Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Beri Beri: Water-Soluble Vitamins Thiamine
Uploaded by
Lyan SamsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Beri Beri: Water-Soluble Vitamins Thiamine
Uploaded by
Lyan SamsonCopyright:
Available Formats
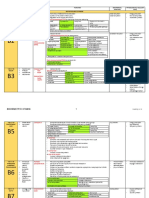
VITAMINS SOURCES DEFICIENCY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS TOXICITY NOTES
WATER-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Vitamin B1 ✓ Meat/ fish BERI BERI NONE
THIAMINE ✓ Beans, nuts, - Severe thiamine deficiency syndrome found in areas where DRY Loss of appetite, weight loss,
yeast polished rice is the major component of the diet muscle wasting, peripheral
B1 ✓
✓
Wheat flour,
unpolished
rice
Liver, meat,
DRY
WET
Degeneration of peripheral nerves, thalamus,
mamillary bodies, and cerebellum (Peripheral
neuritis)
Cardiac Involvement WET
neuritis with numbness, tingling
sensations in the lower legs and
feet, and ataxic gait
Vasodilation, tachycardia, wide
eggs SOSHIN a more rapid form of wet beri beri follows inability of pulse pressure, sweating, warm
heart muscle to satisfy body’s demands because of skin → lactic acidosis → heart
RDA: its own injury (Acute fulminant CV beri beri) failure → orthopnea pulmonary
1-1.5 mg/day CEREBRAL In association with chronic alcoholism, due to dietary and peripheral edema →
insufficiency or impaired intestinal absorption of vasodilation → shock
thiamine (Wernicke- Karsakoff syndrome) SOSHIN Edema may not be present,
INFANTILE Due to low thiamine content of breast milk cyanosis of hands and feet,
tachycardia, distended neck
veins, restlessness, and anxiety
CEREBRAL Intelligence disturbance, ataxia,
double vision, nystagmus,
progresses to Wernicke-
Korsakoff psychosis
INFANTILE Anorexia, tachycardia, vomiting,
convulsions, edema
Vitamin B2 Milk – 1quart = 1.7 ARIBOFLAVINOSIS - Epithelial changes in the oral cavity: NONE Assay for riboflavin status:
RIBOFLAVIN mg - Causes: malnutrition, malabsorption, anorexia, chronic ➢ Cheilosis or perleche – fissuring of lips ERYTHROCYTE GSH REDUCTATSE
alcoholism ➢ Glossitis – magenta tongue ACTIVITY
B2
Vitamin B3
RDA:
A: 2 mg/day
C: 1.2 mg/day
✓ Enriched
- Pure riboflavin deficiency is rare
PELLAGRA - 3Ds
-
-
-
Corneal vascularization
Seborrheic dermatitis
Photophobia
Pellagra “rough skin”- 3Ds NONE
-
-
Plasma riboflavin
concentration tend to reflect
recent dietary intake
High doses of niacin used to
NIACIN grains - Disease involving the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and CNS - Dermatitis -skin exposed to sunlight treat hyperlipidemia
✓ Milk ➢ Casal’s necklace - TRYPTOPHAN can be
B3 ✓
RDA:
Lean meats
(liver)
A: 16-20 mg/day
-
-
-
➢ Gloves and stockings lesions
Diarrhea
Dementia
Severe cases: GIT hemorrhagic
converted to NAD
(60 mg Trp= 1mg niacin): milk
and eggs rich in Trp
C: 9-16 mg/day
I: 5-8 mg/day
Vitamin B5 ✓ Eggs Rare NONE
PANTOTHENIC ✓ Liver - Vitamin B5 is very widespread in natural foods
ACID ✓ Yeast - Most symptoms are vague and mimic those of other B vitamin
RDA: deficiencies
B5 A: 5-10 mg/day
C: 4-5 mg/day
I: 1-2 mg/day
BIOCHEMISTRY B: VITAMINS 1 SAMSON, A.C.B.
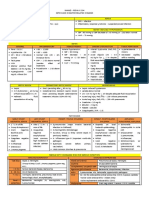
Vitamin B6 ✓ Whole grain Rare - Epileptiform seizures in infants YES - Deficiency can be induced by
PYRIDOXINE ✓ Poultry & fish - Mostly specific as nonspecific stomatitis, glossitis, irritability, - Pellagra-like skin lesions isoniazid sensory neuropathy
PYRIDOXAL ✓ Potatoes, eggs confusion, and depression, pellagra-like skin lesions and possibly - GIT involvement: distention, vomiting, occurs at high doses
PYRIDOXAMINE ✓ Organ meats peripheral neuropathy diarrhea
RDA: - Intake of isoniazid (isonicotinic acid hydrazide) - Anemia (hypochromic and microcytic)
B6
Vitamin B7
A: 2.2 mg/day
C: 1.2mg/day
I: 3 mg/day
✓ Almost all Rare
➢ Drug frequently used to treat tuberculosis, can induce a
vitamin B6 defieciency by forming an inactive der
- Acrodynia in rats
Men (rare) NONE
BIOTIN foods - Widely distributed in natural foods as biocytin (epsilon- amino- - Fine scaly skin desquamation
✓ Liver biotinyllysine), which is released on proteolysis. It is synthesized - Anorexia
B7 ✓ Milk
✓ Egg
✓ Yolk
RDA: 400 ug/day
-
-
by intestinal flora in excess of requirements
From synthesis of bacteria -deficiency is caused by defects in
utilization and not dietary
From long-term antibiotic treatment or excessive consumption of
-
-
-
-
Nausea
Lassitude
Muscle pains
Depression/ hallucination
raw egg - Alopecia
AVIDIN- a protein in raw egg white which combines very tightly with - Graying of hair
biotin, preventing its absorption leading to biotin deficiency
Vitamin B9 ✓ Green leafy MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA Symptoms of anemia NONE - Administration of high levels of
FOLIC ACID vegetables - Folic acid deficiency affects cells that are diving rapidly because - Yellowing eyes folate can mask vitamin B12
✓ Liver they have a large requirement for thymidine for DNA synthesis. - Skin paleness, coldness and yellowness deficiency
B9 ✓
✓
Lima beans
Whole grain
cereals -
Clinically this affects the bone marrow, leading to megaloblastic
anemia
Deficiency can be caused by:
➢ Increased demand, poor absorption caused by pathology of
-
-
-
-
Shortness of breath
Muscle weakness, fatigue, dizziness
Change in stool color
Low blood pressure
- METHOTREXATE – inhibits
dihydrofolate reductase used
in the conversion of Folate to
tetrahydrofolate, a folic acid
the small intestine, alcoholism - Palpitations analogue used to treat
➢ Treatment with drugs that are dihydrofolate reductase - Spleen enlargement psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis,
inhibitors- for example METHOTREXATE - Severe anemia: chest pain, angina, fainting, neoplastic diseases, and acute
Neural tube defects (SPINA BIFIDA AND ANENCEPHALY) heart attack lymphocytic anemia in children
- Folic acid supplementation before conception and during the first - SULFONAMIDE – an anti-
trimester has been shown to significantly reduce the defects bacterial agent that inhibits
- RENI of 400 ug folate supplement for all women of child-bearing dihypteroate synthetase, used
age for the conversion of PABA to
Growth failure Folate
Vitamin B12 ✓ Liver, eggs PERNICIOUS ANEMIA Pernicious anemia: NONE - Pernicious anemia treated
COBALAMIN ✓ Whole milk - most commonly a result of an autoimmune destruction of the ➢ Megaloblastic or macrocytic anemia with IM or high dose oral
✓ Oysters gastric parietals cells that are responsible for the synthesis of ➢ Lesions of the nervous system vitamin B12
B12 ✓ Fresh shrimp
✓ Pork, Chicken
RDA:
A: 2 ug/day
-
intrinsic factor. Lack of intrinsic factor prevents the absorption of
vitamin B12, resulting to pernicious anemia
no healthy RBC
Abnormal fatty acid synthesis
➢ Mucosal atrophy and inflammation of
the tongue (glossitis), mouth
(stomatitis), and pharynx (pharyngitis)
Neuropsychiatric symptoms
C: 3ug/day Dementia
P/L: 4ug/day Spinal degeneration
Cell membrane defects/ neurological abnormalities
Vitamin C ✓ Citrus fruits SCURVY - sore, spongy gums NONE - benefits of supplementation
ASCORBIC ACID ✓ Tomatoes - Symptoms can be explained by a deficiency in the hydroxylation - loose teeth not established in controlled
✓ Green of collagen, resulting in defective connective tissue - poor wound healing trials
C RDA:
vegetables
A: 60 mg/day
C: 40 mg/day
Failure of steps in collagen synthesis results in:
-
-
-
Impaired wound healing
Defective tooth formation
Deficient osteoblasts and fibroblasts
-
-
-
-
fragile blood vessels
swollen joints
anemia
splinter hemorrhages in nails
- petechial, subcutaneous hemorrhages
- scorbutic rosary beads- swelling at the ends of
long bones
BIOCHEMISTRY B: VITAMINS 2 SAMSON, A.C.B.
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS
Vitamin A ✓ liver Night blindness - Increased visual threshold YES - Beta-carotene is not acutely
RETINOL ✓ kidney Xeropthalmia - Dryness of cornea toxic, but supplementation is
✓ cream Infertility not recommended
A ✓
✓
✓
butter
egg yolk
yellow and
dark green
Growth retardation - Excess vitamin A can increase
incidence of fractures
Retinoic acid as treatment:
- TRETINOIN (all-trans retinoic
vegetables acid)- topical application for
mild cases of acne, Darier
disease (keratosis follicularis),
and skin aging
- ISOTRETINOIN (13-cis retinoic
acid)- administered orally for
severe, recalcitrant, cystic acne
- Also used as treatment of
promyelocytic leukemia
Vitamin D ✓ Liver RICKETS (in children) - Soft, pliable bones YES - Vitamin D is not a true vitamin
CALCIFEROL ✓ Kidney - Inadequate calcification of cartilage and bone because it can be synthesized
✓ Fatty fish OSTEOMALACIA (in adults) – demineralization of bone in skin: application of
D ✓ Egg yolk
RDA:
A/C (>8 yrs of age):
100 mcg/day
-
-
Softening and weakening of the bones and may lead to
deformities and easy fracturability
Serum calcium is reduced and may also lead to tetany
-
-
TOXICITY
Moat toxic of all vitamins
CALCINOSIS – deposition of calcium in organs
and arteries, kidney stones
sunscreen lotions or presence
of dark skin color decreases
this synthesis
- Toxicity from too much Vitamin D is more
likely to occur from high intake of
supplements than from high intake of food
containing Vitamin D
- Excessive sun exposure does not cause vit D
toxicity
Vitamin E ✓ Vegetable oils Rare - Anemia, breakdown of red blood cells NONE - Benefits supplementation for
TOCOPHEROL ✓ Liver - Heart disease disease prevention not
✓ Eggs - Defective cell membranes TOXICITY established in controlled trials
E
Vitamin K
RDA:
15 mg/day
✓ Cabbage
-
Rare
Cataract formation -
-
-
Least toxic of the fat-soluble vitamins
No toxicity has been observed at doses of 300
mg/day
Bleeding RARE - Vitamin K produced by
MENADIONE ✓ Cauliflower - Rare because our own bacterial flora of the intestines supplies us intestinal bacteria
MENAQUINONE ✓ Spinach with vitamin K TOXICITY - IM treatment with vitamin K is
PHYLLOQUINONE ✓ Egg yolk - Can be hemorrhagic due to defective formation of clotting factors - Prolonged administration of vitamin K can recommended at birth
✓ Liver - Due to extensive use of antibiotics- sterilization of the GIT cause red blood cell fragility that leads to - WARFARIN – vitamin K
K RDA:
M: 120 ug/day
F: 90 ug/day
HEMORRHAGIC DISEASE OF NEWBORN
- Newborn infants are vulnerable to vitamin K deficiency because
the placenta dose not pass the vitamin to the fetus and the gut is
sterile immediately after birth
hemolytic anemia and jaundice antagonist that inhibits the
recycling of vitamin K at two
dithiol-dependent steps
BIOCHEMISTRY B: VITAMINS 3 SAMSON, A.C.B.
You might also like
- Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TTP) Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TTP)Document4 pagesThiamine Pyrophosphate (TTP) Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TTP)Lyan SamsonNo ratings yet
- Hi Yield Internal Medicine and Pedia JC Luces ScribdDocument9 pagesHi Yield Internal Medicine and Pedia JC Luces ScribdTrisNo ratings yet
- Harmacology: (Trans) Autonomic Pharmacology Topic OutlineDocument7 pagesHarmacology: (Trans) Autonomic Pharmacology Topic OutlineMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesIntegumentary SystemAliyah ZalzosNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Shanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Document4 pagesShanz - Pedia Ii 2.04Petrina XuNo ratings yet
- Reseau Pass24Document7 pagesReseau Pass24maxleproNo ratings yet
- Hi Stop Hath Ology 2Document22 pagesHi Stop Hath Ology 2vivek govardhanamNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Document5 pagesClinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Justin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Im-Ugib PudDocument6 pagesIm-Ugib PudTrisNo ratings yet
- Triage FormDocument2 pagesTriage FormCael LayugNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology 1 Unit 5 Psycho Pharma Cological Agents Notes by MahendraDocument39 pagesPharmacology 1 Unit 5 Psycho Pharma Cological Agents Notes by MahendraKim Nicole Villaflores0% (1)
- 1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma AttackDocument4 pages1 Ge Stimulations Mast Cell Degeneration Asthma Attacknebbie06No ratings yet
- 97Document79 pages97HATLERNo ratings yet
- Low BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood FlowDocument2 pagesLow BP - Decreased Cardiac Output - Improved Renal Blood Flowtantalizin marieNo ratings yet
- Microscopic ExaminationDocument9 pagesMicroscopic ExaminationMariella DingleNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Course PackDocument29 pagesCytogenetics Course Packanonymous squashNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Osce: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Document34 pagesRespiratory Osce: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Abby LiewNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationDocument8 pagesCellular AberrationRaymund IdicaNo ratings yet
- (PHARMA A) 3.3 - Antibiotics I - Dr. Cruz (2024)Document15 pages(PHARMA A) 3.3 - Antibiotics I - Dr. Cruz (2024)Miguel Luis NavarreteNo ratings yet
- CH10Document17 pagesCH10Kim BasicNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSISDocument9 pagesTUBERCULOSISAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Marrow Study PlannerDocument2 pagesMarrow Study Plannerpooja singh50% (2)
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDocument276 pagesInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeNo ratings yet
- Present at 4-12 Months, Development Arrest From Pre-B To BDocument2 pagesPresent at 4-12 Months, Development Arrest From Pre-B To BWaoNo ratings yet
- Hema Lec Prefinals ExamDocument18 pagesHema Lec Prefinals ExamMark jay LlanoNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGYDocument36 pagesHEMATOLOGYMA. ANDREA NICOLE BITOINNo ratings yet
- PEDIATRIC SURGERY - A Comprehensive Textbook For africa.-SPRINGER NATURE (2019) - 631-827Document197 pagesPEDIATRIC SURGERY - A Comprehensive Textbook For africa.-SPRINGER NATURE (2019) - 631-827adhytiyani putriNo ratings yet
- HTTPS://WWW - Tvsmotor.com/iqube?utm Source Quora&utm Medium Paid&utm Campaign Quora Postlaunch Pratical ECDocument21 pagesHTTPS://WWW - Tvsmotor.com/iqube?utm Source Quora&utm Medium Paid&utm Campaign Quora Postlaunch Pratical ECAjithNo ratings yet
- Tumor Immunology: I. Common Tumor MarkersDocument2 pagesTumor Immunology: I. Common Tumor MarkersDivineGloryMalbuyoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map On HypertensionDocument1 pageConcept Map On Hypertensionleh XDNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- A Review ThrombocytopeniaDocument5 pagesA Review ThrombocytopeniaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Unknown 5Document9 pagesUnknown 5Heran TeferiNo ratings yet
- Gallstone-Disease Pankaj IngaleDocument48 pagesGallstone-Disease Pankaj IngalePankaj IngleNo ratings yet
- Common Abbreviations For The Patient Note USMLE Step 2CSDocument1 pageCommon Abbreviations For The Patient Note USMLE Step 2CSTiondi francisNo ratings yet
- Virus ClassificationDocument5 pagesVirus ClassificationNUR AIN NADHIRAH SHAMSUL BADRINo ratings yet
- Normal Body FloraDocument1 pageNormal Body FloraJulia IshakNo ratings yet
- OB - Ulcers and VaginitsDocument4 pagesOB - Ulcers and VaginitsNouf Cathrese BarrozoNo ratings yet
- Psy101: Psychiatric Foundations and Psychological Reaction To DisabilityDocument30 pagesPsy101: Psychiatric Foundations and Psychological Reaction To DisabilityAlexia Ofel DinsonNo ratings yet
- Med - CVSDocument31 pagesMed - CVSTHIRAVIYAM RAJNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry FinalsDocument43 pagesBiochemistry FinalsInday de DiosNo ratings yet
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex & NtmsDocument4 pagesMycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex & NtmsCindy Mae Flores UtlegNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OtherDocument3 pagesVasculitis: Disorder Vessels Pathology Presentation Test TX OthermcwnotesNo ratings yet
- 13 - NS6 SC Sensory Pathways All Sites (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Document38 pages13 - NS6 SC Sensory Pathways All Sites (Handout) F2022 (Exported)Lucky NguyenNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Metabolic DisordersDocument16 pagesGenetic and Metabolic DisordersErin HillNo ratings yet
- Disease Signs and Symptoms Deficiency/Problem Notes AmyloidosisDocument14 pagesDisease Signs and Symptoms Deficiency/Problem Notes AmyloidosisSriKavya DevineniNo ratings yet
- NCP.1.SOAPIE Cardiacoutput CHFDocument5 pagesNCP.1.SOAPIE Cardiacoutput CHFMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Genital Ulcer Differential Diagnosis of Genital UlcersDocument3 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Genital Ulcer Differential Diagnosis of Genital UlcersNurhayati HasanahNo ratings yet
- Head Neck TMJDocument4 pagesHead Neck TMJNinjaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy TablezDocument15 pagesAnatomy TablezLeni BBMNo ratings yet
- Leukopenia and Bone Marrow TransplantationDocument20 pagesLeukopenia and Bone Marrow Transplantationdhanya jayanNo ratings yet
- Every Drug EverDocument72 pagesEvery Drug EverMalNo ratings yet
- Use of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in The Emergency DepartmentDocument2 pagesUse of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in The Emergency DepartmentJenzo TejadaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Block 3Document62 pagesCardio Block 3Maya LaPradeNo ratings yet
- JR Ppi 3Document8 pagesJR Ppi 3Bombong Nurpagino100% (1)
- CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Nephrology & Hypertension, 2009 Chapter 46. Cystic Diseases of TH e KidneyDocument1 pageCURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Nephrology & Hypertension, 2009 Chapter 46. Cystic Diseases of TH e KidneyFate ChanNo ratings yet
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 pagesDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPENo ratings yet
- 2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentDocument3 pages2.02 - Nutritional Status AssessmentPrincess MarielleNo ratings yet
- Quiz - B VitaminsDocument1 pageQuiz - B VitaminsDegoma, Mary NoelynNo ratings yet
- 7625-300 Vitamin B12 AccuBind ELISA Rev 6Document2 pages7625-300 Vitamin B12 AccuBind ELISA Rev 6carlosalfredorivasNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients Vitamins Report 3Document53 pagesMicronutrients Vitamins Report 3XanderNo ratings yet
- The Vitamins Fundamental Aspects in Nutrition and Health 6Th Edition Gerald F Combs JR All ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Vitamins Fundamental Aspects in Nutrition and Health 6Th Edition Gerald F Combs JR All Chapteramanda.dangerfield238100% (7)
- Nutritional Requirements of RabbitsDocument10 pagesNutritional Requirements of RabbitsBorz BennyNo ratings yet
- HakdoggggDocument2 pagesHakdoggggHarry Venzon JaboliNo ratings yet
- Caracterização Da Enzima Bifuncional BioDA Envolvida Na Síntese de Biotina e Patogenicidade em Aspergillus FlavusDocument11 pagesCaracterização Da Enzima Bifuncional BioDA Envolvida Na Síntese de Biotina e Patogenicidade em Aspergillus FlavusRenan Guilherme de Oliveira GuihNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Use of Biotin For Hair LossDocument4 pagesA Review of The Use of Biotin For Hair LossAdi PurnomoNo ratings yet
- Every VitaminDocument9 pagesEvery VitaminNur AlahiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 7-9 - Biomolecule PresentationsDocument21 pagesChapters 7-9 - Biomolecule Presentationsapi-457044119No ratings yet
- The Internship Report OnDocument18 pagesThe Internship Report OnMazhar HaseebNo ratings yet
- Vitality For LifeDocument23 pagesVitality For LifeNatasha LimNo ratings yet
- NBS - SOP - Galactosemia, BiotinidaseDocument13 pagesNBS - SOP - Galactosemia, BiotinidaseUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Biotin Deficiency in ChickensDocument6 pagesBiotin Deficiency in ChickensShah NawazNo ratings yet
- The FDA Warns That Biotin May Interfere With Lab Tests FDA Safety CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe FDA Warns That Biotin May Interfere With Lab Tests FDA Safety CommunicationneofherNo ratings yet
- 13.VITAMIN B'sDocument106 pages13.VITAMIN B'sNgetwa TzDe TheWirymanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals: MicronutrientsDocument69 pagesVitamins and Minerals: MicronutrientsRajal PratapNo ratings yet
- Vitamins, Minerals & FluidsDocument32 pagesVitamins, Minerals & FluidsEzekiel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Pomelo FinalDocument28 pagesPomelo FinalNerisa M. Mantilla75% (8)
- Biotin SOL PH LiteraturaDocument5 pagesBiotin SOL PH LiteraturawaddydiNo ratings yet
- Co Q10Document27 pagesCo Q10Zaid JasimNo ratings yet
- Hatchability Problem Analysis1Document13 pagesHatchability Problem Analysis1AbdisamadNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Metabolism and Its Regulation 1984Document223 pagesFatty Acid Metabolism and Its Regulation 1984عمار مصعب عادلNo ratings yet
- Hair, Nails, and Skin: Differentiating Cutaneous Manifestations of Micronutrient DeficiencyDocument14 pagesHair, Nails, and Skin: Differentiating Cutaneous Manifestations of Micronutrient DeficiencyIrving EuanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Terms:: Changed To Active VitaminsDocument10 pagesVitamins: Terms:: Changed To Active VitaminsKaye Hayakawa CaibiganNo ratings yet
- Nutrition - Vitamins Part 2Document29 pagesNutrition - Vitamins Part 2jeshemaNo ratings yet
- AdrenalDocument37 pagesAdrenalMada MadalinaNo ratings yet
- Biotin Content Table of Select Foods and Biotin Intake in JapaneseDocument17 pagesBiotin Content Table of Select Foods and Biotin Intake in JapaneseainhoamsNo ratings yet
- PediatricDocument188 pagesPediatricLenin Pazmiño CanoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b52c b62cb72cb9b12 Final 1Document53 pagesVitamin b52c b62cb72cb9b12 Final 1Anonymous zJcGQRnQCNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Nutritional DisordersDocument15 pagesPathology of Nutritional DisordersbumfromjerseyNo ratings yet