Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Glossary
Uploaded by
Aurora Quijada0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesDNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged in a double helix capable of self-replication and encoding RNA synthesis. Amino acids are the subunits that form proteins, differing in their composition. Starch is a food storage substance in plants. Hallucinogens produce hallucinations. Amplification is an increase in copies of a specific DNA fragment. Anabolism forms complex substances from simpler ones. Antibodies produced by B cells combine with antigens to inactivate foreign substances. Antigens initiate antibody production. RNA consists of a polynucleotide chain with a ribose sugar, phosphate group and nitrogenous bases. ATP is the main energy storage molecule in cells. Autotrophs synt
Original Description:
Original Title
BIOLOGY GLOSSARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged in a double helix capable of self-replication and encoding RNA synthesis. Amino acids are the subunits that form proteins, differing in their composition. Starch is a food storage substance in plants. Hallucinogens produce hallucinations. Amplification is an increase in copies of a specific DNA fragment. Anabolism forms complex substances from simpler ones. Antibodies produced by B cells combine with antigens to inactivate foreign substances. Antigens initiate antibody production. RNA consists of a polynucleotide chain with a ribose sugar, phosphate group and nitrogenous bases. ATP is the main energy storage molecule in cells. Autotrophs synt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesBiology Glossary
Uploaded by
Aurora QuijadaDNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged in a double helix capable of self-replication and encoding RNA synthesis. Amino acids are the subunits that form proteins, differing in their composition. Starch is a food storage substance in plants. Hallucinogens produce hallucinations. Amplification is an increase in copies of a specific DNA fragment. Anabolism forms complex substances from simpler ones. Antibodies produced by B cells combine with antigens to inactivate foreign substances. Antigens initiate antibody production. RNA consists of a polynucleotide chain with a ribose sugar, phosphate group and nitrogenous bases. ATP is the main energy storage molecule in cells. Autotrophs synt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
1.
DNA: A nucleic acid composed of two polynucleotide chains arranged
around a central axis forming a double helix, capable of self-replication
and encoding the synthesis of RNA.
* DNA contains genetic instructions*
2. Amino acids: The subunits (monomers) that form proteins (polymers).
Each amino acid possesses at least one amino (basic) functional group and
one carboxyl (acidic) functional group and differs from other amino acids
by the composition of its.
* During intestinal absorption, glucose and amino acids pass
into the blood, while fats pass into the lymph. *
3. Starch: Food storage substance of plants.
* Potatoes contain starch*
4. Hallucinogen: Substance capable of producing hallucinations.
* Hallucinogenic mushrooms exist*
5. Amplification: An increase in the number of copies of a specific DNA
fragment.
* Gene or DNA Amplification is the increase in the number of
copies of a particular DNA fragment. *
6. Anabolism: In an organism, the set of biosynthetic reactions, that is,
reactions in which small molecules form larger molecules.
*Anabolism forms a complex substance from simpler substances,
either organic or inorganic. *
7. Antibodies: Proteins produced by cells of the immune system (B
lymphocytes) that combine specifically with molecules foreign to the
organism (antigens) in order to inactivate them.
*The immune system detects the antigens and produces
antibodies that destroy the substances that contain them. *
8. Antigens: Molecules, generally foreign to the receptor organism, that
initiate the production of antibodies, generally proteins or combinations
of proteins with polysaccharides.
*An antigen can be a foreign substance from the environment,
such as chemicals, bacteria, viruses or pollen. *
9. RNA (ribonucleic acid): Nucleic acid consisting of a polynucleotide
chain. Its nucleotide consists of a molecule of the sugar ribose, a phosphate
group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, uracil, cytosine and
guanine.
*The main cellular RNAs are messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA and
transfer RNA. *
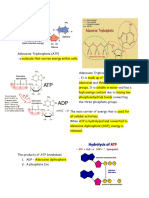
10. ATP (adenosine triphosphate): The main chemical used by living
systems to store energy, it consists of a base (adenine) linked to a sugar
(ribose) and three phosphates.
*ATP is a nucleotide that is fundamental in obtaining cellular
energy. *
11. Autotrophs: Term used to name organisms that synthesize their own
nutrients from inorganic raw materials.
*Autotrophic organisms obtain their energy through
photosynthesis. *
12. Catalyst: A substance that decreases the activation energy of a chemical
reaction, accelerating the rate of the reaction.
*Catalysis is the process by which the rate of a chemical reaction
is increased. *
13. Cell: The smallest structural unit of living things capable of functioning
independently.
*The three main parts of the cell are the cell membrane, the
nucleus and the cytoplasm. *
14. Double helix: The shape that the two strands of DNA take when they
are joined together.
*The double helix shape is basically the way all life forms are
connected to each other. *
15. Enzyme: Protein molecule that acts as a catalyst in biochemical
reactions.
*The enzyme acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions,
accelerating the rate of reaction. *
You might also like
- Characteristics of Life. PP PDFDocument45 pagesCharacteristics of Life. PP PDFPaige-MorganNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Worksheet Answers - OdtDocument4 pagesMacromolecules - Worksheet Answers - OdtRachel JimenezNo ratings yet
- 18 Dna Structure and Replication-SDocument5 pages18 Dna Structure and Replication-Sapi-2623786400% (2)
- Biology Final Exam Study Guide (FULL)Document18 pagesBiology Final Exam Study Guide (FULL)MandsNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Concepts For OCR (A) Biology A-Level: Topic 2 - Foundations in BiologyDocument13 pagesDefinitions and Concepts For OCR (A) Biology A-Level: Topic 2 - Foundations in Biologywarrior girlNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES Lesson 2Document3 pagesBIOMOLECULES Lesson 2Mekka Mae Taday JunasaNo ratings yet
- Biology Fall Final ReviewDocument5 pagesBiology Fall Final ReviewtaemintNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab ListsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab ListschereewhaleNo ratings yet
- Biology Test Review 9/12: Vamsi Kotta Miss Nyberg 5th BlockDocument4 pagesBiology Test Review 9/12: Vamsi Kotta Miss Nyberg 5th BlockVamsi KottaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 by TGDocument61 pagesChapter 1 by TGyonas solomonNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1 BiochemistryDocument28 pagesLecture No 1 Biochemistryw777yyd9k4No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry: Asma Ali Shaheen Department of BiochemistryDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry: Asma Ali Shaheen Department of BiochemistryFarah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesFaith SNNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsDocument6 pagesMacromolecules - Are Large Molecules Composed of Thousands of Covalently Connected AtomsBon Joey BernestoNo ratings yet
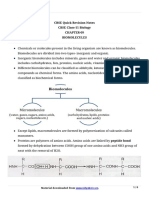
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesHARSH PahwaNo ratings yet
- Description of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesDescription of Cell Structure and FunctionAin SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 3Document4 pagesLab Assignment 3Darcelle PaulNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Free RadicalsDocument37 pagesCell Structure & Free RadicalsSAMANTHA WHITTAKERNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Reference NotesDocument5 pagesCell Biology Reference NotesAnirudh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BMS 204 Introduction To Biochemistry: Dr. Reem Arafa Prof. of Biomedical SciencesDocument36 pagesBMS 204 Introduction To Biochemistry: Dr. Reem Arafa Prof. of Biomedical SciencesRamy El-HadadNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument1 pageCell Biology Noteslog.pfoNo ratings yet
- 1.A Introduction To Biochemistry and LifeDocument29 pages1.A Introduction To Biochemistry and Lifepaulinebacomo10No ratings yet
- NCHEM Lecture Notes:: BiochemistryDocument8 pagesNCHEM Lecture Notes:: BiochemistryJoymae Olivares TamayoNo ratings yet
- Wa0004 PDFDocument39 pagesWa0004 PDFZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- The Cell Group 5Document10 pagesThe Cell Group 5Nyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its FunctionsDocument28 pagesThe Cell and Its Functionsأمال داودNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- Dr. Marhaen Hardjo, M.Biomed, PHD: Bagian Biokimia Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hasanuddin MakassarDocument63 pagesDr. Marhaen Hardjo, M.Biomed, PHD: Bagian Biokimia Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hasanuddin MakassarAn iNo ratings yet
- An IntroductionDocument21 pagesAn IntroductionOmar GardiNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Guide (Wheaton) Complete)Document7 pagesBiology Study Guide (Wheaton) Complete)Jireh HuangNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsDocument121 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsJoan Ano CaneteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument44 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryFrance Jan First SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument3 pagesBiology NotesSuraj ReddyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- BiolohiyaDocument3 pagesBiolohiyaapi-26570979No ratings yet
- What Is BiochemistryDocument11 pagesWhat Is BiochemistryBalangat Regine L.No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Molecular BiologyDocument140 pagesTopic 2 - Molecular BiologyyourstrulyrahulNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Document10 pagesBio 101 - Integrated Principles of Zoology 18th Edition (Summary of Chapter 2)Kaeya's asscheeksNo ratings yet
- Science Biology AssignmentDocument4 pagesScience Biology AssignmentFunny Videos of all TimeNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaDocument3 pagesActivity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Bio Long NoteDocument12 pagesBio Long Notejacob guerreroNo ratings yet
- Science 1-3-1Document46 pagesScience 1-3-1Cesareann A RamosNo ratings yet
- Science Test 1Document2 pagesScience Test 1PranayaNo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument4 pagesBiology Cellssarmientoangelica672No ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument10 pagesBio ReviewerPau VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument5 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBNo ratings yet
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesabhiNo ratings yet
- WK 4Document5 pagesWK 4kathleen D.No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Classification and StructurDocument4 pagesBiomolecules Classification and StructurChristine Ainah Pahilagao SalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Types VocabDocument2 pagesCell Types Vocabauqa reefieNo ratings yet
- UPDATED Annotated Cell DiagramDocument3 pagesUPDATED Annotated Cell DiagramJ pNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7AlexandraNo ratings yet
- 2 6 Bilogical MoleculesDocument36 pages2 6 Bilogical Moleculesıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument10 pagesHuman BodyTurky TurkyNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam For Biochem (Student Nurses)Document2 pagesSample Exam For Biochem (Student Nurses)nicoNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument14 pagesBioenergeticsmunozayshiaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Arevalo, Dela Cruz, SullaDocument14 pagesGroup 4 - Arevalo, Dela Cruz, SullaArchan Dom ReyesNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology (Zeb 361)Document7 pagesMolecular Biology (Zeb 361)Jacob WalterNo ratings yet
- MHT Cet 2009 BiologyDocument5 pagesMHT Cet 2009 BiologyATHARVA AyurvedaNo ratings yet
- Kim, Minjung Bioen 315 Last HomeworkDocument5 pagesKim, Minjung Bioen 315 Last Homeworkapi-281990237No ratings yet
- Strawberry DNA Extraction: Objective: The Purpose of This Activity Is To Become Familiar With Lab Procedures ForDocument3 pagesStrawberry DNA Extraction: Objective: The Purpose of This Activity Is To Become Familiar With Lab Procedures ForWarner PalpallatocNo ratings yet
- SSR PrimersDocument53 pagesSSR PrimersAlamgir HossainNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Document7 pagesExercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Azyrah Lyren Seguban UlpindoNo ratings yet
- NBP Planner - NEET-2022Document21 pagesNBP Planner - NEET-2022Mruthyun120% (1)
- Biologi MolekulerDocument58 pagesBiologi MolekulerNanda SapitriNo ratings yet
- SG50 Singapores Scientific PioneersDocument63 pagesSG50 Singapores Scientific PioneerszeewonkaNo ratings yet
- Science Adh8615Document13 pagesScience Adh8615bobzlzhuNo ratings yet
- Biology AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Answershari shankar singh100% (1)
- Microbiology Test For Examanswer by Assel MaamDocument157 pagesMicrobiology Test For Examanswer by Assel MaamAMAN SINGHNo ratings yet
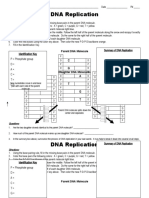
- DNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDocument4 pagesDNA Replication: C G A T G T Identification Key P Phosphate Group D A C T GDanielle DavisNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 10 I. ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Science 10 I. ObjectivesGiovani CalivaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 2nd YearDocument2 pagesQuestion Paper 2nd YearRay MrinalNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument17 pagesModule 6 - Prokaryotes and EukaryotesKimberly CelisNo ratings yet
- 1985 - Giles - Maternal Lineage mtDNADocument5 pages1985 - Giles - Maternal Lineage mtDNAMallory CandlerNo ratings yet
- BIO110-Biotechnology Interactive AssignmentDocument2 pagesBIO110-Biotechnology Interactive AssignmentLeah Edgerton100% (1)
- Activity For Grade 9 RubbyDocument5 pagesActivity For Grade 9 RubbyJocelyn Petallar BalasuelaNo ratings yet
- DNA Complete The DrawingDocument2 pagesDNA Complete The DrawingMariana Cecilia Isola MarinNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology LectureDocument50 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology LectureJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- DNA Microarray Technology 1Document5 pagesDNA Microarray Technology 1NoorNo ratings yet
- Applied Genetics Questions PDFDocument2 pagesApplied Genetics Questions PDFMARK DEFREITASNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - PPT Slides 2022Document59 pagesChapter 13 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance - PPT Slides 2022aruzhan begaliyevaNo ratings yet
- Taqman Probe Design Guidelines - May 2018Document5 pagesTaqman Probe Design Guidelines - May 2018AviNo ratings yet
- Protein SysthesisDocument47 pagesProtein SysthesisPrincess Camille SorianoNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified Foods - Boon or BaneDocument6 pagesGenetically Modified Foods - Boon or BaneushapvermaNo ratings yet
- Primer3 Input Help: Start, Length Start Length Start, LengthDocument2 pagesPrimer3 Input Help: Start, Length Start Length Start, LengthDiki Rizzal FauziNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Ms - Tasneem RababahDocument15 pagesDNA Replication: Ms - Tasneem Rababahzakaria AlshurmanNo ratings yet
- @MedicalBooksStoreS 2018 Pre Clinical PDFDocument243 pages@MedicalBooksStoreS 2018 Pre Clinical PDFahmed saadNo ratings yet