Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Uploaded by
yadhu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageConfined spaces such as tanks, vats, vessels, hoppers, and bins can present physical hazards in addition to dangerous atmospheres. These physical hazards include poor entry and exit conditions, cramped working spaces, temperature extremes, rotating or moving equipment, electrical hazards, and uncontrolled movement of liquids or solids. Before entering a confined space, one should inspect for hazardous contents, lock out any electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic equipment, block and secure any moving equipment, use safety harnesses and lifelines, develop a rescue plan, and use an entry permit system to identify hazards and controls.
Original Description:
Original Title
confined_spaces_physical_hazards
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConfined spaces such as tanks, vats, vessels, hoppers, and bins can present physical hazards in addition to dangerous atmospheres. These physical hazards include poor entry and exit conditions, cramped working spaces, temperature extremes, rotating or moving equipment, electrical hazards, and uncontrolled movement of liquids or solids. Before entering a confined space, one should inspect for hazardous contents, lock out any electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic equipment, block and secure any moving equipment, use safety harnesses and lifelines, develop a rescue plan, and use an entry permit system to identify hazards and controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageConfined Spaces Physical Hazards
Confined Spaces Physical Hazards
Uploaded by
yadhuConfined spaces such as tanks, vats, vessels, hoppers, and bins can present physical hazards in addition to dangerous atmospheres. These physical hazards include poor entry and exit conditions, cramped working spaces, temperature extremes, rotating or moving equipment, electrical hazards, and uncontrolled movement of liquids or solids. Before entering a confined space, one should inspect for hazardous contents, lock out any electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic equipment, block and secure any moving equipment, use safety harnesses and lifelines, develop a rescue plan, and use an entry permit system to identify hazards and controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
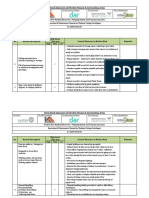
Confined spaces—Physical hazards
Explain dangers • Inspect the space for dangerous contents
such as grain or sand that could slide, shift,
In addition to dangerous atmospheres, confined and bury you inside.
spaces such as tanks, vats, vessels, hoppers, and • Lock out any electrical, hydraulic,
bins can present physical hazards such as or pneumatic equipment that could
• Poor entry and exit unexpectedly rotate, drop, roll, or snap shut
in the space.
• Cramped working conditions
• Block and secure any equipment that
• Temperature extremes could move because of gravity or stored
• Rotating or moving equipment momentum.
• Reactive or corrosive residues • Wear safety harnesses and lifelines to make
rescue more efficient in case of an emergency.
• Electrical hazards
• Develop a rescue plan for the space and
• Uncontrolled movement of liquids or solids.
practice to make sure that everyone knows
Some of these hazards involve greater risk inside what to do.
a confined space than outside.
• Use an entry permit system. This helps
For example, electrical flashover can be more identify hazards and controls, and keeps track
dangerous in a cramped maintenance hole where of who is inside.
there’s limited escape than in an electrical room
with clear exits. And fire in a confined space can Demonstrate
be far more dangerous than fire in an open work
area. Review procedures for lockout, tagging, and
entry. Discuss some of the controls shown in the
Identify controls diagram below.
• Isolate the space by disconnecting supply
and drain lines. Lock out and tag the lines so
they won’t be reopened while you’re working
inside.
72 Confined Spaces
You might also like
- Ultimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionFrom EverandUltimate Guide: Wiring, 8th Updated EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- 8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceDocument16 pages8.EXACAVATION and Confined SpaceIhuhwa Marta TauNo ratings yet
- Safety - Mast ClimbingDocument78 pagesSafety - Mast ClimbingparadigmanNo ratings yet
- Safety ManagementDocument19 pagesSafety ManagementDave Khyl Josol BosqueNo ratings yet
- Confined SpaceDocument33 pagesConfined SpaceDesta WidayatNo ratings yet
- Common Office HazardsDocument2 pagesCommon Office HazardsbosesubrataNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar 313c SR Track Type Excavator Parts Manual Japonesa 2010Document20 pagesCaterpillar 313c SR Track Type Excavator Parts Manual Japonesa 2010michael98% (49)
- Excavation Trench SafetyDocument31 pagesExcavation Trench SafetyBipin Babu100% (1)
- Job Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankDocument1 pageJob Hazard Analysis Cleaning Water TankRamy100% (5)
- VD 1233 330 Dig 001 1Document12 pagesVD 1233 330 Dig 001 1Reza AranNo ratings yet
- Confined Space AwarenessDocument49 pagesConfined Space Awarenesstejas gajelli100% (1)
- A22009BDocument162 pagesA22009BInstalatii CivileNo ratings yet
- Chemical DosingDocument24 pagesChemical DosingIskerNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Preheater Cyclone Choke WIDocument5 pagesCleaning Preheater Cyclone Choke WIErmiyas MistreNo ratings yet
- Attachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)Document10 pagesAttachment R (Draft Offshore Decommissioning Safety Requirement Guideline)mustaffa bakriNo ratings yet
- Aviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsDocument20 pagesAviva Tank Farms - Fire Safety LpsSiwaNo ratings yet
- Blueridge Multi Zone Service Manual PDFDocument108 pagesBlueridge Multi Zone Service Manual PDFMatthew SalceNo ratings yet
- PR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkDocument6 pagesPR RFR P07 27 v1-0 How To Ensure Safety For Cyclone Lining WorkJuan Nacimba NacimbaNo ratings yet
- X-Bow & X-Stern Hull Lines: Studies, Documentation and ExperiencesDocument11 pagesX-Bow & X-Stern Hull Lines: Studies, Documentation and ExperiencesjasanuNo ratings yet
- The EdgeDocument10 pagesThe EdgeSakshmjot Singh100% (5)
- Dangers and Hazards of Entering Live Substations and Enclosures - Barry GassDocument101 pagesDangers and Hazards of Entering Live Substations and Enclosures - Barry Gassnp_bhuvaneswar100% (1)
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsKUSNONo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces Physical HazardsDocument1 pageConfined Spaces Physical HazardsAaquil RaziNo ratings yet
- LCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFDocument10 pagesLCS Multi-Page 06-06-19 PDFhendrawanNo ratings yet
- JSA Any OprationDocument12 pagesJSA Any Oprationn.aboshhewaNo ratings yet
- 02 Risk AssessmentDocument8 pages02 Risk Assessmentيوسف خضر النسورNo ratings yet
- DOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Document1 pageDOCS AND FILES-19128068-v1-DIT Min Const Safety Expectations Second Edition Aug 2022Nuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures of Power Tools 2Document1 pageStandard Operating Procedures of Power Tools 2singenaadamNo ratings yet
- Aerial LiftsDocument2 pagesAerial LiftsHous BoukadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Hazard IdentificationDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Hazard IdentificationRawsht MuradyNo ratings yet
- AB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBDocument19 pagesAB-B20&C20-MS-Formwork-PC & GBsokeara phoungNo ratings yet
- Hydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingDocument1 pageHydrojetting Safety: Safe Hydro-Jetting Activity PPE's Used During Hydro-JettingSKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification PlanDocument9 pagesHazard Identification PlanLijo JohnNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146Document38 pagesConfined Space Entry: OSHA Standard 1910.146SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsDocument2 pagesHousekeeping: Control Measures/SafeguardsShamel Jen FacundoNo ratings yet
- Family Emergency Plan PDF - WebDocument36 pagesFamily Emergency Plan PDF - WebSergio B. Goco Jr.No ratings yet
- 2022 - SM - LC (Ga) - R410a - 3D Inv - Eu - NB - H - 2108 - 34Document486 pages2022 - SM - LC (Ga) - R410a - 3D Inv - Eu - NB - H - 2108 - 34Técnico ElectrónicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5JRyan Babiera NangkilNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Document4 pagesJob Safety Analysis Worksheet (JSA)Kyle Garagara-MogolNo ratings yet
- Confined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteDocument13 pagesConfined Spaces: Health and Safety Guidance NoteWaleed MorsyNo ratings yet
- 2019-04-25 Toolbox Talk Seasonal Hazards - SpringDocument2 pages2019-04-25 Toolbox Talk Seasonal Hazards - SpringreneeNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Rescue Awareness PDFDocument36 pagesConfined Space Rescue Awareness PDFEr. Shamim AnsariNo ratings yet
- Electric Tools Basic SafetyDocument1 pageElectric Tools Basic Safety谢磊No ratings yet
- EXC Training 02Document41 pagesEXC Training 02Burdang PinoyNo ratings yet
- E Series Ciac Service Manual-1 Cg-Ch41eDocument78 pagesE Series Ciac Service Manual-1 Cg-Ch41eAnthony Pineda ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 123432Document145 pages123432avramusNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Document5 pagesJob Safety Analysis:: RTR DRAIN LINE REPLACEMENT (Excavation and Backfilling)Madhan KannanNo ratings yet
- User Manual: UBD-M7500Document99 pagesUser Manual: UBD-M7500NayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)Document51 pagesChapter 3-3.5. (Shoring Design)akhjazrNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines I Laboratory ManualDocument99 pagesTheory of Machines I Laboratory ManualrdyesslNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Before Installation (Environment)Document15 pages1.1. Before Installation (Environment)wavehayiathNo ratings yet
- IOM Splic AC - MitsuDocument4 pagesIOM Splic AC - MitsuwavehayiathNo ratings yet
- HSE-BMS-019 Excavations SafetyDocument34 pagesHSE-BMS-019 Excavations Safetykhan jadoonNo ratings yet
- TB TrenchDocument4 pagesTB TrenchNuragus HariyadiNo ratings yet
- HPK Emergency Ch2Document5 pagesHPK Emergency Ch2yourxmen2910No ratings yet
- FA18-EPE-007HVELab Report 2Document3 pagesFA18-EPE-007HVELab Report 2ali khanNo ratings yet
- Focus Four HazardsDocument115 pagesFocus Four HazardsrazambaNo ratings yet
- CD 00000129Document89 pagesCD 00000129Risto PetkovNo ratings yet
- Commercial-Kitchen-SOPs - EquipmentDocument11 pagesCommercial-Kitchen-SOPs - EquipmentTyrone SmithNo ratings yet
- Situation: Earthquake - Intensity 7.0 Forced Evacuation While Evacuating - May Faulty Wiring Na Nagresult Sa FireDocument2 pagesSituation: Earthquake - Intensity 7.0 Forced Evacuation While Evacuating - May Faulty Wiring Na Nagresult Sa FireAndrea Shane TorresNo ratings yet
- Tcs 220Document3 pagesTcs 220yeralNo ratings yet
- Capstan (OSRV) SOPDocument7 pagesCapstan (OSRV) SOPakbar muslimNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines I: Laboratory ManualDocument99 pagesTheory of Machines I: Laboratory ManualcayericaNo ratings yet
- MultimediaDocument2 pagesMultimediaarman setyawanNo ratings yet
- Midea Error CodesDocument186 pagesMidea Error Codesmateovera24No ratings yet
- High Voltage Rubber Techniques To 36 KV SPGDocument68 pagesHigh Voltage Rubber Techniques To 36 KV SPGyadhuNo ratings yet
- Entry and Work in Confined SpacesDocument51 pagesEntry and Work in Confined Spacesyadhu100% (1)
- Carbon MonoxideDocument1 pageCarbon MonoxideyadhuNo ratings yet
- A Diagnostic Toolkit For Physicians and Primary Health Providers. Prevention Information For Workers.Document4 pagesA Diagnostic Toolkit For Physicians and Primary Health Providers. Prevention Information For Workers.yadhuNo ratings yet
- Mobile Diesel Fuel DispenserDocument6 pagesMobile Diesel Fuel DispenserIonel PortasăNo ratings yet
- SEA Process For Environmental Humanity, Green Housing and Green Hospitality - DR - Vijayan Gurumurthy IyerDocument34 pagesSEA Process For Environmental Humanity, Green Housing and Green Hospitality - DR - Vijayan Gurumurthy IyerDr.Vijayan Gurumurthy IyerNo ratings yet
- EFI Installation Manual Rotax 4-1 Rev5Document26 pagesEFI Installation Manual Rotax 4-1 Rev5Esteban POPO ECHEVERRYNo ratings yet
- 33 KV SubstationDocument19 pages33 KV Substationraju chandanshiveNo ratings yet
- Step Outside The Box - 3Document2 pagesStep Outside The Box - 3Violet VioletNo ratings yet
- Totalenergies Travel-Journal 2022Document18 pagesTotalenergies Travel-Journal 2022Joash MabsNo ratings yet
- 01.Catalogue-Lubi FLBS 50 HZDocument16 pages01.Catalogue-Lubi FLBS 50 HZmyatthura870No ratings yet
- Excelente Ev SimulinkDocument11 pagesExcelente Ev SimulinkDEVIL JIM KAZUYANo ratings yet
- Hidroizolatie Acoperis TerasaDocument11 pagesHidroizolatie Acoperis TerasaMuntean FabianNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q3 M4 v4Document16 pagesScience7 Q3 M4 v4John Maricc RemediosNo ratings yet
- Genesis 3.8L Section 9Document52 pagesGenesis 3.8L Section 9Nacho MowjiNo ratings yet
- Aatma Ko ParichayaDocument13 pagesAatma Ko ParichayarameshneupaneNo ratings yet
- UPSC PrelimsDocument17 pagesUPSC PrelimsKaran Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Role of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferDocument1 pageRole of ATP in Energy Coupling and TransferOmbrog JustinNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of 186650x21700 Energy - Density - of - Cylindrical - Li-Ion - CellsDocument8 pagesA Comparison of 186650x21700 Energy - Density - of - Cylindrical - Li-Ion - CellsRodrigo VieiraNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Physics - MotionDocument18 pagesYear 10 Physics - MotionKevin XiaoNo ratings yet
- Cleair O2-002 User ManualDocument10 pagesCleair O2-002 User ManualMaman SajaNo ratings yet
- 40QBG QBU CatalogDocument4 pages40QBG QBU CatalogKhun WunNo ratings yet
- 1+2 LecturesDocument28 pages1+2 LecturesHammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Radar-Measuring PrincipleDocument25 pagesRadar-Measuring PrincipleBen FranNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Hybrid Strategies in Jakarta Housing TKDocument90 pagesEffectiveness of Hybrid Strategies in Jakarta Housing TKSilvana YenNo ratings yet
- 2 - Resistance, Resistance Variation, and BatteriesDocument23 pages2 - Resistance, Resistance Variation, and BatteriesArmiee InfiniteNo ratings yet
- Water Delivery Time Calc For Preaction SystemDocument2 pagesWater Delivery Time Calc For Preaction SystemrajaNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiology & Electrotherapy For Clinical Practice Physiotherapy (Autosaved)Document60 pagesElectrophysiology & Electrotherapy For Clinical Practice Physiotherapy (Autosaved)Novita Dwi RachmawatiNo ratings yet