Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shallow Foundations
Shallow Foundations
Uploaded by
Nazeel NazirOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shallow Foundations
Shallow Foundations
Uploaded by
Nazeel NazirCopyright:
Available Formats
CE6611 – Shallow Foundations – Tutorial Problems
1 Calculate the ultimate bearing capacity of a strip footing, 1.5 m wide, founded 0.75 m
into a uniform silty sand. The properties of the sand are:
= 19 kN/m3 , c’ = 0, k‘ = 32°
Assume the ground water table is at significant depth.
2 The applied permanent vertical action in (1) is 400 kN/m run including the weight of
the footing itself and any soil on top of it which acts centrally on the footing. Does the
design conform to the requirements of Eurocode 7 Design Approach 1?
3 Is the design in (2) satisfactory if the ground water table rises to 0.5 m below existing
ground level?
4 A 2.2 m square footing supporting a column is to be founded 1 m below ground level.
The footing is 0.75 m thick. The founding soil is a stiff clay with the following
properties:
= 20 kN/m3, cuk = 120 kN/m2
The concrete has a weight density, conc = 25 kN/m3
Using Design Approach 1 calculate the maximum characteristic permanent vertical
load that can be taken from the column.
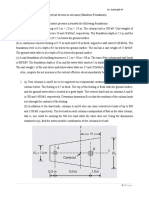
5 A rectangular footing 0.5 m thick is to be founded 1.5 m below ground level. The
footing is 1.2 m wide by 1.8 m long and is supporting a column which is subject to a
permanent vertical action of 500 kN acting through the centre of the footing, coupled
with a variable vertical action of 100 kN and a permanent horizontal action of 100 kN
acting in the direction of the long axis of the footing and 1.7 m above the base of the
footing.
500 kN permanent
1.8 m 100 kN 100 kN variable
1.2 m 1.7 m 1.5 m
0.5 m
PLAN SECTION
The ground water table has been established at 1.9 metres below ground level.
The soil properties are:
= 19 kN/m3 , ck’ = 5 kN/m2, k‘ = 28o
Using Design Approach 1 assess the suitability of the proposed design.
You might also like
- TD3 Shallow FoundationDocument3 pagesTD3 Shallow FoundationMonny MOMNo ratings yet
- Soil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Document1 pageSoil 7 April 2023 1 of 2Nica SudamaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation Settlement Examples 1 - Solutions (2) - 2Document14 pagesConsolidation Settlement Examples 1 - Solutions (2) - 2Sujani MaarasingheNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesFoundation Engineering Exam QuestionsRamiz Keyra0% (1)
- Selective Numerical - Lateral Earth Pressure 075Document4 pagesSelective Numerical - Lateral Earth Pressure 075Rajesh Khadka100% (1)
- Problem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFDocument1 pageProblem Set 1 (Bearing Capacity Equations) PDFMark Joseph Bandojo VargasNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1Document7 pagesQuestion Bank: Cem701 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Ii Unit 1RaNo ratings yet
- Ceu313 CT2Document3 pagesCeu313 CT2Krishna Prasad ENo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document1 pagePs 1amor Bagon0% (2)
- Tutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationsNametso MoatsheNo ratings yet
- Ce 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Document2 pagesCe 441 Foundation Engineering - 2021 Fall Homework 1Yusuf DuranNo ratings yet
- Ce162P Geotechnical Foundation Engineering: Public For Public UseDocument5 pagesCe162P Geotechnical Foundation Engineering: Public For Public UseMiGz ShiinaNo ratings yet
- Problems of SoilsDocument3 pagesProblems of SoilsFaheem Ali AsgharNo ratings yet
- A y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallDocument1 pageA y C 3 3 DL LL DL LL C Y: Section For Moment Is Halfway Between Middle and Edge of WallMau MauNo ratings yet
- CV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFDocument3 pagesCV3013 - Tutorials 1 To 3 (2015) PDFlevanviet0410100% (1)
- AgtDocument7 pagesAgtVijay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD EXAMIN Geo WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesPREBOARD EXAMIN Geo WPS Officemichael SonuganNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Assignment2Document4 pagesEarthquake Assignment2Faisal MohammedNo ratings yet
- CE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsDocument31 pagesCE407 - Updated Midsem SolutionsManan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Monika AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Nse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFDocument16 pagesNse-1491259045342336576-Examples - CH 8 Shallow Foundations-1 - 221020 - 010533 PDFTiago PhillipeNo ratings yet
- DRC IIDocument3 pagesDRC IIgobinathdpiNo ratings yet
- RCD Assignment 5Document4 pagesRCD Assignment 5CE-Cret KuyaaDeeeNo ratings yet
- Show All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsDocument2 pagesShow All The Necessary Steps To Solve The Following ProblemsMistireselassieNo ratings yet
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Document2 pages3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for Nov 2022 - Geotechnical Engineering 8JuDeNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument4 pagesProblemsbalaNo ratings yet
- Afe QuesDocument8 pagesAfe Questkumar111No ratings yet
- Geotech Engg QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeotech Engg QuestionsYashasviNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document4 pagesHomework 2Ali AratNo ratings yet
- Ce 342 Tutorial 2Document5 pagesCe 342 Tutorial 2Deus IrechoNo ratings yet
- Drbms TutorialsDocument4 pagesDrbms TutorialsUmar Saba100% (1)
- Foundation Engineering Tutorial Questions 1Document2 pagesFoundation Engineering Tutorial Questions 1emmanuel alimaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Design DataDocument3 pagesGeotechnical Design DataJoe BirdNo ratings yet
- Practice AssignmentDocument2 pagesPractice AssignmentAditya PadaviNo ratings yet
- FE Imp QuestionsDocument8 pagesFE Imp QuestionsYeswanth PaluriNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Foundation EngineeringDocument5 pagesProblem Set Foundation EngineeringJohn Mathew BrionesNo ratings yet
- TD1 Shallow FoundationDocument2 pagesTD1 Shallow FoundationSokvisal MaoNo ratings yet
- M. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesM. H. S. S. College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringjay shankar prabhatNo ratings yet
- 07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiDocument7 pages07a70101 Geotechnical Engineering-IiSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- 3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Document2 pages3 1965kg/m sat γ: CE Review for April 2023 - Geotechnical Engineering 8Nica SudamaNo ratings yet
- Uplift StabilityDocument4 pagesUplift StabilityUtaya Kumar VeelmuruganNo ratings yet
- Student Self-Led Activity Exercises On Supported Vertical Sided ExcavationsDocument1 pageStudent Self-Led Activity Exercises On Supported Vertical Sided ExcavationsZaid AlsarayrehNo ratings yet
- Q2 Sa RC2Document1 pageQ2 Sa RC2Quicksilver 1975No ratings yet
- FAD KTU Question Paper - May 2016Document3 pagesFAD KTU Question Paper - May 2016Jimmy ThomasNo ratings yet
- PS1Document1 pagePS1Matt Benjoemin PuertoNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentsajjadsiyal144No ratings yet
- GT 2 QBDocument6 pagesGT 2 QBPrajakta ShindeNo ratings yet
- Questions FinalDocument9 pagesQuestions FinalRavindra JagadaleNo ratings yet
- Openbook Test On Geotechnical Design 2017Document4 pagesOpenbook Test On Geotechnical Design 2017Chongchuen FongNo ratings yet
- Test On GeotechnicalDocument4 pagesTest On GeotechnicalChongchuen FongNo ratings yet
- 5 6149912092880142413Document10 pages5 6149912092880142413Rushikesh patilNo ratings yet
- 0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionDocument16 pages0753.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.02 - Tutorial - 4 - Settlements Due To Tunnel ConstructionErolNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentDawit AyeleNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Shalllow FoundationDocument2 pagesBearing Capacity of Shalllow Foundationrx135boyNo ratings yet
- CE 631 Assignment 1&2Document4 pagesCE 631 Assignment 1&223mce012No ratings yet
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Document5 pagesTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNo ratings yet
- SJBIT - Geotech - II Assignment 2Document1 pageSJBIT - Geotech - II Assignment 2sagar_srNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem On Rectangular Footing and Eccentric FootingDocument32 pagesSample Problem On Rectangular Footing and Eccentric FootingJade ParrenoNo ratings yet
- University of Batangas College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument12 pagesUniversity of Batangas College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentVenus Gjervie Yu - AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173From EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, Vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 A Concrete Water Tower, Paper No. 1173No ratings yet