Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3 - Elbow All Joints - Odt
Uploaded by
Abdulrahman HosnyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3 - Elbow All Joints - Odt
Uploaded by
Abdulrahman HosnyCopyright:
Available Formats
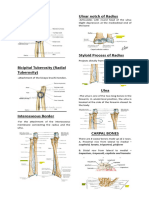
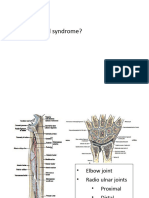
Elbow Joint (cubital joint)
Joint Classification Synovial hinge joint (2 articulations)
Axis of movement One degree of movement available! (transverse axis)
(flexion-extension)
Articular surfaces • Humero-ulnar joint(medially)
Trochlea of humerus
- Circular pulley-shaped trochlea with oblique groove
- Medial side inferiorly tiltedcreates carrying angle
- Concave in frontal plane
- Convex in sagittal plane
Trochlear notch of ulna
- Deep trochlear notch
- Ridge running from tip of olecranon to tip coronoid process
- Congruent fit to groove on trochlea
-
• Humero-radial joint(laterally)
Capitulum of humerus
- Incomplete hemispherical shape with variable radius of curvature
- Covered in hyaline cartilage (thickest centrally)
Head of Radius
- Superior concave surface for articulation with capitulum
- Raised edge for Capitulo-trochlear groove
All surfaces are covered in Hyaline cartilage
Joint Capsule - Single fibrous capsule
- Lined with synovial membrane
- Shared capsule with superior radioulnar
joint
- No direct attachment to radius
- Blends with collateral ligaments
↗ strength
- Weaker anteriorly & posteriorly
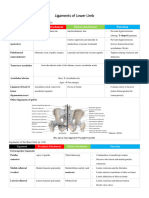
Ligaments - 2 triangular band on each side blending with joint capsule
• Ulnar collateral ligaments
Bands: Anterior Posterior Transverse Intermediate
From: Medial Medial Epicondyle Coronoid Medial
Epicondyle (posteriorly) process epicondyle
(anteriorly)
To: Coronoid Olecranon Olecranon Transverse
process band
Action Limits abduction,
Anterior band limits extension
• Radial collateral ligaments
Radial collateral
From: Lateral Epicondyle
(deep to extensor tendon)
To: - Blends with annular
ligament of radius
- Margins of radial notch
of ulna
Action: Limits adduction
Superior Radioulnar Joint
Joint Synovial pivot joint
Classification
Axis of vertical
movement
Articular • Head of radius: oval shaped, lined with hyaline cartilage
surfaces • Radial notch on ulna: creates 1/5 of ring, lined with hyaline cartilage
• Annular ligament : creates 4/5 of fibro-osseous ring, lined with
fibrocartilage
Joint Capsule • Extensive, shared with elbow
Synovial • Hangs as fold below annular ligament - allows for rotation of radius
membrane
Ligaments
Annular ligament Quadrate ligament
Features: - Creates 4/5 ring From: lower border of radial notch
- Strong & flexible so of ulna
oval head rotates freely
- Attached to anterior & To:
posterior margins of - Adjacent medial surface of
radial notch neck of radius proximal to
- Superior support radial tuberosity
provided by radial - Fibres run in a crisscross
collateral ligament + orientation
blends with annular in any position (pronation &
ligament & margins of supination) some fibres are
the radial notch under tension
- Upper part is lined with - Overall constant tension in
synovial membrane ligament
-
Action - Prevents displacement - Limits pronation
of radial head - Limits supination
- Stabilisation of joint
Inferior Radioulnar Joint
Joint Synovial pivot joint
Classification
Axis of movement vertical
Articular surfaces • Distal ulna: crescent shaped,
lined with hyaline cartilage
• Distal radius: Biconcave ulnar
notch, lined with hyaline cartilage
• Articular disk: Triangular
fibrocartilage, apex at root of ulnar
styloid and base at inferior edge
ulnar notch on radius
Joint Capsule Loose to allow movement
Synovial • Hangs as fold below annular ligament - allows for rotation of radius
membrane
Articular disk - Triangular fibrocartilaginous discthicker on peripherally
From:
- (apex) lateral side of the base of the styloid process of the ulna
To:
- (Base) sharp inferior edge of ulna notch on the radius
Principle structure uniting the radius and ulna
Increases stability at joint
Interosseous membrane
Joint classification - Strong fibrous sheet between interosseous borders of radius & ulna
Direction of fibres Downwards and medially in oblique fashion
- Transmits forces from handradius, ulna, humerus
- Oblique cord superiorly
- Opening distally (pass way for vessels)
- Tightest in mid-position
Functions - Divides forearm into anterior & posterior compartments
- Shock absorption and dissipation
- Attachment site for deep muscles
You might also like
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- MSK 7Document72 pagesMSK 7Noor KhalidNo ratings yet
- M1 Anatomy Tutorial - Bones, Joints and Proximal Muscles of The Upper Limb (David)Document8 pagesM1 Anatomy Tutorial - Bones, Joints and Proximal Muscles of The Upper Limb (David)Tony NgNo ratings yet
- Bones of The Forearm and Hand ULNA - Longer Proximally, Pinky SideDocument3 pagesBones of The Forearm and Hand ULNA - Longer Proximally, Pinky SideJeanne Waldo ReminajesNo ratings yet
- Spine LectureDocument54 pagesSpine LectureDewi Lucy PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- PT Ligaments NotesDocument6 pagesPT Ligaments NotesngharrisonngNo ratings yet
- Lectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuDocument7 pagesLectured By: Dr. Jesus J. Gracilla Transcribed By: Beverly YuFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Spine LectureDocument55 pagesSpine LectureLeoNo ratings yet
- 5-Thoacolumbar SpineDocument20 pages5-Thoacolumbar SpineJULIONo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column and ContentsDocument5 pagesVertebral Column and ContentsJewelNo ratings yet
- Elbow Handout StudentsDocument8 pagesElbow Handout StudentsAdrielle Paul CostillasNo ratings yet
- MMB (018) Elbow Joint Cubital Fossa (Practical) 2022Document39 pagesMMB (018) Elbow Joint Cubital Fossa (Practical) 2022Mohamed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wrist and Hand TransesDocument5 pagesWrist and Hand TranseskatrizmaervillagantolNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Joints - Quick Revision Table by Anatomy DecodedDocument8 pagesUpper Limb Joints - Quick Revision Table by Anatomy DecodedJuned LabbaiNo ratings yet
- Upper ExtremityDocument216 pagesUpper ExtremityChester VergilNo ratings yet
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 pagesElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- All Bat NotesDocument1,048 pagesAll Bat NotesAfk SystemNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SpineDocument33 pagesAnatomy of SpineMaria RobertaNo ratings yet
- Spine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiDocument59 pagesSpine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiJho AggasidNo ratings yet
- Knee Ankle JointsDocument38 pagesKnee Ankle JointsmaggieNo ratings yet
- The Ligamentum Flavum:: Present Throughout Vertebral ColumnDocument9 pagesThe Ligamentum Flavum:: Present Throughout Vertebral ColumnUmar JawadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Elbow - ForearmDocument34 pagesLecture 7 Elbow - Forearm15 I Komang Saskaraning RadikaNo ratings yet
- Joints ChartDocument1 pageJoints Chartbkpad026No ratings yet
- Anatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Document10 pagesAnatomy 03 - Pectoral and Scapular Region (Pre Med 101)Navoda Dulshan PereraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NotesDocument29 pagesAnatomy NotesAna TsereteliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spine: DR Pankaj N Surange MBBS, MD, Fipp Interventional Pain and Spine SpecialistDocument72 pagesAnatomy of Spine: DR Pankaj N Surange MBBS, MD, Fipp Interventional Pain and Spine SpecialistMohammad Riedho Cahya AtazsuNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson 4Document40 pagesSkeletal System Lesson 4Ella Nika FangonNo ratings yet
- Radioulnar JointsDocument25 pagesRadioulnar JointsHARSHINI KNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesSkeletal SystemmelendezramesesjosephNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument33 pagesMuscles of The Backtaha makhloufNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or JointsDocument4 pagesShoulder Problem Evaluation: 6 Articulations or JointsMARY GIZETH GACHONo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column of DogDocument3 pagesVertebral Column of DogEmit Rosary PenetranteNo ratings yet
- Joints of Lower Limb 2017Document77 pagesJoints of Lower Limb 2017yasrul izadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Knee Joint and Popliteal Fossa: Prof. Dr. Nabil Khouri MDDocument37 pagesAnatomy of Knee Joint and Popliteal Fossa: Prof. Dr. Nabil Khouri MDBadria Al-najiNo ratings yet
- 5.back and Scapular RegionDocument72 pages5.back and Scapular RegionGish KioiNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: The Shoulder JointDocument7 pagesLearning Objectives: The Shoulder JointLaura TapiaNo ratings yet
- Muscle Innervation Chart IIDocument7 pagesMuscle Innervation Chart IIkimsue9448No ratings yet
- Orbit - Head & NeckDocument57 pagesOrbit - Head & NeckNandini BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spinal Anatomy: Spine Made Up FromDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Spinal Anatomy: Spine Made Up Fromh_sadeghiNo ratings yet
- Gluteal Region 1Document49 pagesGluteal Region 1S.BrindhaNo ratings yet
- Imaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesDocument12 pagesImaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesChristian ToalongoNo ratings yet
- Axial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Document11 pagesAxial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Jose Emmanuel DolorNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Wall NotesDocument11 pagesThoracic Wall NotesAlfNo ratings yet
- XX Popliteal Fossa and Knee JointDocument43 pagesXX Popliteal Fossa and Knee JointAlistair WalkerNo ratings yet
- Ocular AppendagesDocument24 pagesOcular AppendagesS De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Spine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineDocument22 pagesSpine: Junior Intern - Csu College of MedicineCris Soliven DucosNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb MusclesDocument19 pagesUpper Limb MusclesVinod Sharma100% (1)
- Muscles of The Lower Limb - RevisionDocument23 pagesMuscles of The Lower Limb - Revisionsrikanth Posa100% (1)
- Examination of ElbowDocument82 pagesExamination of Elbowbhavikaagarwal07No ratings yet
- Table 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeDocument14 pagesTable 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeReham QueNo ratings yet
- Elbow, Wrist and Radioulnar JointsDocument35 pagesElbow, Wrist and Radioulnar JointsGaurav ThapaNo ratings yet
- Anatomia Da ColunaDocument59 pagesAnatomia Da ColunaPaula Duarte MarquesNo ratings yet
- 02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEDocument18 pages02 IVD Hernia Case Report MedBac&IEClaude ReyesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Points: at The End of Your Study, You Should Be Able ToDocument1 pageClinical Points: at The End of Your Study, You Should Be Able ToMihaelaNo ratings yet
- 2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDocument3 pages2.08 Brachial Region (Arm) - Compartments, Muscles, Nerves, and VesselsDi CanNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb TransDocument18 pagesUpper Limb Transashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Hip & Thigh MusclesDocument34 pagesHip & Thigh MusclesJeffrey SchrankNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics and Pathomechanics of Elbow JointDocument44 pagesBiomechanics and Pathomechanics of Elbow JointAshwini BajajNo ratings yet
- 2 Bones of Upper Limb 2Document29 pages2 Bones of Upper Limb 2Abdelrhman AbubakrNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patients With Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care For Patients With Musculoskeletal DisordersMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Diagram: Nerves in Rope BondageDocument1 pageAnatomical Diagram: Nerves in Rope BondageGabrielaNo ratings yet
- Part 17: First Aid: 2010 American Heart Association and American Red Cross Guidelines For First AidDocument13 pagesPart 17: First Aid: 2010 American Heart Association and American Red Cross Guidelines For First Aidrinda deswitaNo ratings yet
- What's New in Sports Medicine (Primary Care) - UpToDateDocument8 pagesWhat's New in Sports Medicine (Primary Care) - UpToDateManuel OpazoNo ratings yet
- Cat Dissection ManualDocument30 pagesCat Dissection ManualJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- Dental ElevatorsDocument20 pagesDental Elevatorsahmed amerNo ratings yet
- Ferm BS 702NDocument88 pagesFerm BS 702NZsolt LaczkóNo ratings yet
- Caz 1 PubmedDocument5 pagesCaz 1 PubmedAdriana Elena DoneNo ratings yet
- A6 Standard Lift Assembly m3 CAN Plasma System: Instruction ManualDocument79 pagesA6 Standard Lift Assembly m3 CAN Plasma System: Instruction ManualJulio De la RosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy-1Document50 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Anatomy-1Yasin AbduNo ratings yet
- DMSO Use ProtocolsDocument3 pagesDMSO Use ProtocolsfreeNo ratings yet
- Nordic Musculoskeletal Questionnaire Form PDFDocument1 pageNordic Musculoskeletal Questionnaire Form PDFkhaista bacha100% (3)
- Facial Nerve Ent NotesDocument8 pagesFacial Nerve Ent NotesJOSHI RAJUNo ratings yet
- EMAHS - Basic First Aid Topic OnlineDocument67 pagesEMAHS - Basic First Aid Topic OnlineWMSU DESCDNo ratings yet
- Fetal ContentDocument5 pagesFetal ContentPratima KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Prosthesis: Presented by Dr. Chiranjeevi.JDocument63 pagesProsthesis: Presented by Dr. Chiranjeevi.JchirusdunnaNo ratings yet
- Peran Penata Anestesi Pada Asuhan Anestesi Pada Kegawatdaruratan Orthopedi Dan TraumaDocument24 pagesPeran Penata Anestesi Pada Asuhan Anestesi Pada Kegawatdaruratan Orthopedi Dan TraumaArya MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Fire and Rescue BKRISEDocument47 pagesFire and Rescue BKRISEVIRUPAKSHA KOOLINo ratings yet
- Scheuermann's Disease: A Patient's Guide ToDocument11 pagesScheuermann's Disease: A Patient's Guide ToOana RindasuNo ratings yet
- M01 00101-15 LPDocument34 pagesM01 00101-15 LPMacelevi Darevi100% (3)
- 1 Structure of Bone: Aziz Nather, HJC Ong and Zameer AzizDocument15 pages1 Structure of Bone: Aziz Nather, HJC Ong and Zameer AzizGaleti EkramNo ratings yet
- BERNARDINO JIMENEZ, Petitioner, vs. CITY OF MANILA and INTERMEDIATE APPELLATE COURT, Respondents.Document3 pagesBERNARDINO JIMENEZ, Petitioner, vs. CITY OF MANILA and INTERMEDIATE APPELLATE COURT, Respondents.Charles Roger RayaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Touching The Void ExtractDocument2 pagesLesson 1 Touching The Void Extractlight LawlietNo ratings yet
- The Apprentice Doctor® Control Bleeding CourseDocument68 pagesThe Apprentice Doctor® Control Bleeding CourseAnton Scheepers100% (2)
- Muscle Testing: Knee Flexion + ExtensionDocument38 pagesMuscle Testing: Knee Flexion + ExtensionHaruka HaganeNo ratings yet
- ICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FractureDocument18 pagesICF-Ankle Trimalleolar FracturedvenumohanNo ratings yet
- EBCPG-diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lower Extremity UlcersDocument34 pagesEBCPG-diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Lower Extremity UlcersPhilippe Ceasar C. BascoNo ratings yet
- Dressing and BandagesDocument11 pagesDressing and BandagesNhemia Evangelista ManaloNo ratings yet
- SubduralhematomaDocument38 pagesSubduralhematomaNinaNo ratings yet
- Vertiv Chilled Water CCU IOM ManualDocument193 pagesVertiv Chilled Water CCU IOM Manualabeon augustineNo ratings yet