Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
ojjeswi gautam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views21 pagesThis document outlines the key considerations for architecture according to Christian Norberg-Schultz, including building tasks, form, technique, and creating a homely environment. It discusses the evolution of architecture, physical requirements like climate control and barriers, the functional relationships between spaces, architecture's role in creating social environments and cultural symbolism, and the need for balance between form and function. The document provides examples to illustrate these concepts and concludes that achieving this balance is challenging but worthwhile.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines the key considerations for architecture according to Christian Norberg-Schultz, including building tasks, form, technique, and creating a homely environment. It discusses the evolution of architecture, physical requirements like climate control and barriers, the functional relationships between spaces, architecture's role in creating social environments and cultural symbolism, and the need for balance between form and function. The document provides examples to illustrate these concepts and concludes that achieving this balance is challenging but worthwhile.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views21 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
ojjeswi gautamThis document outlines the key considerations for architecture according to Christian Norberg-Schultz, including building tasks, form, technique, and creating a homely environment. It discusses the evolution of architecture, physical requirements like climate control and barriers, the functional relationships between spaces, architecture's role in creating social environments and cultural symbolism, and the need for balance between form and function. The document provides examples to illustrate these concepts and concludes that achieving this balance is challenging but worthwhile.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
POKHARA UNIVERSITY
MADAN BHANDARI MEMORIAL ACADEMY NEPAL
DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECTURE
URLABARI-3, MORANG
SUBMITTED BY: SUBMITTED TO:
ASMIR GAJMER (06) ASST.PROFF.UMESH DHIMAL
DIKSHYA SITAULA (07) DEPARTMENT OF
NIRAJ SUBEDI (21) ARCHITECTURE
RANJU SODARI (32)
SURAJ SHRESTHA (44)
DATE: 31ST JANUARY 2023
TABLE OF CONTENT:
1. INTRODUCTION
2. BACKGROUND/ EVOLUTION
3. PHYSICAL REQUIREMENTS AND CONTROL
4. FUNCTIONAL FRAME
5. SOCIAL MILIEU
6. CULTURAL SYMBOLISM AND PSYCHOLOGICAL NEEDS
7. CONCLUSION
8. REFERENCE
1. INTRODUCTION: BUILDING TASKS
Christian Norberg Schultz has describe architecture as
➢Building tasks,
➢ Form
➢ Technique
23rd May 1926- 28th March 2000
Part of the modernist movement
Architect, Author, educator.
Buildings are developed with some purpose no any or very
rare buildings are there without any purpose.
What is the purpose of a building then?
An order or response to environment or
atmosphere>>Plato>> A building should be warm in
winter and cool in summer.
Should be capable enough to create an atmosphere
inspiring life>> one would not commit suicide
Just because of his/her house, if he or she does so, the
architecture is a failure
Building: Homely environment
Homely environment non measurable Architecture deals
not only with measurable aspects
Rather it will deal with both measurable and non-
measurable aspects
Homely atmosphere deals with physical and psychological
comfort
A building is said to be comfortable if it is capable enough
to moderate the climate, should be cool in summer and
warm in winter<<PHYSICAL CONTROL
It has got appropriate functional relationship between
different spaces inside<<FUNCTIONAL FRAME.
It is capable to create a social milieu enabling the exposure
of the building, its owner and the
Use<< SOCIAL MILIEU.
2. BACKGROUND:
Architecture is nothing more
and nothing less than the gift of
making building for human
purpose. It has been evolved
along with the civilization. In terms of time and technology
it is the comprehension of experience. Early civilization
had developed architecture, which are still alive as
evidence. For example
Pyramid of Egypt (3000BC),
Temple of Tigawa, India.
If it symbolizes the culture of the territory on which it
stands << CULTURAL SYMBOLIZATION
3. PHYSICAL CONTROL:
Contribute for desired degree of comfort
Protection or contribute for the reduction of intensity of
climate
Also should have same for
following elements
Light,
Sound,
Smell,
Dust,
Smoke,
Insect, animal,
Person,
Radioactivity
Need all elements in desired intensity
Building elements Function Reason
Doors and windows Switch Possibility for opening
as desired
Wall Filter and Filters temperature
barrier and protects from
light
Corridors and Connector Horizontal vertical
Staircase and filter combination
PHYSICAL COMPFORT- CONTROL
Provision of comfort and degree of comfort
Maintaining a moderate climates
Protect its inhabitants from pollution
Protect from animals and pests
Physical provision
Barriers such as fences
Allowances such as doors and windows
Provision of physical comfort provided the possibility of
psychological comfort when combined
physical and psychological comfort allows for a user’s
general wellbeing
Spatial planning location planning design of building
elements such as walls and
opening and energy planning
and the use of materials.
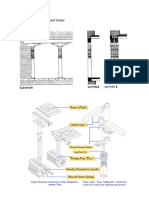
4. FUNCTIONAL FRAME:
Skeleton of a building provides
rigidity good skeleton is
important for a person so do
the building
Relationship diagram or bubble
diagram
Bubble diagram is relationship
between different rooms and
spaces within a building Walls
and floors create the frame within which different
functional spaces are enclosed, and the relationship we
create are between the activities or functions of these
spaces
TYPES OF RELATION BETWEEN SPACES
Essentials: when spaces are required to interact with each
other, example connection between kitchen and dining
room in a residence
Desired: when it is preferable that two spaces interact
with each other, but not absolutely vital.
Example, direct connection between living room and
kitchen
Tolerable: when a connection between two spaces are
acceptable but not desirable. Example direct connection
between dining room and master bedroom
Intolerable: when it is absolutely unacceptable to have a
particular relation between two spaces.
Example, connection between the puja room and toilet
5. SOCIAL MILIEU:
Sociology:
▪ is the systematic study of social behavior and human
groups
▪ is to see through the outside appearances of people’s
actions and organizations
▪ is to identify underlying, recurring patterns of and
influences on social behavior
▪ identifies the pattern of social behavior and attempts
provide explanation to those Patterns
The word Milieu >> persons surrounding OR SOCIAL
ENVIRONMENT
Humans are social animals so they cannot live without the
presence of society. Experiments are evident that working
efficiency of a person can be added if is working alone but
it does not continue for a long duration this is because a
person cannot work if s/he has no way to share the ideas
and it will be too monotonous.
Important task in architecture to create a surrounding
that responds to this human need
To reflect social status
To have better social environment and represent society
through architecture
Create better neighborhood-a degree of comfort is
achieved simply by living in a well functioning Society
Possibility of social life for the person only in well and fit
surrounding
In an open and democratic society, it isn’t so comfortable
to talk about the
hierarchy as all are said to
be equal by the state; but
the concept do not die
and it exists all over.
Inequality exists and this
is the beauty of the
society however the gap
between different class
people should be fairly
limited.
Inequality is reflected in hierarchy >>hierarchy is clearly
seen in the form of social Status
Example a peon >< Boss
Karl Marx and Max Weber
▪ Each and every building has its own peculiar social
character that’s why one can easily predict its social
status.
▪ A palace and a hut are clearly
differentiated from a glance. That’s
why; one of the major tasks of a
building is to display its social identity.
▪ Social milieu is not only for the
exposure of building character rather it
also help people to create a better
neighborhood.
Examples
✓ clusters as example where people
prefer to buy a large plot and to reside
dividing the plot in pieces just to find a
desired degree of comfort by sharing
their common daily life.
✓ Housing colonies
6. CULTURAL SYMBILISM:
Culture- a comprehensive term that people live and grow
with that shapes a person to what they are or become
Gives meaning to things and objects
Can be understood as a system of beliefs, values, customs
and behaviors that members of a society use to cope with
their world and with one another and that are transmitted
from generations to generation through learning
Is a complex concept
Is necessary for social development and for institutional
building
Is practiced in different forms like karuna, ahimsa daan,
brata jyotis shastra
Culture provides meaning of object an abstract term and
comes through various social practices practiced as
common values, empirical constructs, philosophical ideas,
moral codes, religious beliefs, ideological convictions and
economical conditions.
Tolerance (Sahishnuta) is a form of culture practiced by
Nepalese society that’s how people from different ethnic
groups are residing in a territory. Hindus and Buddhists go
to each other’s temples. The common values are
symbolized by such temples
Empirical science is manifest in Astronomy: astronomers
are found to be very prominent in society and play a very
useful role
Six philosophical ideas: Nyaya, yoga, Samkhya, Viveshika,
Advaita, Mimamsa
Important aspect of building
In Nepali concept building is a representation of whole
universe and similar concept can be found
in Greek architecture
Examples
Foundation represents serpents
Windows – eyes
Bricks -9 lakh stars
Soil- sky
Posts- Shiva
Architraves- mother goddess
Beams – bhairavs
Rafters- 64 yogini
Struts- garud, roof represents
umbrella for god and store
represent laxmi.
7. CONCLUSION:
How a building works is equally as important as how that
same building looks. When it comes to building design,
architects often have to make compromises between
form and function. Form should not follow function but be
fused together in order to add to the aesthetic dimension
of a city and to make building task worthy. It is
undoubtedly more challenging, expansive and time
consuming to achieve this kind of balance, but it is also
worth the effort.
8. REFERANCE:
▪ Wikipedia
▪ Teacher consultation
You might also like
- Theory of Architecture EssentialsDocument45 pagesTheory of Architecture EssentialsOjhi Gonzales SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Sociology in Architecture OF KeralaDocument7 pagesSociology in Architecture OF KeralaratnadeepNo ratings yet
- Christopher AlexanderDocument10 pagesChristopher AlexanderAditya P KUMARNo ratings yet
- Architecture As A Dynamic SceneDocument10 pagesArchitecture As A Dynamic SceneMorisseyVillanuevaNo ratings yet
- The Built Environment and Spatial Form PDFDocument54 pagesThe Built Environment and Spatial Form PDFkptandreasNo ratings yet
- The Built Environment and Spatial FormDocument54 pagesThe Built Environment and Spatial FormMuskan ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Abstract TemplateDocument20 pagesAbstract Templateaditi arudeNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Architecture FundamentalsDocument9 pagesIntroduction to Architecture FundamentalsArul PaulNo ratings yet
- Designing Communal Spaces in Residential Complexes: ARTSEDU 2012Document7 pagesDesigning Communal Spaces in Residential Complexes: ARTSEDU 2012Bagus Iqbal Adining PratamaNo ratings yet
- Nili Portugali Architect - Holistic Approach To ArchitectureDocument25 pagesNili Portugali Architect - Holistic Approach To ArchitectureniliportugaliNo ratings yet
- Local Building Materials and Psychology PDFDocument9 pagesLocal Building Materials and Psychology PDFArchita DuttaNo ratings yet
- RSW 1. Arc 077Document12 pagesRSW 1. Arc 077Fernandez ArnelNo ratings yet
- Synopsis PDFDocument13 pagesSynopsis PDFRia NathNo ratings yet
- An Anthropological Analysis of Home InteriorsDocument14 pagesAn Anthropological Analysis of Home InteriorsJJ__martinezNo ratings yet
- House From and Culture by AMOS RAPOPORT (Review)Document2 pagesHouse From and Culture by AMOS RAPOPORT (Review)Zarkima RanteNo ratings yet
- Cultural Influence On Evaluation System of Social Sustainability in Turkish Housing ProjectsDocument7 pagesCultural Influence On Evaluation System of Social Sustainability in Turkish Housing ProjectsIEREKPRESSNo ratings yet
- Trabajo OrlenyDocument7 pagesTrabajo Orlenyorleny guillenNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Architecture: Design Students and Physically Disabled PeopleFrom EverandRethinking Architecture: Design Students and Physically Disabled PeopleNo ratings yet
- How Architecture Regulates Social InteractionsDocument6 pagesHow Architecture Regulates Social InteractionsBianca EtcobañezNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The OrdinaryDocument16 pagesThe Structure of The OrdinaryPooja MantriNo ratings yet
- Architectural Expression: Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed To Be University College of Architecture PuneDocument3 pagesArchitectural Expression: Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed To Be University College of Architecture PuneCHILLHOP MUSICNo ratings yet
- AHolistic Approachto ArchitectureDocument47 pagesAHolistic Approachto ArchitectureTudosa TomaNo ratings yet
- A Holistic Approach To Architecture and Its Implementation in The Physical and Cultural Context of The Place-1-20Document20 pagesA Holistic Approach To Architecture and Its Implementation in The Physical and Cultural Context of The Place-1-20prasetyo prasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Cultural IdentityDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 - Cultural IdentityUmair HassanNo ratings yet
- 2003 Glenn MDocument45 pages2003 Glenn MKunal ChouguleNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Architecture in Comparison To Iconic or Organic BuildingsDocument10 pagesSustainable Architecture in Comparison To Iconic or Organic BuildingsDinozzoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Paper - Architect Aditi GuptaDocument83 pagesDissertation Paper - Architect Aditi GuptaAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Architecture 1Document9 pagesBehavioral Architecture 1Ashwini Karuna100% (1)
- Architecture and Human BehaviourDocument16 pagesArchitecture and Human BehaviourVictra JuliiNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document15 pagesDocument 1Chari GaromsaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Arts AppreciationDocument7 pagesModule 8 Arts AppreciationAngel MejiaNo ratings yet
- Effective Factors in Shaping The Identity of ArchitectureDocument8 pagesEffective Factors in Shaping The Identity of ArchitectureMonaNo ratings yet
- Essay The Idea of DesignDocument3 pagesEssay The Idea of DesignBob Peniel InapanuriNo ratings yet
- Lect. 00. TOA OverviewDocument11 pagesLect. 00. TOA OverviewKzy ayanNo ratings yet
- 14-2-2019 Paper 1 The Implications of Culture OnDocument20 pages14-2-2019 Paper 1 The Implications of Culture OnFatma HelalyNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Theory of ArchitectureDocument43 pagesUnit-1 Theory of ArchitectureSiva Raman75% (4)
- Xar 905 DissertationDocument15 pagesXar 905 DissertationPriya BalajiNo ratings yet
- Open-Built Dichotomy in ArchitectureDocument69 pagesOpen-Built Dichotomy in Architecturejiteshkohli0% (1)
- Modifying Factors of House Form Socio-Cultural Factors and House FormDocument5 pagesModifying Factors of House Form Socio-Cultural Factors and House Formmoni johnNo ratings yet
- Title:: CultureDocument6 pagesTitle:: CultureMansi SethiNo ratings yet
- Designing Communal Spaces in Residential ComplexesDocument7 pagesDesigning Communal Spaces in Residential ComplexesWaqasskhanNo ratings yet
- Architecture EmpathyDocument7 pagesArchitecture EmpathyIrene Syona, ST., M.Tp.No ratings yet
- House Form & CultureDocument11 pagesHouse Form & CultureSneha PeriwalNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topic SanjDocument22 pagesThesis Topic SanjSanjay Durai100% (1)
- Manual Clc6 EjaDocument80 pagesManual Clc6 EjaMaria XistoNo ratings yet
- On 'The Invisible in Architecture': An Environment-Behaviour Studies PerspectiveDocument8 pagesOn 'The Invisible in Architecture': An Environment-Behaviour Studies PerspectiveAhmad BorhamNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: Assignment No 1Document55 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Islamabad: Assignment No 1Javed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Licenciatura en Arquitectura - Jhusset A. Condori Paucara - Es.enDocument25 pagesLicenciatura en Arquitectura - Jhusset A. Condori Paucara - Es.enAlejandra J. C. PaucaraNo ratings yet
- Isu Module Template Subject: Arch 114: Theory of Architecture 1Document9 pagesIsu Module Template Subject: Arch 114: Theory of Architecture 1Jojemar RosarioNo ratings yet
- BK6AC3 Research Paper PaulVarghese 4472152 FinalVersionDocument13 pagesBK6AC3 Research Paper PaulVarghese 4472152 FinalVersionIron HeartNo ratings yet
- Memory Without MonumentsDocument2 pagesMemory Without MonumentsrucheshaNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Genius LociDocument5 pagesThe Concept of Genius LociNiyAz AhammadNo ratings yet
- Vogler Space ArchitectureDocument10 pagesVogler Space ArchitecturemareNo ratings yet
- Understanding Society Through ArchitectureDocument66 pagesUnderstanding Society Through ArchitectureIlda DobrinjicNo ratings yet
- Reading 20Document18 pagesReading 20Christine ChowNo ratings yet
- Sem 9 DD ElectiveDocument36 pagesSem 9 DD ElectiveSoham ShipurkarNo ratings yet
- Карточки ARCHITECTURE! - QuizletDocument7 pagesКарточки ARCHITECTURE! - QuizletNM 156No ratings yet
- Design is a Communication MediumDocument3 pagesDesign is a Communication MediumsamarNo ratings yet
- Between Notion and Reality DoshiDocument6 pagesBetween Notion and Reality DoshiAbraham Panakal100% (1)
- Unit 3Document39 pagesUnit 3SivaRaman100% (1)
- post-lintel-and-beams constructionDocument5 pagespost-lintel-and-beams constructionojjeswi gautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Fireplace and Chimney: TerminologyDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Fireplace and Chimney: TerminologyYu HanaNo ratings yet
- Temporary ConstructionDocument9 pagesTemporary Constructionojjeswi gautamNo ratings yet
- Hindu Architecture of the Vedic PeriodDocument33 pagesHindu Architecture of the Vedic Periodojjeswi gautamNo ratings yet
- DRRMQ 3 W1Document44 pagesDRRMQ 3 W1Edelmar BenosaNo ratings yet
- Amazon Food Review Clustering Using K-Means, Agglomerative & DBSCANDocument79 pagesAmazon Food Review Clustering Using K-Means, Agglomerative & DBSCANkrishnaNo ratings yet
- SDT Pipedrive Sales Dashboard TemplateDocument10 pagesSDT Pipedrive Sales Dashboard TemplateMANEESH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Probability Spinner WorksheetDocument2 pagesProbability Spinner WorksheetSara ShaiboonNo ratings yet
- LectureNotes8 PDFDocument8 pagesLectureNotes8 PDFGuoXuanChanNo ratings yet
- CPCCCA3025 Self Study GuideDocument9 pagesCPCCCA3025 Self Study GuidePranay BansalNo ratings yet
- DAY 1 Passage 1Document2 pagesDAY 1 Passage 1wick90715No ratings yet
- Produk Fermentasi Tradisional Indonesia Berbahan Dasar Pangan Hewani (Daging Dan Ikan) : A ReviewDocument15 pagesProduk Fermentasi Tradisional Indonesia Berbahan Dasar Pangan Hewani (Daging Dan Ikan) : A Reviewfebriani masrilNo ratings yet
- ECG Synthtetic - Cloudias - 07311840000004Document8 pagesECG Synthtetic - Cloudias - 07311840000004Wheel ChairNo ratings yet
- Special MantrasDocument5 pagesSpecial Mantrasvenkataramanneralla100% (2)
- Effectiveness of STEM learning approach among Malaysian secondary studentsDocument11 pagesEffectiveness of STEM learning approach among Malaysian secondary studentsJHON PAUL REGIDORNo ratings yet
- CS-D Series: Protuner Software User ManualDocument33 pagesCS-D Series: Protuner Software User ManualRudy TorrezNo ratings yet
- Non Aqueous Titrations by Gunja ChtaurvediDocument10 pagesNon Aqueous Titrations by Gunja ChtaurvediGunja Chaturvedi88% (8)
- I Am Wondering If There Is Any Value To Adding Cdms To My GT With Dln. Does Anyone Have These Systems? and If So Which Ones Would You RecommendDocument11 pagesI Am Wondering If There Is Any Value To Adding Cdms To My GT With Dln. Does Anyone Have These Systems? and If So Which Ones Would You RecommendSahariar Bin ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Leadership+from+the+Inside+Out Cashman EBSDocument13 pagesLeadership+from+the+Inside+Out Cashman EBSRepublik DakasakaNo ratings yet
- NGS QC MetricsDocument7 pagesNGS QC MetricsAgustin BernacchiaNo ratings yet
- SA5000QSG2FDocument2 pagesSA5000QSG2FYuliia TsyhanskaNo ratings yet
- EE129 Answers 724Document12 pagesEE129 Answers 724gma.roseangelikaNo ratings yet
- PGDM-IIPR Final Research Based ReportDocument9 pagesPGDM-IIPR Final Research Based Reportnavneet dubeyNo ratings yet
- How to Win Friends and Influence PeopleDocument7 pagesHow to Win Friends and Influence PeoplejzeaNo ratings yet
- Garlic As Mosquito RepellentDocument18 pagesGarlic As Mosquito Repellentagnes80% (5)
- Manual de Usuario Marco A VXMT - V1.1 - IngDocument4 pagesManual de Usuario Marco A VXMT - V1.1 - IngDiego Fernando HenaoNo ratings yet
- Md. Sabbir Hossain Khan: Contact InformationDocument4 pagesMd. Sabbir Hossain Khan: Contact InformationHimelNo ratings yet
- Eth 41276 02 PDFDocument428 pagesEth 41276 02 PDFBiljana PetrusevskaNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument5 pagesLetterSameer NaveenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic SymbolsDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Organs of Speech and Phonemic Symbolsnoah granja2No ratings yet
- MS 2015-1-2017 - Public Toilets Part 1 Design Criteria (First Revision)Document77 pagesMS 2015-1-2017 - Public Toilets Part 1 Design Criteria (First Revision)qwertypepeheheNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Forensic Interviewing Sattler JeromeDocument9 pagesClinical and Forensic Interviewing Sattler Jeromeraphael840% (1)
- Add Math SbaDocument17 pagesAdd Math SbaYana TvNo ratings yet
- A. Badal', R. Barbera, A. Bonasera, M. Gulino, A. Palmeri (Auth.), Wolfgang Bauer, Hans-Georg Ritter (Eds.) - Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 (1998, Springer US)Document389 pagesA. Badal', R. Barbera, A. Bonasera, M. Gulino, A. Palmeri (Auth.), Wolfgang Bauer, Hans-Georg Ritter (Eds.) - Advances in Nuclear Dynamics 4 (1998, Springer US)ramiphysicsNo ratings yet