Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Audit Diagnostic 1
Uploaded by
Mukarla Dejavu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesOriginal Title
AUDIT DIAGNOSTIC 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views5 pagesAudit Diagnostic 1
Uploaded by
Mukarla DejavuCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
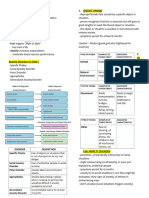
ANXIETY, TRAUMA AND STRESSOR - Interferes with an individual’s ability to
RELATED AND OBSESSIVE function
COMPULSIVE AND RELATED FOUR MAJOR OF SPECIFIC PHOBIA
DISORDER - Blood injection
Anxiety- negative mood state - Planes, elevators, or enclosed places
- Heights, storms, water
- Physical tension - Animal type
- Apprehension (fear) about the future - Situations that lead to choking, vomiting
Fear- quick emotional reaction to current danger loud sound
PANIC ATTACK Claustrophobia- phobia of plying
- Sudden experience of intense fear or SEPARATION ANXIETY DISORDER
difficult discomfort - Children unrealistic and persistent worry
- Heart palpitation, shortness of breath - Something will happen to their parents
and dizziness or important people in their life (lost,
- Co-occur with certain medical kidnapped, killed or hurt)
conditions, cardio, respiratory, and - Refuse to go to school
vestibular (inner ear) disorders.
SOCIAL ANXIETY DISORDER
Unexpected attack (uncued)- don’t know or clue
when or where next panic attack - More exaggerated shyness
- Unpredicted Performance anxiety- Do something in front of
many people, possibly embarrass themselves
Expected attack (cued)- know you are afraid of
high place or driving over bridges - Public speaking front of people
- Predicted Anxiety provoking physical reaction- blushing,
sweating, trembling, urinating in public restroom
Fight/flight system- produces immediate alarm
and escape response Selective mutism- rare childhood disorder
GENERALIZED ANXIETY DISORDER - Lack of speech in one or more setting
which speaking socially expected
- 6 months Excessive anxiety or worry - Common at school “selective”
- Muscle tension, fatigue (result chronic - Lack speech must occur for more than
excessive muscle tension) some one month
irritability, and difficulty sleeping
- Common among older adults POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER
(PTSD)
Benzodiazepines- some reliefs, at least in short
term - Exposure to a traumatic event
- Experiences or witnesses’ death, or
- Damage both cognitive and motor threatened death, actual or threatened
functioning serious injury or actual threatened
- Don’t seem to be alert sexual violation
AGORAPHOBIA - Reexperience, memories and nightmares
- Flashback
- PD closely related disorder - Avoid anything reminds them of the
- Fear and avoidance of situation which trauma
person feels unsafe or unable to escape - Unable remember certain aspects of
- Fear or anxiety to public transportation, event
open spaces, enclosed places, standing - Overaroused, easily startled and quick
in line or being in crowd, being outside anger
the home alone. - Reckless or self-destructive behavior
- Fear marketplace - Dissociative subtype
ADJUSTMENT DISORDER
PANIC DISORDER - Anxious or depressive reaction to life
stress
- Experience severe, unexpected panic - Generally milder but nevertheless
attacks impairing
- Think dying or losing control - Interfering with work or school
- Anxiety over possibility of having performance, interpersonal relationships,
another attack or other areas of living
- Fear attack might occur if too active - Unable cope with demands of situation
SPECIFIC PHOBIA - Chronic
- Irrational fear of specific object or ATTACHMENT DISORDER
situation
- Disturbed and developmentally - Excessive acquisition of things,
inappropriate behaviors in children difficulty discarding anything, living
before 5 years with excessive clutter
- Unable or unwilling form normal - Acquiring things during teenage years
attachment relationships with caregiving - Experience strong anxiety and distress
adults about throwing anything away
- Inadequate or abusive child rearing - Everything has either some potentials
practice use or sentimental value in their minds
- Failure to meet child’s basic emotional - Extension of their own identity
needs for affection, comfort, basic
necessities of daily living TRICHOTILLOMANIA (HAIR PULLING
DIORDER) AND EXCORIATION (SKIN
REACTIVE ATTACHMENT DISORDER PICKING DISORDER)
- Very seldom seek out caregiver for TRICHOTILLOMANIA- urge to pull out ones
protection, support, and nurturance own hair from anywhere on the body (scalp,
- Lack of responsiveness, limited positive eyebrows, arms)
affect, fearfulness, and intense sadness
- Noticeable hair loss, distress, and
DISINHHIBITED SOCIAL ENGAGEMENT significant social impairments
DISORDER - Females reporting the problem more
than males
- Early persistent harsh punishment
- Child shows no inhibitions whatsoever EXCORIATION- skin picking disorder
to approaching adults
- Repetitive and compulsive picking of
- Willingness to immediately unfamiliar skin, leading to tissue damage
adult figure - Significant embarrassment, distress, and
OBSESSIVE COMPULSIVE DISORDER impairment in terms of social and work
functioning
- Dangerous event is a thought, image, or - Largely a female disorder
impulse that the client attempts to avoid - Impulsive control disorders
- Repeatedly checking stove - Do not evidence tension relief
- Counting can also be compulsion
SOMATIC SYMPTOMS DISORDER
Obsession- intrusive nonsensical thoughts,
images and urges that individual tries to resist or - Briquets syndrome now somatic
eliminate symptoms disorder
- Do not always feel the urgency to take
Compulsive- thoughts or actions used to action but continually feel weak and ill
suppress the obsession and provide relief - Avoid exercising, thinking it will make
them worse
Symmetry- ordering and arranging or repeating
rituals ILLNESS ANXIETY DISORDER
Forbidden thoughts or actions- feel about to yell - Formerly known hypochondriasis
out a swear word in church - Severe anxiety focused on possibility of
having or developing a serious disease
- Lead checking rituals - Primarily with idea of being sick instead
Tic disorder- involuntary movement (sudden of physical symptoms itself
jerking of limbs)
BODY DYSMORPHYC DISORDER CONVERSION DISORDER (FUNCTIONAL
NEUROLOGICAL SYMPTOMS DISORDER)
- Normal looking people think they are so
ugly - Physical malfunctioning, such as
- Preoccupation with some imagined paralysis, blindness, or difficulty
defect in appearance who looks speaking without any physical organic
reasonably normal pathology
- Imagined ugliness Functional- symptoms without organic cause
- Physical issues
- Repeatedly looking in mirrors Conversion- anxiety resulting from unconscious
- Seek health professionals such as plastic conflicts
surgeons and dermatologists
- Men- body build, genitals, thinning hair - Converted into physical symptoms to
- Women- varied body areas, eating find expression
disorder DEPERSONALIZATION-DEREALIZATION
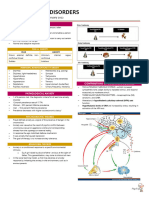
HOARING DISORDER DIORDER
Depersonalization- Temporarily lose the sense
of own reality
- You were in dream and reality of the MANIC EPISODE
external watching yourself
- Cognitive deficits on measures of - Abnormally exaggerated elation, joy, or
attention, processing of information, euphoria
short tern memory and spatial reasoning - Extreme pleasure in every activity
- Reduced emotional responding - Compare their daily experience of mania
- Tendency to selectively inhibit with continuous sexual orgasm
emotional expression - Little sleep, grandiose, plans
- Flight of ideas
Derealization- sense of the reality of external
world is lost MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
- Feeling of unreality are so severe and - Absence of manic, or hypomanic
frightening episodes before or during disorder
- Dominate an individual’s life and - Two or more depressive episode
prevent normal functioning occurred and were separated by 2
months during the individual was not
DISSOCIATIVE AMNESIA depressed
- Unable to remember anything, including PERSISTENT DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
who they are (DYSTHYMIA)
- Failure to recall specific events, usually
traumatic, that occur during specific - Fewer symptoms as 2
period - Remains relatively unchanged over long
- Forgetting is selective for traumatic periods
events or memories - Depressed mood continues at least 2
- Unexpected trip or trips years, patients cannot be symptoms free
- Find themselves in new place, unable to for more then 2 months
remember why or how they got there - Low self esteem, feeling of
- Sometimes assumes a new identity, hopelessness, poor appetite or
confused about the old identity overeating
DISSOCIATIVE IDENTITY DISORDER PREMENSTRUAL DYSPHORIC DISORDER
(PMDD)
- May adopt as many as 100 new
identities - Severe and sometimes incapacitating
- Average number is closer to 15 emotional reactions during premenstrual
- Identities are complete, own behavior, period
tone of voice, and physical gestures - Very stigmatizing
- Few characteristics are distinct - Combination of physical symptoms,
- Physical transformation occurs during severe mood swings and anxiety
switches, posture, facial DISRUPTIVE MOOD DYSREGULATION
expression, patterns of facial wrinkling and even DISORDER
physical disabilities may emerge - No evidence of periods if elevated mood
Alters- different identities or personalities in (mania)
DID - Negative affect that seems to be driving
the irritability and marked inability to
Host- person who becomes the patient and asks regulate mood
for treatment - Mistakenly diagnosed with bipolar
disorder
Switch- transition from one personality to
another BIPOLAR DISORDER
MAJOR DEPRESSIVE EPISODE - Tendency of manic episodes to alternate
with major depressive episode in an
- Mostly common diagnosed and most unending roller coaster ride
severe depression - Direct transition from one mood state to
- Extremely depressed mood state lasts 2 another happens
weeks - Rapid switching or rapid mood
- Feelings of worthlessness and switching
indecisiveness - Rapid cycling specifier
- Altered sleeping patterns, significant
changes in appetite and weight or a Bipolar II- major depressive episodes alternate
notable loss of energy with hypomanic episodes
- General loss od interest in things and
inability to experience any pleasure Bipolar I- individual experiences a full manic
from life episode
Anhedonia- loss of energy and inability to CYCLOTHYMIC DISORDER
engage in pleasurable activities or have any fun
- Milder but more chronic version of - Clearest and most comprehensive
bipolar disorder picture of sleep habits
- Chronic alternation of mood elevation
and depression that does not reach the INSOMNIA DISORDER- most common sleep
severity of manic or major depressive wake disorder
disorder - Being wake all the time
- Moody - Is not possible to go to completely
EATING AND SLEEP WAKE DISORDERS without sleep
- Trouble falling sleep at night
Bulimia nervosa- out control eating episode - Can’t go back sleep (difficulty
maintaining sleep)
- Followed by self-induced vomiting, - Not rested the next day (nonrestorative
excessive use of laxatives or other sleep)
attempts to purge (get rid of) food
HYPERSOMNOLENCE DISORDERS
Anorexia nervosa- body weight sometimes drops
dangerously - Sleeping too much
- Similar excessive sleepiness (sleep
Binge eating disorder- binge repeatedly and find apnea)
it distressing, do not attempt to purge the food
NARCOLEPSY
Obesity- not considered an official disorder, one
of the most dangerous epidemics Sleep paralysis- brief period after awakening
when they cant move or speak
BULIMIA NERVOSA
Hypnagogic hallucinations- vivid and often
- Eating larger amount of food typically terrifying experiences that begin at the start of
more junk food sleep
- Out of control
- Self induced vomiting NIGHTMARE DISRODER
- Compensate binge eating
- Bingeing, purging, overconcern with - Making person too anxious to try to
body shapes sleep at night
- Awaken the sleeper, bad dreams
Purging type- vomiting, laxatives or diuretics - Genetics, trauma, medication use
- Abuse, borderline disorder,
Nonpurging type- fasting schizophrenia
ANOREXIA NERVOSA Sleep terrors- commonly afflict children, begin
- Excessive exercise with piercing scream
- Proud of both diets and extraordinary NON RAPID EYE MOVEMENT SLEEP
control ARAUSAL DISORDER
- Decrease body weight
- Limit calorie intake - Extremely upset, sweating, rapid
heartbeat
BINGE EATING DISORDER - Appear resemble nightmares
- Marked distress because of excessive - Do not remember sleep terrors
eating but do not engage extreme Sleepwalking- not acting out a dream
compensatory behavior
- Severe obesity - Person leave the bed
- Sense of lack control over eating during - Sitting up in bed and picking at the
episode blanket or gesturing
- Cannot stop eating or control what or - Person wakened but will not remember
how much one is eating
Nocturnal eating syndrome- ride from beds and
SLEEP WAKE DISORDERS: THE MAJOR eat while they are still sleep
DYSSOMNIAS
RAPID EYE MOVEMENT SLEEP
Sleep problems- result from some disturbance BEHAVIOR DISORDER
common to a psychological disorder
- Different than the night eating syndrome
Dyssomnias- difficulties in getting enough of
sleep Sexsomnia- masturbation and sexual intercourse
with no memory of event
- Problems with sleeping when you want
to - Relationship problems, legal problems,
- Complaints about the quality of sleep occur without consent or with minors
Parasomnias- abnormal behavioral or SEXUAL DYSFUCNTION, PARAPHILIC
physiological events that occur during sleep DISORDERS, AND GENDER DYSPHORIA
- Nightmare and sleepwalking Sexual dysfunction- difficult to function
adequately while having sex
Paraphilic disorder- new term for sexual
deviation, sexual arousal occurs primarily in
context of inappropriate objects or individuals
Philia- strong attraction or liking
Para- attraction is abnormal
Gender dysphoria- incongruence and
psychological distress and dissatisfaction with
the gender one has been assigned at birth (boy or
girl)
SEXUAL DYSFUCNTION
- Problem arise in context of sexual both
heterosexual and homosexual
relationships
Premature (early) ejaculation- only in males
Genitopelvic pain/penetration disorder- painful
contraction or spasms of vagina
- Only in females
SEXUAL AROUSAL DISORDER
Erectile disorder- not desire
- Sexual urges, fantasies, strong desire
-
You might also like
- (PSYCH) Mood DisordersDocument15 pages(PSYCH) Mood DisordersThesa TagalogNo ratings yet
- Personality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidDocument4 pagesPersonality Disorder A: Cluster Types Description Approach A. ParanoidEben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- OCD and Related Disorders 1Document67 pagesOCD and Related Disorders 1Catherine Faith100% (1)
- Psy202-2021 Dissociative DisordersDocument4 pagesPsy202-2021 Dissociative DisordersJustin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Specific Phobia: Causes and Perspectives.: Presented by Susmitha RDocument19 pagesSpecific Phobia: Causes and Perspectives.: Presented by Susmitha RSusmiNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology (Outline Reviewer) PDFDocument39 pagesAbnormal Psychology (Outline Reviewer) PDFClaire Irish D. BorjaNo ratings yet
- English10 q4 CLAS2 Giving Technical and Operational Definition of Words Final-Carissa-CalalinDocument14 pagesEnglish10 q4 CLAS2 Giving Technical and Operational Definition of Words Final-Carissa-CalalinSophia Erika Largo100% (3)
- Abpsych Barlow Reviewer 1 Abpsych Barlow Reviewer 1Document30 pagesAbpsych Barlow Reviewer 1 Abpsych Barlow Reviewer 1Sharemax Holdings, Inc.No ratings yet
- Anxiety NeurosisDocument34 pagesAnxiety Neurosisilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- AbpsychmidtermDocument25 pagesAbpsychmidtermJohnaliza Laban100% (1)
- What Is Specific Phobia ?Document10 pagesWhat Is Specific Phobia ?joanneNo ratings yet
- Skript Jeffrey Zeig 1Document5 pagesSkript Jeffrey Zeig 1api-3856363100% (1)
- Anxiety DisordersDocument6 pagesAnxiety DisordersAlliyah Roma CadaNo ratings yet
- Personality DisorderDocument33 pagesPersonality DisorderIulia Moldovan100% (1)
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Group PresentationDocument11 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder Group Presentationapi-315727817No ratings yet
- Patients or Champions?: A Presentation By: Jessica Manohar and Ashley LautureDocument24 pagesPatients or Champions?: A Presentation By: Jessica Manohar and Ashley LautureAshley LautureNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument3 pagesAnxiety DisorderfebieNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing With DSM V (50 Terms)Document4 pagesDiagnosing With DSM V (50 Terms)Ashley MichealsNo ratings yet
- DisordersDocument10 pagesDisordersAra MiaNo ratings yet
- Socsci - Stress NotesDocument3 pagesSocsci - Stress NotesBryle GarayNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psych 2Document4 pagesAbnormal Psych 2Chelsea BuyucanNo ratings yet
- Separation Anxiety Disorder 309.21Document6 pagesSeparation Anxiety Disorder 309.21Richelle MaeNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument4 pagesPersonality DisordersAngela Abigail AbingNo ratings yet
- This Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Document4 pagesThis Person Is Not Manifesting To Reality Perception (Ego)Nica VictoriaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 - AbpsychDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 5 - AbpsychehhlluhhNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disordersallen cabasagNo ratings yet
- Interpretative Considerations IN THE DRAW A Person TEST Interpretative Considerations IN THE DRAW A Person TESTDocument13 pagesInterpretative Considerations IN THE DRAW A Person TEST Interpretative Considerations IN THE DRAW A Person TESTSuresh LukoseNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia (Buang Problem With Dopamine)Document4 pagesSchizophrenia (Buang Problem With Dopamine)Patricia RivasNo ratings yet
- Assignment For PsychDocument3 pagesAssignment For PsychJadeRuinsNo ratings yet
- Ab Psy New M2 ReviewerDocument14 pagesAb Psy New M2 ReviewerMARIANO, AIRA MAE A.No ratings yet
- PERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDocument1 pagePERDEV REVIEWER 2nd QuarterDell OleahNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related DisordersDocument14 pagesAnxiety Related DisordersKhrisha Anne DavilloNo ratings yet
- PSM107 MidtermDocument20 pagesPSM107 MidtermChurva EklavuNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Disorders and Personality Disorders NotesDocument6 pagesDissociative Disorders and Personality Disorders NoteselaineNo ratings yet
- PSY3018 - Ch11 Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and Somatic Symptom Disorder - 7 Sept 2023Document41 pagesPSY3018 - Ch11 Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and Somatic Symptom Disorder - 7 Sept 2023AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer Anxiety Phobia OcdDocument3 pagesAlzheimer Anxiety Phobia OcdChora BaguiyacNo ratings yet
- Group2 B Concepts and Patterns of Human BehaviorDocument3 pagesGroup2 B Concepts and Patterns of Human Behaviorjackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- Neurotic DisordersDocument13 pagesNeurotic DisordersSushmita BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyDocument39 pagesAnxiety Disorde RS: Abnormal PsychologyMariella LimNo ratings yet
- 117A-PRELIM-ELEARNING-2nd SemDocument4 pages117A-PRELIM-ELEARNING-2nd SemJovielyn KowetNo ratings yet
- Psy 325 LecturesDocument14 pagesPsy 325 LecturesErika BalaniNo ratings yet
- Psych Oral Reviewer AllDocument23 pagesPsych Oral Reviewer Allweyqt0277No ratings yet
- Missing Hehe : Anxiety Related DisordersDocument7 pagesMissing Hehe : Anxiety Related DisordersLorraineNo ratings yet
- NOTES SCHIZOPHRENIA and EATING DISORDERSDocument10 pagesNOTES SCHIZOPHRENIA and EATING DISORDERSshaimb.portuguezNo ratings yet
- InterpretationsDocument7 pagesInterpretationsmacazoadelynNo ratings yet
- Psychological Aspects of PolygraphyDocument7 pagesPsychological Aspects of PolygraphyALJHON SABINONo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Anxiety-DisordersDocument74 pagesLesson 6 - Anxiety-DisordersKristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisordersDocument14 pagesAnxiety DisordersOana Maria PopaNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument4 pagesPersonal Developmentanika janaeNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Depression AnxietyDocument3 pagesAnxiety and Depression AnxietyDeng MasinopNo ratings yet
- AFFECTIVE DisordersDocument3 pagesAFFECTIVE DisordersJanine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Consider The Effect of Nature & Nurture Predisposing & Precipitating FactorDocument6 pagesConsider The Effect of Nature & Nurture Predisposing & Precipitating FactorMarichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders - HTMLDocument28 pagesAnxiety Disorders - HTMLLealiza B. BruceNo ratings yet
- Ab Psych MidtermDocument25 pagesAb Psych MidtermJohnaliza LabanNo ratings yet
- ANXIETY DISORDERS & TREATMENTS - Part 4s Feb 2020-1Document66 pagesANXIETY DISORDERS & TREATMENTS - Part 4s Feb 2020-1AnoobisNo ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument10 pagesAnxietyPsyNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia NOTESDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia NOTESCamille GraceNo ratings yet
- Obsessive-Compulsive and Related DisordersDocument8 pagesObsessive-Compulsive and Related DisordersOana Maria PopaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles of Human BehaviorDocument47 pagesConcepts and Principles of Human BehaviorTricia Mae TalplacidoNo ratings yet
- Human Behavior Midterm Class AbnormalitiesDocument4 pagesHuman Behavior Midterm Class Abnormalitieswensly intongNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationDocument43 pagesAnxiety Disorders: Powerpoint Lecture Notes PresentationErsido SamuelNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 SchizophreniaDocument4 pagesLesson1 SchizophreniaAngelica PabelloNo ratings yet
- Sensory DisabilityDocument8 pagesSensory DisabilityYerro, Rhone Julienne May C.No ratings yet
- Crib Sheet E4Document2 pagesCrib Sheet E4Anais Hall-GarrisonNo ratings yet
- Anxiety DisorderDocument16 pagesAnxiety DisorderPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- Advanced PSYDocument201 pagesAdvanced PSYPetracharles AkashiNo ratings yet
- ATIENZADENISSE - Group 1-LAB - EXERCISE11&13 - BLOOD - BLOOD - VESSEL - RevisedDocument4 pagesATIENZADENISSE - Group 1-LAB - EXERCISE11&13 - BLOOD - BLOOD - VESSEL - RevisedMukarla DejavuNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 PsychDocument5 pagesLab 5 PsychMukarla DejavuNo ratings yet
- As A 4th Year StudentDocument1 pageAs A 4th Year StudentMukarla DejavuNo ratings yet
- Career GoalsDocument1 pageCareer GoalsMukarla DejavuNo ratings yet
- IO TRANSEsDocument1 pageIO TRANSEsMukarla DejavuNo ratings yet
- Summary of Somatic Symptoms DisorderDocument3 pagesSummary of Somatic Symptoms DisorderMarlon BubaNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument11 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-321537874100% (1)
- Social Anxiety in College Students: Journal of Anxiety Disorders May 2001Document14 pagesSocial Anxiety in College Students: Journal of Anxiety Disorders May 2001nailahNo ratings yet
- Disorders Common Among Children and Adolescents 14Document14 pagesDisorders Common Among Children and Adolescents 14api-566036687No ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument12 pagesAnxietyRengeline LucasNo ratings yet
- (Stanley) Joc90025 - 1460 - 1467Document8 pages(Stanley) Joc90025 - 1460 - 1467niia kurniiasihNo ratings yet
- Phobia: The Word Itself Comes From The Greek Word Phobos, Which Means Fear or HorrorDocument9 pagesPhobia: The Word Itself Comes From The Greek Word Phobos, Which Means Fear or HorrorNermeenNo ratings yet
- Specify The Specific Intoxicant (I.e., Amphetamine-Type Substance, Cocaine, or Other Specify IfDocument4 pagesSpecify The Specific Intoxicant (I.e., Amphetamine-Type Substance, Cocaine, or Other Specify IfAnyaNo ratings yet
- J Jbtep 2011 10 006Document7 pagesJ Jbtep 2011 10 006shahramk80No ratings yet
- List of Phobias A To Z SmallDocument13 pagesList of Phobias A To Z SmallPARVEJ RANANo ratings yet
- BZD Benzodiazepine Use Cognitive Impairment and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Anxiety Disorder PDFDocument5 pagesBZD Benzodiazepine Use Cognitive Impairment and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy For Anxiety Disorder PDFClinica de Psihiatrie PediatricaNo ratings yet
- SodaPDF-splitted-Abnormal Psychology - An Integrative Approach (PDFDrive)Document58 pagesSodaPDF-splitted-Abnormal Psychology - An Integrative Approach (PDFDrive)Aura MunadillaMdyNo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 Mental Health Final PresantationDocument23 pagesGROUP 3 Mental Health Final PresantationtonewainainaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Treatment of TrichotillomaniaDocument13 pagesBehavioral Treatment of TrichotillomaniaLucian Balasz100% (1)
- Kuehner 2016Document13 pagesKuehner 2016Claudio Angulo100% (1)
- Circus Psychology An Applied Guide To Thriving Under The Big Top 2022018105 2022018106 9781032266343 9781032266435 9781003289227 - CompressDocument151 pagesCircus Psychology An Applied Guide To Thriving Under The Big Top 2022018105 2022018106 9781032266343 9781032266435 9781003289227 - CompressLaura GăvanNo ratings yet
- MEDICAL - APPLICATIONS - OF - YOGA of DR NAGARATNA PDFDocument86 pagesMEDICAL - APPLICATIONS - OF - YOGA of DR NAGARATNA PDFKIRAN GARGYANo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mental and Emotional HealthDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Mental and Emotional HealthNovalonNo ratings yet
- What's My M3? The Catchy New Question Everyone Should Be AskingDocument3 pagesWhat's My M3? The Catchy New Question Everyone Should Be AskingJamie Rose RatliffNo ratings yet
- Academic Burnout and Its Relationship On The Anxiety of The Senior High School Students Amidst The Online Learning ModalityDocument9 pagesAcademic Burnout and Its Relationship On The Anxiety of The Senior High School Students Amidst The Online Learning ModalityPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-581977726No ratings yet
- AlcoooDocument8 pagesAlcooofilimon ioanaNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology FinalDocument29 pagesAbnormal Psychology FinalRihana DilshadNo ratings yet