Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSTP Reviewer
Uploaded by
Trexy Norial0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pages.
Original Title
NSTP-REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views4 pagesNSTP Reviewer
Uploaded by
Trexy Norial.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Introduction to First Aid Characteristics of a Good First Aider
First Aid
An immediate help provided to a sick Communication Skills
or injured person until professional The Ability to Work Under
medical help arrives or becomes Pressure
available. Initiative and Leadership
The Ability to Work in a Team
Positivity
Objectives of First Aid Gentle
1. Preserve life. Resourceful
2. Prevent the escalation of the Observant
illness or injury Tactful
3. Seek immediate medical Emphatic
help. Respectful
4. Provide reassurance.
Hindrances in Giving First Aid
Legal Concerns 1. Unfavorable
1. Consent surroundings
2. Duty to Act 2. The presence of crowds
3. Standard of Care 3. Pressure from victim or relatives
4. Negligence
5. Abandonment
6. Confidentiality Disease Transmission
Infectious diseases are those that
can spread from one person to
First Aider’s Responsibilities another through the following ways:
• Assess the situation quickly and ❑ Direct Contact
calmly ❑ Indirect Contact
• Comfort, reassure, stay calm and ❑ Airborne Transmission
take charge. ❑ Vector Transmission
• Protect yourself and the casualty
from any danger
• Prevent infection between you and Prevention and Protection
them. Body Substance Isolation (BSI) -
• Assess the casualty. are precautions taken to isolate or
• Give first aid treatment prevent
• Arrange for the right kind of help. risk of exposure from any type of body
substance.
Basic Precautions & Practices
● Personal Hygiene
● Protective Equipment SHOCK
● Equipment Cleaning and Disinfecting
A condition in which the circulatory
system fails to deliver enough oxygen
First Aid Equipment and Supplies – rich blood to the body tissues and
vital organs.
First Aid Basic
Equipment
❖ Spine Board Dangers of Shock
❖ Short / Kendrick’s Extrication
Lead to death
Device Predisposes body infection
❖ Sets of Splints Lead to loss of body parts
❖ Poles
❖ Blankets
Causes of Shock
Spine Board
Kendrick’s Extrication 1. Severe bleeding
Device 2. Crushing injury
3. Infection
4. Heart attack
Basic First Aid Kit Contents 5. Perforation
• Rubbing alcohol 6. Shell bomb and bullet wound
• Gloves 7. Rupture of tubal pregnancies
• Povidone iodine 8. Anaphylaxis
• Scissors 9. Starvation and disease
• Cotton
• Forceps
• Gauze pads Types of Shock
• Triangular Bandage
Hypovolaemic
• Tongue depressor
- meaning not enough blood volume
• Elastic roller bandage
Cardiogenic
• Penlight
- caused when the heart cannot
• Occlusive dressing
effectively pump blood around the body.
• Band aid
Neurogenic
- injury to a person’s spine may damage
Cloth Materials the nerves that control the diameter
Commonly Used in First Aid (width) of blood vessels.
1. Dressing - any sterile cloth material Septic
used to cover the wound. - an infection makes the blood vessels
2.Bandage - any cloth material sterile dilate, which drops blood pressure
or not, used to hold the dressing in Anaphylactic
place. - a severe allergic reaction causes blood
vessels to dilate, which results in low
blood pressure FIRST Aid and Preventive
Obstructive Management for Shock
- blood flow is stopped
Endocrine
- in a critically ill person PROPER
Posture
Heat
Anaphylaxis Transfer
Angioedema of the face such that the
boy is unable to open his eyes. This
reaction was caused by an allergen WOUND
exposure. is a break in the continuity of a tissue of
the body either internal or external
Signs and Symptoms of Shock Two classifications of WOUND
1. Face-pale - Close Wound
2. Skin-cold and - Open Wound
clammy
3. Breathing-irregular
4. Pulse-rapid and weak 1. Closed wound
5. Nausea and vomiting Causes:
6. Weakness •Blunt objects result in contusion
7. Thirsty or bruises
•Application of external forces
Objectives of First Aid for Shock Signs and Symptoms of Closed
Wound
Improve circulation of blood. Ensure an ✔ Pain &Tenderness
adequate supply of oxygen. Maintain
✔ Swelling
normal body temperature.
✔ Discoloration
✔ Hematoma
First Aid Management for Shock ✔ Uncontrolled
restlessness
1. Make the person lie down.
✔ Thirst
2. Control any external bleeding.
3. Legs may be raised 6 to 12 inches. ✔ Symptoms of shock
4. Help the person maintain normal ✔ Vomitting or
body temperature. cough-up blood
5. Do not give the person anything to ✔ Passage of blood in
eat or drink. the urine or feces
6. Reassure the person every so often. ✔ Sign of blood along mouth, nose and
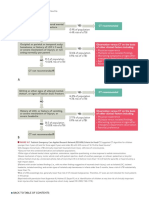
First Aid Management for
ear Open Wound With Severe Bleeding
C- Control Bleeding
C- Cover the wound
First Aid Management for Closed
C- Care for shock
Wound
C- Call or refer to physician
I Ice application
C Compression
E Elevation First Aid Management
S Splinting
Wound With Bleeding Not Severe
(Home Care)
2. Open wound ■ Clean the wound with soap and water.
■ Apply mild antiseptics.
■ Cover wound with dressing and
Classifications of Open Wound bandage.
Dangers of Open Wound
■ Hemorrhage
■ Infection
■ Shock
You might also like
- NSTP 002 - Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesNSTP 002 - Midterm ReviewerDENIEL MIKE DUKANo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument59 pagesBasic First AidRegina Angelica MacapagalNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument32 pagesFirst Aid GuideSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Deftact ReviewerDocument4 pagesDeftact ReviewerKIMBERLY MARGARETTE REDNo ratings yet
- First Aid 2Document4 pagesFirst Aid 2ivy gliezelle tabafaNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID and BANDAGINGDocument36 pagesFIRST AID and BANDAGINGAlzeia Presto Agas100% (1)
- FIRST AID Rot 1Document12 pagesFIRST AID Rot 1lofrancobrentNo ratings yet
- Emergency Preparedness - First AidDocument96 pagesEmergency Preparedness - First AidFerdinand DillaNo ratings yet
- CH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIDocument42 pagesCH161 Lecture 9-10 - GIKIHabny ShaaNo ratings yet
- Firstaid 12Document30 pagesFirstaid 12Roseman TumaliuanNo ratings yet
- First Aid ProgramDocument55 pagesFirst Aid ProgramYudha PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Module First AidDocument12 pagesModule First AidHermie JosephNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument18 pagesFirst AidMDRRM MangaldanNo ratings yet
- First Aid Powerpoint SASDocument50 pagesFirst Aid Powerpoint SASMahmoud HalimNo ratings yet
- Jonathan C. Lubag Unintentional Injuries Q3M1 W1-3Document26 pagesJonathan C. Lubag Unintentional Injuries Q3M1 W1-3Jonathan LubagNo ratings yet
- 59212615-Emergency-Nursing 2Document35 pages59212615-Emergency-Nursing 2Chernobyle Tolentino BattadNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid: Sameer Shaikh (B.Sc.,ADIS.)Document22 pagesBasic First Aid: Sameer Shaikh (B.Sc.,ADIS.)DJadee Anuppur AmlaiNo ratings yet
- First Aid Lesson HandoutsDocument3 pagesFirst Aid Lesson HandoutsGuia Camandang100% (1)
- Introduction To First Aid and Basic Life Support Prof.M.villanuevaDocument130 pagesIntroduction To First Aid and Basic Life Support Prof.M.villanuevalanlanpare07No ratings yet
- First Aid UpdatedDocument116 pagesFirst Aid UpdatedOmar SaturnoNo ratings yet
- Transferring and BandagingDocument8 pagesTransferring and BandagingDarwin AndalNo ratings yet
- Efat PDFDocument56 pagesEfat PDFjs enterprisesNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID Deft 003Document36 pagesFIRST AID Deft 003Velano, Areanne, A.No ratings yet
- Course: Emergency Procedures and Patient Care Lecture-7Document33 pagesCourse: Emergency Procedures and Patient Care Lecture-7saba ramzanNo ratings yet
- 1st Aid AdultDocument71 pages1st Aid Adultzygomatic medicalresourcesNo ratings yet
- Firstaid 190724134425Document93 pagesFirstaid 190724134425Nina BachoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Q1-Unintentional Injury Prevention Safety and First AidDocument17 pages3rd Q1-Unintentional Injury Prevention Safety and First AidRobelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- First Aid CourseDocument13 pagesFirst Aid Course胡欣苓No ratings yet
- Basic First Aid 0808Document72 pagesBasic First Aid 0808BS AnilKumarNo ratings yet
- First Aid Guide: Brand Adhesive BandagesDocument11 pagesFirst Aid Guide: Brand Adhesive BandagesRebecca Park TotiloNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument25 pagesShockMohammad Ali Al-garniNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument75 pagesFirst Aidamila_vithanage100% (1)
- Basic First Aid 0808Document70 pagesBasic First Aid 0808pokiriNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyDocument25 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyCasNo ratings yet
- FIRST AID Is The Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Have Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllDocument4 pagesFIRST AID Is The Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Have Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllNat CatalanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPrancisco Yuan VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury, Prevention, SafetyDocument42 pagesUnintentional Injury, Prevention, SafetyMaika Jimenez100% (1)
- P.E 1 Basic Life Support (BLS) 1: Check For ResponsivenessDocument5 pagesP.E 1 Basic Life Support (BLS) 1: Check For ResponsivenessThea GailNo ratings yet
- Health Group3Document29 pagesHealth Group3Angela OrenseNo ratings yet
- CPR and First Aid GuidelinesDocument145 pagesCPR and First Aid Guidelinesprecious maningasNo ratings yet
- Alcalde Jose Street, Kapasigan, Pasig City: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Pasig College of NursingDocument64 pagesAlcalde Jose Street, Kapasigan, Pasig City: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Pasig College of NursingJhester de leonNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument117 pagesBasic First AidAstrero Kristle Jeian V.No ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF TACTICAL COMBAT CASUALTY CARE For PPSCDocument80 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF TACTICAL COMBAT CASUALTY CARE For PPSColiver garcianoNo ratings yet
- Basic First AidDocument70 pagesBasic First AidJames100% (1)
- First AidDocument7 pagesFirst AidElla MarieNo ratings yet
- Roles and Responsibilities of The First AiderDocument8 pagesRoles and Responsibilities of The First AiderPascual Ronald PatrickNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument39 pagesFirst AidMiguel Carlos Navarro TacderanNo ratings yet
- Skills 118 Final LizaDocument66 pagesSkills 118 Final LizaojiNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid 0808Document71 pagesBasic First Aid 0808Vishwa ReddyNo ratings yet
- First - Aid Common Emergencies and Safety Practices in Outdoor ActivitiesDocument14 pagesFirst - Aid Common Emergencies and Safety Practices in Outdoor ActivitiesJhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- First Aid Course 2006 Siw Sandell First Aid InstructorDocument47 pagesFirst Aid Course 2006 Siw Sandell First Aid InstructorkhurramNo ratings yet
- First Aid LessonDocument26 pagesFirst Aid Lessoncharisse grace esquivelNo ratings yet
- NSTP Lesson 10-14 ReviewerDocument9 pagesNSTP Lesson 10-14 ReviewerJulianne P. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Responding EmergencyDocument25 pagesResponding EmergencyJjorie OmbajinNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument171 pagesFirst AidJoseph RamirezNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Self Learning PackageDocument40 pagesWeek 1 Self Learning PackageShelly Marie LuganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To First Aid (Week 1 & 2) First AidDocument12 pagesIntroduction To First Aid (Week 1 & 2) First AidZirc Molina100% (2)
- Basic First Aid Leading To Gawad KalasagDocument85 pagesBasic First Aid Leading To Gawad KalasagCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument50 pagesFirst AidsreesajeshNo ratings yet
- Suicide An Overview For CliniciansDocument12 pagesSuicide An Overview For CliniciansJuan Dario Mogollon SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- VATI Mental Health RemediationDocument2 pagesVATI Mental Health RemediationestberryNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-548908089No ratings yet
- Anosmia (Lost Sense of Smell) - Definition, Causes, SymptomsDocument10 pagesAnosmia (Lost Sense of Smell) - Definition, Causes, Symptomsrizvee.pdb21No ratings yet
- Neurology Request FormDocument4 pagesNeurology Request FormMegen PLCNo ratings yet
- Split ReportDocument23 pagesSplit Reportjomer ryanNo ratings yet
- Management of Psychotic SymptomsDocument25 pagesManagement of Psychotic Symptomsmisstheatricality130No ratings yet
- Demographic Profile and Risk Factors of Stroke Patients in A Tertiary Care Centre of NepalDocument4 pagesDemographic Profile and Risk Factors of Stroke Patients in A Tertiary Care Centre of NepalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Biology INVESTIGATORY PROJECT ON ADHDDocument14 pagesBiology INVESTIGATORY PROJECT ON ADHDVIGNESH50% (2)
- Slipped Capital Femoral EpiphysisDocument22 pagesSlipped Capital Femoral Epiphysisrithesh ramachandranNo ratings yet
- 2020 AHA Guidelines For CPR & ECCDocument42 pages2020 AHA Guidelines For CPR & ECCArun100% (1)
- Birth Defects Congenital Malformations)Document4 pagesBirth Defects Congenital Malformations)Ting Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- Suicide Risk Management ProtocolDocument3 pagesSuicide Risk Management Protocolleeperlhan2000No ratings yet
- Price & Services Quotation ListDocument3 pagesPrice & Services Quotation ListNurmunirah DasnanNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan Bahasa Inggris Hardianti YahyaDocument3 pagesRingkasan Bahasa Inggris Hardianti YahyaHardianti YahyaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pengaruh Musik Mozart Terhadap Perubahan Perilaku Hiperaktif Anak Adhd Usia 7-12 TahunDocument16 pagesJurnal Pengaruh Musik Mozart Terhadap Perubahan Perilaku Hiperaktif Anak Adhd Usia 7-12 TahunroryputrisartikaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOTHERAPEUTICS - II CASE PRESENTATION ON PSORIASIS by SRIRAM ADocument21 pagesPHARMACOTHERAPEUTICS - II CASE PRESENTATION ON PSORIASIS by SRIRAM ASriram Surya100% (1)
- Bipolar Case Study 1Document15 pagesBipolar Case Study 1api-545034336No ratings yet
- Case Study FormatDocument4 pagesCase Study FormatNeru RoriNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching PlanAno BaIto100% (1)
- Denistya Amalia - Task and Answer Task 3.3 Writing Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesDenistya Amalia - Task and Answer Task 3.3 Writing Nursing DiagnosisNazimatul FitriyahNo ratings yet
- GI DisordersDocument47 pagesGI DisordersSinchan GhoshNo ratings yet
- Psychosis Case StudyDocument3 pagesPsychosis Case StudyYolaWidyaMelaniNo ratings yet
- Maschio Et Al (2019) Management of Epilelsy in Brain TumorsDocument18 pagesMaschio Et Al (2019) Management of Epilelsy in Brain TumorssitialimahNo ratings yet
- PECARN Criteria For Head CTDocument1 pagePECARN Criteria For Head CTwhitecoatNo ratings yet
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument21 pagesMental Status ExaminationAthul RajNo ratings yet
- Guadiana & Okashima, 2020)Document3 pagesGuadiana & Okashima, 2020)Jenina Marinelle AndresNo ratings yet
- Case Based Discussion 2-Adjustment Disorder Year 5 Rotation 5Document26 pagesCase Based Discussion 2-Adjustment Disorder Year 5 Rotation 5Priya GKNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFDocument5 pagesUrine Screening For Metabolic Disorders PDFJustine Nicole Clavel LachicaNo ratings yet
- Delusional Disorder DSM 5Document11 pagesDelusional Disorder DSM 5Mohamed Asri Zaini100% (1)