Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dexamethasone
Uploaded by
Xyries Manuel Villena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesOriginal Title
dexamethasone
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views4 pagesDexamethasone
Uploaded by
Xyries Manuel VillenaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
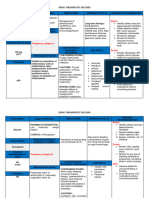
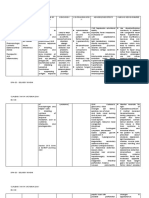
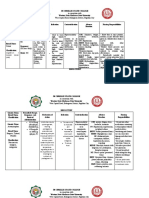
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION / ADVERSE EFFECT NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
CONTRAINDICATION
GENERIC: INDICATIONs: CNS: euphoria, insomnia, Assessment and drug effects
Dexamethasone Decreases inflammation by Cerebral edema,Palliative psychotic behavior,
suppression of neutrophil management of recurrent or Question for hypersensitivity to any corticosteroids.
pseudotumor cerebri, vertigo,
BRAND: inoperable brain Obtain baselines for height, weight,
migration, decreases headache,
Decadron, tumors,Inflammatory B/P, serum glucose, electrolytes.
production of inflammatory paresthesia, seizures,
Dexamethasone Intensol, conditions, neoplasias,Acute, Question medical history as listed in Precautions.
mediators. Reverses increased depression. CV: HF, HTN, Monitor I&O, daily weight, serum glucose.
Dexasone, Solurex, and self-limited allergic disorders;
capillary permeability. acute exacerbations of edema, arrhythmias, Assess for edema.
Baycadron.
CLASS: Suppresses normal immune chronic allergic thrombophlebitis, Evaluate food tolerance.
response disorders,Dexamethasone thromboembolism. EENT: Report hyperacidity promptly.
THERAPEUTIC suppression test for Cushing cataracts, glaucoma. GI: Check vital signs at least twice daily.
Corticosteroids syndrome
peptic ulceration, GI irritation, Be alert to infection (sore throat, fever, vague
increased symptoms).
PHARMACOLOGIC: SOURCE:Kizior, R. J., Bs, R. J. K., CONTRAINDICATION:
• Contraindicated in patients appetite, pancreatitis, nausea, Monitor serum electrolytes, esp. for
Glucocorticoids RPh, & Hodgson, K. (2022).
Saunders Nursing Drug hypersensitive to drug or its vomiting. GU: menstrual hypercalcemia, hypokalemia, paresthesia
DOSAGE: Handbook 2023. Saunders. ingredients, in those with irregularities, increased urine (esp. lower extremities, nausea/vomiting,
Elixir: 0.5 mg/5 mL* systemic glucose irritability). Assess emotional status, ability to sleep.
Oral concentrate: 1 mg/mL* fungal infections, and in those
and calcium levels. Abrupt withdrawal may cause
Oral solution: 0.5 mg/5 mL receiving immunosuppressive
Metabolic: hypokalemia, adrenal insufficiency; taper dose gradually
Tablets: 0.5 mg, 0.75 mg, 1 doses together with live-virus
hyperglycemia, carbohydrate
mg, 1.5 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg, 6 mg vaccines. IM administration is Family/Patient Teaching
intolerance,
contraindicated in patients
hypercholesterolemia,
with ITP. Do not change dose/schedule or stop
hypocalcemia, sodium
ROUTE: • Use cautiously in patients taking drug. • Must taper off gradually
retention, weight gain.
ORAL with recent MI. under medical supervision. • Report
Musculoskeletal: growth
• Use cautiously in patients fever, sore throat, muscle aches, sudden
suppression in children,
with GI ulcer, renal disease, weight gain, edema, exposure to
muscle weakness,
HTN, osteoporosis, diabetes measles/chickenpox. • Severe stress (serious
osteoporosis, tendon rupture,
mellitus, infection, surgery, trauma) may require increased
myopathy. Skin:
hypothyroidism, cirrhosis, hirsutism, delayed wound dosage. • Avoid alcohol,
diverticulitis, nonspecific healing, acne, various skin limit caffeine.
ulcerative colitis, recent eruptions, atrophy at IM
intestinal injection site, thin
anastomoses, fragile skin. Other: cushingoid
thromboembolic disorders, state, susceptibility to
seizures, myasthenia gravis, infections, acute adrenal
HF, TB, active hepatitis, insufficiency
ocular HSV infection, after increased stress or
emotional instability, or abrupt withdrawal after long-
psychotic tendencies. term therapy, angioedema.
• Because some forms After abrupt withdrawal:
contain sulfite preservatives, rebound inflammation,
also use cautiously in patients fatigue, weakness, arthralgia,
sensitive to fever, dizziness,
sulfites. lethargy, fainting, orthostatic
hypotension, dyspnea,
anorexia, hypoglycemia. After
DRUG TO DRUG INTERACTION: prolonged
Antidiabetics, including
use, sudden withdrawal may
insulin: May decrease
be fatal.
response. May need dosage
adjustment.
Aspirin, indomethacin, other
NSAIDs: May increase risk of GI (Highlight or emphasize
distress and bleeding. Use adverse effects manifested by
together cautiously. the patient by underlining the
Barbiturates, carbamazepine, sign and symptoms)
phenytoin, rifampin: May
decrease corticosteroid
effect. Increase
corticosteroid dosage.
Cardiac glycosides: May
increase risk of arrhythmia
resulting from hypokalemia.
May need
dosage adjustment.
Cyclosporine: May increase
toxicity. Monitor patient
closely.
Ketoconazole: May decrease
metabolism of
dexamethasone and increase
risk of corticosteroidrelated
adverse effects. Consider
therapy modification.
Oral anticoagulants: May alter
dosage requirements. Monitor
PT and INR closely.
Potassium-depleting drugs
such as thiazide diuretics: May
enhance potassium-wasting
effects of
dexamethasone. Monitor
potassium level.
Salicylates: May decrease
salicylate level. Monitor
patient for lack of salicylate
effectiveness.
Skin-test antigens: May
decrease response. Postpone
skin testing until therapy is
completed.
Toxoids, vaccines: May
decrease antibody response
and may increase risk of
neurologic
complications. Avoid using
together
DRUG TO FOOD INTERACTION:
interferes with calcium
absorption.
You might also like
- Self-test on the COSO ERM frameworkDocument6 pagesSelf-test on the COSO ERM frameworkLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Folktalesofkeral 00 MenoDocument124 pagesFolktalesofkeral 00 Menoreena sudhirNo ratings yet
- E-Way BillDocument1 pageE-Way BillShriyans DaftariNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameMacarayo AldemaeNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOTROPIC AGENTS - ActivityDocument13 pagesPSYCHOTROPIC AGENTS - ActivityANNA V. LARITANo ratings yet
- Before: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesBefore: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIcel Jean QuimboNo ratings yet
- DS Isph GS DRDocument7 pagesDS Isph GS DRTanya Victoria Lean ClaudioNo ratings yet
- PREDNISONEDocument3 pagesPREDNISONEChelsea CuevasNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy JRODDocument4 pagesDrugstudy JRODPeyjeyNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument81 pagesFinal Drug StudyMinaNo ratings yet
- Clozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesClozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Pedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGDocument3 pagesPedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BDocument4 pagesNCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BBethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesDexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- Drugs PediaDocument3 pagesDrugs PediaMark Ianne AngNo ratings yet
- Thioridazine Drug Study for Psychotic DisordersDocument6 pagesThioridazine Drug Study for Psychotic Disordersshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Clozapine DiazepamDocument2 pagesClozapine Diazepamalteahmichaella.mintuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyCyril_Cybernat_1553No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLyka PerezNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument7 pagesDexamethasoneCookies CreamNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone effects, uses, and nursing responsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDexamethasone effects, uses, and nursing responsibilitieskeannaNo ratings yet
- Clonidine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageClonidine HydrochloridebluetonksNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument1 pageHaloperidol PDFAda AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CLOZAPINEDocument6 pagesDrug Study CLOZAPINESandra ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Dexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesDocument2 pagesDexmedetomidine ICU Sedation and UsesWinter HyuckNo ratings yet
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Prednisone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPrednisone Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study on Methyldopa for PreeclampsiaDocument6 pagesDrug Study on Methyldopa for PreeclampsiaDayanaj OngNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsDocument4 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: CnsRoxy TofyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document4 pagesDrug Study 2EARL GERALD RICAFRANCANo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- DS DR RodasDocument7 pagesDS DR RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyshakiraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument3 pagesDrug Study FormKC KENT LORILLANo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIADocument8 pagesDRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIAKent Martin AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyrubie ann tillorNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesHaloperidol DRUG STUDYaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Cosep Drug Study For Case PresentationDocument4 pagesCosep Drug Study For Case PresentationMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLizeth Querubin100% (30)
- Anti PsychotisDocument21 pagesAnti Psychotissuresh sataguniNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Hydrocortisone)Document1 pageDrug Study (Hydrocortisone)Pauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- Narce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsDocument1 pageNarce, Almera Rose F. Pharmacology BSN-2A Instructor: Ms. Kenvyne Quides-Calugay, RN, Man Drug Study 2 FinalsAlmera Rose NarceNo ratings yet
- Nursing implications for drug administrationDocument9 pagesNursing implications for drug administrationKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Mina Drug StudyDocument7 pagesMina Drug StudyChi Chaw Giselle HilarioNo ratings yet
- 13 3pm PrednisoneDocument1 page13 3pm PrednisoneReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- QuetiapineDocument1 pageQuetiapineHanna Se100% (1)
- Clozapine Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesClozapine Nursing ResponsibilitiesJvWoodzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- DonepezilDocument2 pagesDonepezilAmberNo ratings yet
- Bridget BadiangDocument15 pagesBridget BadiangKrystelle RoslindaNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Emergency DrugsDocument19 pagesEmergency DrugsMean Elepaño50% (2)
- Urinary CatheterizationDocument25 pagesUrinary CatheterizationXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Document4 pagesNCP Post Op (Impaired and Risk For Infection)Carl J.No ratings yet
- HeparinDocument8 pagesHeparinXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Journal Pone 0252852Document17 pagesJournal Pone 0252852Stephen Niroshan XavierNo ratings yet
- DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesDexamethasoneXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- NCM-105A-Exercise 16 OlderAdultDocument4 pagesNCM-105A-Exercise 16 OlderAdultXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Parcetamoliv Drug StudytDocument1 pageParcetamoliv Drug StudytXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument8 pagesHeparinXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- HeparinDocument8 pagesHeparinXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- MorphineDocument4 pagesMorphineXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Journal FORMAT2018 StudentDocument1 pageJournal FORMAT2018 StudentXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- National Dengue Prevention and Control Program: A Policy Impact AnalysisDocument10 pagesNational Dengue Prevention and Control Program: A Policy Impact AnalysisXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With Apparatus and Equipment Used in Testing of MaterialsDocument5 pagesFamiliarization With Apparatus and Equipment Used in Testing of MaterialsEmanoAce33% (6)
- Cognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingDocument2 pagesCognitive Load Theory (John Sweller) : Information ProcessingNik ZazlealizaNo ratings yet
- List of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument16 pagesList of Trigonometric IdentitiesArnab NandiNo ratings yet
- X-Plane Installer LogDocument3 pagesX-Plane Installer LogMarsala NistoNo ratings yet
- Bizagi Licensing Explained ENGDocument7 pagesBizagi Licensing Explained ENGGuidoNo ratings yet
- 1605 HOBAS Jacking Pipes WebDocument16 pages1605 HOBAS Jacking Pipes Weballouche_abdNo ratings yet
- Gen Z WhitepaperDocument13 pagesGen Z Whitepaperjurgute2000No ratings yet
- Max-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsDocument21 pagesMax-OT For Dummies - Bodybuilding - Com ForumsPhong QuachNo ratings yet
- January 2011Document64 pagesJanuary 2011sake1978No ratings yet
- Sustainability - Research PaperDocument18 pagesSustainability - Research PapermrigssNo ratings yet
- Piano: Grade 2: PiecesDocument4 pagesPiano: Grade 2: PiecesnolozeNo ratings yet
- Pilot StudyDocument11 pagesPilot StudySatya Prakash80% (5)
- Gender Essay Outline Eng102Document3 pagesGender Essay Outline Eng102Ella BobsNo ratings yet
- Telangana Energy Dept Contact NumbersDocument27 pagesTelangana Energy Dept Contact Numbersstarpowerzloans rjyNo ratings yet
- CUMSUM Process ControlDocument6 pagesCUMSUM Process Controljess fantonalgoNo ratings yet
- CN Assignment 1 COE-540Document5 pagesCN Assignment 1 COE-540Ghazanfar LatifNo ratings yet
- UFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection NoteDocument5 pagesUFD/MMC/SD Controller Flash Support Limitation and Interconnection Noteمہرؤآنہ آبہرآهہيہمہNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Procedures in Cleaning Utensils and EquipmentDocument26 pagesLesson 2 - Procedures in Cleaning Utensils and EquipmentReizel TulauanNo ratings yet
- BITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Document21 pagesBITS ZG628T Dissertation (For Students of M. Tech. Software Systems)Shiva Beduduri100% (1)
- Perlis V. Composer's Voices From Ives To Ellington PDFDocument506 pagesPerlis V. Composer's Voices From Ives To Ellington PDFOleksii Ternovii100% (1)
- Chemists 12-2023Document7 pagesChemists 12-2023PRC BaguioNo ratings yet
- PIRA - 2022 - ESTIMATED FMV As of October 2022Document48 pagesPIRA - 2022 - ESTIMATED FMV As of October 2022Aggy ReynadoNo ratings yet
- A Very Rare Type of NeuralgiaDocument2 pagesA Very Rare Type of NeuralgiarosaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3vDocument4 pagesTugas 3vRomie SyafitraNo ratings yet
- RJR Nabisco LBODocument14 pagesRJR Nabisco LBONazir Ahmad BahariNo ratings yet
- 3M SS Filters Data SheetDocument4 pages3M SS Filters Data SheetbinnisfquoteNo ratings yet