Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gujarat Provincial Architecture - Group Work
Uploaded by
Chinmay BopcheOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gujarat Provincial Architecture - Group Work
Uploaded by
Chinmay BopcheCopyright:
Available Formats
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE
HISTORY OF ARCHITECTURE – IV
ADITI , AMAN , ANURAG , ARUSHI , ATHUL , CHINMAY , SIDDHANT LABDE , SIDDHANT MORE
MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B
INDEX
Introduction
Timeline /Era
Major periods of style
a)First Phase
b)Second Phase
c)Third Phase
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE -1
INTRODUCTION
Gujarat is a state in the western part of India known
locally as Jewel of the Westernport of India. It has
an area of 196,204 km2 (75,755 sq. mi) with a
coastline of 1,600 km (990 mi), most of which lies on
the Kathiawar peninsula, and a population in
excess of 60 million. The state is bordered by
Rajasthan to the north, Maharashtra to the south,
Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea,
as wells the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west.
Its capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is
Ahmedabad.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE - 2
The Gujarat style is the most important of all
the provincial styles in India. Two factors are
responsible for the prodigious output of
architecture in this region: a) The egotism of
the powerful Ahmed Shahi dynasty who
wanted to surround themselves with
architectural evidences of their might's) The
supply of skilled indigenous workmen. The
Gujarat style is the most indigenous Indian
style of all the provincial styles. Many
structures are adaptations or extracts of local
Hindu and Jain temples.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE - 3
TIMELINE ERA -
First Phase (till first half of the 14th century):• It was marked by thè demolition of the Hindu
temples and their reconversion into Muslim buildings.
Second Phase (first half of the 15th century):• It shows signs of hesitant maturity of a distinctive
style . Ahmad Shah I (1411-42):• He was a great builder, and beautified the town with many
magnificent palaces and bazars , mosques and madrasas.• He drew on the rich architectural
tradition of the Jains of Gujarat to devise a style of building which was markedly different from Delhi
Some of its features are:• slender turrets , exquisite stone-carving, and•
highly ornate brackets . Example of architecture : Jama Masjid in Ahmedabad:• in 1424 during the
reign of Ahmed Shah I . situated outside Bhadra Fort
Third Phase (latter half of the 15th century)• Gujarat style emerges in its own magnificent form.•
The Gujarat style of architecture is one of the most indigenous in character.• In some of the finer
examples of this style considerable portions of the buildings are in fact adaptations from either Hindu or
Jain temples . structure of a temple is fitted into the sanctuary of the mosque in the form of a central
compartment• Almost all the mosques from the second and third phase are composed in this manner,
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE -4
MAJOR PERIODS OF THE STYLE
First period (14th cent.)
Second period (15th cent.).
Third period (1550- 16th cent)
REASONS FOR GOOD ARCHITECTURE-
Got most accomplished artisans of
India in their region Unrivalled aesthetic
resources in their region.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE -5
Three phases of the Gujarat style:
First Phase - (till first half of the
14thcentury)
It was marked by the demolition of the Hindu temples and their
reconversion into Muslim buildings.
Buildings don't have definite character because of having
formative and experimental appearance. Materials of Hindu
temples were used. Walls were built of original masonry while pillars
would be used as they were . Ex Jami masjid. Bharuch. Jami
masjids , Cambay.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE -6
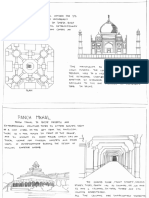
Jami Masjid (Bharuch) :
Probably dates from about the beginning of the1300's.Largely composed of temple materials, it was planned and
constructed as per mosque principles. Consists of a courtyard with gateways on 3 sides and sanctuary in the west. The
sanctuary is of the open pillared variety i.e. Without a screen of arches put across the front. It is merely an elaborated loggia
or verandah . All 48 pillars of the sanctuary are of bracket pattern. They are arranged so as to divide the interior into
3compartments, each corresponding to the three temple mandapas from where the pillars were taken.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE - 7
jami masjid cambay -
jami masjid cambay -
• Built in the year 1325 A.D Judging from the appearance, it is
probable that local artisans were reinforced by a group of
artisans from Delhi to build this structure . The sanctuary of the
masque is having an enclosed facade with a screen of arches.
The shape and position of the arches, the masonry consisting
of alternate broad and narrow courses and the overall
architectural treatment is reminiscent of the architectural style
of Delhi under the Khalji dynasty . The arrangement of pillars
inside the arch ways of the facade borrows from the Ajmer
type of mosque , The pillars have been enriched by an
engrailed arch similar to one found in temples, a motif which
later figures prominently as the flying arch within the central
openings of mosque facades in Gujarat.
Second Phase (first half of the 15thcentury)-
It shows signs of hesitant maturity of a distinctive style.
Ahmad Shah :
He was a great builder, and beautified the town with
many magnificent palaces and bazars, mosques
madrasas.
He drew on the rich architectural tradition of the Jains
of Gujarat to devise a style of building which was
markedly different from Delhi.
Some of its features are:
slender turrets exquisite stone-carving and highly ornate
brackets.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE – 8
Information about second phase
• In this period, we see the art approaching an early
consummation, with slightly tentative qualities.
• - There is more directional authority in the buildings
and increased assurance in the design.
• - This can also be called the Ahmed Shahi period,
after the Sultan Ahmed Shah
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE-9
JAMI MASJID AT AHMEDABAD-
• Built by Sultan Ahmed
Shah in A.D. 1423.
• Considered to be the high
water mark of mosque
design on western India .
• Most of the architectural
effect is concentrated in
the sanctuary.
• The flagged courtyard is
255' X 220'
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE-10
• Sanctuary consists of
around 300 slender pillars,
closely set at an average
intercolumniation of 5 .
• The columns are
symmetrically arranged to
form 15bays across the long
ads of the hall.
• Each is surmounted by a
dome and connected to
the next through a
columned interspace.
• Columns are symmetrically
arranged to form 15 bays
across the long axis of hall.
GUJRAT PROVINCIAL ARCHITECTURE MITSOA 2021-22 SYBARCH DIV- B SLIDE-11
SANCTUARY EXTERIOR-
• Combination of two types of sanctuary
facades , the screen of arches and the
pillared portico . The screen is on centre
and portico on wings.
• The juxtaposition of the two elements
creates contrast between the volume and
strength of the wall surface and the depth
and airy lightness of the colonnade .
• The large central archway has large
moulded buttresses of minarets on either
side .
• Two smaller archways are placed on either
side of the central one .
• Directly visible through the archway is the
colonnade of the interior with its engrailed
arch springing lightly from its slender
columns
SANCTUARY INTERIOR-
• The sanctuary is a hypostyle hall
of 64 mX30 m .
• It consists of 300 slender pillars,
closely set at an average
intercolumniation of 1.6m.
• The columns are symmetrically
arranged to form 15 bays across
the long axis of the hall, each
surmounted by a dome.
• The central compartment of the
nave rises up to 3 storeys , the
side aisles are 2 storeys and the
rest of the hall is single storeyed
• Nave is composed of two pillared
galleries one above the other.
Third period -
• THIRD PERIOD- (Second half of 15'h cent. A.D.)
• This is the most magnificent aspect of the style .
• Most of the development in this phase happened
under Sultan Mahmud I Begarha (1458-1511).
• Mahmud Begarha-1 founded three main cities
Bitwa , Mehmudabad and Champaner . Major ex-
Jami Masjld , Champaner ,
BAI HARI'S VAV
• Built in A.D. 1499 at Ahmedabad
• Only kiosks on two ends are visible above
ground, the rest of the structure being
subterranean.
• The wav is 125' long, 18' wide and. 30'
deep.
• The subterranean passage takes the form
of a series of galleries interconnected by
stairways.
• At each stage, the gallery is expanded
into a pillared compartment. Due to the
balconies around each compartment,
each storey becomes a cool and quiet
retreat .
• The pillars, capitals, railings, wall surfaces,
cornices and borders are exquisitely
crafted .
JAMI MASJID, CHAMPANER
• Built with the Jami Maid at Ahmedabad as
model except on a smaller scale.
• The entire structure is a rectangle of 270' X 180'.
A bit less than half the space is taken up by the
sanctuary .
• The entire structure is rectangle and the
courtyard is surrounded by a range of arched
cloisters, one aisle deep.
• The entrance pavilion projects from the centre
of each of the north, south and east cloisters.
• Sanctuary facade is of enclosed type
containing 5 pointe arch ways with two slender
minarets flanking the central opening
• Sanctuary is a pillared hall, total mosque
measuring 86.4 mm X 57.6 m, containing 176
pillars.
Cloisters
• The courtyard is surrounded by a
range of arched cloisters, one
aisle deep.
• An imposing entrance pavilion
projects from the centre of each
of the north, south and east
cloisters. The eastern pavilion is a
fine example of architecture in
itself.
• A series of moulded buttresses
along the exterior of the qibla wall
along with traceried openings at
close intervals along the entire
periphery makes the exterior of the
mosque attractive as well.
Thank you .
You might also like
- SEM4 007 - Session - 7 - Provincial - Style - 17042016Document76 pagesSEM4 007 - Session - 7 - Provincial - Style - 17042016Vala Vraj M.100% (1)
- Module 3 HoaDocument12 pagesModule 3 HoaIndigo CupcakeNo ratings yet
- Unit V: History of Architecture & Culture - IiDocument49 pagesUnit V: History of Architecture & Culture - IiMohammed MuthaharNo ratings yet
- Hoa ProvincialDocument24 pagesHoa ProvincialBharat GouripurNo ratings yet
- Islamicguj 150417064625 Conversion Gate01Document39 pagesIslamicguj 150417064625 Conversion Gate01Bharat GouripurNo ratings yet
- Gol Ghumat Architecture in ,: BijapurDocument18 pagesGol Ghumat Architecture in ,: Bijapurchaudhari prajaktaNo ratings yet
- 6 Gujarat Provincial Indo Islamic ArchitectureDocument40 pages6 Gujarat Provincial Indo Islamic ArchitectureDakshata Koli100% (1)
- 01mixed Styles Hindu IslamicDocument34 pages01mixed Styles Hindu IslamicChris AbhilashNo ratings yet
- 13 Gujrat PDFDocument58 pages13 Gujrat PDFShonak Singh100% (1)
- 7 Deccan Provincial Indo Islamic ArchitectureDocument49 pages7 Deccan Provincial Indo Islamic ArchitectureDakshata KoliNo ratings yet
- Hoa GujaratDocument23 pagesHoa GujaratSanju Chowdary PeddineniNo ratings yet
- Provincial Gujarat Style PDFDocument26 pagesProvincial Gujarat Style PDFSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hoa-Provincial Introduction & Bengal Style PDFDocument16 pagesHoa-Provincial Introduction & Bengal Style PDFSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mughal Art and ArchitectureDocument23 pagesMughal Art and Architectureanon_44947867100% (1)
- Unit 5Document133 pagesUnit 5Mithra ThandalaeNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument14 pagesMughal ArchitectureAfzal BadharudheenNo ratings yet
- Sites & MonumentsDocument100 pagesSites & MonumentsAbhishek RankaNo ratings yet
- Fatehpur SikriDocument45 pagesFatehpur SikriJinal PatelNo ratings yet
- Imperial Style-Khalji DynastyDocument10 pagesImperial Style-Khalji Dynastyshruti mantriNo ratings yet
- Indian Art & Architecture: Jury Assignment '22 15th - 19th Century Indian Art by - Manya Singh, DFT Sem 7Document51 pagesIndian Art & Architecture: Jury Assignment '22 15th - 19th Century Indian Art by - Manya Singh, DFT Sem 7manya singhNo ratings yet
- Gujrat Architecture 1 1Document16 pagesGujrat Architecture 1 1Zoe SinghNo ratings yet
- MUQARNASDocument15 pagesMUQARNASRevathi HariharanNo ratings yet
- HOA - Islamic Architecture in India & Qutub ComplexDocument36 pagesHOA - Islamic Architecture in India & Qutub Complexsteve thomasNo ratings yet
- The Provinical StyleDocument29 pagesThe Provinical StyleManish SinghNo ratings yet
- 3AR2: History of Architecture-IDocument71 pages3AR2: History of Architecture-ISaurabhNo ratings yet
- Slave Dynasty Shams-Ud-Din-IltutmishDocument9 pagesSlave Dynasty Shams-Ud-Din-Iltutmishshruti mantriNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - ISLAMIC ARCHITECTURE-PROVINCIAL STYLE GUJARATDocument16 pagesModule 2 - ISLAMIC ARCHITECTURE-PROVINCIAL STYLE GUJARATAzra ShahalNo ratings yet
- Malwa ProvincialDocument45 pagesMalwa ProvincialSrividhya KNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3 Provincial StylesDocument31 pagesUNIT-3 Provincial StylesAman sevenElevenNo ratings yet
- Indo Islamic ArchitectureDocument21 pagesIndo Islamic ArchitectureAr Srinivas PullogiNo ratings yet
- Mughal Architecture in IndiaDocument34 pagesMughal Architecture in IndiaAnonymous TliwocWNo ratings yet
- Deccan and BijapurDocument53 pagesDeccan and BijapurChania BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Report On Provincial Architecture of Bijapur, Mandu, JaunpurDocument24 pagesReport On Provincial Architecture of Bijapur, Mandu, JaunpurVidhi JainNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PDFDocument29 pagesModule 2 PDFIndigo CupcakeNo ratings yet
- Background: Delhi Sultanate Mughals Madrasas TughlaqDocument2 pagesBackground: Delhi Sultanate Mughals Madrasas TughlaqJuhainah C. Guro LptNo ratings yet
- Gujarat StyleDocument36 pagesGujarat StyleSabyasachi MohantyNo ratings yet
- Across Place and Time - Exploring Deccan ArchitectureDocument39 pagesAcross Place and Time - Exploring Deccan ArchitectureAh AnNo ratings yet
- PRovincial Architecture GujratDocument31 pagesPRovincial Architecture GujratPiyush Mahakalkar67% (3)
- Medieval ArchitectureDocument14 pagesMedieval ArchitectureMuditNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07 Dhar & ManduDocument23 pagesLecture 07 Dhar & ManduRiddhi KumarNo ratings yet
- HoA Module 4Document22 pagesHoA Module 4Aswathy Mullakkal RavindranNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument28 pagesMughal ArchitectureSakshi SalunkeNo ratings yet
- 002 Session 2 Indo-Islamic Architecture 22022016Document26 pages002 Session 2 Indo-Islamic Architecture 22022016Vala Vraj M.No ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument11 pagesMughal ArchitectureJatin TilwaniNo ratings yet
- Revival of Indian Architecture Under British PatronageDocument21 pagesRevival of Indian Architecture Under British PatronagevijayaratnaNo ratings yet
- HOA-V - Module 1 - Part 1Document26 pagesHOA-V - Module 1 - Part 1reethikav02No ratings yet
- Mughal Architecture in IndiaDocument15 pagesMughal Architecture in IndiaVala Vraj M.No ratings yet
- 2Document16 pages2Afzal BadharudheenNo ratings yet
- Indo-Islamic Part 1Document27 pagesIndo-Islamic Part 1Megha SarnaNo ratings yet
- Islamic ArchitectureDocument98 pagesIslamic ArchitectureKalindi PsNo ratings yet
- Module-1 4Document36 pagesModule-1 4Sanjana SudeepNo ratings yet
- Provincial ArchitectureDocument44 pagesProvincial ArchitectureNihal Singh Verma89% (19)
- Islamic Architecture: History of Architecture & Human Settlement IiDocument81 pagesIslamic Architecture: History of Architecture & Human Settlement IiPriya ManeNo ratings yet
- Art & Culture Upsc Cse: (Prelims + Mains) Architecture & Sculptures Indo Islamic ArchitectureDocument12 pagesArt & Culture Upsc Cse: (Prelims + Mains) Architecture & Sculptures Indo Islamic ArchitectureSHU789IJKNo ratings yet
- Provincial Architecture in BijapurDocument43 pagesProvincial Architecture in Bijapursanam67% (3)
- Unit 2 Part I The Slave DynastyDocument51 pagesUnit 2 Part I The Slave DynastyMutant NinjaNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument7 pagesIndian Architecturejohn.tabinasNo ratings yet
- Provincial Styles: Unit Iv-1.Malwa 2.DECCAN-Gulbarga - Bidar - Golconda 3.bijapurDocument71 pagesProvincial Styles: Unit Iv-1.Malwa 2.DECCAN-Gulbarga - Bidar - Golconda 3.bijapurUd BsecNo ratings yet
- Indian Architecture (Buddhist and Hindu Period)From EverandIndian Architecture (Buddhist and Hindu Period)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- c0JIJ.: Ru A .2& UDocument12 pagesc0JIJ.: Ru A .2& UChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 StaircaseDocument8 pagesUnit-1 StaircaseChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- British Colonial PhaseDocument3 pagesBritish Colonial PhaseChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- History OF Architecture: Comparison Between Fatehpur Sikhri and Red Fort By:Murtuza Hilal Chinmay BopacheDocument11 pagesHistory OF Architecture: Comparison Between Fatehpur Sikhri and Red Fort By:Murtuza Hilal Chinmay BopacheChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- TM?L 1-A: I. ',LAV . DYNAH 1l / (Hin DYNA ST) "Document3 pagesTM?L 1-A: I. ',LAV . DYNAH 1l / (Hin DYNA ST) "Chinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- Mahal: "LL.$ 1:Nc - Q.E) Yie, Le All (1-Rt, 1Cc - Ture. 1:1 Ljnivfrsally Spa - Rkl"I.Nc. JT - Wel of Musl"I.M TN "L.N'Iyia. Buil1Document3 pagesMahal: "LL.$ 1:Nc - Q.E) Yie, Le All (1-Rt, 1Cc - Ture. 1:1 Ljnivfrsally Spa - Rkl"I.Nc. JT - Wel of Musl"I.M TN "L.N'Iyia. Buil1Chinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- Green Building Rating SystemsDocument2 pagesGreen Building Rating SystemsChinmay BopcheNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice: Module - 1Document31 pagesProfessional Practice: Module - 1DevikavkNo ratings yet
- Ar - Habib RahmanDocument13 pagesAr - Habib RahmanZohair ArshedNo ratings yet
- Container House BRDDocument17 pagesContainer House BRDjaykhor9328No ratings yet
- Theory of Design: Single and Double Loaded CorriorDocument21 pagesTheory of Design: Single and Double Loaded CorriorMohammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- LamellaDocument3 pagesLamellaRomeo Padilla IIINo ratings yet
- Design Parameters For Longitudinal Bars (Beams - BS 8110)Document4 pagesDesign Parameters For Longitudinal Bars (Beams - BS 8110)Lavanyan Satchithananthan100% (1)
- Rrs Unit 4Document19 pagesRrs Unit 4api-297121029No ratings yet
- Sans10400 TDocument89 pagesSans10400 TSphiwithemba Dube100% (4)
- Burj KhalifaDocument15 pagesBurj Khalifakavyareddy_17100% (1)
- World's Famous Parabolic ArchesDocument5 pagesWorld's Famous Parabolic ArchesIzumi KuroganeNo ratings yet
- Shambu Staff Apartment BOQDocument37 pagesShambu Staff Apartment BOQMikuNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Introduction (1-13) - 2016Document14 pagesCh1 Introduction (1-13) - 2016Rafi SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design: Methodology/ ProcessDocument2 pagesArchitectural Design: Methodology/ ProcessdeanarchNo ratings yet
- Customization Customization Customization: 450-2200SF 1000-1200SF 450-2200SF 1000-1200SF 450-2200SF 1000-1200SFDocument21 pagesCustomization Customization Customization: 450-2200SF 1000-1200SF 450-2200SF 1000-1200SF 450-2200SF 1000-1200SFEA3No ratings yet
- Zago An Awkward Position PDFDocument15 pagesZago An Awkward Position PDFZachariah DeGiulioNo ratings yet
- Topic: Types of Concept in Architectural Design-Analogy and It's TypesDocument26 pagesTopic: Types of Concept in Architectural Design-Analogy and It's Typessummaya karimNo ratings yet
- Building An Enterprise Architecture PracticeDocument212 pagesBuilding An Enterprise Architecture PracticeJuan100% (1)
- Iko Undertile 1f Felt Data SheetDocument2 pagesIko Undertile 1f Felt Data Sheetade_macNo ratings yet
- Critical Structures Construction Issues: Self Study CourseDocument63 pagesCritical Structures Construction Issues: Self Study CourseenesNo ratings yet
- Nepalese Architecture 2Document2 pagesNepalese Architecture 2Bibek JoshiNo ratings yet
- Design Check Certificate: Drawings Certified: Certificate Reference: DateDocument3 pagesDesign Check Certificate: Drawings Certified: Certificate Reference: DateJemicah YumenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Zones: City of Grover Beach Zoning Code 2-1 Public Review Draft - June 10, 2011Document14 pagesChapter 2. Zones: City of Grover Beach Zoning Code 2-1 Public Review Draft - June 10, 2011Ranga KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Kgo - BoqDocument2 pagesKgo - BoqJoanne PastoresNo ratings yet
- Unihomes 3Document8 pagesUnihomes 3api-207562225No ratings yet
- IELTS Vocabulary - HOMEDocument8 pagesIELTS Vocabulary - HOMETeaching StuffNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Meets Old in Rehabilitating Historic BuildingsDocument13 pagesContemporary Meets Old in Rehabilitating Historic BuildingsGogyNo ratings yet
- Plastic Shrinkage Cracking (BPS)Document36 pagesPlastic Shrinkage Cracking (BPS)shingkeongNo ratings yet
- Media Office Interiors: Koregaon ParkDocument21 pagesMedia Office Interiors: Koregaon ParkgauriNo ratings yet
- Pre Historic ArchitectureDocument19 pagesPre Historic ArchitecturePeter SmithNo ratings yet
- As Built LOG FORMATDocument25 pagesAs Built LOG FORMATbryanpastor106No ratings yet