Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Matching Type
Uploaded by
Mary Jane Mondelo Cabiltes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesOriginal Title
MATCHING TYPE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesMatching Type
Uploaded by
Mary Jane Mondelo CabiltesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
MATCHING TYPE * diabetes mellitus
Glucose - Double sequential enzyme reaction hepatitis
Leukocytes - Leukocyte esterase Proteus infection
Specific Gravity - pKa change of polyelectrolyte Choose the incorrect match between metabolic
Biilirubin - Diazo reaction
urine disorder and the corresponding urine
Protein - Sorensen's error of indicator
pH - Double Indicator system abnormality. *
alkaptonuria: dark blue urine
Nitrite - Greiss reaction Lesch-Nyhan disease: orange sand in diaper
Urobilinogen - Ehrlich reaction PKU: mousy odor
Blood - Pseudoperoxidase activity of Hemoglobin cystinuria: sulfur odor
Ketones - Sodium nitroprusside reaction Mousy urine is associated with which of the
Matching Type * following disorders? *
Glucose - Green to Brown methionine malabsorption
Bilirubin - Violet Trimethylaminuria
Ketones - Purple PKU
Specific Gravity - Blue to Yellow Tyrosinemia
Leukocytes - Purple What is the characteristic odor of urine in
Nitrite - Pink trimethylaminoaciduria? *
pH - Orange to Blue rancid
Protein - Blue mousy
Blood - Speckled or spotted rotting fish
sweaty feet
Urobilinogen - Red
Which of the following medications can be
Which of the following substances contributes to
associated with a red urine color? *
specific gravity but not to osmolality? *
Rifampin
glucose
Methyldopa
protein
Mepacrine
salt
Phenindione
urea
Which biochemical component is likely to be You should add 0.005 to SG reading when pH is
present in an increased amount in an amber >6.5. *
True
urine? * False
urobilinogen Maybe
urobilin I Don't know
bilirubin
Soluble in Butanol and Chloroform: *
biliverdin
Other Ehrlich Reactive Compounds
An ammonia-like odor is is characteristically Urobilinogen
associated from a patient who has: * Porphobilinogen
yeast infection NOTA
Match the descriptions found in the row with their
corresponding crystals in the column. *
Yellow-brown, spherical; "Thorny apple" - Ammonium
biurate
"X" of this crystal pops out of the field; envelope
shaped crystal - Calcium oxalate
colorless, refractile, hexagonal plates with equal or
unequal sides - Cystine
Large, flat, transparent, with notched corners -
Cholesterol
Yellow or red-brown, six sides, diamond or rhombic
prisms - Uric acid
Salts of Sodium, Magnesium, Potassium, Calcium;
brick dust, yellow in color; soluble in heat/alkali -
Amorphous urates
Dumbbell, spherical, in alkaline urine; may form gas
in acetic acid - Calcium carbonate
Acetic acid soluble, whote or colorless,
grave/sandlike - Amorphous phosphates
highly refractile, yellow or brown spheroids, with
radial and concetric striations - Leucine
Ammonium-magnesium phosphate; 3-6 sides with
oblique coffin-lid ends - Triple phosphate
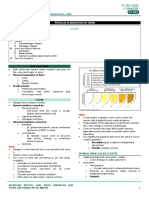
Which of the following conditions presents with 2.016
1.008
polyuria ang hypersthenuria? *
1.004
diabetes insipidus
diabetes mellitus In calibrating the refractometer using 9% sucrose,
dehydration it should read: *
intake of diuretics 1.021-1.023
Acidic urine containing hemoglobin darkens due to 1.015
1.033-1.035
the formation of: *
1.000
homogentisic acid
methhemoglobin The following are pathological causes of urine
bilirubin turbidity, EXCEPT: *
carboxyhemoglobin Bacteria
Identify the urine constituents below. * Lipids
None of the choices
Erythrocytes
Which of the following may be responsible for the
non-pathologic white turbidity of an alkaline urine? *
spermatozoa
squamous cells
amorphous phosphates
phenazopyridine
Isovaleric acidemia will cause the urine to smell: *
sweaty feet
ammoniacal
rancid
fecaloid
Effect of improperly preserved urine specimen on
nitrite reagent strip: *
False decrease
False negative
False positve
Either false positive or negative
A urine specimen diluted 1:2 with a reading of
1.025, would have an actual specific gravity reading
of: *
1.012
1.025
16 - Epithelial cell cast 1.050
1.075
9 - Ammonium biurate
13 - Uric acid Test for microalbuminuria: *
12 - Tyrosine crystal SSA Precipitation Test
Micral Test
2 - Transitional ECs
Clinitest
3 - Transitional ECs Ictotest
14 - Cholesterol
The normal value for albumin excretion rate is: *
6 - Calcium oxalate 20-200 ug/min
15 - Hyaline cast 0-20 ug/min
19 - Bacteria >200 ug/min
5 - Struvite 10-100 ug/min
7 - CaOx monohydrate Calculate the corrected specific gravity given the
20 - RBCs following data: Urinometer reading=1.017;
4 - RTE cells
temperature=23 deg. C; Glucose=1 g/dL;
1 - SEC
17 - Waxy cast Protein=2000mg/dL; dilution 1:2 *
1.016
18 - Yeast
2.016
11 - Leucine 1.008
10 - Cystine 1.018
8 - Bilirubin crystal Feedback
A urine specimen has a specific gravity of 1.025 When the urine is diluted, multiply the decimal points
only with the dilution factor. The result is the specific
measured by a refractometer. If the specimen gravity of the undiluted urine.
contains 2g/dL glucose and 3 g/dL protein, how For example: Dilute urine specific gravity=1.015;
dilution=1:5;
should the actual specific gravity be reported? *
SOLUTION: 0.015 (5) = 0.075. The specific gravity of
1.016
the UNDILUTED urine is 1.075 (Probably due to
radiographic contrast media).
https://www.coursehero.com/file/p52edvc/Put-the- diluted-urine-in-the-urinometer-and-measure-
its- specific-gravity-The/
Micral test sensitivity: *
0-10 mg/dL
160-180 mg/dL
10-150 mg/dL
0-100 mg/dL
Which of the following is the main pigment of a normal urine? *
Uroeryhtrin Urobilin Bilirubin Urobilinogen Urochrome
Ketone not detected with sodium nitroprusside reagent pad: *
Acetoacetic acid Betahydroxybutyric acid Acetone
NOTA
Which of the following tests is least affected by standing or improperly stored urine?
Glucose Protein pH Bilirubin
What is the relationship between pH and Hydrogen ions? *
Directly proportional Inversely proportional AOTA
NOTA
Match the following descriptions in the row with their corresponding casts/cells in the column.
*
Most common epithelial cells to form syncytia -
Transitional cells
Exhibit Brownian movement - WBCs
Most clinically significant of all epithelial cells in the urine - RTE cells
Most common casts in routine, strenuous activities - Hyaline
Ghost cells - RBCs
May have vacuoles and irregular nuclei due to viral infection - Transitional cells
Composed entirely of uromodulin - Hyaline
fat droplets and oval fat bodies attached to protein matrix and are highly refractile - Fatty casts
Most common epithelial cells in urologic procedures
- Transitional cells
Representative casts of extreme urine stasis - Waxy casts
Most common cast associated with pyelonephritis - WBCs
End-stage renal disease casts - Waxy casts
Most brittle casts, may appear jagged, and have notches - Waxy casts
An epithelial cell with absorbed lipids - RTE cells Largest cells in the urine - SECs
Glitter cells - WBCs
Identification is difficult due to several elements present in the matrix - Mixed cellular casts
May have Gardnerella vaginalis in the cytoplasm - SECs
Casts commonly associated with renal tubular necrosis - RTE cells
You might also like
- Physical ContaminationDocument10 pagesPhysical ContaminationGlenn BanlaygasNo ratings yet
- AUBF Laboratory Exercise I-ADocument6 pagesAUBF Laboratory Exercise I-AVelez LecturesNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination AubfDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination AubfHANNA CASANDRA GARCIANo ratings yet
- Urochrome Yellow: Uroerythrin PinkDocument6 pagesUrochrome Yellow: Uroerythrin Pink3CBSMLSBRILLO Ma. Therese CabantingNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Urine PDFDocument25 pagesLec 1 Urine PDFArooma KhalidNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab NotesDocument5 pagesBiochem Lab NotesSofiaRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Urine ExaminationDocument8 pagesUrine ExaminationAnban SureshNo ratings yet
- Aubf - Chapter 4Document6 pagesAubf - Chapter 4Kristin SoquilloNo ratings yet
- Red Urine: Basic (Routine) UrinalysisDocument4 pagesRed Urine: Basic (Routine) UrinalysisMonica DomingoNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument4 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineIceNo ratings yet
- AUBF LEC - Physical ExaminationDocument3 pagesAUBF LEC - Physical Examinationcherrycayari13No ratings yet
- Clinical MicrosDocument28 pagesClinical MicrosKristine Jamella Maris NaragNo ratings yet
- Normal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Document8 pagesNormal Daily Urine Output: 600-2000mL (With Night Urine 400mL) Average Urine Output: 1200-1500mL (1% of The Filtered Plasma Volume)Chrissa Mae Tumaliuan CatindoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Analysis: Analysis of Urine and Body FluidsDocument8 pagesPhysical Analysis: Analysis of Urine and Body FluidsChristin SchlittNo ratings yet
- Mtap 1 Lecture 1 AubfDocument13 pagesMtap 1 Lecture 1 AubfKRISTINE JOY PANGAHINNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Physical Examination 033230Document24 pages2.1 Physical Examination 033230Taladua Cayla Grace O.No ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument34 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineLawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsBEVERLY JANE LLUVERASNo ratings yet
- Urine Examination - PhysicalDocument12 pagesUrine Examination - PhysicalAbheet NagarNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument2 pagesCulture MediaJobelleNo ratings yet
- Chem41 Postlabexpt.n0.3Document36 pagesChem41 Postlabexpt.n0.3HJakansjakkaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument7 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineChie HisuganNo ratings yet
- Clin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2Document7 pagesClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysis Part 2api-3743217100% (3)
- Anurbf AssignmentDocument3 pagesAnurbf AssignmentARRIANE CYREL CAMACHONo ratings yet
- Aubf Topic 1Document25 pagesAubf Topic 1Bernadette VillegasNo ratings yet
- Mtap URINALYSIS4Document55 pagesMtap URINALYSIS4Hazel Joyce Gonda RoqueNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of Urine SummaryDocument3 pagesPhysical Examination of Urine SummaryBiancake Sta. AnaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYdocxDocument2 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYdocxGrace Benero PequeroNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of UrineDocument5 pagesPhysical Examination of UrineYasmeen JovesNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lec Week#4 Physical Examination of UrineDocument19 pagesAUBF Lec Week#4 Physical Examination of UrineLexaNatalieConcepcionJuntadoNo ratings yet
- Examination of Body Fluids (Urinalysis)Document109 pagesExamination of Body Fluids (Urinalysis)kiedd_04100% (9)
- Parasitology Lab M2 Routine FecalysisDocument4 pagesParasitology Lab M2 Routine Fecalysiseumhir7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Physical Examination PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Physical Examination PDFJulie Anne Soro ValdezNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus - Pseudomonas Putida - Klebsiella OxytocaDocument4 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus - Pseudomonas Putida - Klebsiella OxytocaJeanette RiosNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiochemistry ReviewerRegine CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab 4Document4 pagesAubf Lab 4Regina SalazarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaDocument5 pagesClinical Microscopy: Definition and Volume Disease and Cause PolyuriaJovanni andesNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics of UrineDocument2 pagesPhysical Characteristics of UrineClair TugnaNo ratings yet
- Exogenous and Endogenous Pigment.....Document30 pagesExogenous and Endogenous Pigment.....Mohan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument13 pagesInborn Error of MetabolismKuzhandai VeluNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 UrineDocument131 pagesUnit 6 UrineAsjad HassanNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument33 pagesUrine AnalysisajaysomNo ratings yet
- BioChem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBioChem ReviewerPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- Causes For Urinalysis Discrepancies TABLEDocument3 pagesCauses For Urinalysis Discrepancies TABLEZllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Prueba AnalisisDocument223 pagesPrueba AnalisisLeydi MaribelNo ratings yet
- New Inborn Error of MetabolismDocument45 pagesNew Inborn Error of Metabolismmannan mangal100% (1)
- Trans Aubf Lec3Document8 pagesTrans Aubf Lec3USLT- Angoluan, Andrei T.No ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Examination of UrineDocument9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Examination of UrineManny James Clark Pagurayan Ebu�aNo ratings yet
- Proteins LASDocument6 pagesProteins LASelly scatusNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-Color Reaction of Proteins (LABORATORY)Document15 pagesBiochemistry-Color Reaction of Proteins (LABORATORY)Aimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Biochem LabDocument24 pagesBiochem Lab813 cafeNo ratings yet
- Histopathologic Technique 2Document71 pagesHistopathologic Technique 2Kimberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Salmonella and Listeria 2Document11 pagesSalmonella and Listeria 2Gurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Urine Physical ExamDocument3 pagesUrine Physical ExamFait HeeNo ratings yet
- Examination of Body FluidsDocument14 pagesExamination of Body Fluidskiedd_04100% (11)
- Biochem Lab Report Group 2Document40 pagesBiochem Lab Report Group 2Keith Jason CortesNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument3 pagesUrinaryIYA LABAO100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Biochemical Tests in MicrobiologyDocument33 pagesChapter 8 Biochemical Tests in Microbiologyits james de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and PorphyrinsDocument10 pagesAmmonia and PorphyrinsNikhatNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial No.8 Combustion of Fuels: - Let's Start by Revising The BasicsDocument25 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial No.8 Combustion of Fuels: - Let's Start by Revising The BasicsKEVIN JOE PEREZ ASENCIOS100% (1)
- 9 Module9 Disinfection 29-03 2022 LFPDocument27 pages9 Module9 Disinfection 29-03 2022 LFPArjun RanabhatNo ratings yet
- Apex Ultima Protek: Product BenefitsDocument2 pagesApex Ultima Protek: Product BenefitssudhatryNo ratings yet
- PTG Gas Filter SeparatorsDocument8 pagesPTG Gas Filter SeparatorsRosa SparksNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Plate: Unit OperationsDocument17 pagesTheoretical Plate: Unit OperationsMehari AsratNo ratings yet
- Molecules 28 04005Document26 pagesMolecules 28 04005Cemerlang StudiNo ratings yet
- Boiling Point DataDocument283 pagesBoiling Point DataKaryshma GillNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Peptides Protein StructuresDocument11 pagesAmino Acids Peptides Protein StructuresGabriel RamosNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chemsitry 0620/42 February/March 2022Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chemsitry 0620/42 February/March 2022Khadeeja MansourNo ratings yet
- Furse Conductor Network SectionDocument21 pagesFurse Conductor Network SectionDoug WeirNo ratings yet
- AHMED 2020 - Aqueous Polymeric CoatingsDocument24 pagesAHMED 2020 - Aqueous Polymeric CoatingsapksantosNo ratings yet
- 2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Document269 pages2000-2019 Nesa Chemistry Advanced Level-1Jeff AlbaNo ratings yet
- C3 ElectrochemistryDocument39 pagesC3 ElectrochemistryaliesyaNo ratings yet
- Dupont Nomex 910 Engineered Cellulose Paper: Preliminary Technical Data SheetDocument2 pagesDupont Nomex 910 Engineered Cellulose Paper: Preliminary Technical Data SheetSNX11No ratings yet
- Developer G128Document9 pagesDeveloper G128ariNo ratings yet
- Datasheet File Conbextra GP PremixDocument4 pagesDatasheet File Conbextra GP PremixLftea AdiNo ratings yet
- Fire-Resistant, Water-Free Hydraulic Re90222 - 2012-05 - 2 PDFDocument16 pagesFire-Resistant, Water-Free Hydraulic Re90222 - 2012-05 - 2 PDFDennis Huanuco CcamaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanical Sludge Handling Study GuideDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Mechanical Sludge Handling Study GuideBuenaventura Jose Huamani TalaveranoNo ratings yet
- Santillan LBYME3A Activity 3Document13 pagesSantillan LBYME3A Activity 3Nygel Gian SantillanNo ratings yet
- Cable Radix Sks-Soaking-PitDocument2 pagesCable Radix Sks-Soaking-PitedisontrianaNo ratings yet
- PultrusionDocument30 pagesPultrusionMukesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityDocument13 pagesCell Membrane and Transport 4-Practical ActivityRohan PaneruNo ratings yet
- Friction and Wear Data Bank: A. William RuffDocument39 pagesFriction and Wear Data Bank: A. William RuffGhania Nashwa FairuzaNo ratings yet
- Draft Fumigation Certificate - SK226485001Document2 pagesDraft Fumigation Certificate - SK226485001Erick TacdolNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0272884219306522 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0272884219306522 MainFábio FriolNo ratings yet
- Abts AssayDocument7 pagesAbts AssayKadashaNo ratings yet
- SPPPL - Profile (Shree Pinak Processing PVT LTD.)Document4 pagesSPPPL - Profile (Shree Pinak Processing PVT LTD.)Amit KaleNo ratings yet
- CHAPTERSDocument46 pagesCHAPTERSnjoku danielNo ratings yet
- Mariane Rabelo - Artigo QuakerDocument10 pagesMariane Rabelo - Artigo QuakerTibis GNo ratings yet
- The Nature Reduced and Excited States of r-Electron-Deficient Complexes Between Re (CO) 3halDocument6 pagesThe Nature Reduced and Excited States of r-Electron-Deficient Complexes Between Re (CO) 3halPablo MellaNo ratings yet