Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study 1-Ward1
Uploaded by
Annaoj Esor Daras0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesDrug Study 1-Ward1
Uploaded by
Annaoj Esor DarasCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
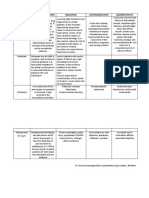
DRUG STUDY 1
DRUG DRUG CLASS INDICATION ACTION CONTRAINDICATION DOSAGE NURSING IMPLICATIONS
AND
ROUTEQ
SIMVASTATIN Lipid-lowering Adjunct to dietary Inhibit the enzyme NS:Headache,asthenia Assess nutrition:
Agent therapy in the 3-hydroxy- , fat, protein,
management of primary methylglutaryl sleep disturbances carbohydrates
hypercholesterolemia coenzyme A (HMG GI: Flatulence,
and mixed dyslipidemia. CoA) reductase, diarrhea, abdominal Monitor bowel
which is pain, cramps, pattern daily
Reduction of responsible for constipation, nausea,
lipids/cholesterol. catalyzing an early dyspepsia, heartburn, Monitor
Reduces the risk for MI step in the liver failure triglycerides,
and stroke sequelae. synthesis of the Respiratory: Sinusitis, cholesterol
cholesterol. pharyngitis baseline
Other: throughout
THERAPEUTIC Rhabdomyolysis, treatment
EFFECTS: acute renal failure, Precautions:
Lowering total & arthralgia, myalgia Past liver disease,
LDL cholesterol alcoholism, severe acute
infections, trauma, severe
metabolic disorders,
electrolyte imbalances,
elderly, renal disease
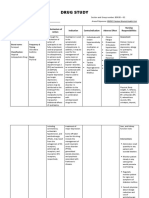
DRUG STUDY 2
DRUG DRUG CLASS INDICATION ACTION CONTRAINDIC DOSAGE NURSING IMPLICATIONS
ATION AND
ROUTE
CITICOLINE Neuroprotec Treatment Pharmacology: Somazine contains as its Patients with 1 gm TIV The cardiovascular
tive of cerebrovascul single active component, parasympathe q8h status of the patient
CNS Drugs & ar accident in cytidine-5-diphosphate choline. CDP- tic hypertonia should be carefully
Agents for acute and choline is a biologic product. It is found evaluatedbefore
ADHD recovery phase, in the body and takes part in the rapidly administering
symptoms and biosynthesis of phospholipids which mannitol since
signs of cerebral integrate into the structures of the sudden expansion of
insufficiency nervous system especially in the theextracellular fluid
eg,dizziness, me membranes of the neurons. The may lead to
mory loss, formation of phospholipids is needed for fulminating
poor the re-structuring of cell membranes by congestive heart
concentration, the damaged neurons. Citicoline is an failure.
disorientation, interneuronal communication enhancer. Somazine must not
recent cranial It increases the neurotransmission levels be administered
trauma and their because it favors the synthesis and along with
sequelae production speed of dopamine in the medicaments
striatum, acting then as a dopaminergic containing
agonist thru the inhibition of tyrosine- meclophenoxate
hydroxylase. Citicoline acts as a
presynaptic cholinergic agent which
favors the synthesis of acetylcholine. It
also decreases the release of serotonin.
Citicoline improves neuronal
metabolism in those cases where there
is a neuronal deterioration due to
degenerative, toxic or ischemic cause.
The cause of poor neuronal metabolism
is brought about by a decrease in
neuronal activity which makes the
astrocytes swell.
Swelling is due to electrolyte imbalance.
Active neurons release potassium
ions. These are taken up by astrocytes
(K+ buffers) and distributed to regions
with less K+. When neuronal activity
decreases, less K+ is released,
astrocytes take up Na+ instead of K+.
The hydrated Na+ is larger than the
hydrated K+ and so the astrocyte swells.
Improvement of neurometabolism is
demonstrated by citicoline's ability of
restoring the activity of mitochondrial
ATPase and of membranal
Na+/K+ ATPase. Citicoline also increases
glucose incorporation aside from
metabolism while at the same time
decreasing blactate accumulation in the
brain. Citicoline makes the neurons
more active, causing the astrocytes to
loosen their grip on the capillaries, thus
improving microcirculation. By virtue of
this action, citicoline has an indirect
effect on microcirculation. It has the
ability to slightly increase cerebral blood
flow and exerts an anti-aggregation
effect on platelets.
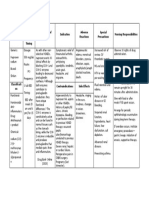
DRUG STUDY 3
DRUG DRUG CLASS INDICATION ACTION CONTRAINDIC DOSAGE NURSING IMPLICATIONS
ATION AND
ROUTE
LACTULOSE Anti-Allergic Constipatio Inhibits bacterial DNA gyrase thus Patient who 30 cc Assess condition
Anti- n, preventing replication in susceptible require a ODHS before therapy and
histamine salmonello bacteria low lactose oral reassess regularly
sis. diet. thereafter to monitor
Treatment Galactosemia drug’s effectiveness
of hepatic deficiency. Monitor patient for
encephalo Intestinal any adverse GI
pathy obstruction. reactions, nausea,
vomiting, diarr
hea.
Assess for adverse
reactions
for pt. with hepatic
encelopathy:
-regularly assess
mental condition
-monitor I & O
-monitor for Inc.
glucose level in
diabetic patients
You might also like
- Drug Study (Olanzapine)Document1 pageDrug Study (Olanzapine)Eden Marie Francisco100% (1)
- Uas MR1Document2 pagesUas MR1IvanNo ratings yet
- Medical Records in Family PracticeDocument22 pagesMedical Records in Family PracticenurfadillahNo ratings yet
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse EffectsDocument2 pagesDrugs Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effectsisprikitik3No ratings yet
- CC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Document11 pagesCC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Rubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Narce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsDocument1 pageNarce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument5 pagesStudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyrubie ann tillorNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 14. 1. Drugs Affecting The CNS Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Important Nursing ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesACTIVITY 14. 1. Drugs Affecting The CNS Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Important Nursing ConsiderationsPatricia Dianne RuizNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- Mina Drug StudyDocument7 pagesMina Drug StudyChi Chaw Giselle HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-PtsdDocument4 pagesDrug Study-PtsdWILMARIE SAPANTANo ratings yet
- Metaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyDocument8 pagesMetaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldoDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldosatruetalagaNo ratings yet
- PTB DrugsDocument4 pagesPTB DrugsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- 6 Drug StudyDocument4 pages6 Drug StudyIvan VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Moa: Interactions Drugs: Adverse Reactions: NR: - Administer LithiumDocument5 pagesGeneric Name: Moa: Interactions Drugs: Adverse Reactions: NR: - Administer Lithiumqwerty280512No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyComia AltheiaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRDocument5 pagesPharmacological Sheet Patient Name: BALDESTOY, Benedict Age: 19 Years Old Sex: Male Diagnosis: Hepatoma CAP-MRIngrid NicolasNo ratings yet
- DS Isph GS DRDocument7 pagesDS Isph GS DRTanya Victoria Lean ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument27 pagesDrug StudyMariefer EsplagoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AsDocument3 pagesDrug Study Askev mondaNo ratings yet
- 13 3pm PrednisoneDocument1 page13 3pm PrednisoneReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Marfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMarfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug Studyckkyle0% (1)
- Drug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingDocument1 pageDrug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameMacarayo AldemaeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Cognitive MedsDocument2 pagesCognitive MedsRNStudent1100% (1)
- Philippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Document5 pagesPhilippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Ric BarrosNo ratings yet
- Lithium DrugstudyDocument2 pagesLithium DrugstudyJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Atenolol TenorminDocument3 pagesAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For FolartDocument1 pageDrug Study For FolartCarl Simon CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- DS & LTsDocument11 pagesDS & LTsLemuel Glenn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study. PsychDocument8 pagesDrug Study. PsychJESSIE PASIANNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, ArcoxiaDocument2 pagesDrug Study Catapres. Losartan, Nootropil Cefuroxime, Arcoxiajoy_monterubioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingDocument1 pageDrug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Contra Indications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJessica FabroaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyEm-cy VillenaNo ratings yet
- Dig Ox inDocument2 pagesDig Ox inJb_Abarado_7467No ratings yet
- CM (Drug Study)Document4 pagesCM (Drug Study)Angel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indications Contraindication S Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indications Contraindication S Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameMae Abigail Mallonga BunaganNo ratings yet
- Threatened Abortion DrugsDocument1 pageThreatened Abortion DrugsDivine Dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Addisons DiseaseDocument5 pagesDrug Study Addisons DiseasekeannaNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- OPSS1213 Mar98Document3 pagesOPSS1213 Mar98Tony ParkNo ratings yet
- Heteropolyacids FurfuralacetoneDocument12 pagesHeteropolyacids FurfuralacetonecligcodiNo ratings yet
- Fast FashionDocument9 pagesFast FashionTeresa GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Neuro M Summary NotesDocument4 pagesNeuro M Summary NotesNishikaNo ratings yet
- Drug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForDocument7 pagesDrug-Nutrient Interaction in Prescriptions ForRafika DitaNo ratings yet
- Feature: SFP Optical Module 1 .25G Double Optical Fiber 20kmDocument2 pagesFeature: SFP Optical Module 1 .25G Double Optical Fiber 20kmDaniel Eduardo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- HUM110 Gilgamesh EssayDocument4 pagesHUM110 Gilgamesh EssaynsmeganNo ratings yet
- Installing Touareg R5 CamshaftDocument1 pageInstalling Touareg R5 CamshaftSarunas JurciukonisNo ratings yet
- Arsenal Strength Catalog 6.2-1Document41 pagesArsenal Strength Catalog 6.2-1Mohammed NavedNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument7 pagesNitric AcidKuldeep BhattNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Exercises Test 1 - Positive Statements ExerciseDocument2 pagesPresent Continuous Exercises Test 1 - Positive Statements Exerciseangel omar peraltaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-2018Document2 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-II - R2015 - 10-04-201818135A0806 MAKKUVA BHAVYANo ratings yet
- Answers To Your Questions About Circumcision and HIV/AIDSDocument2 pagesAnswers To Your Questions About Circumcision and HIV/AIDSAlex BrownNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsHazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Itc LimitedDocument64 pagesItc Limitedjulee G0% (1)
- Science 9 Q4 SML17 V2Document15 pagesScience 9 Q4 SML17 V2HotdogNo ratings yet
- Pantera 900Document3 pagesPantera 900Tuan Pham AnhNo ratings yet
- Join Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsDocument24 pagesJoin Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 41 Assignment Worksheets For SchoolDocument26 pages41 Assignment Worksheets For Schoolsoinarana456No ratings yet
- Leather & Polymer - Lec01.2k11Document11 pagesLeather & Polymer - Lec01.2k11Anik AlamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pure Copper - A Comparison of Analytical MethodsDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Pure Copper - A Comparison of Analytical Methodsban bekasNo ratings yet
- What Is A VolcanoDocument2 pagesWhat Is A VolcanonatachaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Packet KeyDocument21 pagesUnit 8 Packet KeyHiddenNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nastiti K - Manajemen Asma Pada Anak 2018 PDFDocument72 pagesDr. Nastiti K - Manajemen Asma Pada Anak 2018 PDFagnesspratiwiNo ratings yet
- EXP 2 - Plug Flow Tubular ReactorDocument18 pagesEXP 2 - Plug Flow Tubular ReactorOng Jia YeeNo ratings yet
- انظمة انذار الحريقDocument78 pagesانظمة انذار الحريقAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal DefectDocument8 pagesVentricular Septal DefectWidelmark FarrelNo ratings yet
- 17-003 MK Media Kit 17Document36 pages17-003 MK Media Kit 17Jean SandiNo ratings yet