Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compare and Contrast The Pharamcology of Ephedrine and Noradrenaline
Uploaded by
DonkeyManOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compare and Contrast The Pharamcology of Ephedrine and Noradrenaline
Uploaded by
DonkeyManCopyright:
Available Formats
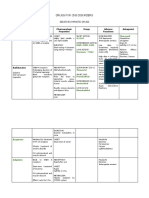
Noradrenaline Ephedrine
Pharmaceutics
MOA Direct agonist, at lower Direct and indirect action,
doses alpha selectivity, at mainly alpha1, some beta
higher doses beta activity Not metabolised by COMT –
Structure Metabolised by COMT – OH no C3 OH group
group on C3 Not metabolised by MAO –
Metabolised by MAO – no alkyl group on alpha C
alkyl group on alpha C Indirect activity – alkyl group
Less beta effect – no group on alpha C
on terminal amine Increased lipid solubility/CNS
effects – no substitutions on
benzene ring
Alkyl substitution on
terminal amine – beta effect
Pharmacokinetics IV only (metabolised in GIT) IV, IM, PO
Poorly lipid soluble, does More lipid soluble, can cross
not cross BBB BBB
Metabolised by COMT and Not metabolised by MAO or
MAO COMT, 35% hepatic
97% excreted renally as metabolism, 65% excreted
VMA, 3% normetanephrine unchanged in urine
T1/2b 2 mins T1/2b 5 hrs
Onset <1 min, duration 5 Onset 1 min, duration 1hr
mins
Pharmacodynamics
CVS Alpha effects low dose – Alpha and beta effects,
vasoconstriction, decrease in increase vasoconstriction,
HR due to BRR, potential inotropy, HR. Indirect action
decrease in CO. Beta effects can cause tachyphylaxis if
at higher dose – increased NAdr stores depleted
inotropy and HR
Respiratory Increased PVR, Similar
bronchodilator, respiratory
stimulant
CNS Decreased CBF from Does cross BBB, thus can get
vasoconstriction. Mydriasis. agitation, confusion,
Does not cross BBB increased MAC requirement
Other Decreases RBF, splanchnic BF Similar
flow, uterine BF. Increases
BGL, FFA, renin release
Side effects Tissue necrosis if Can be given IM and
extravasation (thus use CVC), peripherally, HTN crisis if on
effects prolonged if on MAOi
MAOis, metabolic acidosis,
HTN crisis, tachyarrythmia,
MI
Uses Vasopressor in critically treat hypotension (e.g. with
ill/vasodilatory shock GA or regional),
bronchospasm, nasal
decongestant, narcolepsy
You might also like
- Compare and Contrast The Pharmacology of Esmolol and PropanololDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast The Pharmacology of Esmolol and PropanololDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- CNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Document10 pagesCNS Pharmacology - 20231120 - 233736 - 0000Meghana MaddaliNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Neostigmine and The Organophosphate CompoundsDocument1 pageCompare and Contrast Neostigmine and The Organophosphate CompoundsDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 pagesBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Atropine and Glycopyrulate, and Discuss The Clinical ImplicationsDocument2 pagesCompare and Contrast Atropine and Glycopyrulate, and Discuss The Clinical ImplicationsDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressantDocument6 pagesAnti Depressantyahyaahmed152000No ratings yet
- Alpha Blockers PharmacologyDocument23 pagesAlpha Blockers PharmacologyHesbon MomanyiNo ratings yet
- Drugsto HAFALDocument3 pagesDrugsto HAFALThanyun YunNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersDocument4 pagesPharmacology - Drugs For CNS DisordersJireh MejinoNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. IndriyantiDocument36 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs (Aed) : R. Anita. Indriyantiandisti2323No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ParkinsonismDocument16 pagesDrugs Used in ParkinsonismShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in ParkinsonismDocument16 pagesDrugs Used in ParkinsonismShahid HameedNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Test 1 Drug ListDocument20 pagesPharmacology Test 1 Drug ListSHRIKANTNo ratings yet
- DR Dewi Farmakologi Pada Gangguan Neurologi - Maret 2021 DewiDocument81 pagesDR Dewi Farmakologi Pada Gangguan Neurologi - Maret 2021 DewiclarissaNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesSedative-Hypnotic Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FreebieDocument3 pagesPharmacology FreebieMohammad Farooq KhanNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFDocument39 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument13 pagesParkinsonKirti SinghNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetic Drugs A. Direct-ActingDocument4 pagesSympathomimetic Drugs A. Direct-ActingZEBINA PIE GENORINGNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- Pcol 2Document9 pagesPcol 2cyk7xcdsj4No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Document3 pagesPharmacotherapy of TB - Handout (Final) 4-08Ahmedshaker21No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Must KnowsDocument7 pagesPharmacology Must KnowsventicompilationNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugsDocument42 pagesPsychiatric DrugsaartiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Final Drug TablesDocument388 pagesPharmacology Final Drug TablesTJNo ratings yet
- ANTICONVULSANDocument18 pagesANTICONVULSANAndi Firda IndiraNo ratings yet
- Adrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFDocument43 pagesAdrenoceptor - Activating Other Sympathomimetic Drugs PDFRupal RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic PharmacologyDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Pharmacologyjess6001No ratings yet
- Adrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenDocument33 pagesAdrenergic Drugs: Pharmacological Department Medical School - UNPAD Ike HusenHendra EfendiNo ratings yet
- Kappa Uptake of Choline: Pharmacology1-FinalsDocument8 pagesKappa Uptake of Choline: Pharmacology1-FinalsJered OlarveNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Drug InteractionsDocument1 pageAlcohol Drug InteractionsAbdualaziz AlmalkiNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Document99 pagesSympathomimetics (Catecholamines & Non Catecholamines)Raheel JavaidNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Document5 pagesPhilippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Ric BarrosNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument45 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- 5 Alpha Adrenergic BlockersDocument34 pages5 Alpha Adrenergic Blockersmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- Plabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsDocument60 pagesPlabable-Gems-28. Pharmacology Plabable GemsHabo HaboNo ratings yet
- 14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyDocument23 pages14-Chapter 17-Drugs For EpilepsyCandilicious10No ratings yet
- Pgx-Guided Dosing in Pain Management: (Group 7)Document1 pagePgx-Guided Dosing in Pain Management: (Group 7)Michelle Kristine DonnellyNo ratings yet
- Cns Part 2 TransDocument3 pagesCns Part 2 TransAriNo ratings yet
- Drugs'Document102 pagesDrugs'Rohan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Side Effects MOA Other Notes: Lahat DecreaseDocument1 pageDrug Indication Side Effects MOA Other Notes: Lahat DecreaseCarl Edward PahuyoNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment For CoughDocument4 pagesDrug Treatment For CoughNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Sympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyDocument10 pagesSympathomimetic Drugs PharmacologyHaroon JavedNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1-Ward1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1-Ward1Annaoj Esor DarasNo ratings yet
- KEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDDocument133 pagesKEMU Guide by Sheraz Ali SOLVEDdrmoazzinivyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BDocument53 pagesPharmacotherapy of Epilepsy: Nandit P BNandit BanawalikarNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugsluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On CNSDocument19 pagesDrugs Acting On CNSAditya sagarNo ratings yet
- Hypnoti and SedativeDocument30 pagesHypnoti and SedativeC velmuruganNo ratings yet
- ANS2Document16 pagesANS2yaya mohaNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticDocument60 pagesSedative HypnoticNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistDocument30 pagesAdrenergic AntagonistOmar AlaamNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgonistsDocument43 pagesAdrenergic Agonistsmatchees-gone rogueNo ratings yet
- 12-PH-Analgesic and NSAIDDocument22 pages12-PH-Analgesic and NSAIDRisang Nur WigunaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Table - GonzalesDocument14 pagesPharmacology Table - GonzalesMark Angelo PonferradoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, HypnoticsDocument32 pagesLecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, Hypnoticsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Muscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorDocument26 pagesMuscarine & Nicotinic: ReceptorCess Lagera Ybanez88% (16)
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Physiol 93 B3Document1 pagePhysiol 93 B3DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- CEACCP - KetamineDocument5 pagesCEACCP - KetamineDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 B14Document2 pagesPharm 00 B14DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 02 A11Document4 pagesPharm 02 A11DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 02 A10Document2 pagesPharm 02 A10DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- CEACCP - Intrathecal Opioids in The Management of Acute Postoperative PainDocument5 pagesCEACCP - Intrathecal Opioids in The Management of Acute Postoperative PainDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- CEACCP - Latex AllergyDocument4 pagesCEACCP - Latex AllergyDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- CEACCP - Illegal Substances in Anaesthetic and Intensive Care PracticesDocument5 pagesCEACCP - Illegal Substances in Anaesthetic and Intensive Care PracticesDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 B15Document2 pagesPharm 00 B15DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 B11Document1 pagePharm 00 B11DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 A12Document1 pagePharm 00 A12DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 A9Document2 pagesPharm 00 A9DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 A14Document2 pagesPharm 00 A14DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Pharm 00 A15Document2 pagesPharm 00 A15DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Define The Mechanisms of Action and Adverse Effects of Metoprolol, GTN, and Diltiazem When Used To Manage MIDocument2 pagesDefine The Mechanisms of Action and Adverse Effects of Metoprolol, GTN, and Diltiazem When Used To Manage MIDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Outline The Physiological Consequences of Hyperosmolar Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 pagesOutline The Physiological Consequences of Hyperosmolar Diabetic KetoacidosisDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care HandbookDocument82 pagesPalliative Care HandbookDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- FS Antimicrobial Dosing Obesity AMS Updates Issue4 - Nov2018Document4 pagesFS Antimicrobial Dosing Obesity AMS Updates Issue4 - Nov2018DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- VOLATILEAGENTSDocument4 pagesVOLATILEAGENTSDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The GIT and The Liver QuestionsDocument44 pagesThe Physiology of The GIT and The Liver QuestionsDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl and Alfentanil: Br. J. Anaesth. (1982), 54, 871Document7 pagesComparative Pharmacokinetics of Fentanyl and Alfentanil: Br. J. Anaesth. (1982), 54, 871DonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDocument4 pagesCholinergic Agents: Cholinergic Receptors Types of Receptor Muscarinic Receptor Nicotinic ReceptorDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Base Excess (Be) Measure of Metabolic Acid-Base Status: Dr. David LynessDocument1 pageBase Excess (Be) Measure of Metabolic Acid-Base Status: Dr. David LynessDonkeyManNo ratings yet
- Infraclavicular: Toolbox: Online Modules 11 RAP Lecture 3 Hands - On Module 6Document4 pagesInfraclavicular: Toolbox: Online Modules 11 RAP Lecture 3 Hands - On Module 6DonkeyManNo ratings yet