet