Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 3.3 Areas Under Normal Curve
Uploaded by
Midoriya IzukuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 3.3 Areas Under Normal Curve
Uploaded by
Midoriya IzukuCopyright:
Available Formats
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
13
STATISTICS
Name: ___________________________________________ Grade Level: ____________
Section: ___________________________________________ Score: _________________
Lesson 3.3
Areas Under the Normal Curve
Background Information for Learners
The normal distribution is the most widely known and used of all distributions. Because
the normal distribution approximates many natural phenomena so well, it has developed into a
standard of reference for many probability problems. Normally distributed data sets are common
in the real world. Real world observations that represent sums or averages of other numbers often
have histograms that are shaped like a normal data distribution. Applications include but are not
limited to business, finance, science and policy.
A key tool for calculating proportions and percentages associated with normal
distributions is the standard normal distribution. The standard normal distribution is a bell-
shaped planar region bounded above by a bell-shaped curve and below by a horizontal line
representing the z-values of the normal distribution.
Total area
is 1
A=1
z-values
Table 1 : The standard normal distribution curve
Possible data values of a standard normal random variable are indicated on the horizontal
line of z-values. The curve above it represents the likelihood of the values occurring in the sense
that the area under the curve to the left of a specific z-value on the horizontal axis represents the
percentage of real world values that are less than that particular z-value. To approximate these data
percentages (e.g. areas under the curve), we use the z-table.
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
14
Key: z-score= z-value A=Area of normal distribution to the left of z
For example, if we focus on the z-value given by z = 1.25 the area under the curve left
of z = 1.25 pictured below is the percentage of data less than z = 1.25; using the table, we get that
this area is A = 0.8944.
z-score A
1.25 0.8944
For another example if we focus on the z-value given by z = − 0.4 the area under the
curve left of z = − 0.4 pictured below is the percentage of data less than z = − 0.4; using the z-
table, we get that this area is A = 0.3446.
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
15
z-score A
-0.4 0.3446
We can also use the complement rule with the z-table to get areas to the right of a
specified z-value. Since the total area under the curve is 1, the area to the right of a specified z-
value is the area to the left subtracted from 1. For example, the area to the right of z = 1.25 pictured
below, is given by 1−0.8944 = 0.1056
For another example, the area to the right of z = −0.4 pictured below is given by1 −0.3466
= 0.6554
Finally, we can determine areas under the normal curve between two specified z-values
by subtracting the area to the left of the smaller z-value from the area to the left of the larger z-
value. For example, if we want to find the area between z = −0.4 and z = 1.25, we subtract the area
to the left of z = − 0.40 from the area to the left of z = 1.25; in this case, we find that the area
between z = − 0.4 and z = 1.25 is given by 0.8944 − 0.3446 = 0.5498 as pictured below.
Source: Canonigo, 2012
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
16
Learning Competency
The learner finds the area under the standard normal distribution, given various z-scores.
Activity 1
Directions: In your answer sheet, plot the z-score/s in the figure and shade the area.
1. Area to the left of z = - 2 2. Area between z = 0 and z = 1.2
3. Area to the right of z = 2.5 4. Area between z = -1 and z = 1
5. Area to the right of z = 2 6. Area between z = 0.4 and z = 2.6
7. Area to the right of z = -2 8. Area between z = -2.4 and z = 0.95
9. Area to the left of z = 1.2 10. Area between z = - 1.6 and z = - 1.4
Activity 2
Directions: Given the z-scores of the standard normal distribution, find the area.
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
17
1. Area to the left of z = - 2
2. Area between z = 0 and z = 1.2
3. Area to the right of 2.5
4. Area between z = - 1 and z = 1
5. Area to the right of z = 2
6. Area between z = 0.4 and z = 2.6
7. Area to the right of z = -2
8. Area between z = -2.4 and z = 0.95
9. Area to the left of z = 1.2
10. Area between z = - 1.6 and z = - 1.4
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
Remove Watermark Wondershare
PDFelement
18
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times.
You might also like
- Stat Las 10Document4 pagesStat Las 10Leamonique AjocNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability 11Document12 pagesStatistics and Probability 11joshcaleboliverosNo ratings yet
- 4 4Normal-DistributionsDocument24 pages4 4Normal-DistributionsRenalyn Palomeras PerudaNo ratings yet
- StatisticsandProbability Week8Document6 pagesStatisticsandProbability Week8Angel TubatNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 Statistics and ProbabilityDocument8 pagesLAS 3 Statistics and Probabilitychad lowe villarroyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresDocument18 pagesLesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresKlarence Timothy Pineda BundangNo ratings yet
- L 5 The Normal CurveDocument37 pagesL 5 The Normal CurveAiza mae MontiagodoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresDocument19 pagesLesson 2.3 Standard Normal Curve and Z ScoresKlarence Timothy Pineda BundangNo ratings yet
- Normal CurveDocument39 pagesNormal CurvePolicios RicaNo ratings yet
- Handout 3 - Normal DistributionDocument7 pagesHandout 3 - Normal DistributionRey SteveNo ratings yet
- GE4 Module StatisticsDocument7 pagesGE4 Module Statisticsc00336155No ratings yet
- LAS4 - STATS - 2nd SemDocument8 pagesLAS4 - STATS - 2nd SemLala dela Cruz - FetizananNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document9 pagesModule 2dariuslloydandres193No ratings yet
- The Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesThe Normal DistributionAllen Kurt RamosNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument17 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionAzeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Region On Normal CurveDocument23 pagesTopic 10 Region On Normal CurveJennilyn FortunadoNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob Q3 Module 7Document8 pagesStat and Prob Q3 Module 7R TECH33% (3)
- Module 2 Stat EulerDocument13 pagesModule 2 Stat EulerkaizerkaletanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6Document79 pagesTopic 6haziz_14No ratings yet
- 5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionDocument10 pages5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionPamela Chimwani100% (1)
- Identifying Regions Under Normal Curve Correponds To DifferentDocument32 pagesIdentifying Regions Under Normal Curve Correponds To DifferentJiro Alejo TutopNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 3Document15 pagesMathematics: Quarter 3Rosario Perez OcamiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 and Lesson 2.4Document35 pagesLesson 2.3 and Lesson 2.4Hayashida KunNo ratings yet
- Stat - Normal Curve. Week 3 4Document40 pagesStat - Normal Curve. Week 3 4Francine Issha Mae RoblesNo ratings yet
- 13 ZscoresDocument13 pages13 ZscoresMhelvyn RamiscalNo ratings yet
- Chapter4A Single-Sample Confidence-Interval SDocument103 pagesChapter4A Single-Sample Confidence-Interval Sduongcattuong172No ratings yet
- 13 Zscores PDFDocument13 pages13 Zscores PDFAna ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Stats Probab Demo 2020 2Document38 pagesStats Probab Demo 2020 2Kevin KeysNo ratings yet
- Standard Normal DistributionDocument22 pagesStandard Normal DistributioncliermanguiobNo ratings yet
- WEEK-4 FinalDocument19 pagesWEEK-4 FinalCrius DiomedesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Advance StatisticsDocument18 pagesModule 1 Advance StatisticsMark Niel BalinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document104 pagesChapter 5July ZergNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Z-TransformDocument16 pagesThe Inverse Z-TransformMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Magsino, R. V. (2020) - Statistics and Probability Learner's MaterialDocument5 pagesNormal Distribution Magsino, R. V. (2020) - Statistics and Probability Learner's MaterialJan RegenciaNo ratings yet
- Stat-Prob Q3 Week4Document18 pagesStat-Prob Q3 Week4arfredbileg08No ratings yet
- Q3 Module 11 CLMD4ASTAT&PROB 135-146Document12 pagesQ3 Module 11 CLMD4ASTAT&PROB 135-146KyotieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4ADocument107 pagesChapter 4AK60 Lê Bảo TrânNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Normal CurveDocument9 pagesModule 6 - Normal CurveAdrianNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument23 pagesNormal Distributionkoreaneminem2No ratings yet
- Understanding The Z - ScoreDocument63 pagesUnderstanding The Z - ScoreRossel Jane CampilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document54 pagesChapter 5KarliNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Document19 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency and Position (Ungrouped Data) : Lesson 3Gemver Baula BalbasNo ratings yet
- Application of Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesApplication of Normal DistributionRochelle Catherine Serrano CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 - Sampling Distribution - SDocument89 pagesChapter4 - Sampling Distribution - SK61BF Lê Ngọc Gia HânNo ratings yet
- L4 Continuous ProbabilityDocument28 pagesL4 Continuous ProbabilityKelyn KokNo ratings yet
- 8MAT 152 Lesson 12Document22 pages8MAT 152 Lesson 12ladaoynnamarieNo ratings yet
- Module On Standard Scores and The Normal CurveDocument27 pagesModule On Standard Scores and The Normal CurveUniversal CollabNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 2023 - 2024 StatDocument4 pagesCot 1 2023 - 2024 StatMaria CongNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet 5 Statistics Probability 1Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet 5 Statistics Probability 1Ronald CambaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Normal DistributionDocument14 pagesModule 6 - Normal DistributionJesusima Bayeta Albia0% (2)
- Hidden Surface Removal - Computer GraphicsDocument10 pagesHidden Surface Removal - Computer GraphicsSyedkareem_hkgNo ratings yet
- Week 5: Statistics and ProbabilityDocument21 pagesWeek 5: Statistics and ProbabilityKriza mae alvarezNo ratings yet
- n$1'q5h n5) Iop) 0chDocument4 pagesn$1'q5h n5) Iop) 0chCamille RalletaNo ratings yet
- Q3 M3 Lesson 2Document9 pagesQ3 M3 Lesson 2Dharyl BallartaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8:: Determining ProbabilitiesDocument56 pagesLesson 8:: Determining ProbabilitiesTrice DomingoNo ratings yet
- Module Contents: Identify Regions Under The Normal Curve andDocument5 pagesModule Contents: Identify Regions Under The Normal Curve anditshennmondigoNo ratings yet
- The Normal CURVEDocument8 pagesThe Normal CURVEMelvin RamosNo ratings yet
- 09 Finding PDFDocument5 pages09 Finding PDFOwlieNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandDifferential Equations (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lesson 2.4 Graphing Linear Functions With Slope and One PointDocument4 pagesLesson 2.4 Graphing Linear Functions With Slope and One PointMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
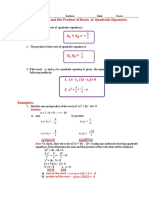
- Lesson 1.4. The Sum and Product of The Roots of A Quadratic EquationDocument3 pagesLesson 1.4. The Sum and Product of The Roots of A Quadratic EquationMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.3 Graphs of Quadratic Functions 2Document3 pagesLesson 2.3 Graphs of Quadratic Functions 2Midoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.5.2 DEoQF GraphDocument4 pagesLesson 2.5.2 DEoQF GraphMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.7 Descartes Rule of SignsDocument2 pagesLesson 3.7 Descartes Rule of SignsMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lava LampDocument7 pagesLava LampMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid BacteriaDocument5 pagesAcetic Acid BacteriaMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Direct Variations Key PointsDocument3 pagesLesson 3.1 Direct Variations Key PointsMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Shapes of DistributionDocument2 pagesLesson 3.1 Shapes of DistributionMidoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.2 Exponential Function of The Form A Greater Than 0.Document3 pagesLesson 4.2 Exponential Function of The Form A Greater Than 0.Midoriya IzukuNo ratings yet
- R7220101 Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesR7220101 Probability and StatisticssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalDocument29 pagesCHAPTER 9 - EXPERIMENTS - FinalVJ DecanoNo ratings yet
- Stat QusDocument3 pagesStat QuskarandwaiNo ratings yet
- TS4Document3 pagesTS4Prinshu RawatNo ratings yet
- Comparative Assessments of Financial Performance of Selected Public Sector Non-Life Insurance Companies of IndiaDocument18 pagesComparative Assessments of Financial Performance of Selected Public Sector Non-Life Insurance Companies of IndiaJash ThumarNo ratings yet
- A Study of Train Dwelling Time at The Hong Kong Mass Transit Railway SystemDocument11 pagesA Study of Train Dwelling Time at The Hong Kong Mass Transit Railway SystemNguyễn Phạm Kiến MinhNo ratings yet
- Answer Sheet Group Number: - 6 - Names of Team Members: - Hongru Bi, Yangxi Gan, Tara Kelley, Jie Xu Data Set - Arlhomes1Document6 pagesAnswer Sheet Group Number: - 6 - Names of Team Members: - Hongru Bi, Yangxi Gan, Tara Kelley, Jie Xu Data Set - Arlhomes1Jie XuNo ratings yet
- 235PracticeFinal1 PDFDocument12 pages235PracticeFinal1 PDFadasdNo ratings yet
- Porighat Bonkimota SuchalotaDocument21 pagesPorighat Bonkimota Suchalotaudya7010No ratings yet
- SQQS1013 Ch6 A122Document27 pagesSQQS1013 Ch6 A122AwnieAzizanNo ratings yet
- A BVAR Model For Forecasting Paraguay's Inflation Rate in Turbulent Macroeconomic Environments - BCP - PortalGuaraniDocument26 pagesA BVAR Model For Forecasting Paraguay's Inflation Rate in Turbulent Macroeconomic Environments - BCP - PortalGuaraniportalguaraniNo ratings yet
- Doomsday ArgumentDocument13 pagesDoomsday Argumentpatty444No ratings yet
- Significant FiguresDocument19 pagesSignificant Figuresసురేంద్ర కారంపూడిNo ratings yet
- Sas Notes Module 4-Categorical Data Analysis Testing Association Between Categorical VariablesDocument16 pagesSas Notes Module 4-Categorical Data Analysis Testing Association Between Categorical VariablesNISHITA MALPANI100% (1)
- ML Practical Journal With WriteupsDocument46 pagesML Practical Journal With Writeupssakshi mishraNo ratings yet
- MLT NotesDocument2 pagesMLT NotesMurthi MkNo ratings yet
- Minitab CheatDocument9 pagesMinitab Cheatwaqas104No ratings yet
- Intro To Data Science SummaryDocument17 pagesIntro To Data Science SummaryHussein ElGhoulNo ratings yet
- Nama: Syafitri Putri Gusasi (2100032) Kelas: A - Akuntansi Mata Kuliah: Statistika Dan Analisis Data 1. ADocument9 pagesNama: Syafitri Putri Gusasi (2100032) Kelas: A - Akuntansi Mata Kuliah: Statistika Dan Analisis Data 1. ASYAFITRI PUTRINo ratings yet
- Bit 2201 Simulation and ModelingDocument3 pagesBit 2201 Simulation and Modelingjames kilonzoNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics (Midterm)Document28 pagesBiostatistics (Midterm)Khylle Camron LuzzieNo ratings yet
- Tugasan Kumpulan - Analisis StatistikDocument41 pagesTugasan Kumpulan - Analisis StatistikNorazlena AwangNo ratings yet
- 2150 - Winter 2018 PDFDocument5 pages2150 - Winter 2018 PDFDevendraReddyPoreddyNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 - MatrikulasiDocument33 pagesPertemuan 2 - Matrikulasibpjstk medanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Jose C Beraun TapiaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument16 pagesCambridge International ExaminationsDiana Sari SMP TARA DenpasarNo ratings yet
- Generation of Quasi-Uniform Distributions and Verification of The Tightness of The Inner BoundDocument18 pagesGeneration of Quasi-Uniform Distributions and Verification of The Tightness of The Inner Bounddauoodsaleem dauoodsaleemNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics Exam Revision Questions: X F (X) X F (X) X F (X)Document3 pagesBasic Statistics Exam Revision Questions: X F (X) X F (X) X F (X)NehemiahNo ratings yet
- RivregressDocument16 pagesRivregresskainaNo ratings yet