Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 12 Ionic Bond
Uploaded by
Ishraq KhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 12 Ionic Bond
Uploaded by
Ishraq KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic: Ionic Bond
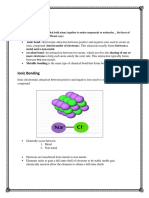
1. Ionic Bond: A type of chemical bond that involves the transfer of electrons from one
atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions.
2. Cation: A positively charged ion that is formed when an atom loses one or more
electrons.
3. Anion: A negatively charged ion that is formed when an atom gains one or more
electrons.
4. Electrovalence: The number of electrons that an atom gains or loses in order to form an
ion.
5. Ionic Compound: A compound that is made up of ions held together by electrostatic
forces.
6. Lattice Energy: The energy required to break apart an ionic compound into its constituent
ions.
7. Coulomb's Law: The law that describes the electrostatic attraction between two charged
particles, which is proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional
to the distance between them.
8. Born-Haber Cycle: A series of steps that describe the formation of an ionic compound
from its constituent elements.
9. Coordination Number: The number of ions that surround an ion in a crystal lattice.
10. Solubility: The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, which is influenced by the
strength of the ionic bonds in the substance.
11. Properties of Ionic Compounds: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points,
are brittle and hard, conduct electricity when molten or in solution, and form crystals.
These are just a few of the topics covered in Class 12 Ionic Bond. Other topics include ionization
energy, electron affinity, and lattice defects.
You might also like
- Chemical Bond Notes by TouhidDocument23 pagesChemical Bond Notes by Touhidnabilnakib0077No ratings yet
- Atoms CombiningDocument12 pagesAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Bonding (Part 2) : Chemical Bonding - Ionic BondingDocument3 pagesUnit 2: Bonding (Part 2) : Chemical Bonding - Ionic BondingHayden KelehanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument22 pagesChemical BondingJr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Why To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentDocument22 pagesWhy To Study - Material Technology & Heat TreatmentdNo ratings yet
- Bond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical BondsDocument29 pagesBond - HTML: SPM Form 4 Chemistry - Chemical Bondseric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ionic Bond PPDocument10 pagesChemistry Ionic Bond PPSaya KacakNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding NotesShaswat PattnayakNo ratings yet
- Bonding A Level NotesDocument5 pagesBonding A Level NotesWashington NyakaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2Muhammad Waheed IqbalNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Chemical BondingDocument50 pages3.0 Chemical Bondingparkinsondilys7No ratings yet
- Class 10th Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesClass 10th Chemistry NotesRehan KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsDocument24 pagesLecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsAbdallah ShaatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1ARTICA CASTILLO Fatima ValentinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument26 pagesChemical BondingShannelle Anne CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document37 pagesChemical Bonding 1Yara GhebariNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument53 pagesChemical Bondingpream.s1323No ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceDocument2 pagesMODULE 1 Chemistry As A Central ScienceEmma Cristie BalahadiaNo ratings yet
- CH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionDocument33 pagesCH 04. Bonding: AP Chemistry Basic Lecture Course Light VersionHARPACANo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding Notesseema sahniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonds and StructureDocument17 pagesChemical Bonds and StructureEddie EvansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemistry-Ch 3 - Chemical BondingHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- VBT MotDocument23 pagesVBT Motskyanan592No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument18 pagesChemical BondingJade GumonayNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision BookletDocument9 pagesChemistry Revision BookletNour MakaremNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument79 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom Holmemuhammad ali shakeelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument79 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDasai KamiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDocument79 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure: Larry Brown Tom HolmeDasai KamiNo ratings yet
- Bonding in Solids Definition: Solid State ChemistryDocument9 pagesBonding in Solids Definition: Solid State Chemistryhaimanot yibeltalNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocument15 pages3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument21 pagesChemical BondingMustafa ghazanfarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 6 ReviewDocument3 pagesChemistry Chapter 6 Reviewjuan carlos quispe mamaniNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondDocument22 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING Ionic BondnwdpggbhktNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesDocument9 pagesScience: Quarter 2 Types of Compounds Based On Their PropertiesAriel Lomugdang PatricioNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument81 pagesChemical BondingkhushiNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument30 pagesRadioactivitybrianna brownNo ratings yet
- CHAP 4-5 GPT PromptDocument4 pagesCHAP 4-5 GPT PromptHanz Josiah Balatero SerranoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 4Document17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 411 A Prasann JamaleNo ratings yet
- Definition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsDocument33 pagesDefinition: What Is A Chemical Bond? Different Types of Chemical Bonds With Examples FaqsMedakayala Nagasravanthi 20PHD7125No ratings yet
- Chemistry Bonding NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Bonding Notesseema sahniNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document4 pagesCB 1Mahmudur Rahman27No ratings yet
- Week # 8 Chemcial BondingDocument3 pagesWeek # 8 Chemcial BondingDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument8 pagesChemical BondingAhmed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL BONDING - NotesDocument30 pagesCHEMICAL BONDING - NotesP YNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Why Do Atoms Bond?Document3 pagesChemical Bonding: Why Do Atoms Bond?Saavelo WinlandNo ratings yet
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZDocument187 pages2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument132 pagesChemical BondingKowser mahmud100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureVishal MalikNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledManureet SinghNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentalishbajaved159No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument41 pagesChemical BondingaswaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesChemical BondsARDIUZNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NotesDocument17 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Notesarjunrkumar2024No ratings yet
- 3-Ionic Bonding PDFDocument2 pages3-Ionic Bonding PDFTahmeed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument12 pagesStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Chemical BondingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Class 12 Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageClass 12 Organic ChemistryIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageClass 12 ThermodynamicsIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PhysicsDocument1 pageClass 12 PhysicsIshraq KhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIshraq KhanNo ratings yet