Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Losses in Steam Turbines&Reheat Factor
Uploaded by
Dev DixitCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Losses in Steam Turbines&Reheat Factor
Uploaded by
Dev DixitCopyright:
Available Formats
Losses in steam turbines refer to energy that is not converted into useful work.
There are
several types of losses that can occur in a steam turbine, including:
1. Friction losses: These losses occur due to friction between moving parts in the turbine,
such as bearings and seals.
2. Heat losses: Heat losses occur due to heat transfer to the environment through the
casing and other components of the turbine.
3. Blade profile losses: Blade profile losses occur due to the inefficiency of the blade
design, which results in some of the steam energy being lost as it flows through the
blades.
4. Leakage losses: Leakage losses occur as steam escapes from the casing or other parts of
the turbine, reducing the amount of energy available to do work.
5. Reheat losses: Reheat losses occur in turbines that use reheat systems, where steam is
returned to the boiler for reheating after passing through the turbine. Some energy is
lost during the reheating process.
It's important to minimize losses in steam turbines in order to maximize their efficiency
and output. This can be achieved through regular maintenance, as well as through the
use of materials and designs that minimize friction and heat loss.
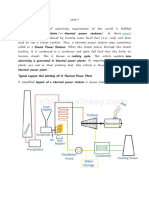
The reheat factor in steam turbines is a measure of the efficiency of a reheat steam
turbine system. It is defined as the ratio of the network produced by the turbine to the
total energy added to the steam in the boiler.
In a reheat steam turbine system, the steam from the boiler is expanded in a high-
pressure (HP) turbine and then sent back to the boiler to be reheated. The reheated
steam is then expanded in a low-pressure (LP) turbine. The reheat factor takes into
account both the HP and LP turbine work, as well as the energy required to reheat the
steam.
The reheat factor is an important parameter in the design and performance evaluation
of reheat steam turbines. A high reheat factor indicates that a large amount of the
energy added to the steam in the boiler is being converted into useful work by the
turbine, while a low reheat factor indicates that a significant portion of the energy is
being lost. Factors that can impact the reheat factor include the efficiency of the reheat
system, the efficiency of the turbines, and the steam conditions at various points in the
system.
You might also like
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions & Answers: Process Auxiliaries and Utilities (GTU-3170516)Document24 pagesImportant Questions & Answers: Process Auxiliaries and Utilities (GTU-3170516)dhruv100% (4)
- Air FanDocument6 pagesAir FanDevi PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Steam PlantDocument102 pagesSteam PlantPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Article JEE7-Boiler EfficiencyDocument6 pagesArticle JEE7-Boiler Efficiencyrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Actual Rankine CycleDocument13 pagesWeek 4 - Actual Rankine CycleLester Jave HechanovaNo ratings yet
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocument101 pagesJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant and BoilersDocument101 pagesSteam Power Plant and Boilersjamunaa83100% (1)
- Class 4. Steam Power PlantDocument37 pagesClass 4. Steam Power PlantsureshlalNo ratings yet
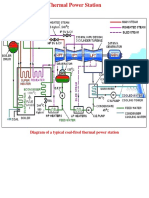
- Thermal Power StationDocument6 pagesThermal Power StationAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Expt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantDocument6 pagesExpt. # 03 Study of A Steam Turbine Power PlantSajeeb SarkerNo ratings yet
- Optimize Fired Heater Operations To Save MoneyDocument8 pagesOptimize Fired Heater Operations To Save Moneyyogitadoda100% (2)
- Boiler Efficiency CalculationDocument17 pagesBoiler Efficiency CalculationSolai100% (4)
- How Does A Gas Turbine Power Plant Work?: 1. CompressorDocument8 pagesHow Does A Gas Turbine Power Plant Work?: 1. CompressorSuresh Ram R100% (1)
- Ukai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3Document13 pagesUkai Thermal Power Plant-Eman Refai Abdelkhaliq-Sec 3eman.refai13lcsNo ratings yet
- Lab 404Document10 pagesLab 404Wasee AbNo ratings yet
- Boiler Learning ModuleDocument158 pagesBoiler Learning ModuleMallinatha PNNo ratings yet
- Automotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Document48 pagesAutomotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Santanu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Boiler Structure and Principle (English)Document28 pagesBoiler Structure and Principle (English)Engr ImranNo ratings yet
- Boiler Draught and Its TypesDocument4 pagesBoiler Draught and Its TypesHamza AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Steam EffDocument4 pagesSteam EffViola ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- Fired Heater Presentation - Final97 2003Document40 pagesFired Heater Presentation - Final97 2003Altif Abood100% (2)
- Assignment in ME 312Document23 pagesAssignment in ME 312jasperNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam Used in Refineries and Their UsesDocument4 pagesTypes of Steam Used in Refineries and Their UsesPrabath MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Report On NTPC Industrial Training at Barh (Patna)Document24 pagesReport On NTPC Industrial Training at Barh (Patna)Gautam KumarNo ratings yet
- Boiler & AuxiliariesDocument13 pagesBoiler & Auxiliariesprats123456No ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant PDFDocument16 pagesThermal Power Plant PDFMoustafa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Air Pre HeaterDocument13 pagesAir Pre HeaterRaghav RajputNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument16 pagesThermal Power PlantmudarNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet ADocument82 pagesGas Turbine Performance Based On Inlet Afateh1982No ratings yet
- Gas Turbine: Olar LoungeDocument34 pagesGas Turbine: Olar Loungepkdevan68100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Power Plant: Fig.1-2: Components of A Basic Gas Turbine EngineDocument22 pagesGas Turbine Power Plant: Fig.1-2: Components of A Basic Gas Turbine Engineام البنين الرياني100% (1)
- Chapter 2-Power CyclesDocument23 pagesChapter 2-Power CyclesbaseakelNo ratings yet
- Ppe Pit Obando's PartDocument8 pagesPpe Pit Obando's PartJane PondulanNo ratings yet
- AES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byDocument25 pagesAES Thermal Power Plant, Lalpir, District Muzaffargarh: Prepared byIrfan UllahNo ratings yet
- هندسة غازDocument3 pagesهندسة غازŴişšăm ŠaŁeĥNo ratings yet
- External Reciprocating Steam EngineDocument8 pagesExternal Reciprocating Steam EngineabdiNo ratings yet
- Boiler EconomizerDocument5 pagesBoiler Economizerreyalene gallegos100% (1)
- BodyDocument69 pagesBodyRoi Benedict BuenaNo ratings yet
- Tugas 3 Sistem Pembangkit Tenaga: "Penjelasan Alur Sistem Pembangkit Dan Hasil Cycle Tempo 5.0 Pada Heat Balance Diagram"Document17 pagesTugas 3 Sistem Pembangkit Tenaga: "Penjelasan Alur Sistem Pembangkit Dan Hasil Cycle Tempo 5.0 Pada Heat Balance Diagram"mitaa jannahNo ratings yet
- The Electric Arc FurnaceDocument11 pagesThe Electric Arc FurnacePushkar KhannaNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PlantDocument7 pagesSteam Power PlantsuganyaNo ratings yet
- Boiler E Ciency: Value-In-Use (VIU) Assessment For Ther-Mal and Metallurgical CoalDocument32 pagesBoiler E Ciency: Value-In-Use (VIU) Assessment For Ther-Mal and Metallurgical CoalBasma IssaouiNo ratings yet
- Economiser LiteratureDocument7 pagesEconomiser LiteratureSteve M D'souzaNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas and Steam Power PlantDocument8 pagesCombined Gas and Steam Power Planttushar1128100% (1)
- Bme NotesDocument34 pagesBme NotesAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Fire Heater Engineering Economics & Design: NOVEMBER 2012Document36 pagesFire Heater Engineering Economics & Design: NOVEMBER 2012Anonymous xMw43TNo ratings yet
- Steam System Basics PDFDocument67 pagesSteam System Basics PDFEduardo Miranda100% (1)
- Electrical Job Questions:Thermal Power Plant (Set 1) : AnswerDocument11 pagesElectrical Job Questions:Thermal Power Plant (Set 1) : AnswerNitin NaharNo ratings yet
- Manual On Boiler Tube FailureDocument69 pagesManual On Boiler Tube FailureAnudeep Chittluri100% (4)
- 3.steam TurbinesDocument23 pages3.steam Turbinesstrategy onesmusNo ratings yet
- Ppe NotesDocument51 pagesPpe NotesCharan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Process Heating: Boiler OperationDocument12 pagesProcess Heating: Boiler Operationagrocel_bhv5591No ratings yet
- Industrial Visit Report On Siddhirganj 210MW Thermal Power StationDocument14 pagesIndustrial Visit Report On Siddhirganj 210MW Thermal Power StationSaibNo ratings yet
- Manual On Boiler Tube FailureDocument69 pagesManual On Boiler Tube Failureyogeshmangal1974100% (2)
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet