Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cells
Cells
Uploaded by
nightcg0900 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesCells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The main cell parts include the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Cells carry out essential functions like reproduction, energy production, protein synthesis, waste disposal, and transport. The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic functional unit of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
Original Description:
The overview and notes for the topic "cells"
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The main cell parts include the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Cells carry out essential functions like reproduction, energy production, protein synthesis, waste disposal, and transport. The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic functional unit of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesCells
Cells
Uploaded by
nightcg090Cells are the basic units of life and come in two main types - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The main cell parts include the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Cells carry out essential functions like reproduction, energy production, protein synthesis, waste disposal, and transport. The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic functional unit of life, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
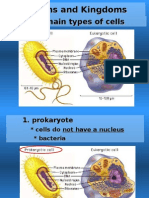
**Cell Types**:
- Prokaryotic cells: Simple, lacking a true nucleus (e.g., bacteria).
- Eukaryotic cells: Complex, with a true nucleus (e.g., animal and plant cells).
2. **Cell Structures**:
- **Cell Membrane**: Outer boundary, controls what enters and exits the cell.
- **Nucleus**: Contains DNA and controls cell activities.
- **Cytoplasm**: Gel-like substance where organelles are suspended.
- **Mitochondria**: Powerhouse of the cell, produces energy (ATP).
- **Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)**: Involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- **Golgi Apparatus**: Modifies and packages proteins for transport.
- **Ribosomes**: Site of protein synthesis.
- **Lysosomes**: Contain enzymes for breaking down waste materials.
- **Vacuoles**: Store water and other substances.
- **Chloroplasts** (in plant cells): Site of photosynthesis.
- **Cell Wall** (in plant cells): Provides structural support.
3. **Cell Functions**:
- Reproduction (cell division).
- Energy production.
- Protein synthesis.
- Waste disposal.
- Transport of molecules.
4. **Cell Theory**:
- All living things are composed of cells.
- The cell is the basic functional unit of life.
- All cells come from pre-existing cells.
5. **Specialized Cells**:
- Different cell types have specific functions (e.g., red blood cells, nerve cells, muscle cells).
6. **Cell Cycle**:
- The process of cell growth and division (interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis).
7. **Importance of Cells**:
- Cells are the building blocks of life and are essential for the survival of organisms.
You might also like
- Cells and Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCells and Cell Structureapi-238197463No ratings yet
- Cells As The Basis of Life 1Document40 pagesCells As The Basis of Life 1Singh Gurleen100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- OrganellesDocument13 pagesOrganellesjanaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument50 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsFarhan Rahman100% (1)
- Biology Cell Structure1Document2 pagesBiology Cell Structure1klabnik.matejNo ratings yet
- Biology Class NotesDocument1 pageBiology Class NotesRuh MattNo ratings yet
- BIO1 The CellDocument52 pagesBIO1 The CellSeth MotaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument1 pageCell Biology Noteslog.pfoNo ratings yet
- 7.2 WKBK KeyDocument13 pages7.2 WKBK KeyJohn WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Major: Pre-PharmacyDocument4 pagesMajor: Pre-PharmacyFatima Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Essay 485833Document3 pagesEssay 485833machitidzenanikoNo ratings yet
- Botany 2Document4 pagesBotany 2Hindreen ObaidNo ratings yet
- A Plant CellDocument3 pagesA Plant CellDurgadharshini 21X-214No ratings yet
- Draw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellDocument3 pagesDraw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellPratik SagarNo ratings yet
- Biology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesBiology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionAndre WelsNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesProkaryotic CellsalyssaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cell Division With MitochondriaDocument11 pagesAnatomy of Cell Division With Mitochondriasabrinabari mohona35No ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 - Chap1Document78 pagesBiology Sem1 - Chap1kotaknotaku100% (1)
- IGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab ListsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Human Bio Cell Structure Vocab ListschereewhaleNo ratings yet
- The Cell FinalDocument48 pagesThe Cell FinalJuliane Caniele IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of BacteriumDocument2 pagesParts and Functions of BacteriumJames Carlo Angelo SaloNo ratings yet
- A. Two Main Types of CellsDocument33 pagesA. Two Main Types of Cellsapi-239353579No ratings yet
- 1.2 P2 Questions Ulrastructure of CellsDocument4 pages1.2 P2 Questions Ulrastructure of CellsMariamNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM CellDocument11 pagesBIOCHEM CellErnesto Dasalla IIINo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEDocument3 pagesAnatomy Ans Physiology Cell Structures and Functions - LAB EXERCISEMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- BIO101Document27 pagesBIO101Ibraheem AribidesiNo ratings yet
- Cells - Fact FileDocument2 pagesCells - Fact FileAsma AbbasNo ratings yet
- Parts & Function of CellsDocument25 pagesParts & Function of CellsHariet ObieNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is The Basic StructuralDocument1 pageA Cell Is The Basic StructuralYomna OmerNo ratings yet
- 1.8: Eukaryotic Cells Maintain Internal Membranes That Partition The Cell Into Specialized Regions. 1. Cellular CompartmentalizationDocument5 pages1.8: Eukaryotic Cells Maintain Internal Membranes That Partition The Cell Into Specialized Regions. 1. Cellular Compartmentalizationapi-415920554No ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument37 pagesCell Structure & FunctionPen-pen Cubillan Aruyal AmbrayNo ratings yet
- Only Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The CytoplasmDocument14 pagesOnly Eukaryotic Cells Have A Nucleus. in Prokaryotic Cells, DNA Is Found in The Cytoplasmrakan ilyasNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument2 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYGerald SouribioNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its FunctionsDocument28 pagesThe Cell and Its Functionsأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Organelles in CellsDocument3 pagesOrganelles in CellsSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument41 pagesUnit 3 The Cellular Basis of LifeEbenezer AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Biology PresentationDocument10 pagesBiology Presentation24 Triệu Vũ Khánh NgânNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade 10 Science NotesDocument2 pagesSubject Grade 10 Science Notesjordan.shapiroNo ratings yet
- Unite 3 CellsDocument44 pagesUnite 3 CellsJo AnNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument26 pagesCell Structure Functionveeramani0% (1)
- Topic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsDocument56 pagesTopic 1.2 - Ultrastructure of CellsAhmed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument28 pagesCell StructureBANQUERIGO I.G. (2201427)No ratings yet
- CellsDocument19 pagesCellsAulia Safri NahriyahNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- K.2-4 Organisasi SelDocument82 pagesK.2-4 Organisasi SelSamuel Assan SiraitNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells Share Many Similarities.: Key ConceptDocument19 pagesEukaryotic Cells Share Many Similarities.: Key ConceptEman ShirriNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- History of CellsDocument14 pagesHistory of CellsKyla Ciara DamgasenNo ratings yet
- Science Biology AssignmentDocument4 pagesScience Biology AssignmentFunny Videos of all TimeNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionDocument3 pagesCell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionDocument3 pagesCell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Short Note of Biology Chapter 3&4Document138 pagesShort Note of Biology Chapter 3&4sami loveNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document27 pagesCH 01Mahmoud OradyNo ratings yet
- Cells & Organelles: Recommended Reading: Mader Chapter 4, Pages 60-84 Ebook Chapter LinkDocument33 pagesCells & Organelles: Recommended Reading: Mader Chapter 4, Pages 60-84 Ebook Chapter LinkTôn Thất HuyNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 1 Study GuideJohans MascardoNo ratings yet