Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instrumentation and Control
Uploaded by
Aadi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pagesOriginal Title
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views5 pagesInstrumentation and Control
Uploaded by
AadiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
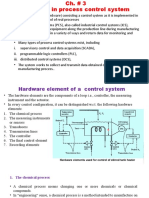
INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL
Instruments are provided to monitor the key process variables during plant
operation. Instruments monitoring critical process variables will be fitted with
automatic alarms to alert the operators to critical and hazardous situations.
The primary objectives of the designer when specifying instrumentation and
control schemes are:
Safe Plant Operation:
➢ To keep process variables within known safe operating limits.
➢ To detect dangerous situations as they develop and to provide alarms and
➢ Automatic shutdown systems.
➢ To provide interlocks and alarms to prevent dangerous operating
procedures.
Production Rate and Quality:
➢ To achieve the designed product output.
➢ To maintain the product composition within the specified quality standards.
Cost:
➢ To operate at the lowest production cost and to compensate with other
objectives.
Process instrumentation is thus brain and nerves of a process plant.
The instrumentation can be pneumatic, hydraulic, or electric. The recent trend
is to go for electronic instrumentation, but pneumatic instrumentation is still in
use. The instrumentation is required to measure temperature, pressure,
flowrate, level, physical properties as density, pH, humidity, chemical
composition etc.
TYPICAL MONITORING SYSTEMS:
10.2.1 Flow Measurement:
Due to nature of flow, it is necessary to provide effective flow measuring
devices in each supply lines. The various types of flow meters available are
orifice meter, venturi meter, pitot tube etc. Despite these the various types of
area flow meters can also be used.
Depending on temperature and velocity condition the suitable meter is
selected for measurement of flow rates and velocity.
Temperature Measuring Devices:
Many devices are used to measure the temperature variations in the process
such as mercury in glass thermometer, bimetallic thermometer, pressure spring
thermometer, thermocouples, resistance thermocouples, radiation pyrometers
and optical pyrometers are used.
Out of all these the industrial thermocouples are competitively good as they
provide large measuring range, without introducing error. Automatic control is
also possible with such devices.
List of Thermometers with temperature Range
Measuring Instrument Temp. Range ºC
Mercury in glass – thermometer -27 to 400
Mercury in pressure thermometer -40 to 540
Vapor pressure thermometer -85 to 425
Resistance -200 to 1700
Thermocouple -250 to 1700
Thermistor Up to 300
Pyrometer 1300 to 2500
Pressure Measuring Devices:
Equipment, in which the important monitoring parameter is pressure, pressure
measuring devices like pressure gauges are widely used. Safety of chemical
plants depends up on the timely measurement of pressure and its control at a
specified level.
Any excess pressure development than the design pressure may damage the
equipment in addition to the fire and other explosion hazard.
Mainly in filter pressures where the pressure is an important criterion, this
device is used.
Various pressure measuring devices are:
• U – Tube Manometer
• Differential Manometer
• Inclined Manometer
• Bourdon Tube
• Bellows
• Diaphragm valve
• Mc Leod gauge
• Pirani gauge
In addition to all measuring devices described above various measurements
like density, viscosity, pH measurements etc. are installed.
For measuring quality standards in laboratory various laboratory instruments
are also necessary.
Liquid Level:
Liquid level detectors measure either the position of a free liquid surface above
a datum level or the hydrostatic head developed by the liquid is measured.
The liquid level is measured both by direct and indirect means. Direct methods
involve direct measurement of the distance from the liquid level to a datum
level. Indirect method follows changing liquid surface position on bubble tube
method, resistance method, radiation method, etc.
DISTRIBUTED CONTROL SYSTEM (DCS):
Caprolactam production process deals with the benzene and cyclohexane
which are having low boiling points. So, the process is risky, and the product
quality is important. Therefore, for the faster control DCS can be used. It
provides ease of constant monitoring the process at a distance much far away
from the site and the changes can be made in the process parameters very
accurately from the control room itself.
Merits of DCS:
1. From quality point of view:
➢ More accuracy and reliability.
➢ Self tuning of any control loop is possible, so optimization of any process is
possible.
2. Management Consideration:
➢ Less cost of cables.
➢ Less cost of installation.
➢ Less space required.
➢ Less hardware required.
➢ Inventory information can be made available.
➢ Less manpower is required.
➢ Less production cost.
➢ Management information can be generated at regular intervals which assist
management to take decisions.
3. Operational point of view:
➢ Ease in operation.
➢ Any combination of control group, trend group, overview path can be
formed.
➢ Because of dynamic graphic role picture of process is available.
➢ Easy diagnostics of trip and emergency conditions.
➢ Automatic logging of data is done by printer and hence eliminating
weakness related human being.
➢ Control is available through dynamic graphics which gives feeling to
operator
as if he is inside the plant and controlling the process.
➢ Alarm systems can be regrouped to various subgroups so that operator can
detect the error and causes easily.
4. Engineer’s Point of view:
➢ Latest software is available for all types of complex function.
➢ Required less time for designing and detail engineering.
➢ Operators action can be logged which eliminates confusions in the event of
plant trips and consequent analysis.
➢ Flexibility is available at each level of hardware and software.
Demerits of DCS:
In present control room lot of paramagnets are seen without any intentional,
efforts hence operator feels himself existing in between the information.
In case of new DCS systems, all information and data though presented in a
systematic format, is hidden behind the CRT and hence to be called by
operator. This requires more skill and knowledge. With acceptance of DCS,
number of operators in control room decreased and hence, in case of
emergency decision must be taken by almost single handed as against group
decision in present situation.
In single loop control system failure of one controller affects only one control
loop, while case of DCS one component / card carries out lot of functions and
hence failure of it causes failure of many loops.
This calls for very high MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) and high degree of
redundancy making such systems costly.
A limitation may be felt in operating number of control loops simultaneously in
case of emergency, if adequate numbers of CRT consoles are not installed.
Skilled personnel are required.
You might also like
- Control & Instrumentation-1Document123 pagesControl & Instrumentation-1Ashish Vashisth100% (8)
- Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionFrom EverandIndustrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: How Infrared Analysis Can be Used to Improve Equipment InspectionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Chapter-3 InstrumentationDocument14 pagesChapter-3 InstrumentationIrtiza RasulNo ratings yet
- Process Control Instrumentation Technology 8th EdDocument69 pagesProcess Control Instrumentation Technology 8th EdAffify AfifyNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Study of Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID), Distributed Control SystemsDocument32 pagesProject Report: Study of Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID), Distributed Control SystemsrockynsitNo ratings yet
- Keys To On-Line Monitoring in Steam Generating SystemsDocument9 pagesKeys To On-Line Monitoring in Steam Generating SystemsShameer MajeedNo ratings yet
- Bee - Code Development Project: Draft Code ON Fluid Piping SystemsDocument49 pagesBee - Code Development Project: Draft Code ON Fluid Piping SystemsNaveen ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Anonymous tytJlPojNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation and ControlDocument7 pagesInstrumentation and ControlhonourNo ratings yet
- Improve Refinery Production and Efficiency With Asset MonitoringDocument11 pagesImprove Refinery Production and Efficiency With Asset MonitoringVishwarajNo ratings yet
- Inline Concentration Measurement with μ-ICC 2.45Document6 pagesInline Concentration Measurement with μ-ICC 2.45TUAN ANHNo ratings yet
- CLB 21303 Process Instrumentatio N and ControlDocument48 pagesCLB 21303 Process Instrumentatio N and ControlanisNo ratings yet
- CLB 21303 Process Instrumentation and ControlDocument48 pagesCLB 21303 Process Instrumentation and ControlSyafiqIsmiNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation in Oil and GasDocument2 pagesProcess Instrumentation in Oil and GasDEEPAK KUMARNo ratings yet
- Proportion AirDocument7 pagesProportion AirNayagi Industrial TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Monitoring and ControlDocument32 pagesCHAPTER 3 Monitoring and Controlmichaelmude16No ratings yet
- IoT r19 Unit 5Document12 pagesIoT r19 Unit 5yasshNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation For Process ControlDocument153 pagesInstrumentation For Process ControlAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation & Measurement LectureDocument22 pagesInstrumentation & Measurement LectureAleeza AshfaqueNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Measuring DevicesDocument12 pagesTopic 1: Measuring DevicesKrizia AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Level MeasurementsDocument5 pagesLevel MeasurementsRobert BanagaNo ratings yet
- 5 Nstrument Selection Criteria and Installation ProceduresDocument5 pages5 Nstrument Selection Criteria and Installation ProceduresAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department College of Engineering and Technology Adigrat UniversityDocument33 pagesChemical Engineering Department College of Engineering and Technology Adigrat Universitykibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument128 pagesREVIEWERDhafnylynn MacasaetNo ratings yet
- Concept of Instrumentation IN Thermal Power StationDocument93 pagesConcept of Instrumentation IN Thermal Power StationShraddha RautNo ratings yet
- Process Control CHP 1Document53 pagesProcess Control CHP 1kishoreprithikaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionSANJAYNo ratings yet
- HTTPWWW - Pc-Education - Mcmaster.cainstrumentationgo Inst - HTMDocument85 pagesHTTPWWW - Pc-Education - Mcmaster.cainstrumentationgo Inst - HTMTaha HasanNo ratings yet
- Measurement Task (4) (D2)Document7 pagesMeasurement Task (4) (D2)Medo ElzaeemNo ratings yet
- AP Instruments RheolabQCDocument6 pagesAP Instruments RheolabQCAndrés MárquezNo ratings yet
- Control & Inst - V-IDocument180 pagesControl & Inst - V-ISiva Kumar TutikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Overview: 3: Sensors and ActuatorsDocument93 pagesChapter Overview: 3: Sensors and ActuatorsGigiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionFrom EverandAdvanced Temperature Measurement and Control, Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Presntation (Installing Instrumentation and Control Devices)Document35 pagesPresntation (Installing Instrumentation and Control Devices)habtemariam mollaNo ratings yet
- Facility ValidationDocument12 pagesFacility ValidationGhanta Ranjith Kumar100% (1)
- Designing of Indigenous Monitoring SystemDocument16 pagesDesigning of Indigenous Monitoring SystemNasir AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Indian Oil Corporation Report on PLC and DCS SystemsDocument19 pagesIndian Oil Corporation Report on PLC and DCS SystemsHimanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring TechniquesDocument28 pagesCondition Monitoring TechniquesMECHA ENGINEEERINGNo ratings yet
- Unit III Condition MonitoringDocument28 pagesUnit III Condition MonitoringMECHA ENGINEEERINGNo ratings yet
- Subject: Moee: Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of Diploma Eng., RDocument4 pagesSubject: Moee: Sanjaybhai Rajguru College of Diploma Eng., RshivamNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation PrinciplesDocument66 pagesProcess Instrumentation PrinciplesnizamuddinNo ratings yet
- My Notes PCTDocument36 pagesMy Notes PCTPortia ShilengeNo ratings yet
- Process InstrumentationDocument71 pagesProcess InstrumentationPrasanna kumar subudhiNo ratings yet
- CD3203 PDFDocument26 pagesCD3203 PDFanggyNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 6: Instrumentation & ControlDocument8 pagesChapter # 6: Instrumentation & ControlAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- 1. MEASUREMENT TechniqueDocument13 pages1. MEASUREMENT Techniqueseherr719No ratings yet
- To Observe, Measure and Control Process VariablesDocument9 pagesTo Observe, Measure and Control Process VariablesKate Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- CH 1 - Intro J5800Document54 pagesCH 1 - Intro J5800mohd_mizanNo ratings yet
- Understand The Necessary Decisions Needed in Making ProcessDocument18 pagesUnderstand The Necessary Decisions Needed in Making ProcessGrazel MDNo ratings yet
- Instrument Selection GuideDocument39 pagesInstrument Selection Guide1meander23100% (1)
- Process Instrumentation and Control and Safety Aspects: Production of LPG From Natural GasDocument2 pagesProcess Instrumentation and Control and Safety Aspects: Production of LPG From Natural Gassaur1No ratings yet
- Flowmeters CourseDocument382 pagesFlowmeters CourseKah Hom100% (3)
- Hardware and Digital Control of Chemical ProcessesDocument6 pagesHardware and Digital Control of Chemical ProcessesAyda Azali50% (2)
- Chemical Enginineering Fourth YearDocument68 pagesChemical Enginineering Fourth YearHabib NuredinNo ratings yet
- Basics of Instrumentation: Measuring PressureDocument96 pagesBasics of Instrumentation: Measuring PressureVishal Kumar Laddha100% (1)
- Automation Systems ArchitectureDocument159 pagesAutomation Systems ArchitectureTeenaNo ratings yet
- 09 Vacuum MeasurementDocument44 pages09 Vacuum MeasurementRamakrisnna GunasegaranNo ratings yet
- Vertical Separator Control and Instrumentation RepeatDocument12 pagesVertical Separator Control and Instrumentation RepeatklpiNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL PARAMETERS CONTROL USING PLC AND SCADADocument48 pagesINDUSTRIAL PARAMETERS CONTROL USING PLC AND SCADAJwala RaginiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentFrom EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Major Equipment DesignDocument22 pagesMajor Equipment DesignAadiNo ratings yet
- HAZOP StudyDocument11 pagesHAZOP StudyAadiNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument10 pagesEnergy BalanceAadiNo ratings yet
- Cost EstimationDocument7 pagesCost EstimationAadiNo ratings yet
- Che 415 Part1aDocument61 pagesChe 415 Part1aChristian NwekeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Data PDFDocument380 pagesThermodynamic Data PDFhumusdelombrizNo ratings yet
- Ad-I QB Updated PDFDocument58 pagesAd-I QB Updated PDFHema priyaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 English PDFDocument214 pagesScience 9 English PDFAham GtyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Section 2: Properties of FluidsDocument55 pagesChapter 14: Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Section 2: Properties of FluidsMohammed AlkubaishNo ratings yet
- Modul Peka Science Year 5Document14 pagesModul Peka Science Year 5Helyza Hayes100% (1)
- Thermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and DefinitionDocument8 pagesThermodynamics 1 Basic Principles, Concepts and DefinitionHENRICK IGLENo ratings yet
- Report Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesReport Fluid Mechanicszatulsyera19No ratings yet
- A General Chemistry II 12 q1m1.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutDocument21 pagesA General Chemistry II 12 q1m1.3 Teacher Copy Final LayoutCristine Mae MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Internal Oil - Gas SeparationDocument36 pagesInternal Oil - Gas SeparationAntonio EstevezNo ratings yet
- Spiral PresentationDocument30 pagesSpiral Presentationmramos4191No ratings yet
- SIMULATIONS OF CHEMICAL ABSORPTIONDocument19 pagesSIMULATIONS OF CHEMICAL ABSORPTIONraz naghizaNo ratings yet
- Science Form1 Chapter 7Document27 pagesScience Form1 Chapter 7Sue Suraya Naza100% (1)
- Edsci ReviewerDocument16 pagesEdsci ReviewerElla GuintoNo ratings yet
- Stefanescu - Science and Engineering of Casting SolidificationDocument354 pagesStefanescu - Science and Engineering of Casting SolidificationThais FernandesNo ratings yet
- Bcga Code of Practice CP 20: Bulk Liquid Oxygen Storage at Production SitesDocument55 pagesBcga Code of Practice CP 20: Bulk Liquid Oxygen Storage at Production Sitesfadlul akbar herfiantoNo ratings yet
- ATA 21. Air Conditioning As-05-02 (PLAN-09)Document81 pagesATA 21. Air Conditioning As-05-02 (PLAN-09)faisalNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces and States of MatterDocument13 pagesIntermolecular Forces and States of MatterCaryl Ann C. SernadillaNo ratings yet
- Physics Ii: Technological University of The Philippines-Taguig Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument129 pagesPhysics Ii: Technological University of The Philippines-Taguig Electrical Engineering DepartmentEsmeralda Tapiz0% (2)
- Sullair Filtration PDFDocument12 pagesSullair Filtration PDFmahmod alrousanNo ratings yet
- N991 Series Spec SheetDocument2 pagesN991 Series Spec SheetJavier GarciaNo ratings yet
- MIBKDocument2 pagesMIBKthomas_v501925No ratings yet
- Offshore Rig Technology Catalog 2014: Cementing Wireline Logging Well Testing Surface and Mud LoggingDocument108 pagesOffshore Rig Technology Catalog 2014: Cementing Wireline Logging Well Testing Surface and Mud LoggingRagu RajanNo ratings yet
- D - Two-Phase Flow Lab ManualDocument23 pagesD - Two-Phase Flow Lab ManualdanielNo ratings yet
- Fire NotesDocument39 pagesFire NotesJovie Masongsong100% (1)
- TF 33 VaporPhaseDesignDocument12 pagesTF 33 VaporPhaseDesignAdnen GuedriaNo ratings yet
- V5X Tropical VRF Outdoor UnitDocument1 pageV5X Tropical VRF Outdoor UnitmohanadalhalabiNo ratings yet
- Chromalox Technical OverviewDocument78 pagesChromalox Technical Overviewalexiuteodor100% (1)
- LPG Cargo Measurement and Calculation Procedure PDFDocument3 pagesLPG Cargo Measurement and Calculation Procedure PDFJohn Green100% (3)
- FloefdDocument12 pagesFloefdPradeep Kumar SrinivasanNo ratings yet