Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orientation: Friday, 20 January 2023 2:51 PM
Uploaded by
JULIANNE BAYHONOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orientation: Friday, 20 January 2023 2:51 PM
Uploaded by
JULIANNE BAYHONCopyright:
Available Formats
Orientation
Friday, 20 January 2023 2:51 PM
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 1
GERD
Saturday, 21 January 2023 10:44 AM
Ingestion problem
Upper GI - mouth to stomach
Lower GI - intestines
- GERD
○ Known as heartburn
○ Backflow of gastric and/or duodenal contents into the esophagus and
past the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), w/out belching or vomiting
○ Reflux may cause symptoms or pathologic changes
▪ Pain
Inflammation cardinal sign
○ Rubor "redness"
○ Tumour "swelling"
○ Calor "heat, body extremities"
○ Dolor "pain & loss of function"
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 2
- Mucus - protects stomach
○ Repetitive reflux causes irritation to the esophageal lining.
- Irritated - constrict - wbc -
- Thin out intima = third shift = extracellular - edema
- Edema - prostaglandin
• Inflammation -
• -itis means inflammation
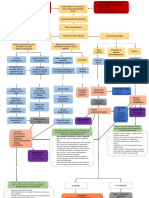
- PATHOPYSIOLOGY
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 3
-
- Full stomach - pressure is greater to than to close sphincter
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 4
-
- Food
- Alcohol'
- These agents causes relax the muscles.
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 5
-
- Esophageal stricture - stricture means like putting straw in flame
○ Is not contracting or moving
○ No motility
- Eso. Ulcer
○ Fistula - tunnelling or pagbutang sa surrounding tissues
- Barrett's esophagus
○ Columnar epithelium grows in the gastroesophageal junction
- Irritation causes minor bleeding.
- Reflux - causes irritation - causes inflammation - thinning intima - third
shifting - low grade bleeding
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 6
- Dyspepsia - hindi natunawan.
- Dysphagia - difficulty swallowing
- Reflux -acid - dental enamel loss
- Odynophagia - pain in swallowing.
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 7
- Pyrosis - GERD
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 8
-
- Mix/dilute hydrochloric acid and saline
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 9
-
- Colas - carbon dioxide
- Tomato products has content that is irritants, also has acids.
- Smoke - constrict blood vessels
- Alcohol - relaxes muscles
○ Irritants to the stomach lining
○ Decreases the LES pressure
- Milk will be converted to lactic acid causes increase to acid
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 10
-
○ KREMIL S
○ PPI can destroy kidneys
○ Once a day to prevent adverse effects
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 11
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 12
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 13
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 14
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 15
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 16
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 17
-
- High fiber - constipation
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 18
Hiatal Hernia
Friday, 27 January 2023 2:54 PM
- Ingestion problem
○ Mouth to the stomach
- Normal anatomy - below the diaphragm
- Hiatal hernia - protruding stomach above the diaphragm
- Risk factor of GERD
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 19
-
- Smoking causes reflux
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 20
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 21
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 22
-
Attacks the symptoms of GERD
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 23
- Attacks the symptoms of GERD
- Antacids - magnesium
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 24
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 25
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 26
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 27
Achalasia
Friday, 27 January 2023 3:43 PM
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 28
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 29
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 30
- No movement or peristalsis means achalasia
- Dysphagia - difficulty on swallowing.
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 31
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 32
-
- *RAT-TAIL APPEARANCE
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 33
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 34
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 35
-
○ COMPLICATION IS GERD
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 36
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 37
-
- Pooling of fluids - pneumonia
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 38
Nausea and Vomiting
Saturday, 28 January 2023 10:52 AM
- Substances that can harm the body itself can result to vomit
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 39
- Primary - obstruction
- Secondary - mentioned above
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 40
-
- VOMITING
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 41
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 42
-
- AFFECTORS - carry stimulation
- EFFECTORS - carry the message
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 43
-
- Medulla oblongata
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 44
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 45
-
- Vertigo - betahistine
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 46
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 47
-
- Ipecac - induced VOMITING REFLEX
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 48
-
- Uremia - presence of urine toxics
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 49
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 50
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 51
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 52
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 53
-
- ANTIEMETICS
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 54
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 55
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 56
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 57
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 58
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 59
Acute GI Bleeding
Saturday, 28 January 2023 1:16 PM
- First part of the small intestine - duodenum
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 60
-
- Cracks/lacerations in anal
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 61
-
- Kasama ba sa first - diluted ang sumunod
- Or sumunod na suka - already diluted
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 62
-
- ASPIRIN AND NSAID - irritate the stomach
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 63
-
- Occult blood
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 64
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 65
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 66
-
- Varices - dilated blood vessels
○ Could led to bleeding
○ Weakened vessels/veins
○ Pressure inserted/imposed to the weak vessels tend to massive
bleeding
○ Management: shunting
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 67
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 68
-
- Active bleeding and unknown cause - admit to ICU
- 2 L via nasal cannula
○ 5 L maximum for nurses to use
○ Check every 2 to 3 mins.
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 69
-
- Omeprazole - nephrotoxic
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 70
-
- Somatostatin - vasoconstriction
○ Decrease bleeding
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 71
-
- Tranexamic acid - prevent coagulation of blood
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 72
-
- Hemodynamic instability
○ HR - fast
○ BP - low
- Anastomosis - tube use to connect
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 73
-
NCM116 - MedSurg II Page 74
You might also like
- Guideline On Pediatric Renal - by DR Damte-3Document172 pagesGuideline On Pediatric Renal - by DR Damte-3Lensa H. BerhanuNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of HypertentionDocument52 pagesDrug Treatment of HypertentionISAH RABIU UNGOGONo ratings yet
- UWorld Notes 2Document49 pagesUWorld Notes 2Dinesh Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Edoc - Pub Switchwords CodebookDocument113 pagesEdoc - Pub Switchwords CodebookARCHANNAA100% (1)
- PantoprazoleDocument10 pagesPantoprazoleTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Step 2 NotesDocument202 pagesStep 2 NotesNaved Rahman100% (2)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument24 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisEcel AggasidNo ratings yet
- Anatomic Therapy English PDFDocument339 pagesAnatomic Therapy English PDFPrasad RaviproluNo ratings yet
- AV UWorld Topic YieldDocument166 pagesAV UWorld Topic YieldFeroz RaZa SoomrOoNo ratings yet
- UW NotesDocument20 pagesUW NotesLinh DangNo ratings yet
- ResponseDocument31 pagesResponseferrys37No ratings yet
- Data Kasus TB RS Hikmah MasambaDocument2 pagesData Kasus TB RS Hikmah MasambaHikmah GroupNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_No ratings yet
- Copia de Copia de Cronograma de Pulidos DF VM Contratista Ing PadillaDocument20 pagesCopia de Copia de Cronograma de Pulidos DF VM Contratista Ing PadillaMayate MatateNo ratings yet
- Retrobulbar HemorrhageDocument35 pagesRetrobulbar HemorrhageGerben VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Opps 20230101Document975 pagesOpps 20230101Jesse ReevesNo ratings yet
- Nbme 22 NotesDocument1 pageNbme 22 NotesGeovy YépezNo ratings yet
- Icu DrugsDocument205 pagesIcu DrugsAli50% (2)
- Practical Echocardiography For Cardiac Sonographers 1St Edition Daniel M Shindler All ChapterDocument67 pagesPractical Echocardiography For Cardiac Sonographers 1St Edition Daniel M Shindler All Chapterjames.mcdaniel211100% (4)
- Myocardial Revascularization and Aortic Valve Replacement Margy P. Paredes Caballero 01180021022 Practice IIIDocument21 pagesMyocardial Revascularization and Aortic Valve Replacement Margy P. Paredes Caballero 01180021022 Practice IIIapi-541444175No ratings yet
- Rutherford CH96 - Unusual Conditions of The Carotid ArteryDocument3 pagesRutherford CH96 - Unusual Conditions of The Carotid Arteryomamah.almousaNo ratings yet
- Site Rehome Site-BSC62 To BSC36 - 21082011 SiteDocument9 pagesSite Rehome Site-BSC62 To BSC36 - 21082011 Sitealoo_chaatNo ratings yet
- Turp 160328193838Document36 pagesTurp 160328193838Right VentricleNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in PregnancyDocument39 pagesDrugs Used in PregnancySneha BencyNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)Document46 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury (TBI)errol.williamson19No ratings yet
- PhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 3 List of Medical Conditions and Procedures Allowed As Second Case RateDocument31 pagesPhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 3 List of Medical Conditions and Procedures Allowed As Second Case RateChrysanthus Herrera0% (1)
- Id Main Division Sub Division NotesDocument16 pagesId Main Division Sub Division NotesLindaLou60% (10)
- Urinary Module NotesDocument22 pagesUrinary Module NotesAthira SureshNo ratings yet
- Medical Management: Medical and Surgical Management of Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 pagesMedical Management: Medical and Surgical Management of Acute Myocardial InfarctionLouie ParillaNo ratings yet
- Coronary AngioplastyDocument2 pagesCoronary AngioplastySiti Hasmah JamilNo ratings yet
- Myocardial Revascularization Margy P. Paredes Caballero 01180021022 Practice IIIDocument17 pagesMyocardial Revascularization Margy P. Paredes Caballero 01180021022 Practice IIIapi-541444175No ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument1 pageNifedipinetaekado50% (2)
- Clinical - Companion in NephrologyDocument249 pagesClinical - Companion in NephrologyMaryam MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- Medicare Inpatient 2017Document8,939 pagesMedicare Inpatient 2017Shashi Shirke100% (1)
- Tabla CanceladosDocument362 pagesTabla CanceladosDaniela EspinozaNo ratings yet
- 6.cardiovascular Supporting DrugsDocument46 pages6.cardiovascular Supporting DrugspraditaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Tarif PIK Pain Rehab Clinic 1Document3 pagesDaftar Tarif PIK Pain Rehab Clinic 1Rochma zahroNo ratings yet
- Grabovoi Numbers For Healing CodebookDocument113 pagesGrabovoi Numbers For Healing Codebookmadmaxjune1755797% (36)
- Diabetes in Clinical Practice: Questions and Answers from Case StudiesFrom EverandDiabetes in Clinical Practice: Questions and Answers from Case StudiesNo ratings yet
- Research 12 Mins VidDocument3 pagesResearch 12 Mins VidJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Article Bayhon WardDocument7 pagesArticle Bayhon WardJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Trimetazidine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTrimetazidine Drug StudyJULIANNE BAYHON100% (1)
- HypoDocument1 pageHypoJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument8 pagesAnxiety NCPJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Marie RRL 1Document3 pagesMarie RRL 1JULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Reporting Script Content of ThoughtDocument4 pagesReporting Script Content of ThoughtJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Related To Inflammation and Distension of The Colon.Document2 pagesAcute Pain Related To Inflammation and Distension of The Colon.JULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Japanese IntroductionDocument2 pagesJapanese IntroductionJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Objectives NCP1Document5 pagesIntroduction, Objectives NCP1JULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Summary of Findings, Conclusions, and RecommendationsDocument4 pagesSummary of Findings, Conclusions, and RecommendationsJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- 22ND JournalDocument6 pages22ND JournalJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: GroupDocument8 pagesQuiz 1: GroupJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab QuipperDocument4 pagesBiochem Lab QuipperJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- C3 CabacunganDocument3 pagesC3 CabacunganJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- As A PHNDocument5 pagesAs A PHNJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Badminton: RacketDocument6 pagesBadminton: RacketJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- English ThesisDocument8 pagesEnglish ThesisJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Pitch Deck 6th EditDocument14 pagesPitch Deck 6th EditJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument3 pagesReview of Related LiteratureJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- C3 CabacunganDocument3 pagesC3 CabacunganJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Intro RationaleDocument1 pageAbdominal Intro RationaleJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - Faulty Eating HabitsDocument2 pagesFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - Faulty Eating HabitsJULIANNE BAYHON100% (1)
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - Presence of Breeding Sites For Insects and PestsDocument2 pagesFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - Presence of Breeding Sites For Insects and PestsJULIANNE BAYHON100% (1)
- Let's Check (Part A) - BayhonDocument1 pageLet's Check (Part A) - BayhonJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Let's Check (Part 2) - BayhonDocument1 pageLet's Check (Part 2) - BayhonJULIANNE BAYHONNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan - Inadequate Living SpaceDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan - Inadequate Living SpaceJULIANNE BAYHON67% (3)
- FAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaDocument1 pageFAMILY NURSING CARE PLAN - AsthmaJULIANNE BAYHON80% (5)
- Oncology TestDocument32 pagesOncology TestPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Day 1. Mohd Sami 1Document67 pagesDay 1. Mohd Sami 1Baebee LouNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis 1Document4 pagesCase Analysis 1Anne Caryl Cabral AfableNo ratings yet
- A Study of Demographic Variables of Violent Asphyxial Death: JPAFMAT, 2003, Vol.: 3 ISSN - 0972 - 5687Document4 pagesA Study of Demographic Variables of Violent Asphyxial Death: JPAFMAT, 2003, Vol.: 3 ISSN - 0972 - 5687Reza ArgoNo ratings yet
- Elc.121.reading Task Question - Dec.2017 Set 1Document9 pagesElc.121.reading Task Question - Dec.2017 Set 1AHMAD MUKHRIZ ROSMINo ratings yet
- Sepsis 3Document82 pagesSepsis 3Solange Vargas LiclaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing 3Document80 pagesPsychiatric Nursing 3Ershelle Mae MorlaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Modelling Time DelaysDocument30 pagesLab 3 - Modelling Time DelayslynNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory InfectionDocument7 pagesUpper Respiratory Infectionhazem barhoomNo ratings yet
- Case-Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics Exercise - TaggedDocument4 pagesCase-Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics Exercise - TaggedAhmed SahilNo ratings yet
- History Taking TemplateDocument6 pagesHistory Taking TemplateNooredin JomaaNo ratings yet
- Biliary AtresiaDocument39 pagesBiliary AtresiaRamesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PEDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 PEJasper BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Concussion - PathophyDocument4 pagesCerebral Concussion - PathophyFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Medstar Pediatrics - 2nd EditionDocument649 pagesMedstar Pediatrics - 2nd Editionmy Lord Jesus100% (3)
- Health Declaration Form D02Document1 pageHealth Declaration Form D02Hizwani ZainalNo ratings yet
- Surgery & Pediatrics SurgeryDocument111 pagesSurgery & Pediatrics SurgeryHIMANSHU GUPTANo ratings yet
- STS Chapter 15Document2 pagesSTS Chapter 15Fritz Dela CernaNo ratings yet
- The Eighth Edition American Joint Committee On Cancer (AJCC) Melanoma Staging System Implications For Melanoma Treatment and CareDocument23 pagesThe Eighth Edition American Joint Committee On Cancer (AJCC) Melanoma Staging System Implications For Melanoma Treatment and CareValentina IndahNo ratings yet
- Peoria County Booking Sheet 03/06/14Document7 pagesPeoria County Booking Sheet 03/06/14Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Perry2008 2Document12 pagesPerry2008 2luis castroNo ratings yet
- Medicine - Irfan MasoodDocument701 pagesMedicine - Irfan MasoodAflaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Case CompilationDocument1 pageCase Compilationjae eNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument10 pagesCase ReportFika Wilda AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- (Upgraded) Complications of Fractures and ManagementDocument65 pages(Upgraded) Complications of Fractures and ManagementroroNo ratings yet
- AML, CML, ALL, CLL, HemophiliaDocument7 pagesAML, CML, ALL, CLL, HemophiliaJamara Kyla Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2023 CC Full WorkbookDocument988 pages2023 CC Full WorkbookZahra Ahmed AlzaherNo ratings yet
- Trastornos de Alimentacion CIE 11Document19 pagesTrastornos de Alimentacion CIE 11Elene MezaNo ratings yet
- Lazaridou Et Al 2023 Biofeedback Emg Alternative Therapy For Chronic Low Back Pain The Beat Pain StudyDocument8 pagesLazaridou Et Al 2023 Biofeedback Emg Alternative Therapy For Chronic Low Back Pain The Beat Pain StudymasreshaNo ratings yet
- Right To Life Movement PowerpointDocument8 pagesRight To Life Movement Powerpointapi-452788589No ratings yet