Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map March 10
Concept Map March 10
Uploaded by
Dinah Rose Vitorillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
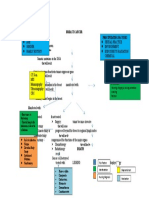
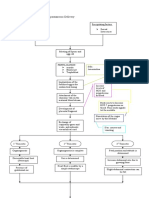
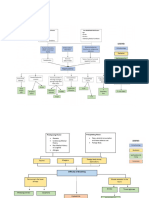
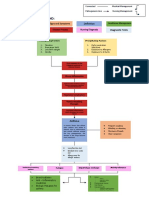
11 views1 pageThe document is a concept map about diaphragmatic hernia (DH). It shows that DH can be congenital or acquired and has predisposing factors like congenital diaphragmatic hernia, genetic factors, and prematurity. Precipitating factors include maternal smoking, alcohol use, and environmental factors. Signs and symptoms include difficulty breathing, blue skin, and abnormal sounds or breathing in the chest. Both congenital and acquired DH require urgent surgery to repair the diaphragm and return organs from the chest to the abdomen.
Original Description:
Original Title
concept-map-march-10 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document is a concept map about diaphragmatic hernia (DH). It shows that DH can be congenital or acquired and has predisposing factors like congenital diaphragmatic hernia, genetic factors, and prematurity. Precipitating factors include maternal smoking, alcohol use, and environmental factors. Signs and symptoms include difficulty breathing, blue skin, and abnormal sounds or breathing in the chest. Both congenital and acquired DH require urgent surgery to repair the diaphragm and return organs from the chest to the abdomen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageConcept Map March 10
Concept Map March 10
Uploaded by
Dinah Rose VitorilloThe document is a concept map about diaphragmatic hernia (DH). It shows that DH can be congenital or acquired and has predisposing factors like congenital diaphragmatic hernia, genetic factors, and prematurity. Precipitating factors include maternal smoking, alcohol use, and environmental factors. Signs and symptoms include difficulty breathing, blue skin, and abnormal sounds or breathing in the chest. Both congenital and acquired DH require urgent surgery to repair the diaphragm and return organs from the chest to the abdomen.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Connected
Pathogenesis Line
Types of DH Prevention
CONCEPT MAP LEGEND:
Predisposing Factors Signs and Symptoms Definition Healthcare Management
Precipitating Factors Disease Process Nursing Diagnosis Diagnostic Tests
Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors
1. Congenital 1. Maternal smoking
diaphragmatic and alcohol use
hernia (CDH)
2. Genetic factors 2. Environmental
3. Maternal age
factors
4. Prematurity
Thin sheet of muscle
separates from the chest
to the abdomen.
A gap is formed.
Driving Safely and
wear seatbelt Abdominal organs occupy
Avoid extreme the gap in the chest cavity.
sports
Limit alcohol and Difficulty breathing
substance abuse Respiratory Complications Blue discoloration of
Cautious using the skin
Rapid heart rate
sharp objects
Lungs tend to grow in a (Tachycardia)
compressed state. Bowel sounds in the
chest area
Diminished or absent
breath sounds
Less full abdomen
Both congenital and acquired
Diaphragmatic
diaphragmatic hernias typically Hernia
require urgent surgery. Surgery
X-rays
must be performed to remove the A congenital condition Ultrasound
abdominal organs from the chest known as a Computed
and place them back into the
diaphragmatic hernia tomography (CT scan)
abdomen. The surgeon will then
involves a hole in the Magnetic resonance
repair the diaphragm.
diaphragm imaging (MRI)
Arterial blood gas test
Acute Pain Risk for injury
Bochdalek Hernia
Morgagni Hernia
You might also like
- Evaluation and Management Documentation GuidelinesDocument3 pagesEvaluation and Management Documentation GuidelinesJim Hoover75% (4)
- Breast CA Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast CA Concept MapDianne Kate CadioganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Preterm LaborDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Preterm LaborLei Ortega42% (12)
- Developmental CareDocument34 pagesDevelopmental CareratullsNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia FinalDocument7 pagesHiatal Hernia FinalbabiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesConcept Map of Acute Pancreatitissalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document4 pagesPathophysiology of Abortion Case Study (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Normal Spontaneous DeliverySummer Rain100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Preterm LaborDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Preterm LaborAdriane Coma100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan No.1: NewbornDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan No.1: NewbornIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Pedia Cases NCPDocument27 pagesPedia Cases NCPDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation OutcomeBethel Ann Cordova100% (1)
- F3B Concept Map March 10Document1 pageF3B Concept Map March 10Dinah Rose VitorilloNo ratings yet
- 4 ConceptDocument1 page4 ConceptStacey GarciaNo ratings yet
- LarynDocument2 pagesLarynsanchezanya34No ratings yet
- Incomplete Abortion Day 2Document25 pagesIncomplete Abortion Day 2Tricia Denise EstabilloNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing Care PlanDocument1 page1 Nursing Care PlanPauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Vs PreviaDocument2 pagesAbruptio Vs PreviaMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: I. Schematic DiagramDocument1 pagePredisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors:: I. Schematic DiagramEileen CeloricoNo ratings yet
- Kelemen 1953Document24 pagesKelemen 1953pico 24No ratings yet
- Common Facial Vein - Radiology Reference ArticleDocument1 pageCommon Facial Vein - Radiology Reference Article89sbp4b7jqNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument4 pagesHerniaZayNo ratings yet
- Emergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteDocument5 pagesEmergency Causes Signs and Symtomps Management NoteAna Victoria JiménezNo ratings yet
- Diane Pills Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDiane Pills Drug StudyDawn EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Sultan - NCP 1 (Preterm Labor)Document2 pagesSultan - NCP 1 (Preterm Labor)Johanisa SultanNo ratings yet
- Complication On Labor and DeliveryDocument5 pagesComplication On Labor and DeliveryMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy AND Physiology: Emmanuel Z. Pagala M.DDocument136 pagesBasic Human Anatomy AND Physiology: Emmanuel Z. Pagala M.DDARLENE SUETOSNo ratings yet
- College of NursingDocument3 pagesCollege of NursingAvery SandsNo ratings yet
- Types of Spontaneous AbortionDocument5 pagesTypes of Spontaneous AbortionAnnalisa TellesNo ratings yet
- Endrenal Reyzelin M.-Concept Map & NCPDocument5 pagesEndrenal Reyzelin M.-Concept Map & NCPReyzelinNo ratings yet
- Print 3Document2 pagesPrint 32080500No ratings yet
- PDF Document 2Document1 pagePDF Document 2n.nuhanashNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching RosillosaDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching RosillosaJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- First Aid For The OBS&GYN Clerkship CH 13 (Contraception & Sterilization)Document15 pagesFirst Aid For The OBS&GYN Clerkship CH 13 (Contraception & Sterilization)黃芳昌No ratings yet
- Appendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghDocument34 pagesAppendicitis: Anetha Jodhan Ravindra SinghMarlon GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plans 211112 153011Document57 pagesNursing-Care-Plans 211112 153011Zahraa AlTahanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map March 11Document1 pageConcept Map March 11Dinah Rose VitorilloNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Complications Acute ChronicDocument10 pagesAntenatal Complications Acute ChronicJennie KimNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Skills LabDocument8 pagesStudy Guide Skills LabKeannu GervacioNo ratings yet
- Equine Medicine DISEASESDocument14 pagesEquine Medicine DISEASESlowi shooNo ratings yet
- Leptomeningeal Enhancement Radiology Reference ArticleDocument1 pageLeptomeningeal Enhancement Radiology Reference ArticleRabi Phui-onNo ratings yet
- Risk For InjuryDocument3 pagesRisk For InjuryAvery SandsNo ratings yet
- Preterm Labor and Pprom: Michelle Schroeder, MD Busitema University Faculty of Health SciencesDocument39 pagesPreterm Labor and Pprom: Michelle Schroeder, MD Busitema University Faculty of Health SciencesMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainJeiza AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map COPDDocument2 pagesConcept Map COPDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Document3 pagesEctopic Phatophysiology Tentative 2Alexe Nicole BiscanteNo ratings yet
- Mat 1Document5 pagesMat 1Shainnie IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Small Group Discussion #4: A Case of A 22-Yr Old Nullipara Who Consulted For Left Lower Quadrant PainDocument36 pagesSmall Group Discussion #4: A Case of A 22-Yr Old Nullipara Who Consulted For Left Lower Quadrant PainRose Ann RaquizaNo ratings yet
- Dinoprostone and Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDinoprostone and Metronidazole Drug StudyMary Shane MoraldeNo ratings yet
- Try To Get English Meanings of The Following Words in PairsDocument4 pagesTry To Get English Meanings of The Following Words in PairsnicokeNo ratings yet
- 1Document3 pages1Naseem Al tajerNo ratings yet
- IUD Complications: Management Strategies: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesIUD Complications: Management Strategies: Learning ObjectivesIndah Putri permatasariNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancybowki namoNo ratings yet
- Developmental CareDocument34 pagesDevelopmental Carelilis lestariNo ratings yet
- Puerperal Sepsis and Abnormalities of PuerperiumDocument10 pagesPuerperal Sepsis and Abnormalities of PuerperiumMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Greater Sciatic NotchDocument1 pageGreater Sciatic NotchTogaju KuboyeNo ratings yet
- NCP NRMFDocument2 pagesNCP NRMFJai CortezNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaDocument21 pagesCase Study 4 CVD Infarct CAP MR HUD RDU DementiaVictoria Mae Irong CabahugNo ratings yet