Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Academic&communicative
Uploaded by
Vito AsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Academic&communicative
Uploaded by
Vito AsCopyright:
Available Formats
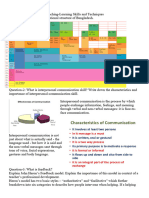
Academic and Communicative Listenings
Academic listening and communicative listening are two distinct types of listening
that differ in their goals, contexts, and strategies.
Academic listening is the type of listening that is practiced in academic settings, such
as lectures, seminars, and conferences. The goal of academic listening is to understand
and process complex information, ideas, and arguments in order to learn and acquire
knowledge. Academic listening requires the listener to be analytical, critical, and
focused, and to use strategies such as note-taking, summarizing, and synthesizing
information.
Communicative listening, on the other hand, is the type of listening that is practiced in
everyday social interactions, such as conversations with friends, family, and
colleagues. The goal of communicative listening is to establish and maintain social
relationships, exchange information, and understand the feelings and perspectives of
others. Communicative listening requires the listener to be empathetic, non-
judgmental, and responsive, and to use strategies such as asking questions,
paraphrasing, and providing feedback.
One of the key differences between academic listening and communicative listening is
their context. Academic listening takes place in formal settings, such as classrooms
and conferences, where the speaker is often an authority figure who is imparting
knowledge to the listener. Communicative listening, on the other hand, takes place in
informal settings, such as social gatherings and workplace conversations, where the
speakers are often peers who are exchanging information and ideas.
Another difference between academic listening and communicative listening is their
purpose. Academic listening is focused on learning and acquiring knowledge, whereas
communicative listening is focused on building relationships and understanding
others. While both types of listening require active and attentive processing of
information, academic listening places a greater emphasis on critical thinking and
analysis, whereas communicative listening places a greater emphasis on empathy and
understanding.
Finally, the strategies used in academic listening and communicative listening differ
as well. Academic listening often involves taking notes, summarizing information,
and analyzing arguments, while communicative listening involves asking questions,
paraphrasing, and providing feedback to the speaker. Academic listening requires the
listener to be more independent and self-directed in their learning, whereas
communicative listening requires the listener to be more interactive and engaged with
the speaker.
Academic listening is the process of actively and attentively processing spoken
information in an academic context. This type of listening is essential for students who
are pursuing higher education, as lectures and classroom discussions are the primary
modes of instruction in most college and university courses.
Academic listening involves much more than simply hearing the words that are being
spoken. Effective academic listening requires a range of skills, including the ability to
concentrate, understand complex vocabulary and sentence structures, identify key
ideas, and take notes. Additionally, academic listening requires the listener to engage
critically with the material being presented and to ask questions for clarification or
deeper understanding.
One of the challenges of academic listening is the fast-paced and dense nature of the
information being presented. Lectures may cover a broad range of topics and include
technical language and specialized vocabulary, which can be difficult to understand
without prior knowledge or preparation. To overcome this challenge, effective
academic listeners often engage in pre-listening activities, such as reading assigned
materials or reviewing notes from previous classes, to familiarize themselves with the
topic and concepts being discussed.
Another important aspect of academic listening is note-taking. Note-taking is the
process of capturing key ideas and information from lectures and discussions in a
format that is easy to review and study later. Effective note-taking strategies can vary
depending on personal preference and learning style, but generally involve writing
down main ideas, supporting details, and any questions or observations that arise
during the lecture. Notes should also be organized and easy to read, with clear
headings and bullet points.
To improve academic listening skills, students can engage in a variety of activities and
exercises. These may include practicing active listening by summarizing lectures or
discussions in their own words, participating in class discussions to clarify their
understanding of concepts, and reviewing lecture materials and notes regularly to
reinforce learning. Additionally, students can seek out resources such as academic
listening workshops or online tutorials to further develop their skills.
There are several strengths of academic listening that are worth discussing.
Improved comprehension: One of the primary strengths of academic listening
is that it improves comprehension. When students listen actively, they can
understand the content more deeply and retain it for longer periods. This is
particularly important in an academic setting, where students are exposed to
complex and challenging concepts.
Enhanced critical thinking: Active listening also promotes critical thinking. By
listening to lectures and discussions, students can analyze, evaluate, and
synthesize information. They can identify key ideas, arguments, and evidence,
and draw connections between them. This helps students develop their
analytical and critical thinking skills.
Improved note-taking: Note-taking is an essential skill for academic success,
and active listening is a key component of effective note-taking. When students
listen attentively, they can identify the most important information and record it
in a concise and organized manner. This helps them review and study the
material later on.
Better communication skills: Academic listening also helps students develop
their communication skills. By listening carefully, students can better
understand the perspectives and ideas of others. This promotes empathy,
tolerance, and respectful communication. It also helps students develop their
own ideas and arguments by considering the viewpoints of others.
Increased engagement: Active listening promotes engagement and participation
in the classroom. When students are actively listening, they are more likely to
ask questions, participate in discussions, and contribute to the learning
environment. This enhances the learning experience for both the student and
the instructor.
Better academic performance: Perhaps the most significant strength of
academic listening is that it leads to better academic performance. By
improving comprehension, critical thinking, note-taking, communication skills,
and engagement, students are better equipped to succeed in their academic
endeavors.
Overall, academic listening is a critical skill for success in higher education and
beyond. By honing their ability to concentrate, understand complex language, identify
key ideas, take effective notes, and engage critically with material, students can
become more confident and effective learners, and achieve greater success in their
academic and professional pursuits.
In conclusion, academic listening is a critical component of effective learning and
academic success. It promotes improved comprehension, enhanced critical thinking,
improved note-taking, better communication skills, increased engagement, and better
academic performance. By developing strong academic listening skills, students can
achieve their academic goals and become more successful learners.
Communicative listening is a process that involves the active and attentive processing
of spoken and non-verbal messages in order to understand and respond to the message
being conveyed. It is an essential aspect of interpersonal communication that involves
not only hearing the words being spoken but also paying attention to non-verbal cues,
such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language. Communicative listening
requires the listener to be fully present and engaged in the moment, and to respond to
the speaker in a way that is empathetic, non-judgmental, and respectful.
Effective communicative listening is essential in building and maintaining positive
relationships, resolving conflicts, and promoting effective problem-solving. It requires
the listener to be open-minded and willing to listen to different perspectives and
experiences. Communicative listening also involves providing feedback to the speaker
in a constructive and respectful manner, in order to ensure that the message being
conveyed has been fully understood.
Communicative listening is a skill that can be developed through practice and self-
reflection. It involves being aware of one's own biases and assumptions, and being
willing to challenge them in order to better understand the message being conveyed.
Effective communicative listening can also help to overcome communication barriers,
such as language and cultural differences, by fostering a sense of mutual respect and
understanding.
Communicative listening is a key component of effective communication in all areas
of life, including personal relationships, professional settings, and even in public
speaking. It is a skill that can be developed and refined over time through practice and
self-awareness.
At its core, communicative listening involves not only hearing the words being spoken
but also actively processing and understanding the message being conveyed. This
includes paying attention to non-verbal cues, such as body language and tone of voice,
which can provide important information about the speaker's thoughts and feelings.
Effective communicative listening requires the listener to be fully present in the
moment, to focus their attention on the speaker, and to respond in a way that is
empathetic and respectful. It involves being open-minded and willing to consider
different perspectives and experiences, even if they are different from one's own.
Communicative listening is especially important in situations where communication
barriers may exist, such as in cross-cultural interactions or when working with
individuals with different language abilities. By actively listening and showing respect
for the speaker's perspective, communicative listening can help to overcome these
barriers and promote understanding and cooperation.
In addition to its role in building positive relationships and promoting effective
communication, communicative listening can also be an important tool for personal
growth and development. By listening actively and attentively to the perspectives of
others, we can broaden our own understanding of the world and develop a more open
and inclusive mindset.
There are several key aspects of communicative listening that are worth discussing.
Active Listening: Another important aspect of communicative listening is active
listening. Active listening involves not only hearing the words being spoken but also
paying attention to nonverbal cues, asking clarifying questions, and providing
feedback to the speaker. Active listening helps to ensure that we understand the
message being conveyed and that the speaker feels heard and validated.
Empathy: One of the key aspects of communicative listening is empathy. Empathy is
the ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. When we engage in
communicative listening, we seek to understand the speaker's perspective, feelings,
and experiences. This allows us to respond appropriately and effectively to their
message.
Non-judgmental Listening: Communicative listening also involves non-judgmental
listening. Non-judgmental listening means listening without forming opinions or
making assumptions about the speaker or their message. This helps to create a safe
and supportive environment for the speaker to express themselves and share their
thoughts and feelings.
Feedback: Providing feedback is an essential part of communicative listening.
Feedback can help the speaker to clarify their message, ensure that they have been
understood, and provide an opportunity for further discussion. Feedback should be
constructive, specific, and focused on the message being conveyed.
Overall, communicative listening is a fundamental skill that can have a powerful
impact on our personal and professional lives. It requires the listener to be present,
engaged, and responsive to the needs of the speaker, and to approach communication
with a spirit of openness, respect, and empathy. By developing strong communicative
listening skills, we can improve our relationships, promote effective communication,
and create a more harmonious and inclusive society.
In conclusion, communicative listening is an essential aspect of effective
communication that involves active and attentive listening to both verbal and non-
verbal cues. It requires the listener to be present, engaged, and responsive to the needs
of the speaker, and to provide feedback in a constructive and respectful manner. By
developing strong communicative listening skills, we can improve our relationships,
resolve conflicts, and create a more inclusive and harmonious society.
In conclusion, academic listening and communicative listening are two distinct types
of listening that differ in their goals, contexts, and strategies. While both types of
listening are important for effective communication and learning, they require
different skills and approaches in order to be effective. By understanding the
differences between academic listening and communicative listening, we can become
more effective listeners in both settings.
You might also like
- Learning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’From EverandLearning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Importance of ListeningDocument4 pagesThe Importance of ListeningAngelo Rebayla OribiaNo ratings yet
- Literacy in EducationDocument7 pagesLiteracy in Educationsha shaNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: 8601-1 General Method of TeachingDocument28 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: 8601-1 General Method of TeachingMasooma IshratNo ratings yet
- English End 21uwsl01c01 - 202304010016 - Kashak AgarwalaDocument13 pagesEnglish End 21uwsl01c01 - 202304010016 - Kashak Agarwala202304010016No ratings yet
- Thesis On Teaching Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesThesis On Teaching Listening SkillsPaperHelperTucson100% (2)
- Instructional Strategies List July 2015Document10 pagesInstructional Strategies List July 2015faquinitoNo ratings yet
- 21 Century SUSD CharacteristicsDocument10 pages21 Century SUSD Characteristicscresta2014No ratings yet
- Unit 5Document14 pagesUnit 5IrynaNo ratings yet
- Teaching, Learning Skills and Techniques, IncourseDocument4 pagesTeaching, Learning Skills and Techniques, IncourseAshraf AtiqueNo ratings yet
- Active Listening EssayDocument5 pagesActive Listening EssaySiewLiZhenNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (And Listening Skills)Document3 pagesOral Communication (And Listening Skills)Faizan ChNo ratings yet
- What Problem Do You Encounter in Dealing With Learning Principles That Affect Your LearningDocument2 pagesWhat Problem Do You Encounter in Dealing With Learning Principles That Affect Your LearningMarie Louise AgbayNo ratings yet
- Speaking and Listening Instructional Philosophy and Teaching SuggestionsDocument13 pagesSpeaking and Listening Instructional Philosophy and Teaching SuggestionsMatsoni LorinsNo ratings yet
- Teaching AptitudeDocument26 pagesTeaching AptitudeAmlan DeNo ratings yet
- 21st CA 2.4Document4 pages21st CA 2.4RODELIZA FEDERICONo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument7 pagesReflectionAriane Grace LopezNo ratings yet
- Teaching Speaking: Towards A Holistic Approach: November 2016Document13 pagesTeaching Speaking: Towards A Holistic Approach: November 2016OvistasNo ratings yet
- Luqman, Aiman, Haziq Teacher's Responsibility To Implement The Psychosocial EnvironmentDocument5 pagesLuqman, Aiman, Haziq Teacher's Responsibility To Implement The Psychosocial EnvironmentLuqmanul HakimNo ratings yet
- ETA RocpaperDocument13 pagesETA Rocpaperjunelot56No ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, IslamabadDocument17 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabadeng.agkhanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesAdvantages of Oral CommunicationFikirini Rashid Akbar100% (2)
- Teaching Listening and Speaking - 1Document26 pagesTeaching Listening and Speaking - 129camziiNo ratings yet
- Notes Fs370usDocument39 pagesNotes Fs370usrosaliaNo ratings yet
- Development of Learning StrategiesDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Learning StrategiesDanielle AkutagawaNo ratings yet
- 61 113 PDFDocument3 pages61 113 PDFSharifah Al-JamalullailNo ratings yet
- Learning Ouput #7Document3 pagesLearning Ouput #7MAUREEN JANE MACTALNo ratings yet
- Discussion As A Teaching StrategyDocument3 pagesDiscussion As A Teaching StrategyGiovane ButlayNo ratings yet
- Facilitating LearningDocument6 pagesFacilitating Learningrosa verdadero100% (1)
- NEXUS INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY Lecture Notes 2Document13 pagesNEXUS INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY Lecture Notes 2Obote DanielNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceapi-135146194No ratings yet
- Pedagogical KnowledgeDocument7 pagesPedagogical KnowledgeDaffodils100% (2)
- Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: General Method of TeachingDocument27 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: General Method of TeachingMuhammad Atif JavaidNo ratings yet
- Post - Listening ActivitiesDocument3 pagesPost - Listening ActivitiesMohammad HossainNo ratings yet
- Strategies For Promoting Critical Thinking Through Questioning 4Document9 pagesStrategies For Promoting Critical Thinking Through Questioning 4omotayoayotundefordeNo ratings yet
- Teaching of The Macro SkillsDocument30 pagesTeaching of The Macro SkillsNiño Naldoza100% (1)
- Class DiscussionDocument2 pagesClass Discussionsoliloquium47No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentsudadpoopmasterNo ratings yet
- EpikDocument1 pageEpiksudadpoopmasterNo ratings yet
- Brophy NotesDocument2 pagesBrophy Notesapi-350262169No ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument8 pagesListening SkillsNet Green IINo ratings yet
- Listening in An Esp Written FormDocument31 pagesListening in An Esp Written FormbennouiouamanelNo ratings yet
- Summative Review of The MATC Portfolio & Synthesis Paper - Evaluation FormDocument3 pagesSummative Review of The MATC Portfolio & Synthesis Paper - Evaluation Formdavidsonkl713No ratings yet
- Thesis Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesThesis Listening Skillsjanaclarkbillings100% (2)
- Communication in EducationDocument6 pagesCommunication in Educationsaidakambarova155No ratings yet
- Academic Debate: Rwandz Private Technical InstituteDocument13 pagesAcademic Debate: Rwandz Private Technical InstituteEnglish TutorNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - The Integrated Language Arts Curriculum Ela Loralie BeldadDocument2 pagesLesson 4 - The Integrated Language Arts Curriculum Ela Loralie BeldadEla BeldadNo ratings yet
- Paradigm Shift - WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesParadigm Shift - WPS Officetakena PowNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument3 pagesListeningA'ron Geron HernandezNo ratings yet
- Accountable Talk SourcebookDocument65 pagesAccountable Talk SourcebookCarlos RabelloNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument3 pagesReflectionjinkycezar1990No ratings yet
- Nature, Kinds, Stages of ListeningDocument10 pagesNature, Kinds, Stages of ListeningGedie RocamoraNo ratings yet
- HLPDocument6 pagesHLPPAULNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-2Document18 pagesUnit 3-2hajraNo ratings yet
- Mulungushi University School of Education: Names: Program: Course CodeDocument6 pagesMulungushi University School of Education: Names: Program: Course CodeRabson HamejaNo ratings yet
- Comprehension and Fluency SlidesDocument25 pagesComprehension and Fluency SlidesAdrian CatapatNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVEDocument5 pagesPURPOSIVERee-Jane Bautista Macaraeg100% (1)
- 34 Methods of Analysis 1Document26 pages34 Methods of Analysis 1Vito AsNo ratings yet
- Types of Listening Skills PDFDocument11 pagesTypes of Listening Skills PDFVito AsNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionVito AsNo ratings yet
- Effective VictorDocument5 pagesEffective VictorVito AsNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Approaches To The Study of The Phenomenon of ListeningDocument6 pages1.1. Approaches To The Study of The Phenomenon of ListeningVito AsNo ratings yet
- Approaches To The Study of Phenomenon of ListeningDocument6 pagesApproaches To The Study of Phenomenon of ListeningVito AsNo ratings yet
- English ID 1 2nd Edition Students Book SSDocument2 pagesEnglish ID 1 2nd Edition Students Book SSWellen LimaNo ratings yet
- EvAUMad ALanguageForAllDocument2 pagesEvAUMad ALanguageForAllEstefaníaBernalFernándezNo ratings yet
- Language Portfolio Ibcp GuidelinesDocument10 pagesLanguage Portfolio Ibcp Guidelinesapi-233401612No ratings yet
- Assignment HBET2103Document33 pagesAssignment HBET2103Shamshurizat HashimNo ratings yet
- 4 Phonetic Symbols by Group 2Document13 pages4 Phonetic Symbols by Group 2Arya WirandaNo ratings yet
- GreekDocument219 pagesGreekHassan Jacob Aguimesheo100% (2)
- Bege 102Document0 pagesBege 102Shashi Bhushan SonbhadraNo ratings yet
- Year 3Document6 pagesYear 3P͜͡i͜͡n͜͡k͜͡T͜͡e͜͡d͜͡d͜͡y͜͡No ratings yet
- Oral Communication For Non-Native Speakers of English: October 2020Document52 pagesOral Communication For Non-Native Speakers of English: October 2020YurielNo ratings yet
- 8 BibliographyDocument3 pages8 BibliographyJihan Nadila AsriNo ratings yet
- Elementary - 3 - A2. 1Document1 pageElementary - 3 - A2. 1Victoria HubertNo ratings yet
- On The Origins of The Japanese LanguageDocument28 pagesOn The Origins of The Japanese LanguageMuhammmad zaki FadhlurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Sumarry of Superlative and ComarativeDocument3 pagesSumarry of Superlative and ComarativekasorimaruNo ratings yet
- SQP Class X - English PDFDocument5 pagesSQP Class X - English PDFArjun R RaoNo ratings yet
- 1.teaching Assessment of The Macroskills Midterm DoneDocument11 pages1.teaching Assessment of The Macroskills Midterm DoneGeralyn Pelayo AlburoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Medical TerminologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction Medical TerminologyGlaiza Mae MasaoyNo ratings yet
- Phonics Patterns Part2Document198 pagesPhonics Patterns Part2yanamaq100% (6)
- Where Is The Gym?: Level 1 Lesson 6Document12 pagesWhere Is The Gym?: Level 1 Lesson 6Willy AntNo ratings yet
- Practical Tips and Techniques in TestingDocument13 pagesPractical Tips and Techniques in TestingTrịnh Minh HiếuNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Exercise 1Document2 pagesParts of Speech Exercise 1Katy HernándezNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect 1 British English Teacher Ver2 BWDocument4 pagesPresent Perfect 1 British English Teacher Ver2 BWDiana Mireya Cuellar SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Simple Present of The Verb To BeDocument4 pagesThe Simple Present of The Verb To BeGeorgina Gómez RiveraNo ratings yet
- Simple Past - Summary FileDocument4 pagesSimple Past - Summary FileWallace ValeNo ratings yet
- Theory Unit 32 - 1993 Listing - Updated 2017Document12 pagesTheory Unit 32 - 1993 Listing - Updated 2017LGFNo ratings yet
- Verbos Irregulares y RegularesDocument2 pagesVerbos Irregulares y RegularesHJVLNo ratings yet
- Language Maintenance and ShiftDocument3 pagesLanguage Maintenance and ShiftInayatul fitriNo ratings yet
- KCSE POETRY REVISION Zoom Summary by Mr. NdivoDocument3 pagesKCSE POETRY REVISION Zoom Summary by Mr. Ndivowanyoikecollins25No ratings yet
- Music and The Politics of Sound: Nationalism, Citizenship, and Auditory SpaceDocument17 pagesMusic and The Politics of Sound: Nationalism, Citizenship, and Auditory SpaceJose Javier ZafraNo ratings yet
- Week 01 - Task Assignment - My Daily RoutineDocument2 pagesWeek 01 - Task Assignment - My Daily RoutinejhonathanNo ratings yet
- CI-Friendly Reading StrategiesDocument25 pagesCI-Friendly Reading StrategiesIELTS Council100% (1)
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistFrom EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Uptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingFrom EverandUptime: A Practical Guide to Personal Productivity and WellbeingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Eat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeFrom EverandEat That Frog!: 21 Great Ways to Stop Procrastinating and Get More Done in Less TimeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3231)
- Summary of Dan Martell's Buy Back Your TimeFrom EverandSummary of Dan Martell's Buy Back Your TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationFrom EverandMastering Productivity: Everything You Need to Know About Habit FormationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (24)
- What's Best Next: How the Gospel Transforms the Way You Get Things DoneFrom EverandWhat's Best Next: How the Gospel Transforms the Way You Get Things DoneRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Writing Without Bullshit: Boost Your Career by Saying What You MeanFrom EverandWriting Without Bullshit: Boost Your Career by Saying What You MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The 80/20 Principle and 92 Other Powerful Laws Nature: The Science of SuccessFrom EverandThe 80/20 Principle and 92 Other Powerful Laws Nature: The Science of SuccessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (220)
- How to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateFrom EverandHow to Be Better at Almost Everything: Learn Anything Quickly, Stack Your Skills, DominateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (861)
- Entrepreneurial You: Monetize Your Expertise, Create Multiple Income Streams, and ThriveFrom EverandEntrepreneurial You: Monetize Your Expertise, Create Multiple Income Streams, and ThriveRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (89)
- The Like Switch: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide to Influencing, Attracting, and Winning People OverFrom EverandThe Like Switch: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide to Influencing, Attracting, and Winning People OverRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- The Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableFrom EverandThe Five Temptations of A CEO: A Leadership FableRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (216)
- Made You Look: How to Use Brain Science to Attract Attention and Persuade OthersFrom EverandMade You Look: How to Use Brain Science to Attract Attention and Persuade OthersNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Rich Dad Library: To Elevate the Financial Well-Being Of HumanityFrom EverandThe Ultimate Rich Dad Library: To Elevate the Financial Well-Being Of HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Becoming Bulletproof: Protect Yourself, Read People, Influence Situations, and Live FearlesslyFrom EverandBecoming Bulletproof: Protect Yourself, Read People, Influence Situations, and Live FearlesslyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (355)
- The Truth Detector: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide for Getting People to Reveal the TruthFrom EverandThe Truth Detector: An Ex-FBI Agent's Guide for Getting People to Reveal the TruthRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (29)
- Get it Done Now! (2nd Edition): Own Your Time, Take Back Your LifeFrom EverandGet it Done Now! (2nd Edition): Own Your Time, Take Back Your LifeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (28)
- Building a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will ListenFrom EverandBuilding a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will ListenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1248)
- Summary: High Output Management: 45 Minutes - Key Points Summary/RefresherFrom EverandSummary: High Output Management: 45 Minutes - Key Points Summary/RefresherRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)
- Master Your Time, Master Your Life: The Breakthrough System to Get More Results, Faster, in Every Area of Your LifeFrom EverandMaster Your Time, Master Your Life: The Breakthrough System to Get More Results, Faster, in Every Area of Your LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (433)
- Protect Your Time: How to Use Your Time Strategically, Eliminate Busy-ness, and Build Constructive Habits to Go from an Outperformer to a GamechangerFrom EverandProtect Your Time: How to Use Your Time Strategically, Eliminate Busy-ness, and Build Constructive Habits to Go from an Outperformer to a GamechangerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (77)
- Dopamine Detox: Reduce Instant Gratification, Beat Social Media Addiction, and Stop Wasting Your LifeFrom EverandDopamine Detox: Reduce Instant Gratification, Beat Social Media Addiction, and Stop Wasting Your LifeNo ratings yet
- 24/6: The Power of Unplugging One Day a WeekFrom Everand24/6: The Power of Unplugging One Day a WeekRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- The First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterFrom EverandThe First 90 Days: Proven Strategies for Getting Up to Speed Faster and SmarterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)