Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem Lec
Uploaded by
Henry Quimba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesOriginal Title
biochem lec
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesBiochem Lec
Uploaded by
Henry QuimbaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Mod 6 – Act.
2
Answer the following questions:
1. What are the major structural features of monosaccharides?
- Simple sugars and their derivatives are classified as monosaccharides. They are the
fundamental carbohydrate units that are used to make more complicated molecules. Carbon
atoms with hydrogen atoms connected, at least one hydroxyl group, and either an aldehyde
(RCHO) or ketone (RCOR) group make up monosaccharides.
2. Why is glucose abundantly found in nature?
- Glucose is a simple sugar which molecular formula is C6H12O6. It is the source of energy for
microbes, plants, animal and human beings. It is also found in many polymers. In plant
glucose found in the form of starch. In microbes, animal, and animal it is found in the form
of glycogen. Since it's provides instant energy in the presence of oxygen without oxygen it
gives less energy. Since each and every organism required energy to do work so it is
compulsory for all so it is found in abundance.
3. What reduction and oxidation products are formed from monosaccharides?
4. What are the major structural features of disaccharides?
- A disaccharide's structure is quite similar to that of a monosaccharide. They also have a
functional group that could be an aldehyde or a ketone, as well as several hydroxyl groups.
The main difference is that the two molecules are connected by a glycosidic bridge.
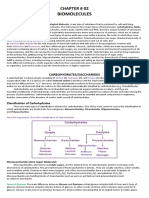
5. What are the differences in the polysaccharides cellulose, starch and glycogen?
- The key distinction between starch, cellulose, and glycogen is that starch is the primary
storage carbohydrate in plants, cellulose is the primary structural component of plant cell
walls, and glycogen is the primary storage carbohydrate energy source in fungi and animals.
6. Give examples of some carbohydrate derivatives that contain amino groups, amides, or
carbohydrate anions
Examples of carbohydrate derivatives that contain amino groups are:
Examples of carbohydrate derivatives that contain amides are:
Examples of carbohydrate anions are:
7. What role do carbohydrates play in determining blood type?
- All people do synthesize a carbohydrate, called the H antigen which is a precursor
carbohydrate, which is attached to lipids or proteins on the outer surface of red blood cells.
Specific enzymes synthesized by the ABO genes attach additional monosaccharides to the H
antigen, and the completed carbohydrate determines that person's blood type.
You might also like
- Amino AcidDocument69 pagesAmino AcidTasmih Rob MowNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Gen Bio 1 Module Final BioMoleculesDocument8 pagesGen Bio 1 Module Final BioMoleculesKristine GraceNo ratings yet
- Kozmeti̇k Kremleri̇ Full YapimDocument63 pagesKozmeti̇k Kremleri̇ Full YapimFeride Elif Ertürk100% (1)
- MacromoleculesDocument91 pagesMacromoleculesSabali NewtonNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4Document11 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Rona Grace MartinezNo ratings yet
- MarineLINE 784 Cargo Resistance ListDocument92 pagesMarineLINE 784 Cargo Resistance ListTimmyJuriNo ratings yet
- Mind Map (Hydrocarbons)Document3 pagesMind Map (Hydrocarbons)Meenakshi NairNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesJohn Brylle UrsuaNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemDocument15 pagesGeneral and Specific Test For Carbohydrates BioChemwynNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week3Document4 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week3Edison Caringal0% (1)
- General Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q1 Week 7 BiomoleculesJohn Brylle UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds: CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesOrganic Compounds: CarbohydratesDhimas MahardhikaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument11 pagesBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument19 pagesBiochemistryUsman AliNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES - WPS OfficeDocument8 pagesCARBOHYDRATES - WPS OfficeSophia ManzanoNo ratings yet
- STB 111 Lecture Three Note 2012Document20 pagesSTB 111 Lecture Three Note 2012Musa HussainNo ratings yet
- Vizcarra, Alyssa Marie D. APSY 1-3Document5 pagesVizcarra, Alyssa Marie D. APSY 1-3ALYSSA MARIE VIZCARRANo ratings yet
- Biochem Research - JaurigueDocument7 pagesBiochem Research - JauriguePauline Yvonne JaurigueNo ratings yet
- Biology Remedial - 2Document54 pagesBiology Remedial - 2Rediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument23 pagesCARBOHYDRATESClassen Mudenda KundaNo ratings yet
- Biotech Reviewer PDFDocument31 pagesBiotech Reviewer PDFGerald LimNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesKey Concepts CarbohydratesJaspreet GillNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Biomolecules ReviewerDocument15 pagesLesson 3 Biomolecules Reviewerjohnromar VilasNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology PorjectDocument27 pagesBiotechnology PorjectAnsh yadavNo ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact3Document4 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact3Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 W 6-8Document38 pagesGeneral Biology 1 W 6-8Emily Munsad AntolijaoNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living FormsDocument6 pagesModule 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living Formsmpstme placementNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument12 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFharshNo ratings yet
- Lapres GlukosaDocument49 pagesLapres GlukosaGayatri DewiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On BiomoleculesDocument28 pagesChemistry Project On BiomoleculesGAMING WITH TGK YTNo ratings yet
- Structure of Carbohydrates FinalDocument8 pagesStructure of Carbohydrates FinalAnonymous KeHF7wbhFNo ratings yet
- Lapres Glukosa PDFDocument47 pagesLapres Glukosa PDFGayatri DewiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six, GeneticsDocument10 pagesChapter Six, GeneticsHashim GhazoNo ratings yet
- Use of Macromolecules and Micromolecules For Human Body: AssignmentDocument10 pagesUse of Macromolecules and Micromolecules For Human Body: AssignmentSwastu Nurul AzizahNo ratings yet
- Dicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsDocument3 pagesDicussion Forum: Carbohydrates ProteinsKim Angelo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 pagesBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesCarbohydratesSHIFA ALTAFNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 5 & 6. Function of CarbohydratesDocument25 pagesLecture No 5 & 6. Function of Carbohydratesmaryam khanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument11 pagesCarbohydrates Notesaliasger786inNo ratings yet
- Mono Sac Cha RidesDocument11 pagesMono Sac Cha RidesMD JAHEDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Physci Q1 Week4 2023Document7 pagesPhysci Q1 Week4 2023MIKU ChanNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY Module 7-9Document32 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY Module 7-9Madelyn PeraltaNo ratings yet
- What Is A CarbohydrateDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Carbohydrateai4138769No ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesBiological MacromoleculesHabiba AmrNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates Biochemsaythename.smmaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 4 - v2Document21 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Q3 Week 4 - v2Evangelyn Patatag-CatacutanNo ratings yet
- What Are The Properties of CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesWhat Are The Properties of CarbohydratesRondel ForjesNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument4 pagesCARBOHYDRATESAfaqNo ratings yet
- Building Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Document12 pagesBuilding Blocks of Life (Carbs To Glycosidic)Chris Francis Cia100% (1)
- How Are Biomolecules Different Than Regular Molecules?: EOB-Tutorial 3 Harsh PittrodaDocument3 pagesHow Are Biomolecules Different Than Regular Molecules?: EOB-Tutorial 3 Harsh PittrodaharshNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument41 pagesCARBOHYDRATESLorine LowrioNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4: The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesLESSON 4: The Structure and Function of Large Biological MoleculesArabela LendioNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Its UsesDocument20 pagesBiomolecules and Its UsesRajendra Swarnakar25% (4)
- Bio 12 AModule 5Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 5Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates and LipidsJasmin RIshel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Module 1.01MC BiochemDocument6 pagesModule 1.01MC BiochemCesar L. Laspiñas IIINo ratings yet
- Carbo HyDocument10 pagesCarbo HyLyka Joy RedobleNo ratings yet
- Hussin Princess Farah P. NURBIO LECDocument5 pagesHussin Princess Farah P. NURBIO LECprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- Handout On MacromoleculesDocument18 pagesHandout On MacromoleculesAshloveNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - BiomacromoleculesWafaaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Molecular Biology IDocument26 pagesLecture Molecular Biology ImartinmulingeNo ratings yet
- Biomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesBiomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)JoshRobertD.ObaobNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1Document44 pagesCh. 1EmilyNo ratings yet
- Post Test Cyto Mod 3Document6 pagesPost Test Cyto Mod 3Henry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Art Appre ReviewerDocument3 pagesArt Appre ReviewerHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Intro-Mod 6.Document1 pageIntro-Mod 6.Henry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Summative Assessment: ResourcesDocument1 pageSummative Assessment: ResourcesHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnDocument3 pagesClinical Chemistry Lecture KayzardnHenry QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Oshareg2 PDFDocument548 pagesOshareg2 PDFGustavo FeisbukeroNo ratings yet
- KLK Oleo EHP EstersDocument1 pageKLK Oleo EHP EstersVandewalleNo ratings yet
- Properties of An Extracellular Protease of Bacillus Megaterium DSM 319 As Depilating Aid of HidesDocument6 pagesProperties of An Extracellular Protease of Bacillus Megaterium DSM 319 As Depilating Aid of HidesSarah Fitriani MuzwarNo ratings yet
- Of Bacterial Cellulose Composites: A Multipurpose Advanced MaterialDocument14 pagesOf Bacterial Cellulose Composites: A Multipurpose Advanced MaterialRuxandra BadiuNo ratings yet
- Us5098778 PDFDocument7 pagesUs5098778 PDFAl Saraaf MohammedNo ratings yet
- Bs en 50525 2 11 BasecDocument2 pagesBs en 50525 2 11 BasecMOHAMMED. HAKAMI100% (1)
- Reliable Hydraulic System OperationDocument18 pagesReliable Hydraulic System OperationArslan ILServices100% (1)
- Alkyl Sulfinates Radical Precursors Enabling Drug DiscoveryDocument27 pagesAlkyl Sulfinates Radical Precursors Enabling Drug DiscoverySơn Nguyễn KimNo ratings yet
- Santol As An Alternative FertilizerDocument10 pagesSantol As An Alternative FertilizerJanica SantosNo ratings yet
- Hilirisasi Hasil RisetDocument25 pagesHilirisasi Hasil RisetBambang NurhadiNo ratings yet
- HF-4760 (BL) : Product Data SheetDocument2 pagesHF-4760 (BL) : Product Data SheetCarito LopezNo ratings yet
- Erection Welding and Lamination of Plastic Pipelines UN 9253-07Document8 pagesErection Welding and Lamination of Plastic Pipelines UN 9253-07Ahmed GomaaNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Investigation of The Space Dust CollectedDocument8 pagesMicrobiological Investigation of The Space Dust CollectedLuisa González BautistaNo ratings yet
- Frank Adu Asante Full ThesisDocument232 pagesFrank Adu Asante Full ThesisRandy FrankNo ratings yet
- 'Alcohols Oralkanols: I I I " I I IDocument97 pages'Alcohols Oralkanols: I I I " I I Inazli meerahNo ratings yet
- Ecology MCQ بيئة وتلوثDocument19 pagesEcology MCQ بيئة وتلوثAli AliNo ratings yet
- Aaravee Ketheeswaran - SCH4U Full Naming Practice PDFDocument8 pagesAaravee Ketheeswaran - SCH4U Full Naming Practice PDFAaravee KNo ratings yet
- HM 11Document51 pagesHM 11body fayezNo ratings yet
- C-Bacterial Metabolism-Springer-Verlag New York (1986)Document370 pagesC-Bacterial Metabolism-Springer-Verlag New York (1986)xuantra100% (1)
- Qd18024-1 - Cosmética - FFDocument2 pagesQd18024-1 - Cosmética - FFAntonio Perez MolinaNo ratings yet
- Dowanol DPNBDocument2 pagesDowanol DPNBpkh29No ratings yet
- 2004 - Rivero - Influence of Compost On Soil Organic Matter Quality Under Tropicl ConditionsDocument7 pages2004 - Rivero - Influence of Compost On Soil Organic Matter Quality Under Tropicl Conditionsreii420No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2B: Organic Chemistry: Session: 3 YEAR: 2020 0.5 Standard UnitDocument2 pagesChemistry Unit 2B: Organic Chemistry: Session: 3 YEAR: 2020 0.5 Standard UnitSreeya DasNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 SolutionsDocument49 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 SolutionsNirvan JainNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2018 FINAL Memo Eng.Document9 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2018 FINAL Memo Eng.Khanyisani MnisiNo ratings yet
- OpainstructionDocument2 pagesOpainstructionDipali SolankiNo ratings yet