Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Drift
Uploaded by
En Seven0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesGenetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies in a population over time, which can lead to the loss of alleles. It is more common in small populations. There are two main types: bottleneck effect, which occurs when a population is reduced in size, such as from a natural disaster, and founder effect, which occurs when a subset of a population establishes a new population. Both result in allele frequencies that are different from the original population due to the random sampling of alleles in the new population. Artificial selection, also called selective breeding, is when humans select for desirable traits in domesticated species to be passed on, contrasting with natural selection. Mutation and recombination also introduce new genetic variation within populations.
Original Description:
Genetic Drift General Biology 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGenetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies in a population over time, which can lead to the loss of alleles. It is more common in small populations. There are two main types: bottleneck effect, which occurs when a population is reduced in size, such as from a natural disaster, and founder effect, which occurs when a subset of a population establishes a new population. Both result in allele frequencies that are different from the original population due to the random sampling of alleles in the new population. Artificial selection, also called selective breeding, is when humans select for desirable traits in domesticated species to be passed on, contrasting with natural selection. Mutation and recombination also introduce new genetic variation within populations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views3 pagesGenetic Drift
Uploaded by
En SevenGenetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies in a population over time, which can lead to the loss of alleles. It is more common in small populations. There are two main types: bottleneck effect, which occurs when a population is reduced in size, such as from a natural disaster, and founder effect, which occurs when a subset of a population establishes a new population. Both result in allele frequencies that are different from the original population due to the random sampling of alleles in the new population. Artificial selection, also called selective breeding, is when humans select for desirable traits in domesticated species to be passed on, contrasting with natural selection. Mutation and recombination also introduce new genetic variation within populations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
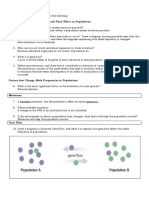
GENETIC DRIFT
Common in small population, no significance in large population.
Some alleles become more common while others become less common overtime (or lost).
When there is only one allele is left for a particular gene pool, that allele is said to be fixed.
TYPES OF GENETIC DRIFT
• BOTTLENECK EFFECT – Reduction in population size
• FOUNDER EFFECT – Subset of population founds new population
The bottleneck effect occurs when a natural disaster or similar
event randomly kills a large portion (i.e. random sample) of the
population, leaving survivors that have allele frequencies that
were very different from the previous population.
These are Northern elephant seals that experience Bottleneck event due to humans hunting in 1890’s.
The population size has been reduced to 20 individuals at the end of the 19th century.
Today, their population increases to 30,000 but their genes still carry the marks of this bottleneck in which they carry
much less genetic variation.
The founder effect occurs when a portion of the population (i.e.
"founders") separates from the old population to start a new
population with different allele frequencies.
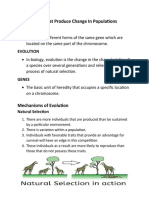
ARTIFICIAL SELECTION
Also called selective breeding, artificial selection is perhaps best understood as a contrast to natural selection, where the
random forces of nature determine which individuals survive and reproduce
Selective breeding tries to establish certain traits that animals will pass to the next generation. These are traits that humans
find desirable in domesticated species such as disease resistance, strength, calmness, more lean meat, endurance, etc.
MUTATION
Any heritable change in the DNA of a cell or an alteration in a DNA sequence
A mutation is a random change in the DNA sequence within a gene or chromosome of a living organism. They
can also be described as copying errors within the DNA.
Mutations can be spontaneous (random), but they can also be triggered by other many internal and external
factors, such as toxins, chemical substances or radiation.
RECOMBINATION
One of the sources of those new combinations of genes is recombination during meiosis. It is responsible for producing
genetic combinations not found in earlier generations.
This crossing-over process results in an unlinking and recombination of parental genes.
You might also like
- 15.2 Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument11 pages15.2 Mechanisms of Evolutionslipper_crazy5335No ratings yet
- Mechanism of EvolutionDocument41 pagesMechanism of EvolutionChristian EstradaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MechanismsDocument15 pagesEvolution of MechanismsJesmin ShumiNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument23 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionVeancy WangNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument36 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionAllenNo ratings yet
- Mendelian and Population GeneticsDocument30 pagesMendelian and Population GeneticsJunia100% (1)
- Mechanisms in EvolutionDocument30 pagesMechanisms in EvolutionakiNo ratings yet
- Natural SelectionDocument31 pagesNatural SelectionAnonymous MvL5rvS100% (1)
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocument44 pagesMechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- REPORT BIO MicroevolutionDocument35 pagesREPORT BIO Microevolutionmichael tamadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15: Mechanisms in Population: General Biology 2 Nicolites Montessori SchoolDocument3 pagesLesson 15: Mechanisms in Population: General Biology 2 Nicolites Montessori SchoolJohn John SierraNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocument45 pagesMechanisms That Produce Change in Populationskaren milloNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument42 pagesEvolutionalayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of EvolutionDocument26 pagesMechanism of Evolutionk15014998No ratings yet
- FIVE Agents of Evolutionary ChangeDocument3 pagesFIVE Agents of Evolutionary Changes.felicitas.shaniekadielleNo ratings yet
- E Volution by Means of Natural SelectionDocument3 pagesE Volution by Means of Natural SelectionNurul HidayahNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity PDFDocument13 pagesBiodiversity PDFMuhammad AkramNo ratings yet
- Biology WRDocument7 pagesBiology WRElene Grace BarteNo ratings yet
- Micro EvolutionDocument9 pagesMicro EvolutionBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Natural Selection TutorialDocument28 pagesEvolution and Natural Selection TutorialAGLDNo ratings yet
- Patters of EvolutionDocument33 pagesPatters of EvolutionJonathan SmithsNo ratings yet
- The Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Document11 pagesThe Process in Genetic Engineering (Crops)Inio JarhylNo ratings yet
- Key Points: Genetic Drift Is A Mechanism of Evolution in Which Allele Frequencies of ADocument10 pagesKey Points: Genetic Drift Is A Mechanism of Evolution in Which Allele Frequencies of APrabhleen KaurNo ratings yet
- W2 Genetic DiversityDocument29 pagesW2 Genetic DiversityMammoth CoffeeNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Mechanisms of Evolution Guided InquiryDocument3 pages9.1 Mechanisms of Evolution Guided InquiryShaun AhujaNo ratings yet
- Genes in PopulationDocument45 pagesGenes in PopulationMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Genetic DiversityDocument31 pagesGenetic DiversityAbegail AvilaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 4 Week 4Document4 pagesGen Bio Module 4 Week 4LouisseNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument4 pagesMechanisms of Evolutionchristopher daniolcoNo ratings yet
- Migrationgene Flow Genetic DriftDocument16 pagesMigrationgene Flow Genetic DriftPhia ViaNo ratings yet
- 9.1mechanisms of Evolution and Their Effect On PopulationsDocument3 pages9.1mechanisms of Evolution and Their Effect On PopulationsbxyrtbgyxcNo ratings yet
- J) Variation and EvolutionDocument3 pagesJ) Variation and Evolutionamarashah182No ratings yet
- P401-01 Microevolutionary Forces - ChapterDocument26 pagesP401-01 Microevolutionary Forces - ChapterBekkem Lavanya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lec 14 PDFDocument4 pagesLec 14 PDFMichael FernoNo ratings yet
- Microevolution: Week 4Document27 pagesMicroevolution: Week 4sidra javedNo ratings yet
- Copy Bio (Complete Infos)Document8 pagesCopy Bio (Complete Infos)marcutoy000No ratings yet
- ,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,MDocument4 pages,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,MAnonymous 51aHkMdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Biology 11Document46 pagesChapter 9 Biology 11ax1leNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25 Evolutionary ProcessesDocument4 pagesLecture 25 Evolutionary ProcessesLol MdrNo ratings yet
- 1.evolution Through Genetic DriftDocument5 pages1.evolution Through Genetic DriftBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Conservation Genetics: A Paradigm For Fisheries ManagementDocument8 pagesConservation Genetics: A Paradigm For Fisheries ManagementMaria Na DhinNo ratings yet
- Variation: and Natural SelectionDocument51 pagesVariation: and Natural SelectionTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Evolution ConceptsDocument2 pagesEvolution ConceptsJavier RosalesNo ratings yet
- Evolution of PopulationDocument9 pagesEvolution of PopulationUj UmarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Population Changes Over Time in Living SystemsDocument23 pagesMODULE 6 Population Changes Over Time in Living SystemsEdward VicenteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document3 pagesChapter 15Salma BondocNo ratings yet
- Ev. Forces of ChangeDocument15 pagesEv. Forces of ChangemgordonNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanism of Evolution Lecture E. SanaDocument6 pagesBasic Mechanism of Evolution Lecture E. SanaEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Drift ReportDocument3 pagesGenetic Drift ReportLiza Mae NeisNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsDocument6 pagesMechanisms That Produce Change in PopulationsTobias Domenite P.No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Micro EvolutionDocument47 pagesLecture 6 - Micro EvolutionirosalejosNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection 2.5Document26 pagesNatural Selection 2.5DequanNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Natural Selection TutorialDocument52 pagesEvolution and Natural Selection Tutorialapi-234891239No ratings yet
- Ch. 23 Lecture Outline PDFDocument15 pagesCh. 23 Lecture Outline PDFCSERM UNASNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document44 pagesModule 6akinolaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- Breeding Strategies and Genetic ConsequeDocument11 pagesBreeding Strategies and Genetic ConsequeRahadian AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument3 pagesBio NotesMarianne BalayoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Unit I - Evolutionary EcologyDocument2 pagesLecture Notes On Unit I - Evolutionary EcologyCheryl MountainclearNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - Evolutionary GeneticsDocument53 pagesModule 11 - Evolutionary GeneticsIngrid ParissNo ratings yet
- Genetic Catastrophe! Sneaking Doomsday?: With<Br> a Dictionary of Genetic DamageFrom EverandGenetic Catastrophe! Sneaking Doomsday?: With<Br> a Dictionary of Genetic DamageNo ratings yet