Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Paper XII JEE Main Exam Dt. 31.05.2021 PDF
Uploaded by
KESHAV VARSHNEYOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Paper XII JEE Main Exam Dt. 31.05.2021 PDF
Uploaded by
KESHAV VARSHNEYCopyright:
Available Formats
CLASS : XII (NON MEDICAL)
FOR JEE (MAIN) : 2022
Test Date : 31.05.2021
Time : 3 hrs. Max. Marks : 300
Instructions :
(i) This question paper consists of three sections. Total number of questions is 75.
(ii) Section - A consists of 25 questions in Physics, Section - B consists of 25 questions in Chemistry, Section - C
consists of 25 questions in Mathematics.
(iii) Each Section in Part – A contains 20 questions Single Choice Type has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) for its
answer, out of which Only One is correct.
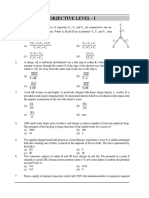
(iv) Each Section in part – B contains 5 Numerical value type questions. Express your answer in 4 digits
including 2 decimal places. For example : If answer is 8 or 12.3, then response should be 08.00 or 12.30
respectively.
(v) Each question is of 4 marks.
(vi) There is NO NEGATIVE marking.
(vii) Use of Calculator / Mobile phones is not allowed.
SECTION – A (PHYSICS)
PART – A
Single Choice Type This section contains 20 Single choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1),
(2), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of which Only One is correct.
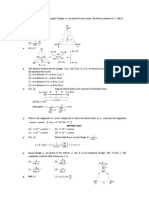
1. Three equal charges, each q , are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side l . The
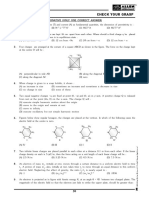
electric field intensity at the centroid of the triangle is
kq 3kq 3kq
(a) 2
(b) 2
(c) 2
(d) zero
l l l
2. It is required to hold equal charges q , in equilibrium at the corners of a square. To do this a
charge Q is placed at the center of the square. The value of Q is
(a)
q
2
1 2 2 (b)
q
2
1 2 2 (c)
q
4
1 2 2 (d)
q
4
1 2 2
3. A charge q is distributed uniformly on a ring of radius a. A sphere of equal radius a is constructed
with its center at the periphery of the ring. Calculate the flux of the electric field through the
surface of the sphere.
q 2q q 3q
(a) (b) (c) (d)
30 30 40 40
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (1)
4. Let V0 be the potential at the origin in an electric field E E x ˆi E y ˆj . The potential at any point
x, y is
(a) V0 xE x yE y (b) V0 xE x yE y
(c) xE x yE y V0 (d) x 2 y2 E 2x E 2y V0
5. Determine the electric field intensity at point P
due to quadruple distribution shown in figure for
r a .
kqa 2 6kqa 2 6kqa 2
(a) 0 (b) (c) (d)
r4 r4 r3
6. Eight charges 1 C , 7 C , 4 C , 10 C , 3 C , 5 C , 3 C and 6 C are situated at the
eight corners of a cube of side 20 cm. A spherical Gaussian surface of diameter 30 cm is
constructed with its center at the center of the cube. Then, the net flux of E through the spherical
surface (in units of Vm) is
3 3
(a) 36 10 (b) 684 10 (c) zero (d) none of these
7. Some equi-potential surfaces are shown in figure. The magnitude
and direction of the electric field is
(a) 100 Vm1 making angle 120 with the +ve x axis
(b) 200 Vm1 making angle 60 with the +ve x axis
(c) 200 Vm1 making angle 120 with the +ve x axis
(d) none of the above
8. The electric field on two sides of a large charged plate is shown in
figure. The charge density on the plate in SI Units is given by
( 0 is the permittivity of free space)
(a) 20 (b) 40 (c) 10 0 (d) zero
ˆ ˆ
9. Charge Q is given a displacement r ai bj in an electric field E E1ˆi E 2 ˆj . The work done by
the electric field is
(a) Q E1a E 2 b E1a E 2 b
2 2
(b) Q
(c) Q E1 E 2 a 2 b 2 E E 22
2
(d) Q 2
1 a 2 b2
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (2)
10. A particle of mass m carrying charge q is projected with velocity v from point A towards an
infinite line of charge from a distance a . Its speed reduces to zero momentarily at point B which
is at a distance a / 2 from the line of charge. If another particle with mass m and charge q is
projected with the same velocity v from A towards the line of charge, what will be its speed at
B?
v v
(a) 2v (b) 3v (c) (d)
2 3
11. n charged drops, each of radius r and charge q , coalesce to form a big drop of radius R and
charge Q . If V is the electric potential and E is the electric field at the surface of a drop, then
2/3 1/ 3 2/3 2/ 3
(a) E big n E small (b) E big n E small (c) V small n V big (d) V big n V small
12. A point charge q is placed inside a conducting spherical shell of inner radius 2R and outer radius
3R at a distance of R from the center of the shell. Find the electric potential at the center of the
shell.
1 q 1 4q 1 5q 1 2q
(a) (b) (c) (d)
4 0 2 R 4 0 3 R 4 0 6 R 4 0 3 R
12
13. An oil drop, carrying six electronic charges and having a mass of 1.6 10 g, falls with terminal
speed v in a medium. What magnitude of vertical electric field is required to make the drop move
upward with the same terminal speed v ? Ignore buoyancy.
(a) 10 NC1 (b) 10 4 NC1 (c) 3.3 10 NC1 (d) 3.3 10 NC1
5 4 5
14. An electric field is expressed as E 2iˆ 3jˆ . Find the potential difference VA VB between two
points A and B whose position vectors are given by r ˆi 2jˆ and r 2iˆ ˆj 3kˆ .
A B
(a) 1 V (b) 1 V (c) 2 V (d) 3 V
15. A thin glass rod is bent into a semicircle of radius r. A charge Q is uniformly
distributed along the upper half and a charge Q is uniformly distributed along
the lower half, as shown in figure. Calculate electric field E at P, the center of
semicircle.
Q 2Q 4Q Q
(a) 2 2
(b) 2 2
(c) 2 2
(d)
0 r 0 r 0 r 4 0 r 2
2
16. There are two thin wire rings, each of radius R, separated by a distance a along a common axis.
The charges on the rings are q and –q. The potential difference between the centers of the rings is
given by
q 1 1 q 1 1
(a) (b)
0 R R2 a2 20 R R 2 a2
q 1 1 2q 1 1
(c) (d)
20 R R2 a2 0 R R2 a2
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (3)
17. A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge in the upper half and negative surface
charge in the lower half. The electric field lines around the cylinder will look like figure
given in:
(a) (b)
(D
(c)
18. The electric flux for gaussian surface A that encloses the Gaussian
surface A
charged particles in free space is (given q1 14 nC, q2 q3
q1
q 2 78.85 nC and q 3 56 nC) Gaussian
surface B
(A) 103 N-m2C1 (B) 103 CN1m2
(C) 6.32 103 N-m2C1 (D) 6.32 103 CN1m2
19. Consider a sphere of radius R which carries a uniform charge density .
R
If a sphere of radius is carved out of it, as shown in figure. Then the
2 R /2
EA
ratio of magnitude of electric field E A and E B , respectively, at A
EB R
points A and B due to the remaining portion is
B
18 21 17 18
(a) (b) (c) (d)
34 34 54 54
20.
An electric dipole of moment p ˆi 3jˆ 2kˆ 10 29 C-m is placed at the origin (0,0,0). The
electric field due to this dipole at r ˆi 3jˆ 5kˆ is parallel to
(A) ˆi 3jˆ 2kˆ (B) ˆi 3jˆ 2kˆ (C) ˆi 3jˆ 5kˆ
(D) ˆi 3jˆ 5kˆ
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (4)
PART – B
This section contains 5 Numerical value type questions. Express your answer in 4 digits including 2 decimal
places.
21. A small sphere with mass 1.2 g hangs by a thread between two parallel
vertical plates 5 cm apart. The plates have uniform surface charge
density as shown in figure. The charge on the sphere is q 9 106 C and
it makes an angle 37o with the vertical. The potential difference between
the plates is _____ V.
22. A uniform electric field E 91 V/m is created between
two charged parallel plates as shown in figure. An electron
enters the field symmetrically between the plates with a
speed v 0 4 10 5 m/s. The length of each plate is 1cm.
The angle of deviation of the path of the electron as it
comes out of the field is _______ degree.
( m e 9.11031 kg and e 1.6 1019 C).
23. An electric field E 4x ˆi y 2 1 ˆj N/C passes
through the box shown in figure. The flux of the electric
field through surface ABCD and BCGF and marked as
1 and 2 respectively. The difference between
2
1 2 is (in Nm /C)________.
24. A charged sphere of diameter 4 cm has surface charge density of 10 4 C/cm2. The work done in
moving a charge of 40 nC from infinity to a point 2 cm from the surface of the sphere is n joule.
The value of n is ______.
25. A solid metal sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric metallic shell
of radius three times that of the sphere. If the potential difference between the two is 36 V, then
the potential of the inner sphere is ______V.
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (5)
SECTION – B (CHEMISTRY)
PART – A
Single Choice Type This section contains 20 Single choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1),
(2), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of which Only One is correct.
26. The crystal defect indicated in the diagram below is
(a) Frenkel defect (b) Schottky defect
(c) Frenkel and Schottky defects (d) Interstitial defect
27. The diastereoisomer (stereoisomer that is not a mirror image) of ‘X’ is
COOCH3
HO H
H OH
COOH
COOH H HO H OH
HO H
(a) (b)
HO H COOHH
COOCH3 COO
OCH3
HO H
H OH
C
COOCH3
(c) HOOC COOCH3 (d) HOOC H
HO H OH
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (6)
28. Lovastatin, a drug used to reduce the risk of cardio vascular diseases has the following structure
HO O
O
O
O CH3
H
H3C CH3
CH3
Lovastatin
The number of stereogenic centers present in lovastatin is
(a) 8 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6
29. A crystal is made up of metal ions ‘M1’ and ‘M2’ and oxide ions. Oxide ions form a ccp lattice
structure. The cation ‘M1’ occupies 50% of octahedral voids and the cation ‘M2’ occupies 12.5%
of tetrahedral voids of oxide lattice. The oxidation numbers of ‘M1’ and ‘M2’ are, respectively:
(a) +2, +4 (b) +3, +1 (c) +1, +3 (d) +4, +2
30. Which of the following compound have chiral carbon atom/s?
(a) I and II (b) I, III, IV and V (c) II, IV and V (d) II, III and IV
31. The compound which would undergo a reaction with ammonia by SN1 mechanism is
Br
Br
(a) (b) Br (c) Br (d)
32. An element crystallises in a face-centred cubic (fcc) unit cell with cell edge a. The distance
between the centres of two nearest octahedral voids in the crystal lattice is
a a
(a) a (b) 2a (c) (d)
2 2
33. The correct pairs(s) of the ambident nucleophiles is (are):
(1) AgCN/KCN (2) RCOOAg/RCOOK (3) AgNO2/KNO2 (4) AgI/KI
(a) (1) and (3) only (b) (2) and (3) only (c) (2) only (d) (1) only
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (7)
34. The order of nucleophilicity of the following anions in a SN2 reaction is
(a) Q > R > S > P (b) Q > P > R > S (c) Q > R > P > S (d) P > S > R > Q
35. Tetragonal crystal system has the following unit cell dimensions:
(a) a b c, 90 (b) a b c, 90
(c) a b c, 90 (d) a b c, 90
36. In the following reaction
Br
H Ph NaI
EtO H
acetone
Ph
the structure of product is
I I
H Ph Ph H
(a) (b)
EtO H EtO H
Ph Ph
Br Br
H Ph H Ph
(c) (d)
I H H I
Ph Ph
37. Which of the following statement(s) is/are incorrect
1. When inversion of configuration takes place in SN2 reaction, the optical rotation also changes.
2. SN1 mechanism is generally favoured in polar solvents.
3. In polar protic solvent, F- ion is a better nucleophile than I-
4. Strong bases are always good nucleophile.
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1, 2 and 4 (b) 1 and 2 (c) 2 only (d) 1, 3 and 4
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (8)
38. Which of the following arrangements shows the schematic alignment of magnetic moments of
antiferromagnetic substance?
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
39.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
40. An element crystallizes in a bcc lattice.Nearest neighbours and next nearest neighboursof the
element are respectively
(a) 8,8 (b) 6,8 (c) 6,6 (d) 8,6
41. Which of the following compounds will show retention in configuration on nucleophilic
substitution by OH– ion?
(a) CH 3 —CH—CH 2 Br (b) CH 3 —CH—Br
| |
C2 H 5 C6 H 5
Br
|
(c) CH 3 —CH—Br (d) CH 3 —C—H
| |
CH 3 C6 H13
42. The major product obtained from E2-elimination of 3-bromo-2-fluoropentane
fluoropentane is:
Br Br
| |
(a) CH 3CH 2 —CH—CH = CH 2 (b) CH 3 —CH 2 —C = CH—CH 3
F
|
(c) CH 3 —CH = CH—CH—CH 3 (d) CH 3CH 2CH = C—F
|
CH 3
43. Which of the following compounds produces an optically inactive compound on hydrogenation?
H CH3 H CH3 H CH3 H CH 3
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (9)
44. The mechanism of SN1 reaction is given as:
Y
R—X R X R || X
R—Y + X
Ion pair Solvent
separated
ion pair
A student writes general characteristics based on the given mechanism as:
(1) The reaction is favoured by weak nucleophiles
(2) R would be easily formed if the substituents are bulky
(3) The reaction is accompained by racemization
(4) The reaction is favoured by non
non-polar solvents.
Which observations are correct?
(a) (2) and (4) (b) (1) and (3) (c) (1), (2) and (3) (d) (1) and (2)
45. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the rate of hhydrolysis
ydrolysis of the compounds (a)
and (b) by SN1 reaction?
(a) A reacts faster than B (b) B reacts faster than A
(c) both A and B reacts at the same rate (d) Neither A nor B reacts
PART – B
This section contains 5 Numerical value type questions. Express your answer in 4 digits including 2 decimal
places.
46. Ga (atomic mass 70 u) crystallizes in a hexagonal close packed structure. The total number of
voids in 0.581 g of Ga is ________ × 1021. (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
[Given: NA = 6.023 × 1023]
47. A certain element crystallizes in a bcc lattice of unit cell edge length 27 Å. If the same element
under the same conditions crystallizes in the f.c.c. lattice, the edge length of the unit cell in Å will
be _________. (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
[Assume each lattice point has a single atom]
[Assume 3 1.73, 2 1.41 ]
48. The total number of monohalogenated organic products in the following (including stereoisomers)
reaction is ______.
(i) H / Ni/
A 2
(ii) X /
(simplest optically 2
active alkene)
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (10)
49. The total number of possible stereoisomers for the compound with the structural formula
CH3CH(OH)CH = CHCH2CH3 is ______.
50. (+)-2-methyl-1-butanol has a specific rotation of +13.5°. The specific rotation of2-methyl1-
butanol containing 40% of the (-)-enantiomer is __________ °.
(Round off to one decimal place)
SECTION – C (MATHEMATICS)
PART – A
Single Choice Type This section contains 20 Single choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (1),
(2), (3) and (4) for its answer, out of which Only One is correct.
51. If A, B and C are n × n matrices and det (A) = 2, det(B) = 3 and det (C) = 5, then the value of the
det (A2BC–1) is equal to
6 12 18 24
(a) (b) (c) (d)
5 5 5 5
a 2 1 ab ac
52. If a, b, c are real then the value of the determinant ab b 1 bc 1 is
2
ac bc c2 1
(a) a + b + c = 0 (b) a + b + c = 1 (c) a + b + c = –1 (d) a = b = c = 0
53. Let Dk is the k × k matrix with zero’s in the main diagonal, unity as the element of Ist row and
(f(k))th column and ‘k’ for all other entries. If f(x) = x – {x} where {x} denotes the fractional part
function then the value of det (D2) + det (D3) equals
(a) 32 (b) 34 (c) 36 (d) None of these
ax b b
54. If x = a + 2b satisfies the cubic (a, b R), f (x) b ax b 0 , then its other two
b b ax
roots are
(a) real and different (b) real and coincident
(c) imaginary (d) such that one is real and other imaginary
sin cos
55. Consider a matrix A() , then
cos sin
(a) A() is symmetric (b) A() is skew symmetric
(c) A 1 () A( ) (d) A 2 () A 2
2
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (11)
1 2r 1 50 1 2r 1
56. For a matrix A , the value of is equal to
0 1 r 1 0
1
1 100 1 4950 1 5050 1 2500
(a) (b) (c) (d)
0 1 0 1 0
1 0 1
57. If the maximum number of distinct elements in a symmetric matrix of order n is 45, then the value
of n is
(a) 9 (b) 10 (c) 15 (d) none of these
58. Let A and B are two square matrices of order 3 such that det (A) = 3 and det (B) = 2, then the
value of det adj. B 1
A 1
1
is equal to
[Note : adj M denotes the adjoint of a square matrix M.]
(a) 6 (b) 9 (c) 18 (d) 36
(1 ix)1/ j 1
59. Let A [a ij ] be a 3 × 3 matrix, where a ij lim for all 1 i, j 3 . Then A2 equals :
x 0 x
(a) 4A (b) 3A (c) 2A (d) A
3 1
1 1
2 2
60. Let A , B and C ABA T , then A T C3 A is equal to
1 3 0 1
2 2
3 1 1 0 3
1 1 3
(a) 2 2
(b) 3 (c) 2
(d)
1 0 1
1 0 2 0 3
61. Statement-1 : Let A be 2 × 3 matrix and B is 3 × 2 matrix such that det. (AB) = 10, then the value
of det. (BA) is equal to zero
Statement-2 : If A and B are two square matrices of order 3, then det. (AB) = det. (A).det.(B)
(a) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is correct explanation for statement-1
(b) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true and statement-2 is NOT the correct explanation for
statement-1
(c) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false
(d) Statement-1 is false, statement-2 is true
62. Let f(x) = (1 + b2)x2 + 2bx + 1 and let m(b) be the minimum value of f(x). As b varies, the range
of m(b) is
1 1
(a) [0, 1] (b) 0, (c) 2 , 1 (d) (0, 1]
2
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (12)
x 2 2x 3
log (0.5 x )
4 x2 4 x 3
63. The domain of the function f (x) (x 0.5) is
1 3 1 1 1 3
(a) (, 3) , 1 , (b) (, 3) , , 1 ,
2 2 2 2 2 2
1 3 1 1 1 3
(c) , 1 , (d) , , 1 ,
2 2 2 2 2 2
x 9x 20
2
64. Range of the function f (x) 2 , x R does not contain
x 6x 8
1 1
(a) (b) (c) 3 (d) 4
2 4
65. If (p 2 1)x 2 2(p 1)x 2 0 for all x R then the true set of real values of p is
(a) R (b) (–3, 1) (c) (d) (, 3) [1, )
3
66. Let P(x) x 2 2kx k . If graph of P(x) does not intersect y-axis, then the range of k is
4
3 3 3 1
(a) , (b) , (c) 2 , (d)
4 4 2
log(x 2 5x 6)
67. The domain of f (x) , is
[x] 1
[Note : where [y] denotes greatest integer function less than or equal to y.]
(a) (, 3) (2, ) (b) (, 3) [2, )
(c) (, 1) (2, ) (d) None of these
68. Let f(x) = min. (4x + 1, x + 2, –2x + 4). Then the maximum value of f(x) is
1 1 2 8
(a) (b) (c) (d)
3 2 3 3
69. Consider f, g, h be real-valued functions defined on R. Let f(x) – f(–x) = 0 for all x R ,
g(x) + g(–x) = 0 for all x R and h(x) + h(–x) = 0 for x R .
If f(1) = 0, f(4) = 2, f(3) = 6, g(1) = –1, g(–2) = 4, g(3) = 5 and h(1) = 2, h(3) = 5, h(6) = 3.
Then the value of f(g(h(1))) + g(h(f(–3))) + h(f(g(–1))) is equal to
(a) –1 (b) 1 (c) –7 (d) 7
70. If the function f(x) and g(x) are defined on R R such that
x 3, x rational x 5, x irrational
f (x) and g(x) then (f – g) (x) is
4x, x irrational x, x rational
(a) one-one and onto (b) neither one-one nor onto
(c) one-one but not onto (d) onto but not one-one
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (13)
PART – B
This section contains 10 Numerical value type questions. Do any 5 questions.
sin 0
71. Let A . If A + AT is a null matrix, then the number of values of in (0, 6), is
0 sin
72. Let P(x) = x4 – 8x2 + 21 and Q(y) = y2 – 6y + 10, x, y R . If P(x).Q(y) = 5, then possible
value(s) of x + y is (are)
4 x x [ x ] cos x
73. The fundamental period of ecos is
(where [x] denotes greatest integer function)
74. If A2 = 3A – 2I and A8 = PA + qI then P + q is
x2 x x 1 x 2
75. If 2x 3x 1 3x
2
3x 3 3 = Ax – 12. If the value of A2 is, 72k, then find k.
x 2 2x 3 2x 1 2x 1
__________
________
_____
Test Paper – JEE (Main) Class XII | Dt. 31.05-2021 (14)
You might also like
- 100 MCQS (3)Document10 pages100 MCQS (3)shiviNo ratings yet
- 100 MCQS (1)Document11 pages100 MCQS (1)shiviNo ratings yet
- Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesSolutions PDFmurugan NishanthNo ratings yet
- PULSE ACADEMY ELECTROSTATICS CLASS XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENTDocument6 pagesPULSE ACADEMY ELECTROSTATICS CLASS XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENTVijay Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Part Test-3 SolutionDocument9 pagesPart Test-3 SolutionAnmol GuptaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Particle Kinetic Energy Capacitor DielectricDocument11 pagesElectric Field Particle Kinetic Energy Capacitor DielectricSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Chapter ProblemsDocument10 pagesElectrostatics Chapter ProblemsRohit SahuNo ratings yet
- Book 20 Dec 2023Document5 pagesBook 20 Dec 2023pratapsneh.spNo ratings yet
- V-XL Study Centre: The Trusted Name in Online CoachingDocument1 pageV-XL Study Centre: The Trusted Name in Online CoachingAnand PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Electrostat-04 - Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesElectrostat-04 - Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperDocument7 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-II-PHY-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Item 0 20180627014138320Document40 pagesItem 0 20180627014138320DEBJIT SHARMANo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot) Pks ElectrostatsDocument10 pages(@bohring - Bot) Pks ElectrostatsxkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Physics: 1 2 y (CM) y 6 CM V 2V CM V 4V CMDocument6 pagesPhysics: 1 2 y (CM) y 6 CM V 2V CM V 4V CMPrashant GargNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Physics TestDocument28 pagesIIT-JEE Physics TestSaumya MundraNo ratings yet
- Vectors 2 PDFDocument3 pagesVectors 2 PDFtrannyNo ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-5Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Electrostatics, Home Work Sheet-5AishwaryNo ratings yet
- Student Copy. DPP No. 24 ElectrostaticsDocument5 pagesStudent Copy. DPP No. 24 ElectrostaticsDushyanth S JNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Level - 01Document5 pagesElectrostatics: Level - 01Om PungleNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Vector Algebra Important Questions (2022)Document22 pagesJEE Main Vector Algebra Important Questions (2022)yashasvikrishnav123No ratings yet
- Exercise 12Document43 pagesExercise 12Gomes RibeiroNo ratings yet
- One Option Correct QuestionsDocument5 pagesOne Option Correct QuestionsJoseNo ratings yet
- 14 ElectrostaticsDocument38 pages14 ElectrostaticskumarNo ratings yet
- IIT Questions Section 1 and 2 Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesIIT Questions Section 1 and 2 Multiple ChoiceRekha BhasinNo ratings yet
- JAM Test Series 1 of Career EndeavourDocument13 pagesJAM Test Series 1 of Career EndeavourSouradip DasNo ratings yet
- Nimcet 2011Document8 pagesNimcet 2011Saumya GangwarNo ratings yet
- Mid-Semester Examination-PHYDocument7 pagesMid-Semester Examination-PHYSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- JEST 2021 Part-A 1-Mark QuestionsDocument12 pagesJEST 2021 Part-A 1-Mark QuestionsMain DdNo ratings yet
- JEE - Physics - Electrostatics - SolutionsDocument15 pagesJEE - Physics - Electrostatics - SolutionsSanjana KumariNo ratings yet
- IIT Questions Section - I Single - Correct Choice Type: N (4n 1) C 6 N (4n 1) C 3 N (4n 1) C 3 N (4n 1) C 6Document6 pagesIIT Questions Section - I Single - Correct Choice Type: N (4n 1) C 6 N (4n 1) C 3 N (4n 1) C 3 N (4n 1) C 6JoseNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Arora: Target 2021 DPP - 6Document4 pagesGaurav Arora: Target 2021 DPP - 6Devansh SangwanNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam Physics 2007 PDFDocument6 pagesIit Jam Physics 2007 PDFKritiraj KalitaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1Document4 pagesElectrostatics 1Kumar AtthiNo ratings yet
- Electrostastics ExDocument28 pagesElectrostastics ExTejus VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper - 2 (Question Paper) - 6Document10 pagesPhysics Paper - 2 (Question Paper) - 6Saumya MundraNo ratings yet
- El RKTDocument6 pagesEl RKTTamanna SahuNo ratings yet
- Iit Jam 2018 QuestionDocument16 pagesIit Jam 2018 Questiondinesh rajputNo ratings yet
- 27 Aug 2021 2nd Shift QuestionDocument4 pages27 Aug 2021 2nd Shift Questionik62299No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of VectorsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of VectorsAparnaNo ratings yet
- Maths SQPDocument8 pagesMaths SQPmuskan manjhiNo ratings yet
- Mid Semester Examination PH 102Document7 pagesMid Semester Examination PH 102Sanyam JainNo ratings yet
- Cbjembpu 02Document9 pagesCbjembpu 02mukeshsgf5No ratings yet
- Physics - Xii - Test 5: Topic - Electric Flux & Gauss LawDocument1 pagePhysics - Xii - Test 5: Topic - Electric Flux & Gauss LawManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Dmath Exam 02oc1Document3 pagesDmath Exam 02oc1ashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- CPT - 2 - Physics Solution PDFDocument10 pagesCPT - 2 - Physics Solution PDFshreyaNo ratings yet
- Maths Unit Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesMaths Unit Test Questionssiddharth rambhiaNo ratings yet
- VECTORS FUNDAMENTALSDocument14 pagesVECTORS FUNDAMENTALSMahendra Panda0% (1)
- Assignement-2 Vector 3D 1633436080134Document4 pagesAssignement-2 Vector 3D 1633436080134Arman SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Electrostatics Except CapacitorDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 Electrostatics Except CapacitorVijay Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- P Ch-14 Electric+Charges+and+FieldsDocument9 pagesP Ch-14 Electric+Charges+and+Fieldsmysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Solved CBSE XII Maths (EF1GH-2)Document26 pagesSolved CBSE XII Maths (EF1GH-2)padmaNo ratings yet
- Class XII Math Sample Question PaperDocument8 pagesClass XII Math Sample Question PaperSaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Physics: Max. Marks: 60: QandqDocument7 pagesPhysics: Max. Marks: 60: QandqK R I S HNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Electrostatics SolutionDocument31 pagesXii Physics Electrostatics SolutionKushal DubeyNo ratings yet
- NEET Electric Potential and Capacitance Important QuestionsDocument33 pagesNEET Electric Potential and Capacitance Important QuestionsAnkita MajumderNo ratings yet
- CAPACITORPOTENDocument5 pagesCAPACITORPOTENAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Ntse QuizDocument9 pagesNtse QuizTEJA SINGHNo ratings yet
- (Cbse Main Iit) i Pcmc n Ipl Cbse Super Chaina Qp 08-04-2024Document14 pages(Cbse Main Iit) i Pcmc n Ipl Cbse Super Chaina Qp 08-04-2024r.selvakumaran2007No ratings yet
- CPT - 3 - XII IC CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - KeyDocument16 pagesCPT - 3 - XII IC CF - Mains Paper - 31-05-2021 - KeyARYAN PANDEYNo ratings yet
- (Xii) First Term Date Sheet and Syllabus Non-Med - 2021-22 PDFDocument1 page(Xii) First Term Date Sheet and Syllabus Non-Med - 2021-22 PDFKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- XII Non Medical Date Sheet and Syllabus PDFDocument1 pageXII Non Medical Date Sheet and Syllabus PDFKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Combined Slotwise Class Time Table Even Sem 2022-23 (17.02.2023)Document10 pagesCombined Slotwise Class Time Table Even Sem 2022-23 (17.02.2023)KESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- ASL Project by Ansh Semwal XII - S2Document25 pagesASL Project by Ansh Semwal XII - S2KESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- PROTECT ENGLISHDocument2 pagesPROTECT ENGLISHKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Y22 UG and M. Sc. Class Time TableDocument6 pagesY22 UG and M. Sc. Class Time TableKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics - Notes (Alt2)Document53 pagesElectrodynamics - Notes (Alt2)KESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Iiit 1 OpenDocument15 pagesIiit 1 OpenKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- Nit 1 Round OpenDocument92 pagesNit 1 Round OpenKESHAV VARSHNEYNo ratings yet
- BONDING: Understanding Chemical AttractionsDocument201 pagesBONDING: Understanding Chemical AttractionsKhaled OsmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Household Services Adiel RavaneraDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Household Services Adiel RavaneraAdielNo ratings yet
- Biomechinics PDFDocument8 pagesBiomechinics PDFImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Corticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalDocument21 pagesCorticosteroid: Saut Samuel Simamora Department Ophthalmology Diponegoro University-Kariadi HospitalSania NadianisaNo ratings yet
- Checklist PDFDocument84 pagesChecklist PDFJeremiah Miko LepasanaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report: Maya Engineering WorksDocument2 pagesA Project Report: Maya Engineering WorksVishwendra SinghNo ratings yet
- SWRO-200C Operation Manual AppendicesDocument38 pagesSWRO-200C Operation Manual AppendicestonbaldinNo ratings yet
- Micro Bio Disease ListDocument168 pagesMicro Bio Disease Listspiff spacemanNo ratings yet
- Halal Policy PDFDocument1 pageHalal Policy PDFSaid SaidiNo ratings yet
- Starbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store PerformanceDocument8 pagesStarbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store Performanceandrea100% (1)
- Pengaruh Ukuran Potongan Kopra Dalam Proses Pengeringan: Effect of The Copra Cut Size in The Drying ProcessDocument5 pagesPengaruh Ukuran Potongan Kopra Dalam Proses Pengeringan: Effect of The Copra Cut Size in The Drying ProcessAlexia Desi Ratnasari Loi 1841100210No ratings yet
- Administrative Case ResolutionDocument2 pagesAdministrative Case ResolutionEunice Osam RamirezNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting MomentDocument13 pagesTorsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting Momentmahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Sea Level Rise Threatens Coastal CommunitiesDocument13 pagesSea Level Rise Threatens Coastal CommunitiesGunawan La OdeNo ratings yet
- Dahong PalayDocument2 pagesDahong PalayAngela MontenegroNo ratings yet
- Market ReseachDocument3 pagesMarket ReseachSam Cy PuyalesNo ratings yet
- Laughter Yoga Benefits Workplace ProductivityDocument2 pagesLaughter Yoga Benefits Workplace ProductivityJose Manuel Araujo OrregoNo ratings yet
- Presley v. Lockwood: Respondent's Trial BriefDocument37 pagesPresley v. Lockwood: Respondent's Trial BriefTony Ortega100% (2)
- Analysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Document8 pagesAnalysis of Drinking Water Quality Parameters (A Case Study of Hanumangarh Town)Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- A Toxicity Study of Methanolic Extract of Calliandra Surinamensis Seeds On Liver Functions in RodentsDocument9 pagesA Toxicity Study of Methanolic Extract of Calliandra Surinamensis Seeds On Liver Functions in RodentsMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciNo ratings yet
- SITE. Defining Project Goals & ObjectivesDocument1 pageSITE. Defining Project Goals & Objectivescoach balaNo ratings yet
- Commercial Law Review Midterm - Without AnswersDocument1 pageCommercial Law Review Midterm - Without AnswersTorni JoNo ratings yet
- ANPATH1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesANPATH1 ReviewerRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Girl Scouts ActivitiesDocument5 pagesGirl Scouts ActivitiessluttybitchNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Field - Bioeffects & SafetyDocument37 pagesRadio Frequency Field - Bioeffects & SafetyAmel AntonyNo ratings yet
- REMOTE Calculator Tool May 21 2013Document77 pagesREMOTE Calculator Tool May 21 2013Leyner Garcia MezquitaNo ratings yet
- Neuro EcDocument234 pagesNeuro EcFeynman2014100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmDocument383 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology - B.pharmkeyurNo ratings yet
- Mesfin A. Agri. Econ. - 2005Document129 pagesMesfin A. Agri. Econ. - 2005Rafez JoneNo ratings yet
- Music and Therapy Bun2Document17 pagesMusic and Therapy Bun2PanteaAlisaNo ratings yet