Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skin Physiolgy
Skin Physiolgy
Uploaded by
Maryah TaylorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skin Physiolgy
Skin Physiolgy
Uploaded by
Maryah TaylorCopyright:
Available Formats
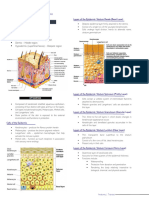
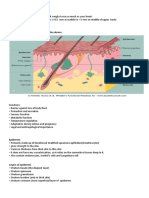
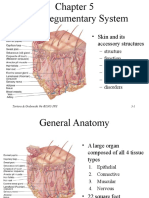
SKIN PHYSIOLGY
• The largest organ of the body
• Most complex organ, other than the brain
• Sensitive and durable, requiring special attention and care to
maintain health, elasticity, color, and vibrancy
• Acts as a shield between your body and your environment
• Skin and layers make up the integumentary system
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 2
▪ ▪ ▪
▪ ▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 3
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 4
A variety of cells make up these different layers, each serving a specific function. The
primary component of skin cells is the protein substance called keratin. There are two forms
of keratin; hard keratin makes up nails and soft keratin makes up skin hair and skin
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 5
The outermost layer of the skin, visible to the eye. Also known as the protective layer. Its primary function is to “keep the
insides in and the outside out.” There are no blood vessels are found here. It receives nourishment from layers below it,
the Dermis. There are 5 different layers of cells in the Epidermis
▪ ▪ ▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 6
▪ ▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 7
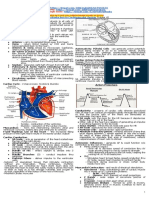
Dermis
• Also called dermal layer, “true skin” or corium • Consist of sweat glands called the Sudoriferous
• Nourishes the lower epidermis and is the glands; Oil glands called sebaceous glands
skin’s main support structure • Consist of sensory nerve endings and receptors,
• Comprised of many connective tissues and is blood vessels
rich in capillaries and blood vessels
• Consist of arrector pili muscles which cause
• Connective tissues have a semi-fluid
substance containing collagen protein and goosebumps
elastin fibers; support to the epidermis and
• Contains major portion of hair follicles
give the skin its elastic quality
• Hair is an appendage of the skin just as nails and
• Collagen protein fibers are strong and flexible
while the elastin fibers are soft and pliable the sweat and oil glands are
• Collagen and elastin fibers deteriorate and • Has 2 layers: papillary and reticular; contain a
cause the skin to wrinkle during the aging
variety of glands; nourishes the epidermis and
process
connect the dermis to layer below
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 9
Skin Pigmentation
• Melanin- producing cells(Melanocytes) are in the basal layer of the epidermis
• Cells move toward the surface at a faster rate than other cells
• Melanin is distributed throughout all epidermal cells and forms an effective barrier from the penetration
of ultraviolet rays to deeper layers of the skin
• Melanin tans the skin to protect it from the burning rays of the sun
• Darker skin contains more melanin, which serves as a more effective barrier to the rays than lighter skin
• Skin with little melanin is light, pale, or pink; the pink tone visible in pale skin is the reflection of red blood
trough the epidermis
• ALL skin need protection form the sun
▪ ▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 11
Lesions
• Diseases and disorders are usually accompanied by skin
lesions.
• Familiarity with skin lesions will lead you to recognize
skin diseases and disorders because lesions indicate
abnormal changes in the structure of an organ or tissue
3 types of skin lesions: primary, secondary, and tertiary; It’d
be helpful to nail technicians to be able to recognize the
first 2.
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 13
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 14
▪ ▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 15
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 16
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 17
▪
▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 18
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 19
▪ ▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 20
Pigment Disorders
A result of abnormal production of melanin in the skin.
An excess production of melanin causes the skin to
appear darker in certain areas and is referred to as
hyperpigmentation. A lack of the production of
melanin causes the skin to appear lighter in spots and
is called hypopigmentation. No service if there is an
infection.
▪ ▪ ▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 22
▪ ▪ ▪
▪
▪
▪
▪ ▪
▪
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 23
▪
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 24
▪ ABCS of Melanoma
A-Asymmetry: Mole is not symmetrical
B-Border: Border is irregular
▪ C-Color: Mole contains multiple colors or
variation in color
D-Diameter: Mole is more than 6mm in
▪ diameter
Refer client to physician. NEVER diagnose
a client!!
3/1/20XX SAMPLE FOOTER TEXT 25
You might also like
- The Sensitive Gut Harvard HealthDocument57 pagesThe Sensitive Gut Harvard HealthFernanda Vasconez100% (2)
- NSCA Functional Training For Swimming PDFDocument7 pagesNSCA Functional Training For Swimming PDFREINONo ratings yet
- Hist CM2 Cu6 IntegumentaryDocument10 pagesHist CM2 Cu6 IntegumentarySteven Joshua DrizNo ratings yet
- Body MembranesDocument8 pagesBody MembranesCellina De LeonNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFDocument14 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Reviewer SHS General Biology 2 PDFKeiNo ratings yet
- Ehap12 ch04 Lecture PresentationDocument10 pagesEhap12 ch04 Lecture PresentationMeg MaxilomNo ratings yet
- BMED 105 Intergumentary System (NOTES)Document7 pagesBMED 105 Intergumentary System (NOTES)Jobelle MalihanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lesson 5: Efreim Louie Sombillo Ilano, MSN, MDDocument66 pagesIntegumentary System Lesson 5: Efreim Louie Sombillo Ilano, MSN, MDPearl CartasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Integumentary SystemDocument41 pagesLesson 3 Integumentary SystemShida HuaEiaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary ReviewerDocument3 pagesIntegumentary ReviewerJomar ManalangNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesTopic 4 Integumentary SystemKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System NotesDocument6 pagesIntegumentary System Notes迪亚No ratings yet
- Skin - HistologyDocument30 pagesSkin - Histologydaw022100% (11)
- Integumentary System - Transes 1Document4 pagesIntegumentary System - Transes 1Jamailah EncenzoNo ratings yet
- StrufunDocument135 pagesStrufunAmalia RizqiNo ratings yet
- Kulit: Produk Kosmetik Lidya AmelianaDocument32 pagesKulit: Produk Kosmetik Lidya AmelianakarinaNo ratings yet
- Hsci Lesson 3Document4 pagesHsci Lesson 3Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- 10 - Skin and AppendagesDocument58 pages10 - Skin and AppendagesMycah Averey AmierolNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Generic Nursing Students By: Zelalem. ADocument48 pagesThe Integumentary System: For Year 1 Generic Nursing Students By: Zelalem. AAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- SKINDocument30 pagesSKINShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- PERPETUA-Integumentary SystemDocument85 pagesPERPETUA-Integumentary SystemMayim LouiseNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument74 pagesIntegumentary SystemririyoruNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument15 pagesReviewerYza Grace S. PayangdoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesIntegumentary Systemmaxpein zein and aceNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Midterms Reviewer 1Document31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Midterms Reviewer 1Zucc mahnut100% (1)
- Overview of The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Medicine Students By: Zelalem. ADocument54 pagesOverview of The Integumentary System: For Year 1 Medicine Students By: Zelalem. AAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaDocument8 pagesSkin and Its Appendages: Lectured By: Dr. Ed Gonzales Transcribed By: Gio PinedaFamela Anne GOmez MadambaNo ratings yet
- Fapc-Chapter-1-Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesFapc-Chapter-1-Integumentary SystemMiñoza, Aeris GabrielleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Integumentary Lec HandoutDocument5 pagesAnaphy Integumentary Lec Handoutpsyche.ladicaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument90 pagesIntegumentary SystemJennyreen LenonNo ratings yet
- جلدية Coppy AllowedDocument118 pagesجلدية Coppy AllowedAssssssNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegeDocument62 pagesThe Integumentary System: Powerpoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community CollegetanarNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM AnaphysioDocument62 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM AnaphysioNAMERAH GOTENo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates'Integumentary System 2021 UpdatedDocument62 pagesVertebrates'Integumentary System 2021 UpdatedLumanlan ArcadioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of The SkinJanak KcNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi KulitDocument80 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Kulitedo100% (1)
- SkinDocument15 pagesSkinSnikitha SaiNo ratings yet
- 1 LG) Histology of The SkinDocument25 pages1 LG) Histology of The SkinJoo Se HyukNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Document28 pagesIntegumentary System: Mary Jane T. Cabataña, RN Instructor, MC1Paul CliffordNo ratings yet
- Chaptertour AlexandriabeersDocument3 pagesChaptertour Alexandriabeersapi-342509632No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument45 pagesIntegumentary SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- 2.2.integumentary SystemDocument97 pages2.2.integumentary Systemmichot feleguNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument138 pagesIntegumentary SystemGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary SystemDocument36 pagesIntergumentary SystemKudzai MashayaNo ratings yet
- Skin PDFDocument57 pagesSkin PDFravindra sharma100% (1)
- Comparative Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesComparative Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemTJ HarrisNo ratings yet
- جلديةDocument88 pagesجلديةestishhad2No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Systemericamaeabellanosa22No ratings yet
- The Integumentary System ReviewerDocument9 pagesThe Integumentary System ReviewerleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- 04 The Integumentary SystemDocument37 pages04 The Integumentary SystemRuthie MendozaNo ratings yet
- CPD (Skin Anatomy & Physiology)Document25 pagesCPD (Skin Anatomy & Physiology)Shahida H. AbdulmajidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 PptintegsystemDocument64 pagesChapter 5 PptintegsystemlorinsyacderminnatNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System 2022Document57 pagesIntegumentary System 2022francisalipio.medNo ratings yet
- Integumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganDocument47 pagesIntegumentray System by Hasnairah M. LimbotonganHasnairah LimbotonganNo ratings yet
- Skin and Its AppendagesDocument4 pagesSkin and Its Appendagesabi dimatulacNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Membrane Accessory StructuresDocument24 pagesCutaneous Membrane Accessory StructuresAMAL SURENDRANNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY-SYS With AnimationDocument43 pagesINTEGUMENTARY-SYS With AnimationsattNo ratings yet
- Oral Mucous MembraneDocument79 pagesOral Mucous MembraneKarthik MungamuriNo ratings yet
- Meow MeowDocument54 pagesMeow MeowCorrie AvreinNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Head and NeckDocument18 pagesEmbryology of The Head and NeckDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- 106 FinalsDocument27 pages106 FinalsCreciabullecerNo ratings yet
- Vasthu - Sleep - StudyDocument3 pagesVasthu - Sleep - StudytsurendarNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyDocument11 pagesDiagnosing Neonatal EncephalopatyLalo LanNo ratings yet
- Deepak Panwar Bachelor of Physiotherapy, School of Physiotherapy, Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences & Research UniversityDocument1 pageDeepak Panwar Bachelor of Physiotherapy, School of Physiotherapy, Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences & Research UniversityAsad AnZariNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Mark Samuel M. Dela TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Anesthetic Management of Intracranial Aneurysms R-MasriDocument66 pagesAnesthetic Management of Intracranial Aneurysms R-MasriadheNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Animal Behaviour PresentationDocument23 pagesPowerpoint Animal Behaviour Presentationapi-320112884No ratings yet
- Chapter 1, Unit 2, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell PharmaDocument5 pagesChapter 1, Unit 2, Human Anatomy and Physiology 1, B Pharmacy 1st Sem, Carewell Pharmatambreen18No ratings yet
- Brain WebquestDocument3 pagesBrain WebquestCarlie100% (1)
- Pelvis and Perinium 2019Document59 pagesPelvis and Perinium 2019Vuluwa George100% (1)
- Biohack Your Brain To Boost Intelligence: Tricks For Increasing Brain PowerDocument23 pagesBiohack Your Brain To Boost Intelligence: Tricks For Increasing Brain PowerMaemunah Bandit100% (1)
- Dhairya Mock Test-03Document7 pagesDhairya Mock Test-03Nirupam RoyNo ratings yet
- IAL Biology SB2 Assessment 8BDocument3 pagesIAL Biology SB2 Assessment 8BsalmaNo ratings yet
- III Assessment For Well-Being APGAR SCORE - Dr. Virginia ApgarDocument30 pagesIII Assessment For Well-Being APGAR SCORE - Dr. Virginia ApgarKennethCallosNo ratings yet
- Meditation and Well Being - PresentationDocument20 pagesMeditation and Well Being - PresentationVictoria Villordo Dangelo100% (2)
- Pharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Adams Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesPharmacology Connections To Nursing Practice 3rd Edition Adams Solutions ManualToniPerryptfo100% (39)
- Hypothermia and HyperthermiaDocument17 pagesHypothermia and HyperthermiaNatnaelNo ratings yet
- Family MolluginaceaeDocument9 pagesFamily MolluginaceaeNeilborn LutraniaNo ratings yet
- Fertilization Fetal DevelopmentDocument97 pagesFertilization Fetal DevelopmentXo Yem100% (1)
- Study of Batik Motif From Molecular Inspiration To Enrich The Composition of Nusantara Batik MotifDocument9 pagesStudy of Batik Motif From Molecular Inspiration To Enrich The Composition of Nusantara Batik MotifSagaria Arinal HaqNo ratings yet
- Heart-Lung MachineDocument4 pagesHeart-Lung Machinearsalanbook100% (2)
- 12bio Assignment ch123Document14 pages12bio Assignment ch123Krishna GovilNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life Mind MapDocument2 pagesCell - The Unit of Life Mind MapAshwath Kuttuva100% (3)
- Emwave Owners Manual v1 2 1Document56 pagesEmwave Owners Manual v1 2 1shaneredwoodNo ratings yet
- One Tequila, Two Tequila, Three Tequila, Floor!: The Science Behind A HangoverDocument3 pagesOne Tequila, Two Tequila, Three Tequila, Floor!: The Science Behind A Hangoverkristal eliasNo ratings yet
- Diacon-N en DT Rev01 0811501 Rev03Document12 pagesDiacon-N en DT Rev01 0811501 Rev03vijayramaswamyNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: EssentialsDocument59 pagesThe Muscular System: EssentialsAPESicaiNo ratings yet