Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab Lists
Uploaded by
chereewhale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesOriginal Title
IGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure vocab lists (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesIGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab Lists
Uploaded by
chereewhaleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
IGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure vocab lists:
p.4~p.11
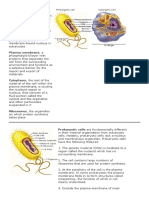
1. **Cell**: The basic structural and functional unit of living organisms.
2. **Cytoplasm**: The jelly-like substance inside the cell, where organelles are
suspended.
3. **Organelles**: Specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions.
4. **Nucleus**: The central part of a cell that contains genetic material (DNA) and
controls cell activities.
5. **Chromosomes**: Thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins, carrying
genetic information.
6. **Genes**: Units of heredity, composed of DNA, that determine traits and are passed
from parents to offspring.
7. **Enzymes**: Biological molecules that speed up chemical reactions in cells.
8. **Cell membrane**: A semi-permeable barrier surrounding the cell, controlling the
movement of substances in and out.
9. **Partially permeable**: Allowing some substances to pass through while blocking
others.
10. **Selectively permeable**: Allowing only certain substances to pass through.
11. **Endoplasmic reticulum**: A network of membranes within the cell involved in
protein and lipid synthesis.
12. **Ribosomes**: Cellular structures where proteins are synthesized.
13. **mRNA (Messenger RNA)**: A type of RNA that carries genetic information from
DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
14. **tRNA (Transfer RNA)**: A type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosomes
during protein synthesis.
15. **rRNA (Ribosomal RNA)**: RNA molecules that form the structural and functional
components of ribosomes.
16. **Transcription**: The process of copying DNA into mRNA.
17. **Translation**: The process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA at the ribosomes.
18. **Protein synthesis**: The process of building proteins from amino acids, involving
transcription and translation.
19. **DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)**: The molecule carrying genetic instructions for
the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms.
20. **RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)**: A nucleic acid molecule involved in various cellular
processes, including protein synthesis.
21. **Codons**: Three nucleotide sequences on mRNA that specify a particular amino
acid during protein synthesis.
22. **Anticodons**: Three-nucleotide sequences on tRNA that complement codons on
mRNA during protein synthesis.
23. **Mutation**: A change in the DNA sequence.
24. **Gene mutation**: A mutation that affects a single gene.
25. **Substitution**: A type of mutation where one nucleotide is replaced by another.
26. **Inversion**: A type of mutation where a segment of DNA is reversed.
27. **Deletions**: A type of mutation where a segment of DNA is lost.
28. **Duplication**: A type of mutation where a segment of DNA is copied.
29. **Gametes**: Reproductive cells (sperm and egg) that carry genetic information to
the next generation.
30. **Polypeptide**: Chain of amino acids, beginning of the protein molecule
You might also like
- Biology Cell Structure1Document2 pagesBiology Cell Structure1klabnik.matejNo ratings yet
- Biology GlossaryDocument6 pagesBiology GlossaryAurora QuijadaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cell Division With MitochondriaDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Cell Division With Mitochondriasabrinabari mohona35No ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsnightcg090No ratings yet
- BiolohiyaDocument3 pagesBiolohiyaapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of BacteriumDocument2 pagesParts and Functions of BacteriumJames Carlo Angelo SaloNo ratings yet
- Essay 485833Document3 pagesEssay 485833machitidzenanikoNo ratings yet
- BIO1 The CellDocument52 pagesBIO1 The CellSeth MotaNo ratings yet
- Histology With AnsDocument166 pagesHistology With AnsAlok Kumar0% (1)
- 2Document2 pages28ib7zlrsyNo ratings yet
- Mastering Cell Biology - A Comprehensive Guide To Terminologies and Concepts For Arizona State University Students (ASU)Document3 pagesMastering Cell Biology - A Comprehensive Guide To Terminologies and Concepts For Arizona State University Students (ASU)Ma. Salvacion BaongNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoyDocument15 pagesCell Biology Lecture #3: Cell Biology Is An Interesting Subject So EnjoySaleh HalasahNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Electron Images of OrganellesDocument10 pagesElectron Images of OrganellesflyinpiggyzzNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells IDocument3 pagesAnimal Cells Irandomscribduser2012No ratings yet
- Cytology The: CellsDocument43 pagesCytology The: CellsJuno SangalangNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- Biyoloji IngilizceDocument21 pagesBiyoloji Ingilizced46smsfpwcNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Eukaryotes: J.Daphne Joy Kiruba B.SC Microbiology 1 YearDaphne joy kiruba.J Micro INo ratings yet
- Description of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesDescription of Cell Structure and FunctionAin SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Quiz1Document6 pagesAnaphy Quiz1Elmer AlexandrewNo ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- The Cell Group 5Document10 pagesThe Cell Group 5Nyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures: The BasicsDocument4 pagesCell Structures: The BasicsParama CinthyaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 P2 Questions Ulrastructure of CellsDocument4 pages1.2 P2 Questions Ulrastructure of CellsMariamNo ratings yet
- Cells QSDocument6 pagesCells QSPessimus KidNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument1 pageBiology Class NotesRuh MattNo ratings yet
- Biology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and ImplicationsDocument19 pagesBiology Review: 1° Central Dogma of Molecular Biology and Implicationsdjxela89No ratings yet
- Physiology of Cell PDocument11 pagesPhysiology of Cell Psabita bhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Cytology - 1Document13 pagesCytology - 1Sumayya KabeerNo ratings yet
- Final Bio VivaDocument49 pagesFinal Bio Vivamanuel ortegaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Function ReviewDocument8 pagesCell Structure & Function Reviewtessajoys50% (2)
- Cell Classification and Composition: Prokaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesCell Classification and Composition: Prokaryotic CellsmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- SMK Jalan Tasek Minggu Sains Dan Matematik Cell Structure and Function CrosswordDocument3 pagesSMK Jalan Tasek Minggu Sains Dan Matematik Cell Structure and Function CrosswordMusliza Rashid Noir IpohNo ratings yet
- Basic Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesBasic Cell Structure & FunctionJawaad AsifNo ratings yet
- 05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Document33 pages05 - Kompart Sorting Protein 1Haddhi WhibowoNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Topic 2 Hand OutDocument14 pagesCytogenetics Topic 2 Hand OutJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument20 pagesNotesUday Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Teacher NotesDocument21 pages4 4 Teacher Notesapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Quiz#1 GenBioDocument1 pageQuiz#1 GenBioHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Pbe Module 1Document38 pagesPbe Module 1MythriNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Document31 pages1.3. Components of The Cell IISubcellular Organelles 070141Angel CaroNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Concepts For OCR (A) Biology A-Level: Topic 2 - Foundations in BiologyDocument13 pagesDefinitions and Concepts For OCR (A) Biology A-Level: Topic 2 - Foundations in Biologywarrior girlNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BiologyDocument48 pagesUnit 3 BiologyefiNo ratings yet
- 04 Structure To FunctionDocument5 pages04 Structure To Function897291868100% (1)
- Cells The Building Blocks of Life - Learning MaterialDocument12 pagesCells The Building Blocks of Life - Learning MaterialRaven BerzabalNo ratings yet
- F4BioC2 Terms Chap 2 - 7 (Space)Document4 pagesF4BioC2 Terms Chap 2 - 7 (Space)CKNo ratings yet
- TR-1 BioenglishDocument11 pagesTR-1 BioenglishReza maulana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- 2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)Document7 pages2-2 - Components and Functions (IB Biology SL)rastete195No ratings yet
- Cellbiologyreview AnswersDocument8 pagesCellbiologyreview AnswersCARLISABEL GALLARDONo ratings yet
- APCellsDocument36 pagesAPCellsAsif Raza SoomroNo ratings yet
- What Is Plants?Document46 pagesWhat Is Plants?Genelie Abuzo CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- K.2-4 Organisasi SelDocument82 pagesK.2-4 Organisasi SelSamuel Assan SiraitNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument1 pageCell Biology Noteslog.pfoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterJoyce Jimenez0% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I II and III 1st Edition Pearson Services Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I II and III 1st Edition Pearson Services Test Bank PDFmichaelcalhounjtypaegbnk100% (11)
- Revised Lab ManualDocument43 pagesRevised Lab ManualLan AnhNo ratings yet
- HEX PG SyllabusDocument124 pagesHEX PG SyllabusJegadeesan MuniandiNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Purification NotesDocument23 pagesEnzyme Purification NotesMadan Rajan100% (1)
- Understandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)Document9 pagesUnderstandings, Applications and Skills (This Is What You Maybe Assessed On)percivalNo ratings yet
- Heat Generated by Dental Implant Drills During Osteotomy - A Review-SKumarMishraDocument13 pagesHeat Generated by Dental Implant Drills During Osteotomy - A Review-SKumarMishraanilsamuel0077418No ratings yet
- Exercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Document7 pagesExercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Azyrah Lyren Seguban UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Concentration and Purification of Whey Proteins by Ultrafiltration - Baldasso Et Al. (2011) PDFDocument6 pagesConcentration and Purification of Whey Proteins by Ultrafiltration - Baldasso Et Al. (2011) PDFdrycamfm100% (2)
- JWT Mock Series 2Document12 pagesJWT Mock Series 2arfa wainceNo ratings yet
- Graded Levels of Moringa Leaf Meal On Haematological - Golden Leash Pet ProductsDocument10 pagesGraded Levels of Moringa Leaf Meal On Haematological - Golden Leash Pet ProductsGolden Leash Pet ProductsNo ratings yet
- Synthetic BiologyDocument64 pagesSynthetic BiologyTaufik RizkiandiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Protein Folding: James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008Document40 pagesLecture 7 Protein Folding: James Chou BCMP201 Spring 2008KaramSoftNo ratings yet
- In-Vitro Interaction of Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument5 pagesIn-Vitro Interaction of Verapamil HydrochlorideIrfan N KhanNo ratings yet
- Practical Methods in Biochemistry 521Document3 pagesPractical Methods in Biochemistry 521Dawlat SalamaNo ratings yet
- The MOR (Mu Opioid Receptor) and FLNA (Filamin A)Document28 pagesThe MOR (Mu Opioid Receptor) and FLNA (Filamin A)lara gay villaruzNo ratings yet
- Viral Vector Production Process Intensification: Analytics, Automation, In-Line Testing and MoreDocument16 pagesViral Vector Production Process Intensification: Analytics, Automation, In-Line Testing and MoreAtrocitus RedNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument20 pagesMolecular BiologyDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology Concepts Applications PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument49 pagesEbook Biology Concepts Applications PDF Full Chapter PDFherman.griffin379100% (26)
- A Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.Document9 pagesA Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.muratout3447No ratings yet
- Biology For Engineers and Other Non-BiologistsDocument317 pagesBiology For Engineers and Other Non-Biologistsgopinadh reyyaNo ratings yet
- Illustrated DIY CRISPR - Freeze Dried DH5a Liquid PlasmidsDocument19 pagesIllustrated DIY CRISPR - Freeze Dried DH5a Liquid PlasmidsKevin LimNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Research: François Ferron, Etienne Decroly, Barbara Selisko, Bruno CanardDocument11 pagesAntiviral Research: François Ferron, Etienne Decroly, Barbara Selisko, Bruno CanardJose QuinteroNo ratings yet
- LSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Document116 pagesLSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Jojo LomoNo ratings yet
- 7.review On Strategies and Technologies For Exosome Isolation and Puri CationDocument18 pages7.review On Strategies and Technologies For Exosome Isolation and Puri Cationsnow silverNo ratings yet
- Food Technology: ObjectivesDocument194 pagesFood Technology: ObjectivesKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 50 ItemsDocument5 pagesBioscience 1 50 ItemsSANCHEZ JUAN CARLOS DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test BankDocument35 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell 5th Edition Alberts Test Bankinsuliteskinch4wjca100% (27)
- Protein Determination by The Lowry MethodDocument1 pageProtein Determination by The Lowry MethodTenzin TashiNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Biology Concepts and Investigations 3rd Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Biology Concepts and Investigations 3rd Edition Hoefnagels Solutions Manual PDFjunemojarrazqmxj100% (17)
- All Living Organisms Require Food To LiveDocument4 pagesAll Living Organisms Require Food To LiveVikash SharmaNo ratings yet