Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definition of Gout: Treatment
Uploaded by
Dalila Sobrina Abd KaderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Gout: Treatment
Uploaded by
Dalila Sobrina Abd KaderCopyright:
Available Formats
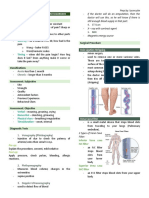
Definition of Gout Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that results from an excess of uric acid in the blood.
BONES OF FOOT: Tarsals (calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuboid & 3 cuneiform), Allopurinol
Metatarsals & Phalanges -decreases the production of uric acid
-decrease high blood uric acid levels
MUSCLE OF FOOT: -a xanthine oxidase inhibitor
Dorsal - Extensor Digitorum Brevis, and Extensor Hallucis Brevis. -taken by mouth or injected into a
Plantar (4 layers) - vein
1. 1st layer - Abductor Hallucis, Flexor Digitorum Brevis & Abductor Digiti Minimi
2. 2nd layer - Quadratus Plantae & Lumbricals Joint fluid test
3. 3rd layer - Flexor Hallucis Brevis, Adductor Hallucis & Flexor Digiti Minimi
X- ray imaging
Brevis Treatment Ulttrasound
4. 4th layer - Plantar Interossei & Dorsal Interossei
Blood test
COMPARTMENT OF FOOT: Interosseous, Medial, Lateral & Central Dual-energy computerized
tomogaphy
Anatomy Diagnosis
Gout
Physiology Prevention
Symptoms
Gout occurs when urate crystals Avoid or limit alcohol
accumulate in your joint, causing the Drink plenty of water
inflammation and intense pain of a gout Intense pain.
Lose excess weight or
attack. Urate crystals can form when you Redness.
maintain a healthy weight
have high levels of uric acid in your blood. Stiffness. Treat sleep apnea
Your body produces uric acid when it Swelling.
breaks down purines — substances that
are found naturally in your body. Tenderness, even to light touch, such as from a bedsheet.
Warmth, or a feeling like the joint is “on fire.”
You might also like
- Vagus Nerve: Vagus Nerve Activities to Relieve Anxiety, Reduce Severe Illness, Relief Depression, Anxiety, Stimulate Vagal Tone, Prevent Inflammation, Trauma, and PTSDFrom EverandVagus Nerve: Vagus Nerve Activities to Relieve Anxiety, Reduce Severe Illness, Relief Depression, Anxiety, Stimulate Vagal Tone, Prevent Inflammation, Trauma, and PTSDRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Info On AyurvedaDocument1 pageInfo On AyurvedaPriyank JivaniNo ratings yet
- The Science of Why, Volume 4: Answers to Questions About Science Facts, Fables, and PhenomenaFrom EverandThe Science of Why, Volume 4: Answers to Questions About Science Facts, Fables, and PhenomenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethergineDocument2 pagesDrug Study MethergineJahmil DulatreNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine LactuloseDocument2 pagesAmlodipine LactuloseDani DaniNo ratings yet
- HospiceDocument10 pagesHospiceJasmineNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Esophagus.Document3 pagesDiseases of Esophagus.Isabel Castillo100% (2)
- Abdominal Assessment HA LectureDocument44 pagesAbdominal Assessment HA LectureKatrina BeltranNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmlodipine - Drug StudyAcads useNo ratings yet
- XLVets Equine Rebranded 013 Arthritis Factsheet 0Document2 pagesXLVets Equine Rebranded 013 Arthritis Factsheet 0karan kambojNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument57 pagesDrug StudyAyessa Camelle DumileNo ratings yet
- RT 102 Medical Terminology FinalsDocument17 pagesRT 102 Medical Terminology FinalsCalessNo ratings yet
- DREAMS e Homoeo 12-2010 1Document4 pagesDREAMS e Homoeo 12-2010 1Saurav AroraNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of Acute PancreatitisDocument2 pagesConcept Map of Acute Pancreatitissalome carpioNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Document16 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia. NCM 109Niña Jean Tormis AldabaNo ratings yet
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPcy belNo ratings yet
- Standard Medical TerminologyDocument18 pagesStandard Medical TerminologyYuanki OlivaNo ratings yet
- MUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingDocument82 pagesMUSCULO-SKELETAL - NursingJan Clarisse RamosNo ratings yet
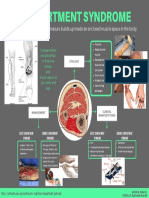
- Compartment Syndrome: It Occurs When Excessive Pressure Builds Up Inside An Enclosed Muscle Space in The BodyDocument1 pageCompartment Syndrome: It Occurs When Excessive Pressure Builds Up Inside An Enclosed Muscle Space in The BodyRachelle Ann CarilloNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Day 5 (Constipation)Document4 pagesConcept Map Day 5 (Constipation)Matt McKinleyNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology Glossary PracticeDocument9 pagesMedical Terminology Glossary Practicefenia dirocieNo ratings yet
- Refrst Sindrom KompartementDocument28 pagesRefrst Sindrom Kompartementdesti cahyantiNo ratings yet
- Herbal Medicine HEALTH10Document1 pageHerbal Medicine HEALTH10Ma. Cristina Angenel RamosNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Changes in Aging Per SystemDocument5 pagesPhysiologic Changes in Aging Per SystemSheila Mae OnatoNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis) Assessment: Pressure MedicationsDocument6 pagesNephrotic Syndrome (Nephrosis) Assessment: Pressure MedicationsArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Acute) HPWDocument1 pageAcute) HPWfredericktingsyNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Doctor'S Order Classifica Tion Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindicat Ions Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Doctor'S Order Classifica Tion Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindicat Ions Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- History Taking: Item DescriptionDocument22 pagesHistory Taking: Item DescriptionBikash Sah100% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineKyla VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Oesophagus - Lecture (1 & 2) SurgeryDocument27 pagesOesophagus - Lecture (1 & 2) Surgeryhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- NCP2 FinalDocument2 pagesNCP2 FinallinlynNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument9 pagesNursing DiagnosisSkyerexNo ratings yet
- Adhesive CapsulitisDocument7 pagesAdhesive CapsulitisMariane GumbanNo ratings yet
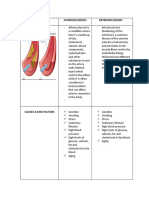
- Arteriosclerosis vs. AtherosclerosisDocument3 pagesArteriosclerosis vs. AtherosclerosisCHRISTIE MONTANONo ratings yet
- DREAMS - e - HomoeoDocument4 pagesDREAMS - e - HomoeoMaya01No ratings yet
- MSI MUST STUDY KEY UpdDocument17 pagesMSI MUST STUDY KEY UpdGabriela AgNo ratings yet
- Asilo, Rosette Justine D. BSN3Y1-2 NCMB312Document5 pagesAsilo, Rosette Justine D. BSN3Y1-2 NCMB312Rosette AsiloNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument3 pagesArthritisGlady mae LimNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyLizli LoredoNo ratings yet
- NCP Urinary RetentionDocument3 pagesNCP Urinary RetentionKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Chapter 36Document3 pagesChapter 36Samantha QuintoNo ratings yet
- Massive AscitesDocument12 pagesMassive Ascitesranitidin100% (1)
- 11.Dr. Manjunath AkkiDocument5 pages11.Dr. Manjunath Akkirashmi vNo ratings yet
- DrugstudyDocument7 pagesDrugstudyJames AbendanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Excess (Fve)Document1 pageFluid Volume Excess (Fve)Kathlene YuNo ratings yet
- Arterial Disease (Critical Limb Ischaemia)Document2 pagesArterial Disease (Critical Limb Ischaemia)dragtoss2No ratings yet
- CeprofloxacinDocument2 pagesCeprofloxacinGabby Robles PajeNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Leukemia PDFDocument7 pagesConcept Map Leukemia PDFDiane AbanillaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Leukemia PDFDocument7 pagesConcept Map Leukemia PDFMichael AmandyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyMaria Teresa VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Manuscript For Anemia: Abrina, Mary Lim, Maverick Malquesto, Aliana Maravilla, Dessa Roleda, Jonel Subejano, RaymartDocument21 pagesManuscript For Anemia: Abrina, Mary Lim, Maverick Malquesto, Aliana Maravilla, Dessa Roleda, Jonel Subejano, RaymartMaverick LimNo ratings yet
- Cardio FinalsDocument17 pagesCardio FinalsNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- (Ilmu Bedah) Akut AbdomenDocument162 pages(Ilmu Bedah) Akut AbdomenSri Ade YanaNo ratings yet
- CPG - ArthritisDocument34 pagesCPG - ArthritisJim Christian EllaserNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD)Document1 pageFluid Volume Deficit (FVD)Kathlene YuNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument2 pagesDrug Study FormMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis HipDocument4 pagesAvascular Necrosis HipVidyasagar ReddyNo ratings yet
- PP Exam 4: Everything That Is in Red Came From Test Your Knowledge!Document15 pagesPP Exam 4: Everything That Is in Red Came From Test Your Knowledge!netanya DoanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudypamelaideaNo ratings yet
- FINALS - MusculoskeletalDocument13 pagesFINALS - MusculoskeletalCrisanta Grace OpondaNo ratings yet
- 5-Troubles de La Motricité - Les ParalysiesDocument6 pages5-Troubles de La Motricité - Les Paralysiesanon_391445722100% (2)
- Sit and Be Fit Neuropathy Exercise GuideDocument8 pagesSit and Be Fit Neuropathy Exercise Guidefitnesadvice11 blogspot comNo ratings yet
- Coronary Arteries: Supervised by Department of Anatomy Jun 2020Document3 pagesCoronary Arteries: Supervised by Department of Anatomy Jun 2020ibrahim AlfrkahiNo ratings yet
- NREMT Study Guide ProjectDocument12 pagesNREMT Study Guide ProjectGabriel SionsNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Primary and Permanent TeethDocument15 pagesDifference Between Primary and Permanent TeetharthisaNo ratings yet
- Passed 5080-13-21MELCS Baguio Panahon Pagbibinata. Corrected EdtDocument31 pagesPassed 5080-13-21MELCS Baguio Panahon Pagbibinata. Corrected EdtChristopher David OlivaNo ratings yet
- Knowing Your Body: Conversation Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesKnowing Your Body: Conversation Cheat SheetClarisse Joyce GenerNo ratings yet
- Radiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDDocument75 pagesRadiological Imaging of Osteoarthritis.: DR/ Abd Allah Nazeer. MDKarthickNo ratings yet
- Diabetic NeuropathyDocument13 pagesDiabetic NeuropathyFatima MehboobNo ratings yet
- What Is Rectum - 3Document9 pagesWhat Is Rectum - 3Ela MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder ExercisesDocument7 pagesFrozen Shoulder ExercisesSumon PhysioNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lats & Upper BackDocument29 pages19 - Lats & Upper Backbreinfout fotos100% (1)
- Mechanism of Muscle ContractionDocument51 pagesMechanism of Muscle ContractionRizcky Naldy Eka Putra100% (1)
- Mcqs Nervuos SystemDocument4 pagesMcqs Nervuos Systemaslam jan100% (2)
- Airway ObstructionDocument32 pagesAirway ObstructionAmirrah LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Saladin: Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, Third Edition Front Matter Clinical EmphasisDocument3 pagesSaladin: Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function, Third Edition Front Matter Clinical EmphasisJelena PopovićNo ratings yet
- Anders Holtz MD PHD, Richard Levi MD PhD-Spinal Cord Injury (2010)Document328 pagesAnders Holtz MD PHD, Richard Levi MD PhD-Spinal Cord Injury (2010)Mikki MoriNo ratings yet
- Operative Treatment of Elbow Injuries PDFDocument169 pagesOperative Treatment of Elbow Injuries PDFBogdan SerbanNo ratings yet
- Prehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionDocument3 pagesPrehension, Mastication, and DeglutitionAnjelica Louise MartinNo ratings yet
- LS 2 - Human Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesLS 2 - Human Respiratory SystemAisha KassandraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Month 42 of Booty by Bret!: This Month Is A & PlanDocument15 pagesWelcome To Month 42 of Booty by Bret!: This Month Is A & Planolle3870No ratings yet
- Emergency Radiology - Dr. YantoDocument93 pagesEmergency Radiology - Dr. YantoLeonardus William KuswaraNo ratings yet
- Sci 9 Q1 Module 1Document22 pagesSci 9 Q1 Module 1John Merby GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Deep Pharyngeal Neuromuscular Stimulation Versus Thermal Gustatory Stimulation in Decreasing Length of Swallow Initiation and Improving Lingual Movements - Maria H WillisDocument54 pagesEffectiveness of Deep Pharyngeal Neuromuscular Stimulation Versus Thermal Gustatory Stimulation in Decreasing Length of Swallow Initiation and Improving Lingual Movements - Maria H WillisconstantineeliaNo ratings yet
- Ms Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Document4 pagesMs Word Notes - Template (May 2022)Jaycee Anne AregloNo ratings yet
- Cs 19 SolvedDocument4 pagesCs 19 SolvedgogoNo ratings yet
- Complications After Cosmetic Periocular Filler Prevention and ManagementDocument13 pagesComplications After Cosmetic Periocular Filler Prevention and ManagementBruna BassoNo ratings yet
- 0/36 Steps: Pistol Squat W/ Kettlebell PressDocument15 pages0/36 Steps: Pistol Squat W/ Kettlebell Pressoussama khelladi100% (1)
- Cranial Nerves - Function and Dysfunctions, 3E (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Document262 pagesCranial Nerves - Function and Dysfunctions, 3E (2010) (PDF) (UnitedVRG)Alvaro RivCalle87% (15)