Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Exercise Affects Breathing Rate
Uploaded by
Selena Winsborrow0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pages1) The document describes an experiment to investigate how breathing rate changes with exercise. A stopwatch and paper/pencil were used to count breaths before, during, and after exercise.
2) Results were recorded in a table showing that breathing rate increased from 22 breaths/min at rest to 31 breaths/min immediately after exercise before gradually decreasing again.
3) The discussion explains that respiration supplies energy through aerobic and anaerobic pathways and can be affected by factors like exercise, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels in ways observed in the experiment.
Original Description:
Original Title
respiration
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document describes an experiment to investigate how breathing rate changes with exercise. A stopwatch and paper/pencil were used to count breaths before, during, and after exercise.
2) Results were recorded in a table showing that breathing rate increased from 22 breaths/min at rest to 31 breaths/min immediately after exercise before gradually decreasing again.
3) The discussion explains that respiration supplies energy through aerobic and anaerobic pathways and can be affected by factors like exercise, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels in ways observed in the experiment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views2 pagesHow Exercise Affects Breathing Rate
Uploaded by
Selena Winsborrow1) The document describes an experiment to investigate how breathing rate changes with exercise. A stopwatch and paper/pencil were used to count breaths before, during, and after exercise.
2) Results were recorded in a table showing that breathing rate increased from 22 breaths/min at rest to 31 breaths/min immediately after exercise before gradually decreasing again.
3) The discussion explains that respiration supplies energy through aerobic and anaerobic pathways and can be affected by factors like exercise, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels in ways observed in the experiment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SBA
Title: Respiration
Aim: To investigate how breathing rate changes with exercise
Apparatus/Materials: stopwatch, Paper, pencil
Procedure/Method:
1. sat quietly for 1 minute to ensure relaxation.
2. The number of breaths taken and recorded for the next minute.
3. Rigorous exercise was done for 3 minutes.
4. The number of breaths were counted and recorded immediately for 1 minute.
5. Rested for 1 minute and number of breaths were taken in the next minute.
6. Step 5 was repeated until breathing rated returned to normal.
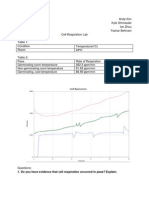
7. Results were recorded in a table.
8. A line graph was constructed to show tabulated results.
Observations:
TABLE SHOWING RATE OF BREATHING
Time (mins) Number of breaths taken
0 ( resting) 22
1(after excercising) 31
2 29
3 26
4 21
Discussion:
Respiration can be defined as the process by which organisms obtain the energy needed to
drive the chemical processes that takes place in their cells. Respiration occurs specifically in the
mitochondria. There are two types of respiration anaerobic and aerobic. Aerobic respiration
takes place in the presence of oxygen. The equation for aerobic respiration is C 6H1206 + 6O2 →
energy + 6CO2+ 6H20 and anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. The
equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells is C6H12O6 → energy + 2C3H6O3. Lactic acid
is the waste product.
A few common zRespiration can be affected by exercise when anaerobic respiration happens in
the muscles during hard exercise. Glucose is not completely broken down so less energy is
released than aerobic respiration.
Another factor that can affect respiration is the temperature rate, a low temperature decreases
cellular respiration in living tissues as the temperature rises and carbon dioxide affects
respiration rate by elevating the concentrations of carbon dioxide reduces rates of respiration.
The heart rate increases during exercise the rate and depth of breathing increases this makes
sure that more oxygen is absorbed into the blood. The breathing rate didn’t go back to its
normal rate after exercise because when you do vigorous exercise the muscles are not supplied
with enough oxygen. After exercising your beathing rate takes a long time because you used so
much oxygen during your exercise.
Sources of Errors: miss counting the amount of breaths and subject may suffer a respiratory
condition
Limitations: A person may have a respiratory condition and Stopwatch started to
malfunction during the experiment.
Precautions: ensure stopwatch starts recording simultaneous to when the subject begins the
experiment and if the subject has asthma ensures they have an asthma inhaler in the event
they get an asthma attack.
Conclusion: After doing this experiment it can be concluded that exercising can change the
rate of you breathing when doing vigorous exercising.
Reflection: This experiment showed that when I did cross countries in places I ran a long
distance and as I was done I was breathing heavy because I used a lot of energy.
You might also like
- Exercise LabDocument3 pagesExercise LabJonatan LeflerNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Lab: Exercise's Effect on Respiration RatesDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Lab: Exercise's Effect on Respiration Ratesur momNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Lab Shows Effect of Temperature on Pea Germination RateDocument6 pagesCell Respiration Lab Shows Effect of Temperature on Pea Germination Rateianzhou1No ratings yet
- Exercise 13 15 HomeostasisDocument11 pagesExercise 13 15 HomeostasisRoxan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- How Breathing Rate Changes With ExerciseDocument2 pagesHow Breathing Rate Changes With ExerciseChris JumanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 15 - External RespirationDocument32 pagesExercise 15 - External RespirationAldrin LozanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- FINAL Lab Report #1Document7 pagesFINAL Lab Report #1Chippy RabeNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2.1b_ Oxygen _ Human RespirationDocument4 pagesActivity 2.2.1b_ Oxygen _ Human RespirationVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Aerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationDocument4 pagesAerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationRana HalabyNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITDocument6 pagesMODULE 4 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITEmie PonceNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemSophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- Respiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PosterDocument7 pagesRespiration BIOLOGY Year 9 PostererinaNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- Ideally It Is Shown You Should Breathe Lightly, in A Calm Fashion, and Only Through The Nose, Not MouthDocument10 pagesIdeally It Is Shown You Should Breathe Lightly, in A Calm Fashion, and Only Through The Nose, Not MouthS KNo ratings yet
- Science and Technology 9: Activity 1 ObjectiveDocument5 pagesScience and Technology 9: Activity 1 ObjectivebchraNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologyDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Lab Exercise 9 Respiratory System PhysiologySetnami DhulNo ratings yet
- Biol 142 Exercise Physiology LabDocument11 pagesBiol 142 Exercise Physiology Labapi-284897006No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument19 pagesRespiration NotesGift Blessed NgoveNo ratings yet
- Biol 141-Exercise Physiology Lab Report Final RevisedDocument11 pagesBiol 141-Exercise Physiology Lab Report Final Revisedapi-252628311100% (1)
- Microscope ReportDocument15 pagesMicroscope ReportMiftha MallaulingNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsDocument5 pagesRespiration in Organisms: A. Short Answers QuestionsnarayanaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Phys Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExercise Phys Lab Reportapi-253190807No ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- LAB - 611.effects of Exercise On HomeostasisDocument7 pagesLAB - 611.effects of Exercise On HomeostasisscarfaceownuNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- HPL 041 Chemical Control of RespirationDocument2 pagesHPL 041 Chemical Control of Respirationhulu12No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingDocument35 pagesThe Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and BreathingScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument10 pagesExercise Physiology Lab Reportapi-253305501100% (1)
- BreathingDocument3 pagesBreathingShara ThamzeerNo ratings yet
- Cardio Yoga PublicDocument5 pagesCardio Yoga PublicSoulyogaNo ratings yet
- Biology notes _ chapter 12 respiration updatedDocument3 pagesBiology notes _ chapter 12 respiration updatedbalsh374No ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Respiratory SubstrateDocument8 pagesRespiration: Respiratory SubstrateEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Mursaleen KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 (Biology) Complete Lecture With Solution. Date:26/6/22 Contact:01715782957Document8 pagesChapter-5 (Biology) Complete Lecture With Solution. Date:26/6/22 Contact:01715782957Ahnaf Rahman RyanNo ratings yet
- The Triple B: Breath andDocument12 pagesThe Triple B: Breath andChristian FarofaldaneNo ratings yet
- Chap. 9 Respiration and Exercise Lab 2018Document2 pagesChap. 9 Respiration and Exercise Lab 2018lucyNo ratings yet
- Oxygen TherapyDocument25 pagesOxygen TherapyIsaiah AmolatoNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms: Aerobic vs AnaerobicDocument4 pagesRespiration in Organisms: Aerobic vs AnaerobicachlaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System E-Notes on Aerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationDocument5 pagesRespiratory System E-Notes on Aerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationAarav AroraNo ratings yet
- Bio 142 Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBio 142 Exercise Physiology Lab Reportapi-34160259975% (4)
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument11 pagesExercise Physiologyapi-284302840No ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument5 pagesRespiration Notesjj mayjNo ratings yet
- Biodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)Document19 pagesBiodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)aekimNo ratings yet
- Wim Hof MethodDocument4 pagesWim Hof MethodNoah MunozNo ratings yet
- Circus WorksheetsDocument16 pagesCircus Worksheetsapi-309893409No ratings yet
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument9 pagesExercise Physiology Lab Reporthumzak199286% (7)
- Respiratory System FunctionsDocument5 pagesRespiratory System FunctionsAnoushia AhmerNo ratings yet
- StethographyDocument3 pagesStethographyglad mohesh100% (4)
- Homeostasis Activity Station InstructionsDocument3 pagesHomeostasis Activity Station InstructionsTamsyn GreenNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ReportDocument19 pagesLab 6 Reportapi-311215267100% (2)
- 6 Human Respiration 2Document10 pages6 Human Respiration 2Harlee QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration and Oxygen DebtDocument14 pagesAerobic Respiration and Oxygen DebtPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Generation GapDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire Generation GapSelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 BiologyDocument1 pageLab 10 BiologySelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Alcohlism - Questionnaire-Social-Studies HelloDocument5 pagesAlcohlism - Questionnaire-Social-Studies HelloSelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Social Studies QuestionaireDocument2 pagesSocial Studies QuestionaireSelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Selena, Amber and Mica ProjectDocument6 pagesSelena, Amber and Mica ProjectSelena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Amber's Agenda 4Document1 pageAmber's Agenda 4Selena WinsborrowNo ratings yet
- Physical FitnessDocument14 pagesPhysical FitnessJudy MagistradoNo ratings yet
- Structuring A Program in Elite Professional Soccer: Strength and Conditioning Journal December 2017Document12 pagesStructuring A Program in Elite Professional Soccer: Strength and Conditioning Journal December 2017Jozef Oki SkumpijaNo ratings yet
- TLS 3 Day Workout RoutineDocument14 pagesTLS 3 Day Workout RoutineamberNo ratings yet
- Manage Stress Through Physical ActivityDocument23 pagesManage Stress Through Physical ActivityNhedzCaidoNo ratings yet
- Asking WH Questions WorksheetDocument3 pagesAsking WH Questions WorksheetMalene Caya100% (1)
- Regents Exam Questions on DistanceDocument8 pagesRegents Exam Questions on DistanceOliver Anthony HastaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Practice TestDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System Practice Testmedic99No ratings yet
- PE11 Q1 TEst QuestionsDocument19 pagesPE11 Q1 TEst QuestionsSemaj Serolf AicragNo ratings yet
- Calisthenics For Beginners Beginner Calisthenics Workout at HomeDocument43 pagesCalisthenics For Beginners Beginner Calisthenics Workout at HomePaolo PolveriniNo ratings yet
- Pathfit Module 2Document1 pagePathfit Module 2Jhanyne CalisaganNo ratings yet
- How Do I Measure Resting Heart RateDocument4 pagesHow Do I Measure Resting Heart Ratejayson acunaNo ratings yet
- Badminton Guide: Skills, Rules & MoreDocument47 pagesBadminton Guide: Skills, Rules & MoreJoseph ConsignadoNo ratings yet
- LIIFT4 Calendar 6.11.18 PDFDocument1 pageLIIFT4 Calendar 6.11.18 PDFRichard James BallinNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q1 - W1Laine Agustin SalemNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Physical Activity and ExerciseDocument15 pagesBenefits of Physical Activity and ExerciseTrisha Mae Dumala-ugNo ratings yet
- Essential Yoga Study GuideDocument6 pagesEssential Yoga Study GuidePradosh Kumar PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- Memorandum in Opposition To Temporary Restraining OrderDocument22 pagesMemorandum in Opposition To Temporary Restraining OrderinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- Developing A Cardio Respiratory Endurance ProgramDocument20 pagesDeveloping A Cardio Respiratory Endurance ProgramKoolecarla BernardoNo ratings yet
- Yoga AssignmentDocument7 pagesYoga Assignmentapi-429649086No ratings yet
- BMR CalculatorDocument1 pageBMR CalculatorSlayerNo ratings yet
- Anterior Knee Pain Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsDocument11 pagesAnterior Knee Pain Guide: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsViswanathNo ratings yet
- Ground Control Month 3: Focus Strength Speed Speed Strength Yielding Strength Contralateral Stability Concurrent AerobicDocument13 pagesGround Control Month 3: Focus Strength Speed Speed Strength Yielding Strength Contralateral Stability Concurrent AerobicDcore Brd80% (5)
- KM RTR Workout 22Document1 pageKM RTR Workout 22Rohit RorNo ratings yet
- Hatha Yoga Guide: Science, Benefits and Insights: ShareDocument10 pagesHatha Yoga Guide: Science, Benefits and Insights: ShareSuhas PatilNo ratings yet
- Read More YogaDocument23 pagesRead More YogaRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Neck ROM Exercises Ver1 01.08.18Document2 pagesNeck ROM Exercises Ver1 01.08.18kang soon cheolNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 PE&HealthDocument14 pagesGrade 11 PE&HealthAldrin Melad0% (1)
- PathFit 1Document28 pagesPathFit 1Alfred AbieraNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 PE Lessons on Locomotor MovementsDocument8 pagesGrade 4 PE Lessons on Locomotor MovementsJennifer AmugodNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anatomy 101Document25 pagesSpinal Anatomy 101Monleau céliaNo ratings yet