Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L4 - The Language of Relations and Functions PDF
Uploaded by
Shane Margarette PalicpicOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L4 - The Language of Relations and Functions PDF
Uploaded by
Shane Margarette PalicpicCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 04: The Language of Relations
and Functions
ARROW DIAGRAM OF A RELATION
LESSON FOUR OUTLINE
I. Relations • Suppose R is a relation from a set A to a set B. The
i. Arrow Diagram of a Relation arrow diagram for R is obtained as follows:
ii. Properties of a Relation 1) Represent the elements of A as a point in one
region and the elements of B as points in another
II. Functions region.
i. Operation on Functions 2) For each x in A and y in B, draw an arrow from x
to y, and only if, x is related to y by R.
RELATIONS ▪ Symbolically:
→ Draw an arrow from x to y
• The objects of mathematics may be related in
If and only if, x R y
various ways.
If and only if, (x, y) R.
o A set “A” may be said to be related to a set “B”
if A is a subset of B, or if A is not a subset of B, or
if A and B have at least one element in common.
o A number x may be said to be related to a
number y if x < y, or if x is a factor of y, or if x2 +
y2 = 1.
• Relation
→ the set of ordered pairs of real numbers (x, y)
such that to each element x of the set X there PROPERTIES OF A RELATION
corresponds at least one element of the set Y
• Reflexive
o The notation for a relation R may be written → if every element of A is related to itself
symbolically as follows:
→ x R y meaning (x, y) R o Notation
→ a R a for all a A
o The notation x R y means that x is not related to
y by R; o Examples of Reflexive Relations
→ x R y meaning (x, y) R ▪ Equality
→ is equal to
▪ Set Inclusion
→ is a subset of
▪ Inequality
→ is less than, greater than, or equal to
▪ Divisibility
→ divides
6 PADAYON, FUTURE RMT., MD! | BSPH-1101
LESSON 04: The Language of Relations and Functions GEd 102
BS Public Health | FIRST YEAR – FIRST TERM
o An example of a non-reflexive relation is the • A function F from a set A to a set B is a relation with
relation "is the father of" on a set of people since domain and co-domain B that satisfies the
no person is the father of themselves. following two properties:
1) For every element x in A, there is an element y in
• Symmetric B such that (x,y) F.
→ if given a R b then b R a → Every element of A is the first element of an
ordered pair of F.
o The relation "is the sister of" is not symmetric on 2) For all elements x in A and y and z in B, If (x,y)
a set that contains a brother and sister but F and (x,z) F, then y = z.
would be symmetric on a set of females. → No two distinct ordered pairs in F have the
▪ The arrow diagram of a symmetric relation same first element.
has the property that whenever there is a
directed arrow from a to b, there is also a • Function Notations
directed arrow from b to a. o The symbol f(x) means function of x and it is
read as “f of x.”
• Transitive
→ if given a R b and b R c then a R c OPERATIONS ON FUNCTIONS
o The arrow diagram of a transitive relation has • The Sum or Difference of f and g
the property that whenever there are directed → denoted by f ± g
arrows from a to b and from b to c then there is → the function defined by (f ± g)(x) = f(x) ± g(x)
also a directed arrow from a to c:
• The Product of f and g
→ denoted by f · g
• Equivalence Relation
→ the function defined by (f·g)(x) = f(x)·g(x)
→ a relation that is reflexive, symmetric, and
transitive
• The Quotient of f and g
o The equality ("=") relation between real numbers
→ denoted by f/g
or sets.
→ the function defined by f(x)/g(x), where g(x) is not
o The relation "is similar to" on the set of all
equal to zero
triangles.
o The relation "has the same birthday as" on the • The Composite Function of f and g
set of all human beings. → denoted by f ο g
→ the function defined by (f ο g)(x) = f(g(x))
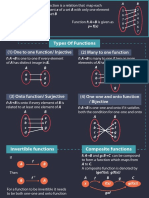
FUNCTIONS
• Function
→ a relation in which every input is paired with REFERENCES
exactly one output
o Discussions and PowerPoint from GEd 102
Instructor
• A function from set X to Y is the set of ordered pairs
of real numbers (x, y) in which no two distinct
TRANSCRIBED BY
ordered pairs have the same first component.
o Similar to a relation, the values of x is called the o Bautista, M.D.
domain of the function and the set of all
resulting value of y is called the range or co-
domain of the function.
7 PADAYON, FUTURE RMT., MD! | BSPH-1101
You might also like
- Mathematics Form 2 RevisionDocument10 pagesMathematics Form 2 RevisionAustin Phua Yun Hock84% (64)
- Relation and FunctionDocument19 pagesRelation and FunctionAshmita thapa100% (1)
- Arihant Class12 Mathematics Revisionnotes-1Document19 pagesArihant Class12 Mathematics Revisionnotes-1Radz100% (1)
- Till Week 2 NotesDocument4 pagesTill Week 2 Notesditi sanghaiNo ratings yet
- Mind Map: Learning Made Simple: Chapter - 1Document1 pageMind Map: Learning Made Simple: Chapter - 1Rishabh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths Notes 2024-245chapter - 1 Relations and FunctionsDocument45 pagesClass 12 Maths Notes 2024-245chapter - 1 Relations and Functionsa.dasNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes: TrackDocument23 pagesRevision Notes: TrackHANSNo ratings yet
- "A Comparative Study On Relations and Vague Relations": Dr. Hakimuddin Khan, Dr. Poonam TariqDocument2 pages"A Comparative Study On Relations and Vague Relations": Dr. Hakimuddin Khan, Dr. Poonam Tariqanil kasotNo ratings yet
- DSCR Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesDSCR Midterm Reviewerjustme2No ratings yet
- Vedantu Notes 12 JeeDocument3 pagesVedantu Notes 12 Jeechinmaymohite0No ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument3 pagesRelations and FunctionsArman SinghNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument19 pagesMathsAshmita GoyalNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument22 pagesRelations and FunctionsJ Anne LatozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Mathematics - Class 12 - Formula - SheetAditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Relations: Discrete Mathematical Structures: Theory and ApplicationsDocument31 pagesRelations: Discrete Mathematical Structures: Theory and ApplicationsKogo VickNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 RelationDocument30 pagesLecture3 RelationAmishNo ratings yet
- s1 1relintroDocument13 pagess1 1relintroPhong ĐâyNo ratings yet
- Representation of Relation: RelationsDocument2 pagesRepresentation of Relation: RelationsDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionsDocument14 pagesRelation and FunctionsArpit KumarNo ratings yet
- Relations AND Functions: Pend. Matematika 1CDocument10 pagesRelations AND Functions: Pend. Matematika 1CYosy CandraningsihNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument10 pagesRelations and FunctionsIntan LestariNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument2 pagesIlovepdf MergedBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- 12 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pages12 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Relations and Functionsroyalrajoria4912No ratings yet
- Relations and Its TypesDocument10 pagesRelations and Its TypesanjuNo ratings yet
- Hasse DiagramDocument8 pagesHasse DiagramAlok kumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Notes Class 12 Chapter 1 - Relations and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Notes Class 12 Chapter 1 - Relations and FunctionsJeffrish raidnNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionsDocument35 pagesRelation and FunctionsakshatNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Predicate LogicDocument10 pagesWeek 7 Predicate Logicyallah.abibi.wahahaNo ratings yet
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Document7 pagesStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Aditya guptaNo ratings yet
- Relations: Jorge Cobb The University of Texas at DallasDocument27 pagesRelations: Jorge Cobb The University of Texas at Dallasshri3415100% (1)
- Dms Mod3Document5 pagesDms Mod3geetha megharajNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - MathematicsDocument1,051 pagesEncyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology - Mathematicsrichard14r03No ratings yet
- Inverse Functions: Teks Focus VocabularyDocument7 pagesInverse Functions: Teks Focus VocabularyAadarsh BalireddyNo ratings yet
- Function: Examples by andDocument2 pagesFunction: Examples by andAngeline AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Maths Formula Print PDFDocument28 pagesMaths Formula Print PDFyaashu0707No ratings yet
- Functions, Composition of Functions and Relations (1.2.3)Document15 pagesFunctions, Composition of Functions and Relations (1.2.3)Narinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Relations & Functions Theory - 9th MayDocument44 pagesRelations & Functions Theory - 9th Mayvedantu495No ratings yet
- Isomorphisms Math 130 Linear AlgebraDocument3 pagesIsomorphisms Math 130 Linear AlgebraMegha VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Test Yourself: Example 1.3.7 Equality of FunctionsDocument2 pagesTest Yourself: Example 1.3.7 Equality of FunctionsHella GraciaNo ratings yet
- 71 Ge2 Set Relation Mapping - Dr. Samir Kumar BhandariDocument32 pages71 Ge2 Set Relation Mapping - Dr. Samir Kumar BhandariPramod PawarNo ratings yet
- All Formulas - RepairedDocument4 pagesAll Formulas - RepairedFilmora EffectsNo ratings yet
- UrjfjfmfkldlfkfmDocument30 pagesUrjfjfmfkldlfkfmAbcNo ratings yet
- Relations&Functions Hot QnsDocument2 pagesRelations&Functions Hot QnsMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RelationsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To RelationsbharathNo ratings yet
- DM Unit 2 Functions McqsDocument12 pagesDM Unit 2 Functions McqsFatherNo ratings yet
- Ad Hoc ProtocolsDocument1 pageAd Hoc ProtocolsSovan KarNo ratings yet
- Xii - Math - ch1 - Relationsfunctions (JPEG) BWDocument4 pagesXii - Math - ch1 - Relationsfunctions (JPEG) BWRajakumaranNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Revision Notes Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesClass 12 Revision Notes Relations and FunctionsHarsh Pandey BCANo ratings yet
- 2021 - 2022 +2 Cbse CM2Document4 pages2021 - 2022 +2 Cbse CM2Sai KishoreNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - 3Document27 pagesModule 2 - 3Ainz Ooal GownNo ratings yet
- Xii Maths Ch1 Relations Functions HssliveDocument4 pagesXii Maths Ch1 Relations Functions HssliveMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument11 pagesRelations and FunctionsTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11Document27 pagesLecture 11chaudhary mananNo ratings yet
- Chap 08 Real Analysis: Improper Integrals.Document20 pagesChap 08 Real Analysis: Improper Integrals.atiq4pk100% (8)
- 11 Maths Solution Converted 746Document111 pages11 Maths Solution Converted 746Sai TharunNo ratings yet
- Definition: Let A and B Be Sets. A Binary Tobisa Ofaxb.: Relation, or Simply, Relation From ADocument13 pagesDefinition: Let A and B Be Sets. A Binary Tobisa Ofaxb.: Relation, or Simply, Relation From AAileen P. de Leon100% (2)
- Discrete Math Lecture #04 (2020) PDFDocument17 pagesDiscrete Math Lecture #04 (2020) PDFHithamNo ratings yet
- Fall22 DS Quiz 2 SolutionDocument3 pagesFall22 DS Quiz 2 SolutionNajeeba ArshadNo ratings yet
- Tut 5Document1 pageTut 5vaishalic2304No ratings yet
- Term First FunctionsDocument17 pagesTerm First FunctionsAmritansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Herstein Topics in Algebra Solution 2.8Document6 pagesHerstein Topics in Algebra Solution 2.8Arun PatelNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Complete Question BankDocument6 pagesMathematics: Complete Question BankJugal JaiswalNo ratings yet
- MCR3U Unit 3 Notes - FunctionsDocument20 pagesMCR3U Unit 3 Notes - FunctionsShanaz ParsanNo ratings yet
- (12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCDocument7 pages(12-17) 1A-Ch.2-Introduction To Algebra - MCsophia yeungNo ratings yet
- Application of Differential CalculusDocument45 pagesApplication of Differential CalculusSadia Afrin ArinNo ratings yet
- Seismic Verification of Updated Finite Element Models of Cable-Stayed Bridges Nick A J LievenDocument8 pagesSeismic Verification of Updated Finite Element Models of Cable-Stayed Bridges Nick A J Lievenjuho jungNo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument5 pagesSummative Assessmentapi-428188337No ratings yet
- Parabolas: Identify The Vertex, Focus, Axis of Symmetry, and Directrix of Each. Then Sketch The GraphDocument4 pagesParabolas: Identify The Vertex, Focus, Axis of Symmetry, and Directrix of Each. Then Sketch The Graphsyd ricafortNo ratings yet
- Transportation & Transhipment PDFDocument73 pagesTransportation & Transhipment PDFdeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- A-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDocument16 pagesA-Levels Pure Mathematics ExemplarDarlingtonNo ratings yet
- Math 8. Quarter 1. Week 3-4Document4 pagesMath 8. Quarter 1. Week 3-4Rose Angela Mislang UliganNo ratings yet
- 1978 An Asymptotic Formula For Reciprocals of Logarithms of Certain Multiplicative FunctionsDocument5 pages1978 An Asymptotic Formula For Reciprocals of Logarithms of Certain Multiplicative FunctionskarrasNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionMuhammad Irfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Solution of Algebric & Transcendental EquationsDocument22 pagesSolution of Algebric & Transcendental EquationsGetsuga TenshouNo ratings yet
- BBS10 PPT MTB ch05Document47 pagesBBS10 PPT MTB ch05AgenttZeeroOutsiderNo ratings yet
- Modern AnalysisDocument9 pagesModern Analysismkvcinemas527No ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis in Metal Forming: A Presentation By: Abhishek V Hukkerikar & Jitendra Singh RathoreDocument38 pagesFinite Element Analysis in Metal Forming: A Presentation By: Abhishek V Hukkerikar & Jitendra Singh Rathorekrunal07786No ratings yet
- Yang 2005Document11 pagesYang 2005pratyush bidikaNo ratings yet
- FVM in Fuel RodDocument12 pagesFVM in Fuel RodAyushmanSrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Hairy BallDocument3 pagesHairy BallParvathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Landscape-Aware Performance Prediction For Evolutionary Multi-Objective OptimizationDocument15 pagesLandscape-Aware Performance Prediction For Evolutionary Multi-Objective OptimizationRichard GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 15-th Korean Mathematical Olympiad 2002: Final RoundDocument2 pages15-th Korean Mathematical Olympiad 2002: Final Rounddhrubajyoti ghoshNo ratings yet
- Exponentials and LogsDocument25 pagesExponentials and LogsAtang GasegaleNo ratings yet
- EEE-228-Lec2.pdf.2012 02 21 Ogretim 2Document17 pagesEEE-228-Lec2.pdf.2012 02 21 Ogretim 2selamicelik65No ratings yet
- Statistics 5.4Document12 pagesStatistics 5.4Ysabel Grace BelenNo ratings yet
- Measuring Change: Differentiation: Skills Check 1 ADocument25 pagesMeasuring Change: Differentiation: Skills Check 1 Ajulia brossardNo ratings yet
- MATH2408/3408 Computational Methods and Differential Equations With Applications 2014-2015Document4 pagesMATH2408/3408 Computational Methods and Differential Equations With Applications 2014-2015Heng ChocNo ratings yet
- Analisos de Variedades LeeDocument68 pagesAnalisos de Variedades LeeLopez Enrique100% (1)
- W2A1Document6 pagesW2A1Suren EzNo ratings yet