Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Covid 19
Uploaded by
leroyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Covid 19
Uploaded by
leroyCopyright:
Available Formats
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known
case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.[5] The disease quickly
spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
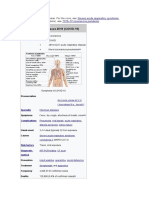
The symptoms of COVID-19 are variable but often include fever,[6] cough, headache,
[7] fatigue, breathing difficulties, loss of smell, and loss of taste.[8][9][10] Symptoms
may begin one to fourteen days after exposure to the virus. At least a third of people
who are infected do not develop noticeable symptoms.[11] Of those who develop
symptoms noticeable enough to be classified as patients, most (81%) develop mild to
moderate symptoms (up to mild pneumonia), while 14% develop severe symptoms
(dyspnea, hypoxia, or more than 50% lung involvement on imaging), and 5% develop
critical symptoms (respiratory failure, shock, or multiorgan dysfunction).[12] Older
people are at a higher risk of developing severe symptoms. Some people continue to
experience a range of effects (long COVID) for months after recovery, and damage to
organs has been observed.[13] Multi-year studies are underway to further investigate
the long-term effects of the disease.[13]
COVID-19 transmits when people breathe air contaminated by droplets and small
airborne particles containing the virus. The risk of breathing these is highest when
people are in close proximity, but they can be inhaled over longer distances,
particularly indoors. Transmission can also occur if contaminated fluids are splashed
or sprayed in the eyes, nose, or mouth, or, more rarely, via contaminated surfaces.
People remain contagious for up to 20 days and can spread the virus even if they do
not develop symptoms.[14][15]
Testing methods for COVID-19 to detect the virus's nucleic acid include real-time
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR),[16][17] transcription-
mediated amplification,[16][17][18] and reverse transcription loop-mediated
isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP)[16][17] from a nasopharyngeal swab.[19]
Several COVID-19 vaccines have been approved and distributed in various countries,
which have initiated mass vaccination campaigns. Other preventive measures include
physical or social distancing, quarantining, ventilation of indoor spaces, use of face
masks or coverings in public, covering coughs and sneezes, hand washing, and
keeping unwashed hands away from the face. While work is underway to develop
drugs that inhibit the virus, the primary treatment is symptomatic. Management
involves the treatment of symptoms through supportive care, isolation, and
experimental measures.
You might also like
- Psychotropic MedicationsDocument87 pagesPsychotropic MedicationsDWAI McJohnsonNo ratings yet
- Case Study Hospital FormatDocument3 pagesCase Study Hospital Formatsenyorakath0% (1)
- C. Raymond Lake Auth. Schizophrenia Is A Misdiagnosis Implications For The DSM-5 and The ICD-11 2012Document442 pagesC. Raymond Lake Auth. Schizophrenia Is A Misdiagnosis Implications For The DSM-5 and The ICD-11 2012Romulus-Dan Nicoara100% (1)
- Micronutrients in Neurology and DiseaseDocument16 pagesMicronutrients in Neurology and DiseaseSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- PREVENTIVE MEASURES IN CAMPUSDocument33 pagesPREVENTIVE MEASURES IN CAMPUSιωαναθαν ρααγασNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Symptoms, Causes, Tests, PreventionDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Symptoms, Causes, Tests, PreventionSwathi KnNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is ADocument1 pageCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is AGangadhar DungaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019Document1 pageCoronavirus Disease 2019poppy mataeoNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is A Contagious Disease Caused byDocument3 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is A Contagious Disease Caused byaisyah diyantiNo ratings yet
- CoronavirusDocument1 pageCoronavirusKavya TummepalliNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Symptoms, Transmission, Testing and PreventionDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Symptoms, Transmission, Testing and PreventionMarvicNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document6 pagesCovid 19ArvindChauhanNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Dise/ase 2019 (COVID-19) Is ADocument40 pagesCoronavirus Dise/ase 2019 (COVID-19) Is Asahil Narang call of dutyNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 WikiDocument76 pagesCOVID-19 WikiUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) : This Article Is About The Disease. For The Virus, See - For The Pandemic, SeeDocument2 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) : This Article Is About The Disease. For The Virus, See - For The Pandemic, Seearif iffatNo ratings yet
- COVID Details Part 1Document8 pagesCOVID Details Part 1sirreNo ratings yet
- Introduction to COVIDDocument7 pagesIntroduction to COVIDqaseem2109No ratings yet
- Omar Taha - Nishteman Farzad - Ahmed Gaeib - Aven Majeed - Abdulwahab Ahmed - Lavan Majeed - Tabark KhawlanDocument45 pagesOmar Taha - Nishteman Farzad - Ahmed Gaeib - Aven Majeed - Abdulwahab Ahmed - Lavan Majeed - Tabark KhawlanAhmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Coronavirus Disease 2019Document2 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Coronavirus Disease 2019waseem555No ratings yet
- Transmission - of - COVID-19 WikiDocument14 pagesTransmission - of - COVID-19 WikiUnggul YudhaNo ratings yet
- Science Projek Power Point AJJ 0608Document7 pagesScience Projek Power Point AJJ 0608qyin2579No ratings yet
- A Project On Business Stratagies Used During Covid 19Document56 pagesA Project On Business Stratagies Used During Covid 19084 UjwalaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019Document46 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019Benjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Origin, History, Transmission & Pathogenesis /TITLEDocument50 pagesCOVID-19 Origin, History, Transmission & Pathogenesis /TITLEJana AbdulrahimNo ratings yet
- Project On Covid-19Document22 pagesProject On Covid-19Yashasvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- COVID1Document3 pagesCOVID1Dez TabiosNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 - WikipediaDocument349 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 - WikipediaWrohit XetriNo ratings yet
- COVID19Document3 pagesCOVID19mohammad abdusalimNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019Document30 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019meNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 presentationDocument25 pagesCOVID-19 presentationGiorgi KenkebashviliNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019Document4 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019Rodmar EscolanoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Prevention and ManagementDocument56 pagesCOVID-19 Prevention and ManagementAhmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus DiseaseDocument5 pagesCoronavirus DiseaseShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Comparative and ContrastDocument6 pagesComparative and ContrastA IiNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is A ContagiousDocument66 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is A ContagiouslydianchromaticNo ratings yet
- Cause: TransmissionDocument6 pagesCause: Transmissionmarcos callaNo ratings yet
- Cause of Covid-19: TransmissionDocument2 pagesCause of Covid-19: TransmissionRodmar EscolanoNo ratings yet
- Apsayan Es Contingency Planning For Covid 19academyDocument23 pagesApsayan Es Contingency Planning For Covid 19academyLloyd Angelo SobredillaNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus (ID 221 29 532)Document7 pagesCoronavirus (ID 221 29 532)Hr RiponNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Report on Virus Outbreak, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument16 pagesCOVID-19 Report on Virus Outbreak, Symptoms and TreatmentSara GuptaNo ratings yet
- Report On The Global Statistical Data of COVIDDocument3 pagesReport On The Global Statistical Data of COVIDChristian Angelo G. MontigoNo ratings yet
- Identification of The Impact of Covid-19 On Pneumonia SufferersDocument7 pagesIdentification of The Impact of Covid-19 On Pneumonia SufferersFaizal NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Septiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - WordDocument21 pagesSeptiya Agestin Cahyaningrum - WordSepty KawaiNo ratings yet
- Medscape All Covid 19Document81 pagesMedscape All Covid 19david dompeipenNo ratings yet
- Transmission of COVID-19 and The Role of Face Masks in Health SettingsDocument2 pagesTransmission of COVID-19 and The Role of Face Masks in Health SettingsMN IrshadNo ratings yet
- Understanding COVID-19: Causes, Symptoms, and PreventionDocument16 pagesUnderstanding COVID-19: Causes, Symptoms, and PreventionHamza AliNo ratings yet
- COVID-19: Paper Assignment Submitted To Fulfill One of The English AssignmentsDocument7 pagesCOVID-19: Paper Assignment Submitted To Fulfill One of The English AssignmentsHasna Rizqi fadilahNo ratings yet
- He COVID-19 Pandemic, Also Known As The Coronavirus Pandemic, Is An OngoingDocument1 pageHe COVID-19 Pandemic, Also Known As The Coronavirus Pandemic, Is An Ongoingoppo f1No ratings yet
- Covid 19Document8 pagesCovid 19AZLINA AZRAAINo ratings yet
- Dr. Rajiv Dahiya - How To Take Precautions Against Corona Virus by DR Rajiv DahiyaDocument1 pageDr. Rajiv Dahiya - How To Take Precautions Against Corona Virus by DR Rajiv DahiyarajivdahiyaNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus DiseaseDocument6 pagesCorona Virus DiseaseSAKET MEHTANo ratings yet
- Dr. Rajiv Dahiya - How To Take Precautions Against Corona Virus by DR Rajiv DahiyaDocument1 pageDr. Rajiv Dahiya - How To Take Precautions Against Corona Virus by DR Rajiv DahiyarajivdahiyaNo ratings yet
- What is CoronavirusDocument2 pagesWhat is CoronavirusImene Amani HouariNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) : Practice EssentialsDocument79 pagesCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) : Practice Essentialsrajesh BNo ratings yet
- COVID-19Document9 pagesCOVID-19k.agnes12No ratings yet
- BY JO1 Anton Steve Lim RN, Pgdip-Ts, Pgdip-SrmDocument49 pagesBY JO1 Anton Steve Lim RN, Pgdip-Ts, Pgdip-SrmDos LimNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Report Covid-19Document11 pagesReviewer Report Covid-19adelaidah sanggacalaNo ratings yet
- Covid 19 Project Work For Class 12Document19 pagesCovid 19 Project Work For Class 12Sambhav ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document11 pagesCovid 19SnehaNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document9 pagesCovid 19Charanpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Symptoms, transmission, and virology of COVID-19Document3 pagesSymptoms, transmission, and virology of COVID-19GrayNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 causes mild to moderate illnessDocument1 pageCOVID-19 causes mild to moderate illnessJordyValenciaNo ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument24 pagesCommon Coldxiang_xiang56No ratings yet
- Jazz OriginDocument1 pageJazz OriginleroyNo ratings yet
- The Avengers Avengers: Age of Ultron: Avengers: Infinity War Is A 2018 AmericanDocument1 pageThe Avengers Avengers: Age of Ultron: Avengers: Infinity War Is A 2018 AmericanleroyNo ratings yet
- The Avengers Avengers: Age of Ultron Avengers: Infinity War: Avengers: Endgame Is A 2019 AmericanDocument1 pageThe Avengers Avengers: Age of Ultron Avengers: Infinity War: Avengers: Endgame Is A 2019 AmericanleroyNo ratings yet
- The Limbang Rebellion ReviewDocument2 pagesThe Limbang Rebellion ReviewleroyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 4th Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformDocument985 pagesPharmacology 4th Semester BSN Notes, Educational PlatformPen N PapersNo ratings yet
- Subgroup 2 Ovarian CystDocument257 pagesSubgroup 2 Ovarian CystCharlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- UTS Semi-Finals Reviewer Discusses Sexuality, Gender, RelationshipsDocument3 pagesUTS Semi-Finals Reviewer Discusses Sexuality, Gender, RelationshipsBellela Dump100% (1)
- Magat, Jescel-Anne Janea D. MED-2B A B C BDocument3 pagesMagat, Jescel-Anne Janea D. MED-2B A B C BJescel-Anne Janea MagatNo ratings yet
- Studi Kasus: Cystolithiasis Akibat Infeksi Pada AnjingDocument11 pagesStudi Kasus: Cystolithiasis Akibat Infeksi Pada AnjingMuhammad Fernanda DanuartaNo ratings yet
- Action Plan For Integrated People-Centred Eye Care in South-East Asia 2022-2030Document45 pagesAction Plan For Integrated People-Centred Eye Care in South-East Asia 2022-2030Eunice DichosoNo ratings yet
- Essential Tremor PamphletDocument2 pagesEssential Tremor PamphletAmirNo ratings yet
- Congenital Malformations and Fetal DevelopmentDocument14 pagesCongenital Malformations and Fetal DevelopmentMartha LubasiNo ratings yet
- Drug Abuse and StrokeDocument10 pagesDrug Abuse and StrokematttNo ratings yet
- 07 Check Your English Vocabulary For MedicineDocument66 pages07 Check Your English Vocabulary For MedicineFaiza KanwalNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Drugs 26269Document10 pagesGastrointestinal Drugs 26269Elena CondicNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kunjungan Pasien 2021Document12 pagesLaporan Kunjungan Pasien 2021Firman IsmailNo ratings yet
- Classification and Causes of Burn InjuriesDocument35 pagesClassification and Causes of Burn InjuriesMAHFUZ ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Adult Cutaneous Fungal Infections 1 DermatophytesDocument61 pagesAdult Cutaneous Fungal Infections 1 DermatophytesAbdur Rachman Ba'abdullahNo ratings yet
- Juicing For HealingDocument10 pagesJuicing For HealingHazel Aikulola GriffithNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: What Is Myasthenia Gravis? How Is It Diagnosed?Document2 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: What Is Myasthenia Gravis? How Is It Diagnosed?Junairah CasidarNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseDocument31 pagesHEALTH 8: Communicable DiseaseElissah S PabilonaNo ratings yet
- Human and Animal Bites Antimicrobial Prescribing PDF 66142021681861Document27 pagesHuman and Animal Bites Antimicrobial Prescribing PDF 66142021681861alialison7666No ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR APPENDICITISDocument7 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR APPENDICITISHanz Abbigail Roco100% (1)
- Autoimmunity Reviews: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesAutoimmunity Reviews: SciencedirectYeni PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- HygieneDocument23 pagesHygienecaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Psyh 118 Presentation HestonDocument12 pagesPsyh 118 Presentation HestonGde KayanaNo ratings yet
- Errata of Medicine Golden Files 1 To 9Document27 pagesErrata of Medicine Golden Files 1 To 9mahaakhNo ratings yet
- Bleeding NeonateDocument38 pagesBleeding NeonateAchyut KanungoNo ratings yet
- Did Alexander The Great Die From Guillain-Barré Syndrome - HallDocument26 pagesDid Alexander The Great Die From Guillain-Barré Syndrome - HallJAVIER AGUILAR CASASOLANo ratings yet
- Roche Et Al. 2017 Faltering GrowthDocument6 pagesRoche Et Al. 2017 Faltering GrowthSatesh BalachantharNo ratings yet