Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Settlement and Urban Growth 15
Uploaded by
rebe fraxanetOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Settlement and Urban Growth 15
Uploaded by
rebe fraxanetCopyright:
Available Formats
URBAN SETTLEMENT AND URBAN GROWTH 15
1) READ PAGES 48 AND 49
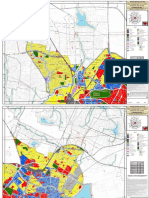
2) HAVE A LOOK AT FIGURE 3.35 (MAPS) AND RELATE THE TYPES OF HOUSING WITH
THE REFERENCES.
Old inner city area:
Many houses as possible were built in a small area; they were built in long
and straight rows and in terraces. There weren’t any open space or gardens
around it. Resulting there was high-density housing and overcrowded
population.
Inner city redevelopment:
Houses were built in huge high rise tower blocks, which were created on
the sites of the old terraced houses; these ones had most modern
amenities. There were lots of green and open space areas, between
houses and flats. There was still a very high housing density.
Suburbia:
Houses have front and back gardens, most of them have garages and bay
windows. Houses are spacious.
Outer city council estate:
There are many types of houses and flats, depending on the size and
accommodation.
3) HAVE A LOOK AT FIGURE 3.36 AND PROVIDE CHARACTERISTICS OF:
OLD INNER CITIES:
They were created because for factories workers.
There was a big demand for cheap housing, so builders constructed as
many houses as possible in a small area. They were built in long straight
rows and in terraces. Houses had few amenities indoor and outdoor.
There was high-density housing and overcrowded population.
INNER CITY REDEVELOPMENT:
Was created in the 1950s and 1960s.
Houses were built in huge high-rise blocks which were created on the
sites of the old terraced houses.
Houses have modern amenities.
There are open spaces and gardens between flats.
Very high housing density.
SUBURBIA:
It began with the introduction of the public transport and the
popularity of private car.
Houses were built in the outer suburbs before The Second World War.
Houses are characterized by front and back gardens, garages, bay
windows, by being well planned and spacious.
OUTER CITY COUNCIL ESTATE:
Was created in the 1950s and 1960s.
Houses have single-storey, with gardens and car parking space.
They vary by the type and size of accommodation.
4) DO EXERCISE 7 ON PAGE 56
A-
i- For map 1 below, suggest the type of houses and age of houses.
Nineteenth-century houses.
Long straight rows and terraces.
Old inner city areas.
Low-quality houses.
ii- For map 2, suggest the type of houses and the age of houses.
1920s and 1930s houses.
Semidetached houses.
Suburbia.
High-quality houses.
iii- Which of the two areas has more:
Gardens: map 2.
Car parking: map 2.
Places of work: map 1.
Open space: map 2.
Residents?: map 1.
B-
First area Second area
Named example Old inner city area Suburbia
Location in city Inner areas Outer suburbs
Type, appearance, age of - Built in long, straight - Semi-detached.
housing rows and in terraces. - Bay windows.
- Few amenities - Back and front
indoor and outdoor. gardens.
- 19ᵀᴴ century - Garages.
terraces. - 2 floors.
- 1920s and 1930s
houses.
- Spacious.
2 main types of - Industries. - Housing.
land use - Housing. - Open spaces and
gardens.
Main type of tenure Factories Commuters.
(ownership)
Road pattern Grid- iron pattern. Linear pattern.
2 main types of socio-
economic group
You might also like
- Windshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community ObservationsDocument6 pagesWindshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community Observationslesliecurtis79100% (12)
- The Modern Courtyard HouseDocument59 pagesThe Modern Courtyard Houselilian_tran_378% (9)
- 6000 Years of Housing (Group-5)Document18 pages6000 Years of Housing (Group-5)Zil Mistry67% (3)
- Enp Ar. Marlou B. Campaner: Chief, Urban Design Division City Planning & Development Office ManilaDocument30 pagesEnp Ar. Marlou B. Campaner: Chief, Urban Design Division City Planning & Development Office ManilaJoharah SevillaNo ratings yet
- Radburn City PDFDocument8 pagesRadburn City PDFFarhan Asim100% (1)
- Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesLiterature ReviewAravindSrivatsan74% (19)
- Garden City PDFDocument23 pagesGarden City PDFGurpreetSinghKalsi100% (1)
- 309139unitedhabitationlecorbusier 180326190022 PDFDocument12 pages309139unitedhabitationlecorbusier 180326190022 PDFAarthi ParivallalNo ratings yet
- Windshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community ObservationsDocument6 pagesWindshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community Observationslesliecurtis79100% (1)
- Case Study 1Document30 pagesCase Study 1xirochrome95% (22)
- Home Sweet Home: A Century of Leicester Housing 1814-1914 by Dennis CalowDocument123 pagesHome Sweet Home: A Century of Leicester Housing 1814-1914 by Dennis CalowBRAUNSTONE HALLNo ratings yet
- History of Urban SettlementsDocument114 pagesHistory of Urban SettlementsMary Ann FiguerasNo ratings yet
- Activity3 BAGSAC MMEP611Document8 pagesActivity3 BAGSAC MMEP611ivy bagsacNo ratings yet
- City OF Glenb Rook: Planning ReportDocument4 pagesCity OF Glenb Rook: Planning ReportJacob SheridanNo ratings yet
- Real Estate DevelopmentDocument6 pagesReal Estate Developmentশশী জান্নাতNo ratings yet
- Scoville - The Labor Market in Prerevolutionary IranDocument14 pagesScoville - The Labor Market in Prerevolutionary Iransar234No ratings yet
- Settlement and Urban Growth 14Document4 pagesSettlement and Urban Growth 14rebe fraxanetNo ratings yet
- Modern Town Planning Thoughts: Pallavi / Lakshmi / Renjith / Irin / Gouthham / AnlinDocument16 pagesModern Town Planning Thoughts: Pallavi / Lakshmi / Renjith / Irin / Gouthham / AnlinsanNo ratings yet
- Green City MovementDocument40 pagesGreen City MovementmohamedNo ratings yet
- Indus Valley CivilizationDocument10 pagesIndus Valley CivilizationResbi vrNo ratings yet
- NONEDocument117 pagesNONEEmerson BolibolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Pioneering Planning ThoughtsDocument35 pagesLecture 2 - Pioneering Planning Thoughts55jinhan66No ratings yet
- Plan2 Group2 Linear-City Garden-City Industrial-City Bs-Arch4-c Martinez Monero Mercurio Basiya Lumampao DumlaoDocument86 pagesPlan2 Group2 Linear-City Garden-City Industrial-City Bs-Arch4-c Martinez Monero Mercurio Basiya Lumampao DumlaoJames Chu100% (1)
- LectureTen - Urban ThinkersDocument59 pagesLectureTen - Urban ThinkersMaloba WangaNo ratings yet
- Literature AStudy On ApartmentsDocument8 pagesLiterature AStudy On ApartmentsAnshuman Samantaray50% (2)
- History-Theories and Movements2-20160315-095449910Document16 pagesHistory-Theories and Movements2-20160315-095449910Shashank SinhaNo ratings yet
- How Should Housing Densities Be Determined? A Comparative Analysis of Brisbane and CopenhagenDocument16 pagesHow Should Housing Densities Be Determined? A Comparative Analysis of Brisbane and CopenhagenMp ScribdNo ratings yet
- Post Modernism, ModernismDocument15 pagesPost Modernism, ModernismArpan PatelNo ratings yet
- Stilski Pravci U Arhitekturi - MODERNADocument40 pagesStilski Pravci U Arhitekturi - MODERNAarchi_buba100% (1)
- Bloomberg - How Leeds Kept The Back-to-Back House Alive by Robert BevanDocument12 pagesBloomberg - How Leeds Kept The Back-to-Back House Alive by Robert BevanrpmbevanNo ratings yet
- Windshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community ObservationsDocument6 pagesWindshield Survey: Elements & Descriptions Community Observationslacurtis100% (1)
- Hoa l2Document40 pagesHoa l2vikeshNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Planning Lessons4-9Document22 pagesReviewer Planning Lessons4-9JasNo ratings yet
- Town PlanningDocument18 pagesTown PlanningshirishaNo ratings yet
- Physical PlanDocument15 pagesPhysical PlanSG18BAR002 AkshataNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Urban Designs and Community ArchitectureDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Urban Designs and Community ArchitectureJay PamotonganNo ratings yet
- Highsett, Cambridge: Built Local AuthorityDocument2 pagesHighsett, Cambridge: Built Local AuthorityDjoudi MohNo ratings yet
- Final Clarence SteinDocument5 pagesFinal Clarence Steingau100% (2)
- Sydenham To Bankstown Urban Renewal Corridor Strategy Built Form Transect Diagram 2016 04 PDFDocument7 pagesSydenham To Bankstown Urban Renewal Corridor Strategy Built Form Transect Diagram 2016 04 PDFAlla ElfallahNo ratings yet
- Sydenham To Bankstown Urban Renewal Corridor Strategy Built Form Transect Diagram 2016 04Document7 pagesSydenham To Bankstown Urban Renewal Corridor Strategy Built Form Transect Diagram 2016 04Esra PanggabeanNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument24 pagesLiterature ReviewAbrsh Wubishet67% (3)
- AM Residence: by Sarah Mineko IchiokaDocument24 pagesAM Residence: by Sarah Mineko IchiokaKayzha Shafira Ramadhani460 105No ratings yet
- HPO Staff Report: 1922 Third ST NWDocument4 pagesHPO Staff Report: 1922 Third ST NWleftforledroitNo ratings yet
- Garden Cities: P.Swathi 13031AA102 VII SemesterDocument16 pagesGarden Cities: P.Swathi 13031AA102 VII SemesterSwathi ProddutooriNo ratings yet
- Clarence SteinDocument11 pagesClarence SteinSharda Uppttu KunniparambathuNo ratings yet
- Different Types of City ModelsDocument56 pagesDifferent Types of City ModelsManpreet Kaur100% (1)
- Urban and Regional Planning Theories and Issues PDFDocument172 pagesUrban and Regional Planning Theories and Issues PDFJohn Michael BlancaflorNo ratings yet
- Urban StructureDocument30 pagesUrban StructureAkhila KanakapodiNo ratings yet
- Alison and Peter SmithsonDocument11 pagesAlison and Peter SmithsonDevika MadhusudhananNo ratings yet
- Garden City of Tommorrow: Ebenezer HowardDocument23 pagesGarden City of Tommorrow: Ebenezer Howarderika maanoNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURE (Reading Assignment)Document3 pagesARCHITECTURE (Reading Assignment)Lexa Denta SinuhajiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - Industrial RevolutionDocument63 pagesLecture 01 - Industrial RevolutionBulbul Yashdeep Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Socialized and Economic HousingDocument4 pagesSocialized and Economic HousingjaybeelibrauxNo ratings yet
- GardenDocument20 pagesGardenLyka Adah100% (1)
- Assignment 3 PDFDocument14 pagesAssignment 3 PDFVishnu RajgopalNo ratings yet
- Row HousingDocument46 pagesRow HousingInduja RaviNo ratings yet
- Ar 6902 - HSP - U3 - PVBDocument29 pagesAr 6902 - HSP - U3 - PVBAishwarya BalajiNo ratings yet
- Definition ofDocument20 pagesDefinition ofDB FasikaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2, Planning TheoriesDocument45 pagesMODULE 2, Planning TheoriesShreenidhi JoshiNo ratings yet
- Industrial RevolutionDocument17 pagesIndustrial RevolutionSahil PruthiNo ratings yet
- C8 Biblio MOMA - 1973 - Evolution of Housing Concepts FramptonDocument10 pagesC8 Biblio MOMA - 1973 - Evolution of Housing Concepts FramptonPetru CordosNo ratings yet
- Urban Design Theories - (Ebenezer Howard) - (Neha Ghatage)Document11 pagesUrban Design Theories - (Ebenezer Howard) - (Neha Ghatage)Neha GhatageNo ratings yet
- Elective Iv - Urban Design: Identification and Analysis of Urban Issues and Their SolutionDocument9 pagesElective Iv - Urban Design: Identification and Analysis of Urban Issues and Their SolutionDivyansha JainNo ratings yet
- 3d.technical Proposal (3D Methodology)Document19 pages3d.technical Proposal (3D Methodology)surendramaharjanNo ratings yet
- Bengaluru Bda RMP 2031 Plu 01Document4 pagesBengaluru Bda RMP 2031 Plu 01aashish gorantiwarNo ratings yet
- Mixed Use DevelopmentDocument8 pagesMixed Use Developmentsumaiya sharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Arrington PC Staff Report 101515Document46 pagesArrington PC Staff Report 101515Fauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Whiteford, Michael. Social Urbanization in The Cauca ValleyDocument14 pagesWhiteford, Michael. Social Urbanization in The Cauca ValleyManuela Leon RojasNo ratings yet
- LGU Invitation For TOD and SWM Seminars (30-31 August 2022)Document17 pagesLGU Invitation For TOD and SWM Seminars (30-31 August 2022)Anne GilbeanNo ratings yet
- Capacity Building Brochure 1Document3 pagesCapacity Building Brochure 1Bengkel Las DekorasiNo ratings yet
- Urbanisation in UttarPradeshDocument13 pagesUrbanisation in UttarPradeshaamirmkhanNo ratings yet
- U2 Lecture 2 NSTP KNOWING YOUR COMMUNITYDocument47 pagesU2 Lecture 2 NSTP KNOWING YOUR COMMUNITYAnne MarielNo ratings yet
- DB WorlduaDocument94 pagesDB WorlduacacaolesNo ratings yet
- GIS Mapping For Population DistributionDocument5 pagesGIS Mapping For Population DistributionAvi KoratNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Rural Development Project in Gidan Waya, Jema'a L.G.a, Kaduna State, NigeriaDocument8 pagesAssessment of Rural Development Project in Gidan Waya, Jema'a L.G.a, Kaduna State, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Garden City Movement: To Real Reform in 1898 (Which Was Reissued in 1902 As Garden Cities of To-Morrow) - His IdealisedDocument6 pagesGarden City Movement: To Real Reform in 1898 (Which Was Reissued in 1902 As Garden Cities of To-Morrow) - His IdealisedPiyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Structure (GWRET) QUANTITY Chainage Length Left RightDocument50 pagesStructure (GWRET) QUANTITY Chainage Length Left RightLokendra KhatriNo ratings yet
- City and Metropolitan PlanningDocument18 pagesCity and Metropolitan PlanningsonamNo ratings yet
- Characteristics, Causes, and ConsequencesDocument3 pagesCharacteristics, Causes, and ConsequencesKIANU STEVENo ratings yet
- Emerging Practices of Compact City Planning and DevelopmentDocument80 pagesEmerging Practices of Compact City Planning and DevelopmentEdwin KisaNo ratings yet
- Determinants of Internal Migration in TanzaniaDocument9 pagesDeterminants of Internal Migration in TanzaniaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- French and Industrial RevolutionDocument4 pagesFrench and Industrial RevolutionAkansha guptaNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 1 2Document10 pagesPractice Test 1 2Quynh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Design Brief-MIXED USE DEVELOPMENTDocument3 pagesDesign Brief-MIXED USE DEVELOPMENTDivya PurushothamanNo ratings yet
- Diversion LandDocument15 pagesDiversion LandVivek SaiNo ratings yet
- DP Plan LaturDocument54 pagesDP Plan Laturshaikh aslam nuroddinNo ratings yet
- Affordable Housingin DhakaDocument11 pagesAffordable Housingin DhakaAlNaeemNo ratings yet