Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSTP Reviewer 2
NSTP Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Jade Paulos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesRff
Original Title
Nstp Reviewer 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRff
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesNSTP Reviewer 2
NSTP Reviewer 2
Uploaded by
Jade PaulosRff
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
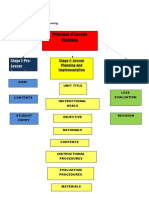
NSTP REVIEWER 5.
Helps teachers have mastery of learning
and responds to learner’s needs inside
MODULE 6: TOOLS IN
classroom;
COMMUNITY/LITERACY SERVICE
6. Helps teachers relearn what they need to
- The Department of Education
teach;
recognizes that instructional planning
is essential to successful teaching and 7. Helps teachers know their learners, teach
learning (Enclosure to DepEd Order what students need to learn – ensures
No. 42, s2016). curriculum coverages, and;
- The legal basis of which is Article IV,
8. Helps teachers identify expectations for
Section 2 of the Code of Ethics for
learners, choose the materials, and organize
Professional Teachers adopted in 1997
the sequential activities.
through Board Resolution No. 435 by
the Board of Professional Teachers LESSON PLANNING
stating that, “Every teacher the highest
The following is a detailed discussion of
standards of quality education, shall
lesson planning as indicated in enclosure to
make the best preparations for the
DepEd No. 42, s. 2016.
career of teaching, and shall be at his
best at all times in the practice of his - is one way of planning instruction.
profession.” - a way of visualizing a lesson before it is
taught.
INSTRUCTIONAL PLANNING
- Lesson planning helps teachers set
- Process of determining what learning learning targets.
opportunities students in school will - It also helps teachers guarantee that
have by: learners reach those targets.
- By planning lessons, teachers are able
1. Planning the content of instruction
to see to it that daily activities inside
2. Selecting teaching materials the classroom lead to learner progress
and achievement or the attainment of
3. Designing the learning activities and
learning outcomes.
grouping methods; and
Scrivener (2005), a planning a Lesson entails
4. Deciding on the pacing and allocation of
“prediction, anticipation, sequencing, and
instructional time.
simplifying.” Lesson planning is a critical part
BENEFITS OF INSTRUCTIONAL PLANNING: of the teaching and learning process.
1. Increases teacher’s chance of carrying out LESSON PLANNING
of a lesson successfully;
A. What should be taught? - The teacher
2. Allows teachers to be more confident must have a deep understanding of the
before starting a lesson; curriculum and strive to teach its
content.
3. Inculcates reflective practice as it allows
B. How should it be taught? - With a
teachers to think about their teaching;
lesson plan, teachers can predict which
4. Facilitates learning and responds to part ofthe lesson learners will have
learner’s needs inside the classroom; difficulty understanding.
C. How should learning be assessed? - 1. PRINT MOTIVATION - the first step of
Effective teachers do not only prepare emergent literacy. Through this step,
lessons plans,they also prepare an children become interested in print
assessment or specifically a formative materials because this step occurs the
assessment plan. child can actually read or write.
2. VOCABULARY - significant predictor to
TEACHING STRATEGIES
a child’s overall academic achievement.
- An instructional strategy is what a Vocabulary can be measured or seen
teacher uses in the classroom to as a child’s ability to know to read or
achieve the objectives of a lesson. write.
- A teacher can use a strategy or a 3. PRINT AWARENESS - the step in which
combination of strategies. children learn how to handle a book
and begin to recognize the differences
EVALUATION TOOLS
between letters and words.
- are necessary to assist teachers, 4. NARATIVE SKILLS - refer to the literacy
specially NSTP students, assess step when children develop the ability
engagement practices and evaluate the to tell a story or describe a sequence of
progress of the children being taught. events.
- Ron Spreeuwenberg (August 25, 5. LETTER AWARENESS - occurs when
2015), listed a number of education children understand that letters are
assessment tools that can be used to unique from each other and begin to
better assess the progress of the recognize different letters and their
children. sounds.
EMERGENT LITERACY 6. PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESS - the
process by which children begin to
- Considering that most of the children being understand that words are made up of
taught in partner communities are a street different sounds or phonemes, and
child and/ or those who have not attended a that stringing these sounds together
formal school yet, it is important to creates words and results in meaning.
understand the concept of emergent literacy,
which is an appropriate approach in the NUMERACY TRAINING SERVICE
conduct of Literacy Training Services. - development of numeracy skills
WHAT IS EMERGENT LITERACY? involves the act of teaching children
the concepts and skills in ways that
- Defined as the developmental steps a relationships and connections are
young child takes prior to actually formed and apply them meaningfully
reading text, including interacting with in their daily experiences.
a book, responding text and
pretending at reading or writing before
actually being able to do so.
A number of skills and abilities define a
student’s acquisition of emergent literacy. To
successfully achieve this, a student should
manifest:
NUMERACY IN THE EARLY YEARS can figure out how to break words into parts
when trying to sound them out.
- Children’s thinking in the early years is
naturally dominated by their
perception or what their senses tell
them. To help them in the learning and
development of various abstract
numeracy concepts, teachers must
provide them with opportunities to:
• explore with objects
• hear the sounds of the words
representing the objects
• look at pictures of the objects
• recognize written words or symbols in
their daily play experiences
• talk about their solutions when solving
problems
COMPUTER-BASED LITERACY
- a comprehensive series of training
courses that teaches the essential
computer concepts and skills needed
in today’s digital world.
Some of the topics in the computer literacy
training course are the following:
a. basic computer skills
b. surfing the internet
c. email
d. Microsoft office
SUGGESTED COMMUNITY OUTREACH
PROGRAM
- Talking, singing, playing sound and
word games, reading, writing, and
drawing with children are great ways to
set a good literacy foundation.
PHONOLOGICAL AWARENESS – HEAR AND
KNOW SOUNDS ON WORDS
When children recognize rhymes, syllables
and beginning sounds in words, they
MODULE 7: PROGRAM MONITORING AND TYPES OF EVALUATION
EVALUATION
• PARTICIPATORY - Evaluation in which
TYPES OF MONITORING AND EVALUATION representatives of agencies and
stakeholders work together in
• MONITORING - the systematic and
designing, carrying out and
routine collection of data during
interpreting an evaluation.
project implementation for the
• PROCESS BASED - an evaluation of the
purpose of establishing whether an
internal dynamics of a project, its
intervention is moving towards the set
policy instruments, its service delivery
objectives or project goals. In this case,
mechanisms, its management
data is collected throughout the life
practices, and the linkages among
cycle of the project.
these.
• PROCESS MONITORING/PHYSICAL
• OUTCOME BASED EVALUATION - it
PROGRESS MONITORING - routine
facilitates the asking if the organization
data is collected and analyzed in order
is doing right activities to bring about
to establish whether the project tasks
the expected outcomes.
and activities are leading towards the
intended project results. It 10 STEPS TO DESIGN A MONITORING AND
authenticates the progress of the EVALUATION (M&E) SYSTEM
project towards the intended results.
STEP 1: DEFINE THE SCOPE AND PURPOSE -
• TECHNICAL MONITORING - involves
This step involves identifying the evaluation
assessing the strategy that is being
audience and the purpose of the M&E
used in project implementation to
system. M&E purposes include supporting
establish whether it is achieving the
management and decision-making, learning,
required results. It involves the
accountability and stakeholder engagement.
technical aspects of the project such as
the activities to be conducted. STEP 2: DEFINE THE EVALUATION QUESTIONS
• ASSUMPTION MONITORING - Any - Evaluation questions should be developed
project has its working assumptions up-front and in collaboration with the primary
which have to be clearly outlined in the audience(s) and other stakeholders who you
project log frame. Assumption intend to report to. Evaluation questions go
monitoring involves measuring these beyond measurements to ask the higher
factors which are external to the order questions such as whether the
project. intervention is worth it or if it could have
• FINANCIAL MONITORING - Just like the been achieved in another way.
name suggests, financial monitoring STEP 3: IDENTIFY THE MONITORING
simply refers to monitoring project/ QUESTIONS - The monitoring questions will
program expenditure and comparing ideally be answered through the collection of
them with the budgets prepared at the quantitative and qualitative data. It is
planning stage. important to not start collecting data without
• IMPACT MONITORING - a type of thinking about the evaluation and monitoring
monitoring which continually assesses questions. This may lead to collecting data
the impact of project activities to the just for the sake of collecting data (that
target population. provides no relevant information to the
programme). organisational indicators, developing
protocols or methodologies for service-user
STEP 4: IDENTIFY THE INDICATORS AND DATA
participation, designing report templates,
SOURCES - In this step you identify what
developing protocols for when and how
information is needed to answer your
evaluations and impact assessments are
monitoring questions and where this
carried out, developing learning mechanisms,
information will come from (data sources). It
designing databases and the list goes on
is important to consider data collection in
Simister, 2009.
terms of the type of data and any types of
research design. STEP 8: USE THE INFORMATION DERIVED
FROM STEP 1-7 ABOVE TO FILL IN THE ‘M&E
STEP 5 IDENTIFY WHO IS RESPONSIBLE FOR
SYSTEM ‘TEMPLATE - You can choose from
DATA COLLECTION, DATA STORAGE,
any of the templates presented in this article
REPORTING, BUDGET AND TIMELINES -
to capture the information. Remember, they
Collection of monitoring data may occur
are templates, not cast in stone. Feel free to
regularly over short intervals, or less regularly,
add extra columns or categories as you see fit.
such as half-yearly or annually. Likewise the
timing of evaluations (internal and external) STEP 9 INTEGRATE THE M&E SYSTEM
should be noted. It is advisable to assign HORIZONTALLY AND VERTICALLY – SIMISTER
responsibility for the data collection and (2009) - Where possible, integrate the M&E
reporting so that everyone is clear of their system horizontally (with other organizational
roles and responsibilities. systems and processes) and vertically (with
the needs and requirements of other
- LogAlto is a user-friendly cloud-based
agencies).
M&E software that stores all
information related to the programme STEP 10: PILOT AND THEN ROLL-OUT THE
such as the entire log frame (showing SYSTEM - Once everything is in place, the M&
the inputs, activities, outputs, E system may be first rolled out on a small
outcomes) as well as the quantitative scale, perhaps just at the Country Office level.
and qualitative indicators with This will give the opportunity for feedback
baseline, target and milestone values. and for the ‘kinks to be ironed out’ before a
full scale launch. This could include guides,
STEP 6: IDENTIFY WHO WILL EVALUATE THE
training manuals, mentoring approaches, staff
DATA HOW IT WILL BE REPORTED - In most
exchanges, interactive media, training days or
programmes there will be an internal and an
workshops.
independent evaluation (conducted by an
external consultant). For an evaluation to be
used (and therefore useful) it is important to
present the findings in a format that is
appropriate to the audience.
STEP 7: DECIDE ON STRANDARD FORMS AND
PROCEDURES - Once the M&E system is
designed there will be a need for planning
templates, designing or adapting information
collection and analysis tools, developing
MODULE 8: ACCOMPLISHMENT AND on paper that will make it look even
NARRATIVE REPORT PREPARARTION better.
4. KEEP TRACK OF TIME PERIOD WHERE
HOW TO FORMAT AN ACCOMPLISHMENT
YOU HAVE TO WRITE DOWN ALL
REPORT – Instead of writing several pages of
ACCOMPLISHMENTS
dense paragraphs, which can be difficult to
- It’s best that you have a journal in
absorb, it’s best to vary the formatting of your
which you can write down all of the
report. It can be done in a tabular format. You
details regarding how certain goals
can include photographs of your activities and
have been accomplished.
those who helped accomplish your goals.
5. PROVIDE VISUALS
EXAMPLE: - Include a few charts or graphs if you
think they will help the reader visualize
I. Project Title:
all of the data you want to present in
II. Duration: the report.
III. Proponent/S: 6. FOCUS ON THE CHALLENGE, ACTIONS,
AND RESULT
IV. Budget/ Source of Fund: - This is one of the best techniques that
V. Project Summary: will help you document and organize
your accomplishments and it’s
VI. Accomplished Activities: recommended that you do this.
So here are the steps that will help you make 7. FOCUS ON YOUR ACCOMPLISHMENTS
a proper accomplishment report summary: - This is the main reason for your entire
report. While you’re picking out all of
1. OPEN WITH A SUMMARY PARAGRAPH the school – related accomplishments
- At the very top of your that you want to present in the report,
accomplishment report, you’re going you have to think about the ones that
to have to provide a summary of the are relevant to the objectives and
report’s entire overview. This will those that you are particularly proud
basically give the reader a short of.
rundown of the things that you’ve 8. EXPLAIN YOUR VALUE
managed to accomplish. - Don’t just point out the results of what
2. PROVIDE DETAILS THAT WILL BACKUP you’ve worked hard for, you also want
THE POINTS IN YOUR SUMMARY to point out just how valuable these
- Since you’ve already provided your accomplishments are to you.
points, the next step is to back them 9. PROOFREAD THE REPORT BEFORE
up. This would mean you’re going to SUBMISSION
have to point out specifics further - Remember to treat this as a
down in the report. Use outline form. formal document as the information
3. MAKE USE OF PROFESSIONAL in here is what you’re going to present
FORMATTING to your professor and classmates if
- You don’t want your report to look like ever.
a jumbled mess or something that you
just decided to cook up last minute.
You want the document to look
organized, in a professional font, and
DISCUSSING NARRATIVE REPORT to know about how to write an
accomplishment and narrative report
- Narrative Report Writing is the process
for a project.
of writing a report in a story-like
manner. It narrates events in a
sequential manner that has a
beginning, body, and conclusion.
THE DETAILS OF NARRATIVE REPORT
- When making a narrative report, you
need to stick to the details that should
be known by the readers. Since this
report focuses on what happened, you
need to spice it with journalistic
elements.
THE STRUCTURE OF A NARRATIVE REPORT
• THE INTRODUCTION - You should
ensure that this section of your report
gives the reader the topic you are
going to discuss. Let it grab the
attention of your reader.
• THE BODY - This section of your report
will have all the details that strengthen
what you introduced in the first
paragraph.
• THE CONCLUSION - This section of
your narrative report should
summarize your ideas as you
presented them in the body. Ensure
that your conclusion interweaves
everything in a single theme.
1. Proofing and editing your report -
You have to proofread the report to
spot and remove any grammar
errors. You should also check it to
ensure that it flows as per the
instructions and whether you have
written everything within your
topic.
This lesson has provided you with a
comprehensive coverage of what you
need
You might also like
- Queena Jessa D. Moratal Learning Episode 9 PDFDocument10 pagesQueena Jessa D. Moratal Learning Episode 9 PDFNelle christine Tanguilan78% (49)
- OB Concepts of Movie Shawshank RedemptionDocument4 pagesOB Concepts of Movie Shawshank RedemptionRaghav Kapoor0% (1)
- Fs 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesFs 4 AnswersDecson Sto Domingo67% (15)
- Blooms Taxonomy Verb WheelDocument1 pageBlooms Taxonomy Verb WheelhansfarkasNo ratings yet
- Google's Organizational Communications and Organizational Culture PaperDocument6 pagesGoogle's Organizational Communications and Organizational Culture PaperKerry SeeleyNo ratings yet
- FS1 WEEK 7 and 11Document12 pagesFS1 WEEK 7 and 11Edrian AngelesNo ratings yet
- Lp2 EED8Document19 pagesLp2 EED8Ronalyn DadaleNo ratings yet
- Mark Roel Ferrer Module 1Document4 pagesMark Roel Ferrer Module 1Mark Roel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Lte 1 Asc 1Document9 pagesLte 1 Asc 1Cyrus CortezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 TeachersDocument5 pagesUnit 3 TeachersbalajoberrylkateNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument31 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentMichelle AcostaNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1: Learning Episode FS1 9Document9 pagesField Study 1: Learning Episode FS1 9Mikee GallaNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Episode 5 Baranquil MarieJustineDocument16 pagesFS 1 Episode 5 Baranquil MarieJustineMarie Justine BaranquilNo ratings yet
- PDP Goal 2Document5 pagesPDP Goal 2api-317085485No ratings yet
- Tools in Community Literacy ServiceDocument11 pagesTools in Community Literacy ServiceMichaela ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Elecen 1 Chapter 2Document19 pagesElecen 1 Chapter 2Angela AlquezaNo ratings yet
- Class (Es) Teacher(s) Date(s)Document4 pagesClass (Es) Teacher(s) Date(s)paulNo ratings yet
- Preparing For Teaching and Learning: Spark Your InterestDocument10 pagesPreparing For Teaching and Learning: Spark Your InterestNica Elamparo AndalesNo ratings yet
- Lp2 EED8Document19 pagesLp2 EED8Ronalyn DadaleNo ratings yet
- TTSC - Module 1 - Midterms and Final Activities - Ana Mae - CostasDocument24 pagesTTSC - Module 1 - Midterms and Final Activities - Ana Mae - CostasMildred MuzonesNo ratings yet
- Paprint WS4Document19 pagesPaprint WS4Sheila Mae CaballaNo ratings yet
- Module 6-Instructional PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 6-Instructional PlanningTimothyLimNo ratings yet
- fs1 Ep 9 UpdatedDocument10 pagesfs1 Ep 9 UpdatedMillet CastilloNo ratings yet
- Curriculum and Its Types - 106Document20 pagesCurriculum and Its Types - 106Shruthi BadamNo ratings yet
- Lesson Obs e Stewart 2021Document6 pagesLesson Obs e Stewart 2021api-474709749No ratings yet
- Learning Task 1Document3 pagesLearning Task 1Ceman Dejamo TudlasanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocument4 pagesCurriculum DevelopmentMerlinda CarilloNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- Episode 5Document17 pagesEpisode 5Angelika Mae BalisbisNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learner-Centered TeachiingDocument3 pagesFacilitating Learner-Centered TeachiingAnne RaycoNo ratings yet
- Թեմա 9 Lesson Planning And Curriculum Design Դասի և դասընթացի պլանավորումDocument6 pagesԹեմա 9 Lesson Planning And Curriculum Design Դասի և դասընթացի պլանավորումSerine ArzanyanNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Midterm ActivitiesDocument18 pagesSocial Studies Midterm ActivitiesJessicaNo ratings yet
- Cy Lte1Document9 pagesCy Lte1Cyrus CortezNo ratings yet
- Thesis (Logronio)Document88 pagesThesis (Logronio)Rebecca CaponongNo ratings yet
- 1 Oxford Teacher Toolkit Foundation PhaseDocument40 pages1 Oxford Teacher Toolkit Foundation Phasegugulethusibanyoni03No ratings yet
- Chapter III: Implementing The Curriculum/Lesson 2 Level of Knowledge Learning Styles Writing Lesson Plan Level of KnowledgeDocument8 pagesChapter III: Implementing The Curriculum/Lesson 2 Level of Knowledge Learning Styles Writing Lesson Plan Level of KnowledgeNorman C. CalaloNo ratings yet
- Principal of Lesson Planning: Stage 1: Pre-Lesson PreparationDocument6 pagesPrincipal of Lesson Planning: Stage 1: Pre-Lesson Preparationjaysel86No ratings yet
- I Made Rai Full PperDocument16 pagesI Made Rai Full PperDaniel RiswandyNo ratings yet
- Bpiapacruz@math31, Act5Document8 pagesBpiapacruz@math31, Act5Billy CruzNo ratings yet
- Session 1: Learner-Centered Learning: Activities and AssessmentDocument10 pagesSession 1: Learner-Centered Learning: Activities and AssessmentLovely Jane AlcoyNo ratings yet
- Intask Completed1Document3 pagesIntask Completed1api-486190068No ratings yet
- Instructional StrategiesSarahDocument47 pagesInstructional StrategiesSarahPaulo B. turaNo ratings yet
- SociDocument3 pagesSocidelacruzjohnalbert660No ratings yet
- FS1-EP-9 Cont..Document11 pagesFS1-EP-9 Cont..Alyzza Javier Vidad IINo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - April 18, 20223Document42 pagesLesson Plan - April 18, 20223JADE THERESE RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Fs 4 AnswersDocument13 pagesFs 4 Answersvenus baliteNo ratings yet
- What Is Lesson Plan?Document3 pagesWhat Is Lesson Plan?Lyzette Joy CariagaNo ratings yet
- As A TeacherDocument3 pagesAs A TeacherKristine Joy T. GaluteraNo ratings yet
- Accteach PrelimsDocument6 pagesAccteach PrelimsKDumpNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 7es and 4asDocument61 pagesLesson Plan 7es and 4asdudzkie angelo100% (1)
- Fs 1 Episode 6.editedDocument3 pagesFs 1 Episode 6.editedMike OptimalesNo ratings yet
- #3 Observation Checklist For FS 1 Topic 2Document2 pages#3 Observation Checklist For FS 1 Topic 2Loraine Magistrado AbonitaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Teaching P.E & Health in Elementary GradesDocument9 pagesModule 4 - Teaching P.E & Health in Elementary GradesMichael MosendeNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLesson PlanningSindhu S NairNo ratings yet
- NRP On Catch Up Fridays 240126120544 20d76274Document38 pagesNRP On Catch Up Fridays 240126120544 20d76274RHOSSEL PEREZNo ratings yet
- Lecture Lesson PlanningDocument4 pagesLecture Lesson PlanningAnne Bautista100% (1)
- Field Study 1 Learning Episode 9Document15 pagesField Study 1 Learning Episode 9Joshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 AVDocument18 pagesModule 3 AVPosy PosyNo ratings yet
- Activity 4: Writing My First Lesson Plan: Here Starts The Lesson!Document31 pagesActivity 4: Writing My First Lesson Plan: Here Starts The Lesson!AngelaNo ratings yet
- Pangasinan State University: Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Social StudiesDocument17 pagesPangasinan State University: Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Social StudiesAila Erika EgrosNo ratings yet
- (SORIANO, DANIEL) Field Study 1 Episode 8Document17 pages(SORIANO, DANIEL) Field Study 1 Episode 8Daniel SorianoNo ratings yet
- The Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesFrom EverandThe Structured Method of Pedagogy: Effective Teaching in the Era of the New Mission for Public Education in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Learning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’From EverandLearning How to Learn: ‘A Guide to Effective Teaching and Learning Strategies’Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Ge Elec 1 Prelim Reviewer: Module 1: Introduction To Ecosystem ECOSYSTEM First Appeared in ADocument11 pagesGe Elec 1 Prelim Reviewer: Module 1: Introduction To Ecosystem ECOSYSTEM First Appeared in AJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- ReviewersDocument18 pagesReviewersJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Prelim ReviewerDocument6 pagesPurposive Communication Prelim ReviewerJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World: Structures of GlobalizationDocument17 pagesContemporary World: Structures of GlobalizationJade PaulosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Telling TimeDocument6 pagesLesson 2 Telling TimeBeth Garchek EddyNo ratings yet
- PIDTuningClassical - ControlsWikiDocument14 pagesPIDTuningClassical - ControlsWikiksameer_coepNo ratings yet
- TSLB3093 Week 1Document13 pagesTSLB3093 Week 1Unknown100% (3)
- Appropriate Technology (CBTP-phase 2) : Jimma UniversityDocument20 pagesAppropriate Technology (CBTP-phase 2) : Jimma UniversitygolhoNo ratings yet
- Baddeley - 1966 - Short-Term Memory For Word Sequences As A Function of Acoustic, Semantic and Formal SimilarityDocument5 pagesBaddeley - 1966 - Short-Term Memory For Word Sequences As A Function of Acoustic, Semantic and Formal SimilarityLaura CannellaNo ratings yet
- EF4e Pre-Int File Test 1B Answer SheetDocument1 pageEF4e Pre-Int File Test 1B Answer SheetB McNo ratings yet
- المرونة الاستراتيجية من النظرية التقليدية الى المواردDocument22 pagesالمرونة الاستراتيجية من النظرية التقليدية الى المواردkaramalfaidNo ratings yet
- DLL in Math 8 1 1Document4 pagesDLL in Math 8 1 1DIOSDADO MARIMON, IINo ratings yet
- Module 2 Day 4 DLPDocument4 pagesModule 2 Day 4 DLPArian Joy BautoNo ratings yet
- Practicum Handbook Semester 3 (Student Teacher)Document106 pagesPracticum Handbook Semester 3 (Student Teacher)kiran Bhatti60% (5)
- Art HealsDocument7 pagesArt Healsapi-509123586No ratings yet
- Feap 2 The Learning EnvironmentDocument10 pagesFeap 2 The Learning Environmentapi-302147620No ratings yet
- David Bloor Remember The Strong ProgramDocument14 pagesDavid Bloor Remember The Strong ProgramJhon LitleNo ratings yet
- Djaes Kindergarten Parent Needs Assessment - Google FormsDocument4 pagesDjaes Kindergarten Parent Needs Assessment - Google Formsapi-574993142No ratings yet
- Design Report - Subsystem.: Benchmarking and LiteratureDocument4 pagesDesign Report - Subsystem.: Benchmarking and LiteratureSOMESH SHARMA (B15ME036)No ratings yet
- Orange D. The Suffering Stranger Chap. 1Document37 pagesOrange D. The Suffering Stranger Chap. 1José Henríquez GalánNo ratings yet
- Andi Nurhikmayani - Ab (Islam Literary Works)Document2 pagesAndi Nurhikmayani - Ab (Islam Literary Works)Andi HikmaNo ratings yet
- School Memo EmsDocument61 pagesSchool Memo EmsNiña Irish CrisolNo ratings yet
- English - Make SentencesDocument16 pagesEnglish - Make SentencesRosana LlinasNo ratings yet
- Frontiers of Social Psychology Robin R Vallacher, Stephen J ReadDocument399 pagesFrontiers of Social Psychology Robin R Vallacher, Stephen J Readsnave lexaNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Differences With Immersive and Non-Immersive Virtual Reality in Memory AssessmentDocument12 pagesAge-Related Differences With Immersive and Non-Immersive Virtual Reality in Memory AssessmentKristineNo ratings yet
- The Self From Various Philosophical PerspectivesDocument31 pagesThe Self From Various Philosophical PerspectivesRyza Jane RequizoNo ratings yet
- Inclusion in The 21st-Century Classroom - Differentiating With Technology - Reaching Every Learner - Differentiating Instruction in Theory and PracticeDocument17 pagesInclusion in The 21st-Century Classroom - Differentiating With Technology - Reaching Every Learner - Differentiating Instruction in Theory and PracticeGeoffrey AlleyneNo ratings yet
- Language Ideology - Issues and ApproachesDocument15 pagesLanguage Ideology - Issues and ApproachesjanmcneillNo ratings yet
- Maccabe On The Classic Realist TextDocument2 pagesMaccabe On The Classic Realist TextDaveShawNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed. 21 Worktext LEpisode 0.6Document6 pagesProf. Ed. 21 Worktext LEpisode 0.6Rezia Rose PagdilaoNo ratings yet
- 21 Business Analytics - DKUDocument6 pages21 Business Analytics - DKUAnant SharmaNo ratings yet