Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromatography Infographic
Uploaded by
Mustafa RezaieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chromatography Infographic
Uploaded by
Mustafa RezaieCopyright:
Available Formats
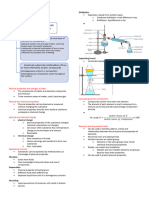
CHROMATOGRAPHY
A method of separating the components of a mixture based on
their different affinities for the stationary and mobile phase
Key terms
Stationary phase: Solid
material onto which
components of mixture are
initially adsorbed.
Mobile phase: Liquid or gas
that carries the components
of a mixture over the
stationary phase as it flows
through it
Adsorb: Attach to the
surface of a material
(stationary phase)
SEPaRATION
The separation is dependent on the
strength of each components interaction
with the stationary and mobile phase.
This is influenced by:
Relative polarities
Polarity of the Size of the
of the stationary
component component
and mobile phase
Eg the most polar
Number/type of Larger molecule-
component will be
polar groups more non polar
most strongly
adsorbed to a polar
stationary phase,
and least soluble in
a non-polar mobile
Comparison phase.
Components can be compared based
on their Rf value or retention time.
Eg for the blue spot The blue spot was least
Rf=8/10 strongly adsorbed to
=0.8 stationary phase and
Rf(purple)=0.6, Rf most soluble in the
(red)=0.2 mobile phase
You might also like
- Separation TechniquesDocument3 pagesSeparation Techniquesallison_nicholasNo ratings yet
- Classification of Chromatography MethodsDocument2 pagesClassification of Chromatography Methods花火No ratings yet
- Chromatography ReviewerDocument4 pagesChromatography ReviewerAnthony Val RolunaNo ratings yet
- Adibah Binti Mohd NoorDocument69 pagesAdibah Binti Mohd NoorNurul AtikaNo ratings yet
- ANACHEM - ChromatographyDocument6 pagesANACHEM - ChromatographyHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption: Based On Direction of Movement of SolventDocument3 pagesAdsorption: Based On Direction of Movement of SolventEllä PabustanNo ratings yet
- Introduccion CromatografiaDocument21 pagesIntroduccion CromatografiaYEIFRI RODRIGUEZ BTCNo ratings yet
- 3.chromatography I 2011Document28 pages3.chromatography I 2011hawyonghongNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument6 pagesPaper Chromatographyjay100% (3)
- Summary ChromatographyDocument3 pagesSummary ChromatographyNUR NADIAH BINTI MATARSIM -No ratings yet
- Chroma TDocument73 pagesChroma TAnonymous XuiUo2ThNo ratings yet
- 3A SeparationDocument6 pages3A SeparationRida Nadeem SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Introduction To ChromatographyDocument62 pagesChapter 4 - Introduction To ChromatographynursuhailahsuhailahsafariNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Raman and IR SpectrosDocument2 pagesComparison of Raman and IR SpectrosSreedevi KrishnakumarNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument2 pagesChromatographya kamranNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Module: Week 6!Document28 pagesChromatography Module: Week 6!ahmed ismailNo ratings yet
- KromatografiDocument32 pagesKromatografiNofrizalNo ratings yet
- Chromatography-Principle and Applications - UpdatedDocument28 pagesChromatography-Principle and Applications - Updatedzubairahmed27272No ratings yet
- MCAT Quizlet Ochem Purification MethodsDocument3 pagesMCAT Quizlet Ochem Purification MethodsAnjali PradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument63 pagesChapter 4 PDFatikah roshanNo ratings yet
- 16 Chromatography Notes 2021Document14 pages16 Chromatography Notes 2021Ibrahim ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Raman IRDocument4 pagesRaman IRanhthigl25No ratings yet
- Chromatography EssentialsDocument4 pagesChromatography EssentialsHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument37 pagesChromatographyPrincess Alyssa AbidNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument24 pagesChromatographysolehah misniNo ratings yet
- CHM 256 7aDocument23 pagesCHM 256 7aAqilah NajwaNo ratings yet
- CHM256Document78 pagesCHM256aliesya5252No ratings yet
- HPLC Additional NoteDocument20 pagesHPLC Additional NotehaqeemifarhanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - ChromatographyDocument73 pages1.4 - ChromatographyMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 3.16. ChromatographyDocument2 pages3.16. ChromatographyPratiksha NavaleNo ratings yet
- Chromatography IntroDocument8 pagesChromatography IntroNishant SainiNo ratings yet
- R Distancetravelled by The Substance Distance Travelled by The SolventDocument4 pagesR Distancetravelled by The Substance Distance Travelled by The SolventshaineNo ratings yet
- Chromatography 1Document24 pagesChromatography 1chaudhary TahiraliNo ratings yet
- BackgroundDocument19 pagesBackgroundShreya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1Document7 pagesChemistry 1Kriezhel Kim TadleNo ratings yet
- 03 - Suspension 1Document35 pages03 - Suspension 1amirNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Group of Techniques Used To Separate Complex MixturesDocument7 pagesChromatography: Group of Techniques Used To Separate Complex MixturesAirah De JesusNo ratings yet
- Liquid Chromatography: General SchemeDocument5 pagesLiquid Chromatography: General SchemeDivya BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Plenary: Column and Paper ChromatographyDocument4 pagesPlenary: Column and Paper ChromatographyManila MedNo ratings yet
- CHROMATOGRAPHY2Document33 pagesCHROMATOGRAPHY2Nurfatihah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Jeremiah John Samontina - Activity 4Document4 pagesJeremiah John Samontina - Activity 4jeremiah john samontinaNo ratings yet
- SuspensionDocument72 pagesSuspensionUkash sukarmanNo ratings yet
- Maloney 2020Document13 pagesMaloney 2020Laalu PrasadNo ratings yet
- Raver A 2006Document9 pagesRaver A 2006Mahdi koolivandNo ratings yet
- Effect of Nanoparticles On The Interfacial Properties of Liquid/Liquid and Liquid/Air Surface LayersDocument9 pagesEffect of Nanoparticles On The Interfacial Properties of Liquid/Liquid and Liquid/Air Surface LayersMahdi koolivandNo ratings yet
- Chromatography Concept MapDocument2 pagesChromatography Concept MapAyumi BoquironNo ratings yet
- KROMATOGRAFIDocument18 pagesKROMATOGRAFIAna YusticaNo ratings yet
- Electrophoretic Light Scattering: Barathithasan.R Application SpecialistDocument35 pagesElectrophoretic Light Scattering: Barathithasan.R Application SpecialistJosé Eleazar Aguilar ToaláNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Theory & Techniques ApplicationsDocument30 pagesChromatography: Theory & Techniques Applicationsresa wulandariNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Chromatography From Greek Chroma Which Means "Color" and Graphein "ToDocument3 pagesChromatography: Chromatography From Greek Chroma Which Means "Color" and Graphein "ToSana BatoolNo ratings yet
- Chromatography: Uses For UDocument12 pagesChromatography: Uses For UMonjur Morshed RonyNo ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy: Kezia BessDocument14 pagesIR Spectroscopy: Kezia Besskezia0% (1)
- Properties of MatterDocument2 pagesProperties of Matterjellyjelly458No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Introduction To ChromatographyDocument62 pagesCHAPTER 4 Introduction To ChromatographyfieyaNo ratings yet
- BrudaDocument6 pagesBrudaemmalin2025No ratings yet
- Summary of SuspensionsDocument42 pagesSummary of SuspensionsEman Saddar El LeithyNo ratings yet
- 1b (Introduction)Document17 pages1b (Introduction)maya mardhiyahNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Alkane WorksheetDocument4 pages3.1 - Alkane WorksheetMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Revision SACE ChemistryDocument15 pagesTopic 1 Revision SACE ChemistryMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 3.1 SACE ChemistryDocument52 pages3.1 SACE ChemistryMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- Titration SolutionsDocument2 pagesTitration SolutionsMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- Titration QuestionsDocument3 pagesTitration QuestionsMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy PosterDocument1 pageAtomic Spectroscopy PosterMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 1.5 - Atomic SpectrosDocument69 pages1.5 - Atomic SpectrosMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - ChromatographyDocument73 pages1.4 - ChromatographyMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Volumetric AnalysisDocument111 pages1.3 - Volumetric AnalysisMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Photochemical SmogDocument30 pages1.2 - Photochemical SmogMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument65 pages1.1 - Global Warming and Climate ChangeMustafa RezaieNo ratings yet