Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3-Ionic Bonding PDF
Uploaded by
Tahmeed Ahmed0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesIons are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, resulting in positively or negatively charged particles. When ions of opposite charge interact, they form ionic compounds through ionic bonding - the strong electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Ions are arranged in a regular lattice structure held together by these ionic bonds, giving ionic compounds high melting and boiling points as it requires significant energy to overcome these attractions. However, the rigid lattice also makes ionic crystals brittle.
Original Description:
Original Title
3-Ionic_bonding.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIons are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, resulting in positively or negatively charged particles. When ions of opposite charge interact, they form ionic compounds through ionic bonding - the strong electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Ions are arranged in a regular lattice structure held together by these ionic bonds, giving ionic compounds high melting and boiling points as it requires significant energy to overcome these attractions. However, the rigid lattice also makes ionic crystals brittle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pages3-Ionic Bonding PDF
Uploaded by
Tahmeed AhmedIons are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons, resulting in positively or negatively charged particles. When ions of opposite charge interact, they form ionic compounds through ionic bonding - the strong electrostatic attraction between positive and negative ions. Ions are arranged in a regular lattice structure held together by these ionic bonds, giving ionic compounds high melting and boiling points as it requires significant energy to overcome these attractions. However, the rigid lattice also makes ionic crystals brittle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Pearson Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Chemistry
Ionic Bonding
Chapter No. 3, Page No. 75
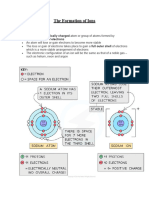
1. What are ions?
Ans. Ions are charged particles formed when atoms or groups of atoms lose
or gain electrons. Ions can have either a positive or a negative charge.
2. What happens when an ionic compound is formed?
Ans. When an ionic compound is formed, electron(s) are transferred from a
metal atom to a non-metal atoms to form positive and negative ions. Ionic
compounds have ionic bonding.
3. What is ionic bonding?
Ans. Ionic bonding is the strong electrostatic attraction between the positive
and negatively charged ions.
4. What is a lattice?
Ans. A lattice is a regular array of particles. The lattice is held together by the
strong electrostatic attractions between positively and negatively charged
ions.
5. Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
Ans. Ionic compounds have high melting points and boiling points because of
the strong electrostatic forces of attraction holding the lattice together. A lot
of energy has to be supplied to break the strong electrostatic forces of
attraction between oppositely charged ions in the giant lattice structure.
6. Why are ionic crystals brittle?
Ans. Ionic crystals tend to be brittle. This is because any small distortion of a
crystal will bring ions with the same charge alongside each other. Like
charges repel and so the crystal splits itself apart.
7. Why don’t ionic compound conduct electricity when they are solids?
Ans. Ionic compounds don’t conduct electricity when they are solids because
the ions are fixed in position and are not free to move around.
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- Activity Ionic BondDocument6 pagesActivity Ionic BondMichelle CaliuagNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding-NotesDocument47 pagesChemical Bonding-NotesHimanshu Meena100% (3)
- Ionic Bonding NotesDocument1 pageIonic Bonding Notesevango21No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- 7.1 7.2Document2 pages7.1 7.2noora.rami48No ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesIonic Bonding and StructureKaren OrlanskiNo ratings yet
- Ions and Ionic BondDocument21 pagesIons and Ionic Bondchickuwa pawawawaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Chemical BondingDocument50 pages3.0 Chemical Bondingparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Structure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGDocument23 pagesStructure & Bonding - IONIC BONDINGTrishana GreenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- CH 3, ChemDocument6 pagesCH 3, ChemAbdullah SalmanNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Ionic BondingDocument6 pages4 1 Ionic BondingNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 3A1 NotesDocument9 pagesIonic Bonding 3A1 NotesmunasheNo ratings yet
- Grade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionDocument65 pagesGrade-11 Chemistry Definitions CollectionMoun Lynn Sythu100% (3)
- Science Test 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesScience Test 2nd QuarterAbbychel AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocument10 pagesBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- 06 ANSWERS SummaryDocument1 page06 ANSWERS SummaryJean AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- GCFGCGCFGFDGDocument15 pagesGCFGCGCFGFDGZabrinaRuizNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 2 ValidatedDocument10 pagesScience 9 Wlas QTR 2 Week 2 ValidatedMYLENE B. ZABALLERONo ratings yet
- Bonding and StructureDocument20 pagesBonding and StructureYusma KhanNo ratings yet
- Primary Bonds: Chemical BondDocument1 pagePrimary Bonds: Chemical BondDhanushka WarnakulasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and BondingDocument18 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 5 - Structures and Bondingchelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- There Are Only Two Known Species ofDocument7 pagesThere Are Only Two Known Species ofmuhammad aslamNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument23 pagesIonic BondingMark DichosonNo ratings yet
- Answers To NCERT/CBSE Chemistry (Class XII) TextbookDocument1 pageAnswers To NCERT/CBSE Chemistry (Class XII) TextbookRohit GrewalNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- Why To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentDocument22 pagesWhy To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentdNo ratings yet
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZDocument187 pages2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1No ratings yet
- Ionic BondsDocument1 pageIonic BondsDivya ShahNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument30 pagesRadioactivitybrianna brownNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocument6 pagesChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Topic 4 Bonding and StructureDocument7 pagesEdexcel Topic 4 Bonding and Structurekmoiz427No ratings yet
- Chemistry Book SummaryDocument2 pagesChemistry Book SummaryTabeaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding in SolidsDocument3 pagesAtomic Bonding in Solidsazmatshahzad786786No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument41 pagesChemical BondingaswaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpDocument36 pagesChemical Bonding/s2 Kimia UnpIda HidayatiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Ionic CompoundsDocument2 pagesIonic CompoundsShenneth De CastroNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument30 pagesIonic BondinghidhhsdfhgidsufgNo ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondDocument22 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondnwdpggbhktNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Ionic BondDocument1 pageClass 12 Ionic BondIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document38 pagesPresentation 1rose ann chavezNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Ionic Bonding and StructureDocument2 pages4.1 Ionic Bonding and StructurelauraNo ratings yet
- Ionic BondingDocument18 pagesIonic Bondingahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Read and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!Document7 pagesRead and Annotate! I Want To See Notes and Highlights and Underlines On This Paper!api-344880038No ratings yet
- Comparing Ionic & Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesComparing Ionic & Covalent BondingRyan MarvinNo ratings yet
- Bond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical BondsDocument29 pagesBond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical Bondseric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.Document34 pagesIonic Bonding Sem II G.E. and D.S.C.allenbrien077No ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: PH 105 Physics-IDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: PH 105 Physics-IkalumamuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PDFDocument5 pagesChemistry Notes PDFTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 02 The Mole ConceptDocument1 page02 The Mole ConceptTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1-The Periodic TableDocument2 pages1-The Periodic TableTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1-The Land and Geography of North AmericaDocument1 page1-The Land and Geography of North AmericaTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 03-Modern CanadaDocument1 page03-Modern CanadaTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2-Indigenous People of North AmericaDocument1 page2-Indigenous People of North AmericaTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet