Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Swoc
Uploaded by
Jessie Estellore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesThis document contains a SWOC (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Challenges) analysis for disaster prevention and mitigation as well as disaster preparedness for a local government. For prevention and mitigation, key strengths include risk maps, early warning systems, and evacuation centers. Weaknesses involve outdated data and a lack of relocation areas. Opportunities center on available funding and technical assistance. Challenges relate to climate change impacts and differing warning protocols. For preparedness, strengths are established councils and trained responders. Weaknesses involve incomplete councils and a lack of resources and training. Opportunities lie in available support and guidelines. Challenges center on inadequate awareness, plans, and
Original Description:
Original Title
SAMPLE-SWOC
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a SWOC (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Challenges) analysis for disaster prevention and mitigation as well as disaster preparedness for a local government. For prevention and mitigation, key strengths include risk maps, early warning systems, and evacuation centers. Weaknesses involve outdated data and a lack of relocation areas. Opportunities center on available funding and technical assistance. Challenges relate to climate change impacts and differing warning protocols. For preparedness, strengths are established councils and trained responders. Weaknesses involve incomplete councils and a lack of resources and training. Opportunities lie in available support and guidelines. Challenges center on inadequate awareness, plans, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views6 pagesSample Swoc
Uploaded by
Jessie EstelloreThis document contains a SWOC (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Challenges) analysis for disaster prevention and mitigation as well as disaster preparedness for a local government. For prevention and mitigation, key strengths include risk maps, early warning systems, and evacuation centers. Weaknesses involve outdated data and a lack of relocation areas. Opportunities center on available funding and technical assistance. Challenges relate to climate change impacts and differing warning protocols. For preparedness, strengths are established councils and trained responders. Weaknesses involve incomplete councils and a lack of resources and training. Opportunities lie in available support and guidelines. Challenges center on inadequate awareness, plans, and
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
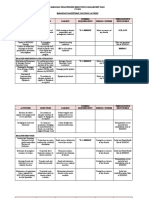
SAMPLE SWOC
Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Challenges
Presence of risk maps Outdated CBMS Availability of Refusal of
Presence of installed early data funding for COVID-19
warning signages Ease of relocation from vaccination of
Presence of early warning implementation of NGAs senior citizens
devices “No Build Zone” Implementation No early
Availability of evacuation No available lot for of warning system
center relocation from the transportation at the barangay
Issuance of DRRM related Municipality modernization level
policies (ordinance, EOs) No established program at the Reluctance to
Forged MOA with private policy requiring national level registration of
sector for the use of essential business Availability of some farmers
sanitary landfill establishment for technical and fisher folks
Presence of approved the installation of assistance from Climate change
solid waste management back-up power warning Poor
plan Absence of agencies maintenance of
Regular collection of laboratory for water Availability of irrigation
waste testing advisories from system
Availability of CDRA result No established early warning Different
Availability of funds for warning system agencies warning
insurance coverage Limited evacuation Advancement of protocols and
Presence of insurance center capacity technology alert systems at
coverage for DRRM Presence of Provision of the national
personnel including job unmanaged, building as level, creating
orders and contract of undeveloped, and evacuation confusion to
service privately owned center from LGUs
90% of farmers and fisher destination sites PAGCOR Unwillingness
folks are registered in a which is hazardous Availability of of farmers to
LGU recognized to individuals NDRRM Fund avail the PCIC
organization visiting the site for the crop insurance
On-going dredging and Schools used as construction of Lack of
desilting of river system evacuation centers evacuation database for
and its tributaries center agriculture at
Availability of crop With available the barangay
insurance risk assessment level
Conduct of clean and tool from the
green program national
Conduct of tree planting Presence of
along riverbanks and PCIC for crop
creeks insurance
Insured government Availability of
Geo Risk PH for
buildings and facilities risk assessment
Regular dissemination of
local advisories.
Presence of CBMS
Disaster Preparedness
Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Challenges
Established LDRRMC LDRRMC Presence of Irregular fuel
Council through E.O. composition is support from rate
Regular conduct of incomplete based the higher No Barangay
council meetings on RA 10121 DRRMCs DRRM plans
Established 24/7 CDP and CLUP for Established Various plans
Operations Center updating Barangay required by
Availability of local DRRM Lack of manpower in Development concerned
fund the LDRRM office Councils national
Established LDRRM Office No separate facility through E.O. government
through E.O. for the operations Presence of agencies
Filled-up plantilla center support from Bureaucracy
positions for the LDRRMO Lack of DRRM OCD regional at the national
including mandatory related trainings office government
staffs (RDANA, PDNA, CP, Availability of Different COA
Availability of trained ICS, PSCP) DRRM-related interpretation
responders/ Lack of responders/ trainings from on some
personnel manpower NGAs national
Regular conduct of fire Lack of ambulance Availability of policies
and earthquake drills Lack of health DRRM-related Limited
Presence of capable personnel policies as awareness
responders ANDAM Lack of DRRM- bases and and
BATOK SA TRAHEDYA related training for guide in preparedness
INGON MAN SA Teachers LDRRMF activities at
KATALAGMAN (ABTIK) Power supply is utilization the
Availability of equipment CEBECO-dependent Presence of community
for disaster response Some areas do not community fire level
Presence of DRRM-H plan have access to auxiliary group Not functional
Regular conduct of water source (CFAG) BDRMMCs
COVID-19 vaccination Lack of water supply Presence of Insufficient
Presence of school DRRM for the irrigation ACDV supply of farm
focal system guidelines from inputs from
Strong coordination No approved DRRM- the NDRRMC other
among DRRMC members related plans (CP, Availability of organizations
Regular conduct of IEC PSCP, SOP, RRP, heavy Lack of
activities RisCom Plan, etc.) equipment on coordination
Availability of back-up No separate office loan basis between
power for critical for GAD Presence of tourism center
establishments Not yet trained in augmentation and the
Presence of renewable Gender Sensitivity support from barangay
solar powered street training neighboring tourism sites
lamps No monitoring and LGUs No standard
Availability of water evaluation scheme Availability of fees for tourist
supply (springs, etc.) for DRRM PPAs solar lamps being
Presence of water tanker implementation from the NGAs implemented
for household use Lack of training in Availability of for the
Presence of water tanker search and rescue water tanker transport tariff
Allocated budget for the Intermittent supply from private No established
improvement of water of water on the far organizations protocol/MOA
systems flung areas Availability of during joint
Presence of design Presence of dead technical and response
software for water spots on some areas financial operations
systems No reorganization of assistance at with
Availability of handheld response clusters the provincial neighboring
radios Lack of permanent level related to LGUs/LDRRMC
Presence of NTC licensed LDRRM staff supply of water
radios and radio Lack of equipment systems
operators storage / warehouse Partnership
Accessible municipal and constraints with civic
barangay road organizations
networking and NGAs
Availability of LGU related to
vehicles water systems
Presence of Barangay Availability of
Animal Health Aide satellite phone
(BAHA) at the
Conduct of regular provincial level
meeting of organized Linkage to the
farmer association provincial and
Availability of surveillance national
drone for agricultural government
assessment Availability of
Presence of tourist funds at the
destination provincial and
Availability of municipal national level
market Availability of
LGU is open for investors DRR-related
Full support from LCE and plans at the
LGU officials regional and
Presence of approved national level
CDP Availability of
Presence of LPDRP technical
Presence IEC materials experts in the
(pamphlets, leaflets, formulation of
brochures) plans
Availability of localized Presence of IEC
IEC materials materials in the
Continuous conduct of regional level
information drive Availability of
Presence of GAD plan, technical
budget with focal person experts for
Presence of inventory of GAD training
resources Water supply
project to be
implemented
by the Cebu
Provincial
Government
Availability of
radio stations
to be tapped
for IEC
Strong support
from the Cebu
Provincial
Government
and
Congressman
in DRRM
programs and
activities
Availability of
capacity
enhancement
training from
the regional
agencies
Established
strong
partnership
with
neighboring
LGUs/LDRRMC
Availability of
funds at the
national level
(NDRRMF)
Presence of
national ACDV
guidelines
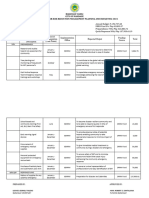
Disaster Response and Early Recovery
Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Challenges
Availability of food Lack of SRR- Availability of No established
assistance for fisher trained responders standard
folks during bad response from protocol during
weather personnel neighboring disaster
Established 24/7 Lack of LGUs for response with
Operations Center augmentation the neighboring
response
With available Availability of LGUs and
resources
communication, national volunteers
No response
rescue, and issuances for No MOA
transportation plans at the the declaration established
equipment for LGU level of state of with
operations and Lack of calamity, neighboring
response response conduct of pre- LGUs in disaster
Conduct of RECOREDA protocols disaster risk response
as preparedness action Report assessment, Reluctance of
Strong partnership with generation utilization of some members
other offices in QRF and among of the
conducting response Lack of mobility others that will community in
and relief operations in the serve as bases the
Availability of quick assessment of for LGU in the implementation
response fund for crops after a implementation of pre-
response intervention disaster of activities emptive/force
With available Trained Availability of evacuation
communication, responders national National
rescue, and need refresher government declaration of
transportation courses in agencies to assistance but
equipment for DRRM. augment different in the
operations and resources to stated policy or
response LGU guidelines.
Availability of Different
National and reporting
Regional templates
Disaster forwarded to
Response Plans LGUs for
and compliance
Contingency for from concerned
various hazards national
Presence of government
Negosyo agencies
Centers for Uncooperative
financial attitude / non-
assistance for compliance of
businesses some members
Availability of of the
support from community in
local and the
foreign implementation
organizations of pre-
emptive/force
evacuation
Disaster Rehabilitation and Recovery
Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Challenges
Regular conduct of No Rehabilitation Availability of Bureaucracy
mental health and and Recovery Plan livelihood training at the
psychosocial (RRP) from private and national level
support Lack of PDNA- government for the
Provision of trained personnel organizations provision of
livelihood Lack of funds for Availability of rehabilitation
program Rehabilitation livelihood
assistance
Conduct of purposes opportunity from
Lack of fund
livelihood training NGAs
(sewing, parents Availability of PDNA at the
and child laborers, teams from higher barangay level
bugasan, soap DRRMCs for
making, women’s Availability of fund rehabilitation
organization) at the national level Procurement
for rehabilitation process
program
You might also like
- Disaster Risk Reduction MGT 01Document25 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction MGT 01arnadokylNo ratings yet
- RD Presentation NV (Autosaved)Document16 pagesRD Presentation NV (Autosaved)Rtwpb Region IINo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 DRRM Planning - 2021-03-06-11-41-22-AmDocument7 pagesAssignment 3 DRRM Planning - 2021-03-06-11-41-22-AmCdrrmc DigosNo ratings yet
- CCA-DRRM Program Presentation TapatanDocument12 pagesCCA-DRRM Program Presentation TapatanMarie AlejoNo ratings yet
- COMMUNITYDocument5 pagesCOMMUNITYYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Amended PDRA GuidelinesDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Amended PDRA GuidelinesCar Dilgopcen100% (1)
- Department of Agriculture (DA) Devolution Transition Plan (DTP) in Compliance To EO 138Document45 pagesDepartment of Agriculture (DA) Devolution Transition Plan (DTP) in Compliance To EO 138John Paul M. MoradoNo ratings yet
- Functio Nal AreaDocument3 pagesFunctio Nal AreaIrismae SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Cluster Required Action Weather DisturbanceDocument5 pagesCluster Required Action Weather DisturbanceAldrin SevillaNo ratings yet
- Tampilisan MDRRMP-2Document8 pagesTampilisan MDRRMP-2Josephine Templa-JamolodNo ratings yet
- 10.2 The NDRRM Plan and Knowledge Transfer (Handout)Document4 pages10.2 The NDRRM Plan and Knowledge Transfer (Handout)KassNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Cebu City Division Contingency PlanDocument11 pagesDepartment of Education Cebu City Division Contingency Planericson maglasangNo ratings yet
- Swoc On Thematic Area MDRRM Plan 2020Document11 pagesSwoc On Thematic Area MDRRM Plan 2020Mdrrmo Sigma-srt Srt100% (3)
- Module 3 - Eng - 3dayDocument70 pagesModule 3 - Eng - 3dayJoseph P. Cagcon100% (1)
- ARTECHE - MAINTSREAMING CDRA TO CDP (Autosaved)Document27 pagesARTECHE - MAINTSREAMING CDRA TO CDP (Autosaved)mamedinaNo ratings yet
- Review Form For LDRRMPs With INPUTSDocument4 pagesReview Form For LDRRMPs With INPUTSErnan Baldomero75% (4)
- Ipcr Jan To June 2022Document9 pagesIpcr Jan To June 2022Decs Del Carmen100% (2)
- DR William Dar - AEWDocument22 pagesDR William Dar - AEWRonel Dimaya CañaNo ratings yet
- Proposed New Appropriation by Program, Activity and ProjectDocument7 pagesProposed New Appropriation by Program, Activity and ProjectMdrrmo Mercedes Camarines NorteNo ratings yet
- Bpops Plan SampleDocument4 pagesBpops Plan SampleQUeen Dai SY RamirezNo ratings yet
- Sample BDRRM 2024 Nnual Investment PlanDocument6 pagesSample BDRRM 2024 Nnual Investment PlanChezielle Mae LapuraNo ratings yet
- LDRRM PlanDocument8 pagesLDRRM PlanRichard Selinel LofrancoNo ratings yet
- LFEWS Local Flood Early Warning SystemDocument54 pagesLFEWS Local Flood Early Warning SystemDemetrio FormalesNo ratings yet
- LDRRMP - Vi Monitoring and EvaluationDocument19 pagesLDRRMP - Vi Monitoring and EvaluationMohrein H. Ismael VI100% (1)
- Action Plan For Research Output ImplementationDocument6 pagesAction Plan For Research Output ImplementationJunell TadinaNo ratings yet
- NIDMDocument30 pagesNIDMGade IndhuNo ratings yet
- Ipcr Jan To June 2022Document8 pagesIpcr Jan To June 2022Decs Del Carmen100% (1)
- WS 1 & 2 Risk Identification - Writing Risk & Opportunity Scenarios Group 2Document16 pagesWS 1 & 2 Risk Identification - Writing Risk & Opportunity Scenarios Group 2Karen Bangibang WalayNo ratings yet
- SitRep No. 4 Icow Observance of Semana Santa 2023 SignedDocument27 pagesSitRep No. 4 Icow Observance of Semana Santa 2023 Signedsaffron crocusNo ratings yet
- DRR EwsDocument12 pagesDRR EwsAnonymous kVuwTMEe1qNo ratings yet
- 04 India Disaster Management 4thTWG 27jan2021Document7 pages04 India Disaster Management 4thTWG 27jan2021DanielNo ratings yet
- Templates For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management PlanningDocument10 pagesTemplates For Local Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Planningjofel delicanaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Disaster Risk Reduction Management PlanDocument3 pagesBarangay Disaster Risk Reduction Management PlanSandy Angenette Catbagan75% (4)
- Aide MemoireDocument59 pagesAide MemoirearcnpcNo ratings yet
- DRM Road Map 2014-19 PDFDocument72 pagesDRM Road Map 2014-19 PDFanon_134728790No ratings yet
- Storm Surges Contingency Plan 2022Document46 pagesStorm Surges Contingency Plan 2022LGU GuimbalNo ratings yet
- LDRRMP Assignment 3Document8 pagesLDRRMP Assignment 3Soriano ArmenioNo ratings yet
- IiedDocument6 pagesIiedQayum AhmadiNo ratings yet
- CBDRRM 3 Year PlanDocument4 pagesCBDRRM 3 Year PlanBarangay Mate TayabasNo ratings yet
- Death Certificate Format in BangladeshDocument25 pagesDeath Certificate Format in BangladeshAnkan DasNo ratings yet
- PAGASADocument29 pagesPAGASAvipereejayNo ratings yet
- NDMA Annual Report 2009Document70 pagesNDMA Annual Report 2009Nehman KhalilNo ratings yet
- Coaches Training On QAS For BDRRM Planning - Documentation - FinalDraftDocument56 pagesCoaches Training On QAS For BDRRM Planning - Documentation - FinalDraftNabbuan Santiago CityNo ratings yet
- 00 Contingency Planning For Basic Education 20190830Document79 pages00 Contingency Planning For Basic Education 20190830Joan Filipina MarceloNo ratings yet
- Dr. Florencio Adonay Livestock DRR Protocol PresentationDocument12 pagesDr. Florencio Adonay Livestock DRR Protocol PresentationDA RFO5 Disaster Risk Reduction UnitNo ratings yet
- Barangay Disaster Preparedness Monitoring Web ApplDocument9 pagesBarangay Disaster Preparedness Monitoring Web AppleuginemagturocaststudentNo ratings yet
- Ca 7992 enDocument8 pagesCa 7992 enyoussefsabri1906No ratings yet
- Ndrrmoc Sopg 2021Document132 pagesNdrrmoc Sopg 2021Joefrey Yu100% (3)
- Early Warning Powerpoint Presentation 2022Document35 pagesEarly Warning Powerpoint Presentation 2022mhibfewsnewbataanddoNo ratings yet
- OPLAN MT - kANLAONDocument14 pagesOPLAN MT - kANLAONgary ann jimenez100% (3)
- Introduction To Contingency PlanningDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Contingency PlanningCabanatuanDRRMO AdminNo ratings yet
- Febi Dwirahmadi PPT ConferenceDocument17 pagesFebi Dwirahmadi PPT ConferenceMann NexNo ratings yet
- Community-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management ProcessDocument50 pagesCommunity-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Management ProcessChannelGNo ratings yet
- Local Government Unit Disaster Preparedness ManualDocument32 pagesLocal Government Unit Disaster Preparedness ManualErnan BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- CCDRR PresentationDocument16 pagesCCDRR PresentationShirley Jean Villamor Sugano100% (1)
- BDRRM Plan 2024Document2 pagesBDRRM Plan 2024casilimandaue2024No ratings yet
- Digital Readiness StrategyDocument67 pagesDigital Readiness StrategygracesomidoNo ratings yet
- FloodDocument48 pagesFloodterpelesetNo ratings yet
- Unlocking the Lower Skies: The Costs and Benefits of Deploying Drones across Use Cases in East AfricaFrom EverandUnlocking the Lower Skies: The Costs and Benefits of Deploying Drones across Use Cases in East AfricaNo ratings yet
- Reducing Poverty and Investing in People: The New Role of Safety Nets in AfricaFrom EverandReducing Poverty and Investing in People: The New Role of Safety Nets in AfricaNo ratings yet
- Boiler OperationDocument97 pagesBoiler Operationdeeli1100% (2)
- Automated Hydroponics Greenhouse: Regulation of PH and NutrientsDocument49 pagesAutomated Hydroponics Greenhouse: Regulation of PH and NutrientsarnuNo ratings yet
- Gifts of NatureDocument2 pagesGifts of NatureŚáńtőśh MőkáśhíNo ratings yet
- Development and Climate Change in Bangladesh: Focus On Coastal Flooding and The SundarbansDocument5 pagesDevelopment and Climate Change in Bangladesh: Focus On Coastal Flooding and The Sundarbanstrong anhNo ratings yet
- Ml12335a508 PDFDocument279 pagesMl12335a508 PDFkangsungjinNo ratings yet
- Simplify Materials Selection: Your Guide To Making Choices That Reduce The Impact of CorrosionDocument37 pagesSimplify Materials Selection: Your Guide To Making Choices That Reduce The Impact of CorrosionInspection EngineerNo ratings yet
- 714 Irrometer Reference Book-WEBDocument24 pages714 Irrometer Reference Book-WEBDiego Lopez MontalvoNo ratings yet
- MSDS Strata Bond W S Comp A 2020-09-03 enDocument7 pagesMSDS Strata Bond W S Comp A 2020-09-03 encarlos_salas80No ratings yet
- Environmental Studies Assignment-1 Topic: - Environmental Problems in Your LocalityDocument11 pagesEnvironmental Studies Assignment-1 Topic: - Environmental Problems in Your LocalityLokesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ppe Midterm Project 1Document14 pagesPpe Midterm Project 1Joanne EscolanoNo ratings yet
- Class VIII EnglishDocument7 pagesClass VIII EnglishIT JPRNo ratings yet
- All Piping Drawings Spec SheetsDocument18 pagesAll Piping Drawings Spec Sheetsc.reidNo ratings yet
- Astro Biolog I ADocument64 pagesAstro Biolog I AAlexei Ochoa100% (1)
- Water Management SystemDocument26 pagesWater Management SystemConstro Facilitator100% (1)
- Basic Terms: Sustainable Agriculture AND Farming System Farming System Ss Rana SrscientistDocument40 pagesBasic Terms: Sustainable Agriculture AND Farming System Farming System Ss Rana SrscientistSofi MehrajNo ratings yet
- The Processes Used in Modern Sewage Treatment PlantsDocument2 pagesThe Processes Used in Modern Sewage Treatment PlantsPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris: Kelas: Xii Ipa / Ips Hari / Tanggal: Jum'at, 19 Maret 2021Document5 pagesBahasa Inggris: Kelas: Xii Ipa / Ips Hari / Tanggal: Jum'at, 19 Maret 2021duren jaya7No ratings yet
- Government of KeralaDocument14 pagesGovernment of Keralaകേറി വാടാ മക്കളെ Song loversNo ratings yet
- Culture of Marine PolychaeteDocument7 pagesCulture of Marine PolychaeteyaumilakbarNo ratings yet
- Cec 201 Exam Question-1Document2 pagesCec 201 Exam Question-1rmpunk1No ratings yet
- Aquacell Research ProposalDocument4 pagesAquacell Research ProposalZay Yan HtetNo ratings yet
- GRIHA LD Master Plan (5 Star) - Nalanda University - GreenTree GlobalDocument22 pagesGRIHA LD Master Plan (5 Star) - Nalanda University - GreenTree GlobalAbdul WajidNo ratings yet
- VICONDocument6 pagesVICONBukhori TamamNo ratings yet
- Regional Studies in Marine ScienceDocument15 pagesRegional Studies in Marine ScienceAzhafiz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359431115005219 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S1359431115005219 Mainkrunal07786No ratings yet
- Nestle - Water Management Strategy - A New Competitive Advantage EFAS 2007 Peer EdererDocument28 pagesNestle - Water Management Strategy - A New Competitive Advantage EFAS 2007 Peer EdererNora ElGharbawyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Document5 pagesChapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- BioFlo 3000 ManualDocument28 pagesBioFlo 3000 ManualAndres Puc SosaNo ratings yet
- Design of Reverse Osmosis System For Reuse of Waste Water From Common Effluent Treatment PlantDocument9 pagesDesign of Reverse Osmosis System For Reuse of Waste Water From Common Effluent Treatment PlantSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Practical Boiler Water TreatmentDocument1 pagePractical Boiler Water TreatmentChristina DavisNo ratings yet