Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 - 16 Notes
6 - 16 Notes
Uploaded by
Fefe Jeje0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views7 pagesThis document provides an overview of the anatomy, function, examination techniques, and common abnormalities of the breasts, lungs, and heart. Key points include:
- The breasts' main purpose is to produce milk, and their internal structure includes glandular tissues and Cooper's ligaments. The lymphatic drainage patterns and the Tanner scale for adolescent development are also discussed.
- The lungs have four main functions: oxygenation, acid-base balance, temperature control, and carbon dioxide removal. Examination involves inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation of the chest. Abnormal findings may include signs of COPD, infections, or scoliosis.
- The heart sounds (S1, S
Original Description:
Original Title
Copy of 6_16 Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the anatomy, function, examination techniques, and common abnormalities of the breasts, lungs, and heart. Key points include:
- The breasts' main purpose is to produce milk, and their internal structure includes glandular tissues and Cooper's ligaments. The lymphatic drainage patterns and the Tanner scale for adolescent development are also discussed.
- The lungs have four main functions: oxygenation, acid-base balance, temperature control, and carbon dioxide removal. Examination involves inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation of the chest. Abnormal findings may include signs of COPD, infections, or scoliosis.
- The heart sounds (S1, S
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views7 pages6 - 16 Notes
6 - 16 Notes
Uploaded by
Fefe JejeThis document provides an overview of the anatomy, function, examination techniques, and common abnormalities of the breasts, lungs, and heart. Key points include:
- The breasts' main purpose is to produce milk, and their internal structure includes glandular tissues and Cooper's ligaments. The lymphatic drainage patterns and the Tanner scale for adolescent development are also discussed.
- The lungs have four main functions: oxygenation, acid-base balance, temperature control, and carbon dioxide removal. Examination involves inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation of the chest. Abnormal findings may include signs of COPD, infections, or scoliosis.
- The heart sounds (S1, S
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
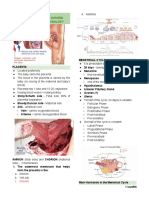
Breasts and regional lymphatics - CH17
● Structure and function
○ Remember the tail of Spence
○ nipple and areola are same color
○ nipple darken for baby to see it better
● Internal anatomy
○ main purpose - produce milk
○ glandular tissues
○ Cooper’s ligaments
■ keep breasts perky
■ in aging breakdown of these leads to breast sagging
● 4 quadrants
○ used to identify and locate abnormalities
● Lymphatics
○ know drainage patterns, not names
● Developmental care
○ Tanner Scale - adolescence measure
○ unbalanced maturation rate is norma
○ aging woman
■ dec of estrogen leads to replacing breast tissue with fibrous tissue
■ dec of adipose tissue
○ men
■ can get breast cancer
■ gynecomastia
● somewhat normal, temporary breast growth during puberty
● Subjective evaluation
○ Breast
■ pain
● localized or generalized?
● PQRSTU
■ lump
● fixed or moveable
● change during period?
● associated skin changes
■ discharge
● unless pregnant or lactating NEVER OK
● assess color, odor, thickness, both breasts?
■ rash
● where? on nipple and areola?
■ swelling
● unilateral, changes in breast size
■ trauma
■ History of breast disease
● benign breast disease - may be normal, but makes it more difficult
to recognize problems.
■ Surgery
● breast augmentation/reduction, mastectomy,
■ Self-care Behavior
● self exam
● last exam
● self exam between days 3-7 of cycle
● mammograms - annual after 40 if you have a history, every 3
years with no history.
■ Axilla
● tenderness
■ Preadolescents
● changes in breasts
● hair
● how do they feel about it?
■ Pregnancy
● plans to breastfeed
● enlargement - fitting bras
■ Menopausal
● changes, location, sagging of breasts
■ changes throughout menstrual cycle
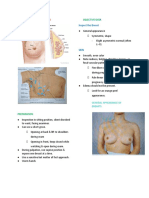
● Objective exam
○ disrobe to waist
○ inspect
■ general color and appearance
■ nipples look about same size shape and direction
■ screen for retraction
● arms above head
○ breasts lift symmetrical
● hands on hip and press
○ breasts should line up
● lean forward and let breasts swing
● put them on the glass
■ inspect and palpate axillae
■ look for supernumerary nipples
○ Breasts
■ normal sized breasts, palpate supine, place cloth under shoulder
■ large breasts - bimanual palpation
■ use any palpation method, just cover all the breast tissue
■ expected findings
● no lumps
● wear gloves and squeeze nipple to check for discharge
■ if lump is found
● location: 7:00, 3cm from nipple
● size
● shape
● consistency
● tenderness
● palpable lymph nodes
○ Teach self exam
■ schedule
● 3rd-7th day of cycle
■ correct techniques
● recommend checking in shower
■ return demonstration
● make sure that the PT can demonstrate proper self exam
○ Male breast
■ can be cause by testosterone deficiency
■ can be in adolescence
■ Should be temporary
■ In older adults, can indicate problems, should be referred to a specialist
Thorax and lungs - Ch18
● Structure and function
○ review anatomy
○ diaphragm sits right at the xyphoid process
○ Reference lines
■ midsternal
● separate left and right
■ midclavicular line
■ anterior axillary line
■ vertebral line
■ scapular line
■ midaxillary line
■ posterior axillary line
○ Thoracic cavity
■ mediastinum
● includes heart, great vessels, esophagus
■ lobes
● right 3
● left 2
● Four functions of respiratory system
○ supply oxygen to body
■ inspiration
● diaphragm lowers, creating vacuum
● O2 enters acinus and then blood
○ expiration
■ passive force
■ hypercapnia is main drive to breathe
○ acid/base balance
■ CO2 is an acid. Respiration can inc or dec CO2 levels
○ Temperature control
■ resp rate increases as body temperature increases
● Subjective questions
○ cough
■ frequency
■ length
■ productive?
● color
● thickness
● bloody - hemoptysis
● continuous thru day?
○ SOB - shortness of breath
■ orthopnea - can’t breathe lying down
■ r/t wheezing?
■ r/t cyanosis?
■ what does pt do when they have SOB?
○ Chest pain
■ localized
■ r/t trauma?
○ History of resp infections
■ family history of allergies
■ unusually frequent colds?
○ Smoking history
■ second hand smoke
■ number/day
■ last time smoking?
○ Environmental exposure
■ valley fever
■ asbestos
○ Self-care behaviors
■ TB test
■ vaccines
■ hospitalization - requires screening for vaccinations and smoking history
● Objective data
○ posterior chest
■ thoracic cage
● shape of chest wall
● accessory muscles - hypertrophy to shoulder muscles
● compare anterior to posterior
○ barrelchest?
■ can be COPD (can be chronic bronchitis or
emphysema)
● position of PT
○ tripod/hunching
● skin color/condition
○ symmetric
○ even coloration
■ palpation
● symmetric expansion
● tactile fremitus
○ feel vibrations
○ p423
○ symmetry of vibration is most important
○ weaker fremitus means more air, stronger fremitus means
consolidation
● palpate chest wall
■ percussion
● p435
● predominant note over lung fields
● diaphragmatic excursion
○ percuss to find movement of diaphragm
■ normal 3-5 cm
■ Auscultation
● breath sounds
○ PT breathes through the mouth
○ 9 places to auscultate p 437
● normal noises
○ bronchial breath sounds
■ trachea and mainstem bronchi
■ bronchoveicular
■ vesicular sounds - in the alveoli
○ adventitious sounds (abnormal)
■ crackles
■ wheeze
■ atelectatic crackles
○ Voice sounds
■ bronchophony
■ egophony
■ Anterior chest
● inspect
○ retraction (pulling on intercostals)
● symmetric expansion
● tactile fremitus
● auscultate
○ breathing sounds
■ Abnormal findings
● barrel chest - anterior/posterior ratio of 1:1
○ can indicate COPD
● scoliosis
○ can cause pressure on lungs
● kyphosis
○ humped back esp in older people
○ can cause problems in lung volume
● Respiratory findings
○ normal breathing - 12-20 breaths per minute
○ >20 - tachypnea
○ <12 - bradypnea
○ hyperventilation
● Discontinuous sounds
○ crackles
○ wheezes
○ stridor
Heart and neck vessels - Ch 19
● S1 - lub - closing of AV valve
● S2 - dub - closing of semilunar valve
● murmurs can be auscultated
○ can be inversely proportional to the size of the defect
■ ie - small hole = big noise and more turbulence
● Neck vessels
○ carotids are palpable
■ don’t palpate both @ same time
● subjective history
○ chest pain
■ referred pain
■ activity
■ emotion
■ associated symptoms
● pale
● cold sweat
● nausea
○ dyspnea
■ difficulty breathing on exertion
○ fatigue
■ increased fatigue caused by decrease of oxygen delivered to body
■ often worse in the evening
■ new onset?
■ duration
○ cyanosis or pallor
■ from low O2 carrying capacity or decrease in cardiac output
○ Edema
■ mostly in lower extremities - dependant edema.
■ does it go away when you put your feet up
■ if related to heart, can be worse in the evening
○ nocturia
■ when sleeping, kidneys are able to work at full capacity
○ cardiac history
■ surgery
■ meds
○ family history
○ personal habits (cardiac risk factors)
■ changeable
● smoking
● diet
● weight
■ non changeable
● genetic
● Objective data
○ carotids
■ equal strength between both
■ auscultate with bell for bruits (whooshing). Not found in healthy PT
○ jugulars
■ inspect, look for venous pulse
○ Precordium
■ inspect anterior chest
● symmetry, expansion, color, abnormal pulsations
■ palpate apical impulse
● 4th intercostal, midclavicular line
■ palpate across precordium
● look for a thrill (abnormal pulsation). Should not be found in
healthy PT
■ percuss to outline cardiac borders
● or just use xray
■ auscultate
● use diaphragm, then bell
● p475 has all locations
■ assess pulse rate and rhythm
You might also like
- Pregnant: AthleteDocument273 pagesPregnant: AthleteVương Vi Vu100% (1)
- PDF - Mark K NCLEX Study GuideDocument38 pagesPDF - Mark K NCLEX Study GuideLudmilla Martins96% (24)
- 100 Diseases Treated by Single Point of AcupunctureDocument209 pages100 Diseases Treated by Single Point of AcupunctureAgeng Rikhmawan100% (31)
- Answers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark SchemesDocument3 pagesAnswers To Eocqs: Notes About Mark SchemesJane W.Carter50% (2)
- Pemeriksaan Fisik PayudaraDocument22 pagesPemeriksaan Fisik PayudaraYohana AzharNo ratings yet
- A Survey On The Awareness of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesA Survey On The Awareness of PneumoniaAshy LeeNo ratings yet
- AMOEBIASISDocument44 pagesAMOEBIASISJorge RabajaNo ratings yet
- 6 - 12 NotesDocument5 pages6 - 12 NotesFefe JejeNo ratings yet
- HEALTH ASSESSMENT - Breasts & Regional LymphaticsDocument5 pagesHEALTH ASSESSMENT - Breasts & Regional LymphaticsMich Hiel OforraNo ratings yet
- 6 - 19 NotesDocument4 pages6 - 19 NotesFefe JejeNo ratings yet
- Health and PromotionDocument22 pagesHealth and Promotionpaulzilicous.artNo ratings yet
- 6 - 9 NotesDocument7 pages6 - 9 NotesFefe JejeNo ratings yet
- Note DR Ikhwan SaniDocument39 pagesNote DR Ikhwan SaniShutter Man100% (1)
- H.A. Lec (L7 B) - Assessing Head and Neck, Eyes and Visual Acuity, Ears and BalanceDocument4 pagesH.A. Lec (L7 B) - Assessing Head and Neck, Eyes and Visual Acuity, Ears and BalanceCastallia LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Week 11 - Assessment of Breast and Lymphatic SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 11 - Assessment of Breast and Lymphatic SystemJuan Miguel TevesNo ratings yet
- Open Pediatric ArcherDocument84 pagesOpen Pediatric Archerbaharada1979No ratings yet
- OPD Orientation (July 26, 2021)Document7 pagesOPD Orientation (July 26, 2021)Jennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- CA Topic 4 - Maternal and Child PDFDocument19 pagesCA Topic 4 - Maternal and Child PDFMarvin Heramis RyanNo ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument34 pagesFundamentalsColleen CalditoNo ratings yet
- SURG Clerkship Must KnowsDocument2 pagesSURG Clerkship Must KnowsKat EstoniloNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Assessment ToolDocument5 pagesPediatric Assessment ToolJude PanlaanNo ratings yet
- Zoology Mammals (Rabbit)Document3 pagesZoology Mammals (Rabbit)PerrieNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing (MCN) IntensiveDocument33 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing (MCN) IntensiveNathaniel VenusNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Pro FormaDocument8 pagesGeriatric Pro FormaAaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment LectureDocument48 pagesHealth Assessment LectureJade Buri100% (1)
- PediatricDocument63 pagesPediatricReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Analec DigestiveDocument8 pagesAnalec DigestiveDalgom's WifeNo ratings yet
- Mammographic Examination ProceduresDocument101 pagesMammographic Examination ProceduresJanine Claire BucoNo ratings yet
- Obstetric HistoryDocument38 pagesObstetric HistoryHannah LeianNo ratings yet
- Breast Disease WucDocument52 pagesBreast Disease WucOTOH RAYA OMAR100% (1)
- Growing FetusDocument23 pagesGrowing FetusCARL JOHN MANALONo ratings yet
- NCM107 Maternal & Child Nursing - Module 2Document10 pagesNCM107 Maternal & Child Nursing - Module 2Marco VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- OB Ch.16,17Document26 pagesOB Ch.16,17Kay99 ManiNo ratings yet
- Fetalautopsy 1Document98 pagesFetalautopsy 1gimspath cme2022No ratings yet
- BLS 01 HX and PE of The Newborn, Child, and Adolescent 11 - 08 and 12 - 06 (Updated)Document17 pagesBLS 01 HX and PE of The Newborn, Child, and Adolescent 11 - 08 and 12 - 06 (Updated)Nikka ReyesNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform Mole: Case Report SessionDocument34 pagesHydatidiform Mole: Case Report SessionSelaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Tickets All 1Document34 pagesGynecology Tickets All 1moamen.nlNo ratings yet
- MDWF 2090 - Examining The Perineum After BirthDocument7 pagesMDWF 2090 - Examining The Perineum After Birthapi-442131145No ratings yet
- 1.2.5 Breast Examination - SendDocument48 pages1.2.5 Breast Examination - Senddanielndaa51100% (1)
- Week 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pagesWeek 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- Pediatric ConceptDocument19 pagesPediatric ConceptAntonio Intia IVNo ratings yet
- GYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsDocument3 pagesGYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- The Newborn Infant RUBIADocument63 pagesThe Newborn Infant RUBIAmatucojulioNo ratings yet
- M4 - Didactic - NCM 118Document4 pagesM4 - Didactic - NCM 118KARL FESARITNo ratings yet
- Functional GynaecologyDocument18 pagesFunctional GynaecologyMelissa DrakeNo ratings yet
- Breast Examination: TutorialDocument27 pagesBreast Examination: TutorialMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- NCM 207 LEC - MidtermsDocument31 pagesNCM 207 LEC - MidtermsTintin HonraNo ratings yet
- NR 602 Week 8 Final Exam Completed Study GuideDocument20 pagesNR 602 Week 8 Final Exam Completed Study GuideTyler HemsworthNo ratings yet
- ASSESSING NEWBORNS and INFANTSDocument71 pagesASSESSING NEWBORNS and INFANTSLaurisse April NecesitoNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document3 pagesWeek 6api-530814583No ratings yet
- Feb 24 2024 Gastrointestinal System ReviewDocument6 pagesFeb 24 2024 Gastrointestinal System ReviewJezzabel Kyra BadayosNo ratings yet
- Breast Self ExaminationDocument81 pagesBreast Self ExaminationAudrie Allyson Gabales100% (1)
- EINCDocument8 pagesEINCneehoshiNo ratings yet
- DRR ReviewerDocument4 pagesDRR ReviewerBong KalotNo ratings yet
- ObsGyn - OSCE NotesDocument69 pagesObsGyn - OSCE NotesMatt McCannNo ratings yet
- Breast LumpDocument22 pagesBreast LumpEsther KhawlhringNo ratings yet
- Assessing The NeckDocument4 pagesAssessing The NeckYudi TrigunaNo ratings yet
- Delivery of Baby (Actual, Assist, and Cord Care)Document3 pagesDelivery of Baby (Actual, Assist, and Cord Care)Jasmin AdoraNo ratings yet
- Perioperative NursingDocument9 pagesPerioperative NursingHannah PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Care and ComfortDocument35 pagesBasic Care and ComfortRebecca TapiaNo ratings yet
- Ha FinalsDocument18 pagesHa FinalsHielal DumpNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: PeristalsisDocument6 pagesReproductive System: PeristalsisJacquiline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCM109 Maternal - Child Nursing (A-C) - Module 5Document6 pagesNCM109 Maternal - Child Nursing (A-C) - Module 5iratsyukieNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Breast 2Document11 pagesAssessment of The Breast 2rara1234No ratings yet
- No-Risk Abs: A Safe Workout Program for Core StrengthFrom EverandNo-Risk Abs: A Safe Workout Program for Core StrengthNo ratings yet
- Exmd 509 Mcgill Stomach 2016Document36 pagesExmd 509 Mcgill Stomach 2016Sora OhNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Immunohistochemical Expression of p16 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Correlation With Clinicopathological ParametersDocument8 pagesAssessment of Immunohistochemical Expression of p16 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Correlation With Clinicopathological ParametersMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Notes For PGDocument24 pagesOphthalmology Notes For PGSHAKEEL1991No ratings yet
- Artsanto R, Doso Sutiyono, Witjaksono : Bagian Anestesiologi Dan Terapi Intensif FK Undip/ RSUP Dr. Kariadi, SemarangDocument12 pagesArtsanto R, Doso Sutiyono, Witjaksono : Bagian Anestesiologi Dan Terapi Intensif FK Undip/ RSUP Dr. Kariadi, SemarangAdhyNo ratings yet
- 846 - Nutritional Problems in India 2Document17 pages846 - Nutritional Problems in India 2Riborlangstar LyngdohNo ratings yet
- NCP To NG PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP To NG PneumoniaGlenn Asuncion PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Immunity and DiseasesDocument11 pagesLesson Plan Immunity and DiseasesAnalyn ValentinNo ratings yet
- Management and Outcome of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) in Older People: A Centre SeriesDocument2 pagesManagement and Outcome of Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH) in Older People: A Centre SeriesDevi Humairah IrawanNo ratings yet
- Exogenous Ochronosis Following Hydroquinone For Melasma: V P Zawar & S T MhaskarDocument3 pagesExogenous Ochronosis Following Hydroquinone For Melasma: V P Zawar & S T MhaskarStella SunurNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure PDFnadzwa velascoNo ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE STUDY ON KENT by GaskinDocument18 pagesCOMPARATIVE STUDY ON KENT by GaskinmdasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IridologyDocument49 pagesIntroduction To IridologyMichael Roughan86% (7)
- InterimGuidelines AHduringCOVID19Document10 pagesInterimGuidelines AHduringCOVID19Shardin Labawan-Juen,RNNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Instrumental Assessesment of Swallowing 2017Document30 pagesLecture 4 Instrumental Assessesment of Swallowing 2017Mbongeni MasilelaNo ratings yet
- Disease of Immune System: Sharon Hazel Joyce C. Sebastian, RMTDocument47 pagesDisease of Immune System: Sharon Hazel Joyce C. Sebastian, RMTGilo IlaganNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)Document20 pagesIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)saiibelieves0% (1)
- Chapter 14Document4 pagesChapter 14Allynne Jane DagasdasNo ratings yet
- Original Article: Survey of Anaphylaxis Management by General Practitioners in ScotlandDocument4 pagesOriginal Article: Survey of Anaphylaxis Management by General Practitioners in ScotlandRiyanti DeviNo ratings yet
- CT Cardiac/Calcium Scoring ExamsDocument4 pagesCT Cardiac/Calcium Scoring Examsalfonso pumarejoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Planthomasfinley44No ratings yet
- Protozoa (Q) PDFDocument4 pagesProtozoa (Q) PDFBhupesh ChandNo ratings yet
- ESMO Guideline 2019 - Early Breast Cancer TreatmentDocument27 pagesESMO Guideline 2019 - Early Breast Cancer Treatmentrahma watiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NaclDocument3 pagesDrug Study NaclNicole Denise PortugalezaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation BSMMU As 3rd AuthorDocument4 pagesCase Presentation BSMMU As 3rd AuthorGovind ChaudharyNo ratings yet