Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WS-15 - KN - 2-D Motion - Mix
Uploaded by
Suman SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
WS-15 - KN - 2-D Motion - Mix
Uploaded by
Suman SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics: Mechanics
Kinematics: 2-D Motion
Projectile Motion
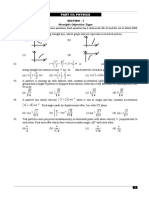
1. A ball thrown upward at an angle of 30° to the horizontal lands on the top edge of a
building 20 m away. The top edge is 5m above the throwing point. The ball was thrown
with a speed of
(a) 40 m/s (b) 10 m/s (c) 20 m/s (d) 30 m/s
2. A river is flowing from west to east at a speed of 5 m/min. A man on the south bank of
the river capable of swimming at 10m/min in still water wants to swim across the river in
shortest possible time. In what direction should he swim?
(a) due north (b) at an angle 30° west of south
(c) at an angle 30° east of north (d) at 60° west of north
3. A particle is thrown with a speed u at an angle with the horizontal. When the particle
makes an angle with the horizontal, its speed changes to v .
(a) v u cos (b) v u cos cos
(c) v u cos sec (d) v u sec cos
4. An aluminum ball X and an iron ball Y of the same volume are thrown horizontally with
the same velocity from the top of a building. Neglecting air resistance, X reaches the
ground
(a) before Y and at the same distance from the building
(b) at the same time as Y and at a near distance from the building
(c) at the same time as Y and at a same distance from the building
(d) at the same time as Y and at a farther distance from the building
1 2
5. The equation of projectile is y 3 x gx . The velocity of projection is
2
(a) 1 m/s (b) 2 m/s (c) 3 m/s (d) 4 m/s
2
x
6. A particle moves along the positive branch of the curve y with x governed by
2
1 2
x t where x and y are measured in metre and t in second. At t = 2s, the velocity of
2
the particle is
(a) 2 iˆ 4ˆj ms 1
(b) 2 iˆ 4ˆj ms 1 (c) 4 iˆ 2ˆj ms 1
(d) 4 iˆ 2ˆj ms 1
7. Two particles are projected simultaneously in the same vertical plane from the same
point, with different speeds u1 and u2, making angles 1 and 2 respectively with the
horizontal, such that u1 cos 1 u2 cos 2 . The path followed by one, as seen by the other
(as long as both are in flight), is
(a) a horizontal straight line (b) a vertical straight line
(c) a parabola
(d) a straight line making an angle 1 2 with the horizontal.
8. An airplane is flying in a horizontal direction with a velocity of 600 km/h and at a height
of 1960 m. When it is vertically above the point A on the ground, a body is dropped from
it. The body strikes the ground at point B. The distance AB will be
MVN Faridabad Page 1 of 3
Work Sheet-15 Kinematics: Projectile Motion
10 1 5
(a) km (b) 10 km (c) km (d) km
3 3 3
9. To a man walking at the rate of 3 km/h the rain appears to fall vertically. When he
increases his speed to 6 km/h it appears to meet him at an angle of 45° with vertical
from the front. The actual speed of rain is
(a) 3 km/hr (b) 4 km/hr (c) 3 2 km /h (d) 2 3 km/hr
10. A ball rolls from the top of a stair way with a horizontal velocity u. If the steps are h high
and b wide, the ball will hit the edge of the nth step if
2 2 2
2uh 2u h 2u h u h
(a) n (b) n (c) n (d) n
gb
2
gb
2
gb gb
2
11. A airplane flying at a constant velocity releases bomb. As the bomb drops away from the
airplane
(a) it will always be vertically below the airplane
(b) it will always be vertically below the airplane only if the airplane was flying
horizontally
(c) it will always be vertically below the airplane only if the airplane was flying at an
angle of 45° to the horizontal
(d) it will gradually fall behind the airplane if the airplane was flying horizontally
Answers
1. (c) 2. (a) 3. (c) 4. (c) 5. (b)
6. (b) 7. (b) 8. (a) 9. (c) 10. (b)
11. (a)
2-D Motion: Projectile Motion
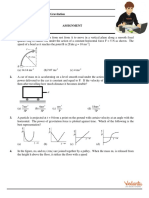
1. A ball is projected upward with velocity 20 2 ms1 at an angle 45 to the ground. If
origin is assumed at the point of projection, then
(a) determine the position and velocity of the ball at t 1 s, 2s, 3s and 4s .
(b) determine the equation of trajectory of the ball.
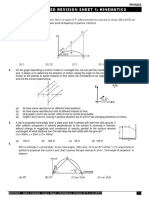
2. A ball is projected horizontally with speed 20 ms1 from the top of a u
tower of height H . If the ball takes 2s to reach the ground then, H
calculate
(a) the value of H d
(b) at what angle with the horizontal it strikes the ground.
(c) the horizontal distance d where the ball strikes the ground.
3. If at the highest point the kinetic energy of a particle is 75% of initial kinetic energy, then
what is the angle of projection?
4. A ball is thrown with speed u at an angle from horizontal. Determine the velocity of
ball at the instant when it makes an angle with the horizontal.
3
5. If the equation of trajectory of a projectile is y x x , then find (a) the angle of
2
4
projection (b) range, R (c) height, H
MVN Faridabad Page 2 of 3
Work Sheet-15 Kinematics: Projectile Motion
6. For the projectile shown in figure, determine the relation
between angle of projection and the angle of elevation . H
7. A projectile fired from A passes through the other corners of B
the triangle as shown in figure. If be the angle of
projection, then show that
tan tan tan
A C
8. Two projectiles fired with same speed at two different angles of projection have equal
range. If the heights of projectile in the two cases are 36 m and 25 m, respectively, then
find the horizontal range of the projectile.
Answers
x2
1. (a) (20, 15); (40, 20); (60, 15); (80, 0) ; (b) y x
80
2. (a) H 20 m (b) 45 (c) 40 m
3. 30
u cos
4. v
cos
3 9
5. (a) 37 (b) R (c) H
4 64
tan
6. tan
2
8. R 120 m
Fill in the Blanks.
1. A particle is thrown from the ground with speed u at angle from the ground. The velocity of
particle at 15m height is v 20iˆ 10 ˆj m/s.
(a) The speed of projection u from ground is ___________ m/s.
(b) Angle of projectile with ground is ___________.
(c) Maximum height from the ground is ___________ m.
(d) Horizontal range on the ground is __________m.
2. Initially at time t 0 , particle A is at the position (1, 2)m and particle B is at position (5,5)m.
The velocity of B is 2iˆ 4 ˆj ms1 and that of particle A is 2 v at 45 with x -axis. If A
collides with B , then
(a) Value of v is _________ m/s.
(b) Time when A will collide with B is __________ second.
Answers
1. (a) 20 2 (b) 45 (c) 20 (d) 80
2. (a) 10 (b) 0.5
MVN Faridabad Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Motion in Two Dimensions - MiscellaneousDocument12 pagesMotion in Two Dimensions - MiscellaneousJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration 96 Solved ExamplesDocument84 pagesMechanical Vibration 96 Solved ExamplesnimaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - 1Document3 pagesProjectile Motion - 1anchlia12345No ratings yet
- Projectile2021Document5 pagesProjectile2021Pranav ParasharNo ratings yet
- 03 KM. Two Dimension Motion (JEE) - I PDFDocument8 pages03 KM. Two Dimension Motion (JEE) - I PDFShikha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 13-14-15Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 13-14-15Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Q P Paper IDocument10 pagesProjectile Motion Q P Paper IsagarNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion - Quesiton BankDocument5 pagesProjectile Motion - Quesiton BankSaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Projectile MotionDocument5 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Projectile MotionAtul100% (1)
- Kinematics Fiitjee AssignmentDocument14 pagesKinematics Fiitjee AssignmentGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- Set 3Document2 pagesSet 3DIPA NAGNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesMotion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsAvik PatraNo ratings yet
- 4-Chapter Test (Projectile Motion) - Zaman AcademyDocument3 pages4-Chapter Test (Projectile Motion) - Zaman AcademyShyam Shankar DasNo ratings yet
- QBank - Motion in A PlaneDocument9 pagesQBank - Motion in A PlaneArshia PatniNo ratings yet
- Mock Phase 1 Mains Test For PractiseDocument3 pagesMock Phase 1 Mains Test For PractiseRocky WaterNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectVivek SreerajNo ratings yet
- Practice Sheet - 7 ( Projectile Motion-I - WithOUT)Document5 pagesPractice Sheet - 7 ( Projectile Motion-I - WithOUT)deepti's kitchenNo ratings yet
- 7Rt7nb - 3. Projectile Motion Worksheet 6Document4 pages7Rt7nb - 3. Projectile Motion Worksheet 6RAEES AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2D - HW - 1Document3 pagesKinematics 2D - HW - 1studyhimansh09No ratings yet
- WS-14 - KN - 2-D Motion - SubDocument3 pagesWS-14 - KN - 2-D Motion - SubSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimension - LDA - 18Document2 pagesMotion in Two Dimension - LDA - 18SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument7 pagesProjectile MotionVermaNo ratings yet
- Iit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only-Diwali Assignment-XiDocument60 pagesIit (M+a) & Jee Mains Only-Diwali Assignment-XiSara WolfNo ratings yet
- Advanced Problem Package Kinematics of A Particle & Motion in Two DimensionDocument166 pagesAdvanced Problem Package Kinematics of A Particle & Motion in Two DimensionSachin100% (1)
- Crash Chapter 4 TestDocument4 pagesCrash Chapter 4 TestKamran Ali100% (1)
- KINEMATICS Sheet PDFDocument21 pagesKINEMATICS Sheet PDFAmazing ThingsNo ratings yet
- JEE Adv Revision-1 Kinematics Final withOUT 13-11-2022Document7 pagesJEE Adv Revision-1 Kinematics Final withOUT 13-11-2022Uday ThakurNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Revision PaperDocument16 pagesMechanics Revision PapersagarNo ratings yet
- 2967 2723-MergeDocument11 pages2967 2723-MergeNancy nainNo ratings yet
- 636026545687341710Document14 pages636026545687341710Kb AshishNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Multiple Choice With Problem KitsDocument7 pagesProjectile Motion Multiple Choice With Problem KitsWilliam A. LarideNo ratings yet
- DPP-4 JeeDocument7 pagesDPP-4 JeeTanmay SagarNo ratings yet
- Level 1 - 30371261 - 2024 - 03 - 07 - 21 - 11Document2 pagesLevel 1 - 30371261 - 2024 - 03 - 07 - 21 - 11nishantyadav8955No ratings yet
- Work Power Energy JEE TestDocument6 pagesWork Power Energy JEE TestAman RolandNo ratings yet
- 04 - Motion in Two DimensionDocument3 pages04 - Motion in Two DimensionMathan KalyanasundaramNo ratings yet
- CD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95Document18 pagesCD 7 e 4 B 01 B 7 e 4 Ad 1 Aa 95RiteshNo ratings yet
- Assignment (PQRS) WADocument9 pagesAssignment (PQRS) WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment (13th) WADocument11 pagesAssignment (13th) WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Sheet 2 JEE 2024: EdunitiDocument2 pagesKinematics Sheet 2 JEE 2024: EdunitiXYZ RACCERNo ratings yet
- DPP 2Document11 pagesDPP 2mstudy1009No ratings yet
- 10 - Revision - Phy - PCMDocument3 pages10 - Revision - Phy - PCMC.M.M GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Ashutosh Chaturvedi: (B.Tech. IIT-BHU)Document3 pagesAshutosh Chaturvedi: (B.Tech. IIT-BHU)Kushagra SahuNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)Document6 pagesAIEEE Module Q.P. Kinematics)MOHAMMED ASIF100% (1)
- Kinematics DPP 08Document4 pagesKinematics DPP 08ROHANNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Definition, Projectile On A Horizontal PlaneDocument10 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Definition, Projectile On A Horizontal PlaneAditya SahayNo ratings yet
- Energy & Momentum - MiscellaneousDocument18 pagesEnergy & Momentum - MiscellaneousJee AspirantNo ratings yet
- TARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017Document20 pagesTARGET: JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017ApurbNo ratings yet
- Chanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar 9888190610 Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesChanana Institute of Physics: 326, Tilak Nagar, Amritsar 9888190610 Projectile MotionAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Important Questions and Solutions For JEE Main and AdvancedDocument19 pagesKinematics Important Questions and Solutions For JEE Main and AdvancedRavindra KumarNo ratings yet
- Kinematics DPP 07Document4 pagesKinematics DPP 07ROHANNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Projectile MotionDocument6 pagesAssignment On Projectile Motionsingh813No ratings yet
- Kinematics 1Document6 pagesKinematics 1Shiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument9 pagesProjectile MotionYash Akhauri100% (1)
- Comp2023 Btest-4 PhysicsDocument13 pagesComp2023 Btest-4 PhysicsJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Open Blank BlackDocument1 pageOpen Blank BlackVarun AroraNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and GravitationDocument5 pagesWork Energy Power and Gravitationaryan aggarwalNo ratings yet
- ABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Document2 pagesABC XI TEST SERIES TEST-02 CHAPTER 2 and 3 2023-24Ashish GargNo ratings yet
- Phy Motion 2,3 DimensionassignDocument3 pagesPhy Motion 2,3 Dimensionassigntuhina27No ratings yet
- WS-17 - KN - Circular MotionDocument5 pagesWS-17 - KN - Circular MotionSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- WS-14 - KN - 2-D Motion - SubDocument3 pagesWS-14 - KN - 2-D Motion - SubSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- WS-16 - KN - Relative MotionDocument4 pagesWS-16 - KN - Relative MotionSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- Ranjeet ShahiDocument529 pagesRanjeet Shahiयash ᴍᴀɴGalNo ratings yet
- WS-13 - KN - 1-D Motion - SubDocument2 pagesWS-13 - KN - 1-D Motion - SubSuman SinghNo ratings yet
- WWW - Jeeneetbooks.in Disha 43 Years JEE Advanced PhysicsDocument656 pagesWWW - Jeeneetbooks.in Disha 43 Years JEE Advanced PhysicsPranoy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Arihant Class 12 Mathematics Term 2 Sample PapersDocument149 pagesArihant Class 12 Mathematics Term 2 Sample Papersrudra k100% (1)
- Arihant Class 12 Mathematics Term 2 Sample PapersDocument149 pagesArihant Class 12 Mathematics Term 2 Sample Papersrudra k100% (1)
- Phys234h Lecture03Document29 pagesPhys234h Lecture03Jessa Balanay GalaponNo ratings yet
- Physics PP1 F3 MSDocument7 pagesPhysics PP1 F3 MSABBY PRECIOCANDYNo ratings yet
- 13-Reinforced Concrete Designers Handbook 10th Edition - Reynolds SteedmanDocument1 page13-Reinforced Concrete Designers Handbook 10th Edition - Reynolds SteedmanCon CanNo ratings yet
- OPTION A-Sight and WaveDocument12 pagesOPTION A-Sight and Wavemardel11No ratings yet
- Thermoflask (Insulator)Document11 pagesThermoflask (Insulator)Jay RanjanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For Mechanical Waves & Sound Waves Deadline: April 12, 2021Document10 pagesProblem Set For Mechanical Waves & Sound Waves Deadline: April 12, 2021I AM DJNo ratings yet
- NU-London Experiment 2 - 1D and 2D MotionDocument5 pagesNU-London Experiment 2 - 1D and 2D Motionsebodev120No ratings yet
- (AC+CD) - (AG +λ/2) : ΔX= 2t (cosθr) - λ/2 =nλDocument4 pages (AC+CD) - (AG +λ/2) : ΔX= 2t (cosθr) - λ/2 =nλkavyaNo ratings yet
- Invisible Waves WorksheetDocument9 pagesInvisible Waves WorksheetAstra - EditsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6Nor Fitrey IbrahimNo ratings yet
- AWP UNIT-1 (Vsem) - Merged-1Document76 pagesAWP UNIT-1 (Vsem) - Merged-1Pavan SaiNo ratings yet
- Acessorios FTIRDocument52 pagesAcessorios FTIRanagabriela12No ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Physics Investigatory Project MouleswaranDocument12 pagesProjectile Motion Physics Investigatory Project MouleswaranYuvaraj .S.S.M100% (1)
- An Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureDocument11 pagesAn Approximate Realization of A Black Body As A Tiny Hole in An Insulated EnclosureamanNo ratings yet
- Concentradores Solares Luminiscentes Basados en Puntos Cuánticos Core-Shell Con Reabsorción Reducida y Eficiencia MejoradaDocument5 pagesConcentradores Solares Luminiscentes Basados en Puntos Cuánticos Core-Shell Con Reabsorción Reducida y Eficiencia MejoradaJulio César Chinchay QuiñonezNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q1 Wk5Document8 pagesScience8 Q1 Wk5Aizelle Taratara FaderoNo ratings yet
- Dyna ProjectDocument58 pagesDyna ProjectCarlo Domanais0% (3)
- HMT PDFDocument30 pagesHMT PDFAnonymous 5iGVjv9d5No ratings yet
- Week Slides Theory of MachineDocument44 pagesWeek Slides Theory of MachineAhmad AbdNo ratings yet
- Practical Conduction Heat TransferDocument14 pagesPractical Conduction Heat TransfertskNo ratings yet
- Filipino GawainDocument4 pagesFilipino GawainAji Nikka AngelesNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument179 pagesNotesz_artist95No ratings yet
- AcousticsDocument56 pagesAcousticsLorraine I. Jamero100% (1)
- General Physics 2 Final Exam 2nd SemDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Final Exam 2nd SemDrew TorresNo ratings yet
- Biofluid MechanicsDocument12 pagesBiofluid MechanicsAyush JaiswalNo ratings yet
- (S3) - Kinematics 2D (Projectile Motion) - 21st Feb. PDFDocument22 pages(S3) - Kinematics 2D (Projectile Motion) - 21st Feb. PDFMalyadip PalNo ratings yet
- Empirical Path Loss ModelsDocument7 pagesEmpirical Path Loss ModelsDatta RajendraNo ratings yet
- Waves and Types of WavesDocument14 pagesWaves and Types of Wavesusman_uet08100% (2)
- Module 1.3 - Applications of IntegrationDocument4 pagesModule 1.3 - Applications of IntegrationJ KimNo ratings yet