Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Three Basic Types of Software Report
Uploaded by
Treesa LouiseOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Three Basic Types of Software Report
Uploaded by
Treesa LouiseCopyright:
Available Formats
REPORTING TOPICS
I Three Basic Types of Software Ismael VII General Devices Jugo L
II Types of Computers Sangcad VIII Central Processing Unit Serencio
III Processing Albano IX Operating System Cortez
IV Types of Databases Gutang X Repetitive Strain Injury Saysip
V Types of Input & Input Device Gerale’s Group XI Correct Posture in Using the Computer Cuaro
VI Data Automation Ijirani
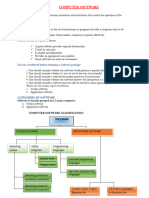
I. THREE BASIC TYPES OF SOFTWARE
SOFTWARE UTILITY SOFTWARE
Software is the general term Utility software consists of programs designed to support
Applied to the instructions that direct the computer’s and optimize the functioning of the computer system itself.
hardware to perform work. These are programs that are used to help maintain the
3 Basic Types of Software system, clean up unwanted programs, protect the system
o SYSTEM SOFTWARE against virus attacks, access the World Wide Web (WWW),
o UTILITY SOFTWARE and the like.
o APPLICATION SOFTWARE CATEGORIES
The categories include at least:
SYSTEM SOFTWARE o Security programs
It “boots up” (starts up and initializes) the computer system; o Disk management utilities
controls input, output, and storage; and controls the o Backup utilities
operations of the application software. o Screen saver
BASIC INPUT/OUTPUT SYSTEM o Archival software
The first level of system control is handled by the basic o Programming environment support programs
input/output system (BIOS) stored on a ROM chip on the
motherboard. The software on the BIOS chip is the first part APPLICATION SYSTEM
of the computer to function when the system is turned on. Applications software includes the various programs that
OPERATING SYSTEM users require to perform day-to-day tasks like to do work,
process data, play games, communicate with others, and
An OS is the overall controller of the work of the computer.
watch videos and multimedia programs on a computer.
The OS is software loaded from the hard drive into RAM as
They are the programs that support the actual work of the
soon as the computer is turned on.
user.
TYPES OF APPLICATION SOFTWARE
EXAMPLES OF SYSTEM SOFTWARE
o For desktop computers, laptops and tablets: Word Processing Software:
Microsoft Windows o Google Docs, Microsoft Word, WordPad and Notepad
MacOS (for Apple devices) Database Software:
GNU/Linux o MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access,
o For smartphones: Oracle, IBM DB2 and FoxPro
Apple’s iOS Spreadsheet Software:
Google’s Android o Google Sheets, Apple Numbers and Microsoft Excel
Windows Phone OS Multimedia Software:
o Media Player, Winamp, QuickTime and VLC Media
Player
Presentation Software:
o Google Slides, Microsoft Powerpoint, Keynotes,
Prezzy
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 1
Midterms - Reporting
II. TYPES OF COMPUTERS
TYPES OF COMPUTERS MICROCOMPUTERS
Supercomputers (PERSONAL COMPUTERS OR PCS)
Mainframes used for an increasing number of independent applications
Microcomputers (personal computers or pcs) as well as serving as a desktop link to the programs of the
Server mainframe.
portable, laptops, notebook, and handheld computers.
Workstation
CLASSES OF COMPUTERS o is part of a computer network and generally would be
Analog Computer expected to have more than a regular desktop PC of
Digital Computer most everything, like memory, storage space, and
Hybrid Computer speed.
MAINFRAMES SERVER
is the workhorse of the business world refers to a computer's function rather than to a specific kind
is the heart of a network of computers or terminals which of computer. runs a network of computers. handles sharing
allows hundreds of people to work at the same time on the of equipment like printers and the communication between
same data computers on the network.
III. PROCESSING
PROCESSING MAJOR WORD PROCESSOR
Is the ability of the computer. Microsoft word
o Calculations WordPerfect
o Comparisons
Lotus WordPro
o Decision
DATABASE
is a collection of data that you want to manage, rearrange,
WORD PROCESSING
and add to later.
is the application that is used most
often and most widely.
IV. TYPES OF DATABASES
TYPES OF DATABASES HIERARCHICAL DATABASES
Relational databases These databases organize data in a tree-like structure, with
NoSQL databases each node having one parent and multiple children.
Object-oriented databases
Hierarchical databases NETWORK DATABASES
Network databases These databases are similar to hierarchical databases, but
In-memory databases allow each node to have multiple parents.
Centralized databases
Distributed databases IN-MEMORY DATABASES
These databases store data in computer memory instead of
RELATIONAL DATABASE on disk, which allows for faster access times.
They use a structured query language (SQL) to access and
manipulate data. CENTRALIZED DATABASE
Store data on a single CPU bound to a single certain
NOSQL DATABASES physical/geographical location.
They do not use tables and SQL, but instead use different
data models, such as document-based, key-value, or graph DISTRIBUTED DATABASE
databases. A database that runs and stores data across multiple
computers, as opposed to doing everything on a single
OBJECT-ORIENTED DATABASES machine.
These databases store data in objects, which are similar to
the objects used in object-oriented programming.
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 2
Midterms - Reporting
V. TYPES OF INPUT & INPUT DEVICE
INPUT DEVICE which the sound signal is converted to a computer signal for
easy processing.
MOUSE SOUND EFFECTS OR VOICES
A ball underneath rolls as the mouse moves across the For music the best results come from using a musical
mouse pad. The cursor on the screen follows the motion of instrument that is connect directly to the computer.
the mouse. Software can combine music recorded at different times.
OPTICAL MOUSE You could be music group all by yourself -singing and
There are new mice that don't have a ball. They use a laser playing the music you want.
to sense the motion of the mouse instead. VIDEO INPUT
No mouse pad needed For music the best results come from using a musical
TRACKBALL instrument that is connect directly to the computer.
Instead of moving the whole mouse around, the user rolls Software can combine music recorded at different times.
the trackball only, which is on the top or side. It does not You could be music group all by yourself -singing and
need as much desk space as a mouse. It is not as tiring playing the music you want.
since less motion is needed. It also requires fine control of A VIDEO CAMERA OR RECORDER (VCR)
the ball with just one finger or thumb. Repeated motion of can record data that can be uploaded to the computer
the same muscles is tiring and can cause carpal tunnel system.
syndrome WEB CAM
GLIDE PAD is a tiny video camera designed specially to sit on your
Uses a touch sensitive pad for controlling cursor. The user computer, it feeds pictures directly to the computer- no tape
slides finger across the pad and the cursor follows the finger or film to develop. Of course, you are limited by the length
movement. For clicking there are buttons, or you can tap on of the cable that connects the camera to the computer.
the pad with a finger. The glide pad is a popular alternate
pointing device for laptops. TYPES OF INPUT
PDA Data is the raw facts given to the computer. Programs are
Used especially in Personal Digital Assistant (PDA). Pen is the sets of instructions that direct the computer. Commands
used for Data input. are special codes or key words that the user inputs to
TOUCH SCREEN perform a task, like run "Accounts. These can be selected
Make selection by just touching the screen. It's natural to do from a menu of commands like "Open” on the File menu.
reach out and touch something. It's tiring if many choices They may also be chosen by clicking on is command button.
must be made It takes a lot of screen space for each choice
since fingers are bigger than cursors. KEYBOARD
DIGITIZERS AND GRAPHICS TABLETS The first input device we will look at is the Keyboard. The
Converts drawings, photos, etc. to digital signal. keyboard is used to type information into the computer or
TERMINALS Input information.
A terminal consists of a keyboard and a screen so it can be KEYBOARD SYMBOLS
considered an Input device, especially some of the The following chart displays the character symbols, name
specialized types. and Latin-1 Number on standard keyboard in their
Some come as single units approximate position on the keyboard. Most characters
o Display from any Roman based language can be created on any
o Video Display Terminal computer using the American Standard Code for
DUMB TERMINAL Information American National Standards Institute's (ANSI)
has no ability to process or store data. It is linked to formatting standards Interchange or ASCII. Most computers
minicomputer, mainframe, or super computer. The and software also recognized well.
keyboard and viewing screen may be a single piece of ALPHABET KEYS
equipment. The letters of the alphabet and some punctuation marks are
AN INTELLIGENT, SMART, OR PROGRAMMABLE in these three rows. The order of the keys is called
TERMINAL QWERTY from the order of the keys on the top row.
can process or store on its own, at least to a limited extent. ALT
PCs can be used as smart terminals.
The Alt key doesn't do anything by itself. But if you hold it
POINT-OF-SALE TERMINAL (POS) down while pressing another key, the effect of that key may
is an example of a special purpose terminal. These have be different from usual. Exactly what will happen will
replaced the old cash registers in nearly all retail stores. depend on what program is running at the time.
They can update inventory while calculating the sale. They
ARROW KEYS
often have special purpose keys.
MULTIMEDIA These four keys are used to move the cursor on the screen.
Multimedia is a combination of sound and images with text The up and down arrows move the cursor up or down one
and graphics. This would include movies, animations, line. The left and right arrows move the cursor one
music, people talking, sound effects like the roar of a crowd character.
and smashing glass. BACKSPACE
SOUND INPUT The Backspace key erases the character on the left of the
Recording sounds for your computer requires special cursor and moves the cursor that direction, too.
equipment. Microphones can capture sounds from the air at
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 3
Midterms - Reporting
CAPS LOCK Numeric Keypad responds as navigation keys using the
When the Caps Lock key is on, pressing any alphabetic key alternate markings on the keys.
will result in an upper case (capital) letter. The number and
symbol keys are not affected, however. Watch out - this is PAGE DOWN
different from typewriters. The Page Down key is navigation key which will drop the
CONTROL displayed area down the page one screen's worth. It doesn't
The control key does nothing all by itself. It must be pressed necessarily move a whole literal page at a time. That would
in combination with other keys. When used in combination, depend on the height of a page.
the control key changes the normal effect of a key. Exactly
what will happen depends on the software in use at the PAGE UP
time. The Page Up key is navigation key which will move the
DELETE cursor up the displayed area one screen's worth. It does not
The delete key is used to erase the character just to the usually move a literal page at a time. That would depend on
right of the cursor any text beyond the erased character is the height of a page.
moved to the left.
END PAUSE
The End key is a navigation key. It will send the cursor to The Pause key is little used under Windows. Under DOS it
the end of the current line. is used to halt actions in progress, often so that messages
on the screen can be read before they scroll off the screen.
ENTER
The Enter key is used in several ways. In word processing, SPACEBAR
it acts like the Return key on a typewriter by starting a new
line. It is also used in placed a mouse click with buttons and The Spacebar is used to enter blank spaces in text.
drop-down menus. Sometimes it can also be used instead of a mouse click on
buttons.
ESCAPE
The Escape key is used to cancel actions in progress before SLASH
they finish. It also used to close certain dialog boxes.
When Num Lock is on, the Slash key acts as a division sign
FUNCTION KEYS
on the numbers entered. When Num lock is off, the Slash
The Function keys are numbered F1, F2, F3,....F12. key types a /.
These are programmable keys. That is, programs can
assign actions to these keys. S the same key might produce SHIFT
different results in different programs.
The Shift key is used in combination with the alphabetic
HOME keys to get upper case. With a numeric/symbol key using
The home key is navigation key for the cursor. It will move the Shift will give the character at the top of the key. The
the cursor to the beginning of the current line. Shift key can be used in combination with the Alt and
INSERT Control keys to change the effects of another key.
The insert key is a toggle key that is, repeatedly pressing it
will alternate between two effects. SCROLL LOCK
o Typing overtypes characters already there The Scroll Lock key is more useful under DOS where
o Typing inserts characters in between the characters pressing it will stop text on the screen from scrolling off the
that are already there. top of the screen. This gives you time to read or print it
NUMERIC KEYPAD before continuing.
When the Num Lock key is on, these keys are used to enter
numbers as with an adding machine. When the Num Lock PLUS
key is off, the keys act as navigation keys using the When Num Lock is on, this key performs addition. When
alternate markings on each key. Num Lock is off, this key prints a +.
MINUS
When Num Lock is on, the Minus key performs subtraction TAB
on the numbers entered. When Num Lock is off, the Minus The Tab key is used to move the cursor over to the right to
key will type a hyphen like this - a pre-set point. This is especially used in word processing
NUMBER/SYMBOL KEYS to line up text vertically.
On this row of keys, you will see two characters, one at the
top of the key and one at the bottom. The upper character PRINT SCREEN
is a symbol and is accessed by holding the Shift key down The Print Screen key is more useful under DOS
while pressing the key. Numbers can also be typed from the than under Windows. Under DOS pressing the Print Screen key
Numeric Keypad. immediately sends the contents of the screen to the printer.
NUM LOCK TIMES
When Num Lock is on, the Numeric Keypad responds with When Num Lock is on, the Times key acts as a
numbers, as an adding machine. When Num lock is off, the multiplication sign on the numbers entered. When Num
Lock is off, the Times key types a *.
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 4
Midterms - Reporting
VI. DATA AUTOMATION
DATA AUTOMATION For example, the old-style cash register would add up your
the process of using software to automatically collect, purchase and calculate the tax. The clerk entered the
process, and store data in databases amounts by hand (the data entry part). Later the numbers
off the store copy of the cash register tapes would have to
FIRST GOAL be added up manually, or entered into a computer program
to avoid mistakes in data entry by making the initial entering (another data entry task). For an up-to- date inventory
of the data as automatic as possible. Different situations someone would have to go count all the things on the
require different methods and equipment shelves (a third data entry task).
SECOND GOAL Increase operational efficiency and reduce errors in data
processing.
to avoid having to re-enter data to perform a different task
with it
VII. GENERAL DEVICES
PAGE SCANNER
The scanner works like a copy machine. It captures a whole STANDARD DISK SIZE AND ITS CORRESPONDING
page and converts it to digital image. The scanned text STORAGE CAPACITY
cannot be edited at this point. DISK SIZE AMOUNT OF STORAGE
5.25 Low density 360 Kb
HAND SCANNER 3.5 Low density 720 Kb
You move the device across the document or picture. It will 5.25 High density 1.2 mb
capture only a section of page or a large image. 3.5 High density 1.44 mb
CD 650 mb
Diagram of the Machine Cycle DVD/DVX 4.5 GB
o Fetch
o Decode
o Execute AUXILIARY STORAGE = SECONDARY STORAGE
o Store Holds what is not currently being processed.
It is NONVOLATILE, meaning that turning the power off
INPUT/OUTPUT STORAGE does not erase it.
When you enter new data, the keystrokes must be stored Auxiliary storage is used for:
until the computer can do something with the new data. o Input - data and programs
o Output - saving the results of processing
MAIN MEMORY= PRIMARY STORAGE
This is where the computer stores the data and commands AUXILIARY STORAGE
that are currently used. When the computer is turned off, all 1. FLASH MEMORY
data in main memory vanishes. A data storage method of
also known as flash storage, these are solid-state devices
this type is called VOLATILE since the data evaporate.
that read and write data electrically, instead of magnetically
2. USB DRIVE
PRIMARY STORAGE DEVICES
1.COMPACT DISK OR CDS Type of memory storage device does not yet have a
generally accepted name. All are small about the size of
Can store large amounts of information. One disk will store your thumb or a large car key.
650mb.
3. REMOVABLE HARD DRIVE
2. DVD DISK
>A type of disk drive system in which hard disks are
Can store over 4 gigabytes. DVD recorders allow you to enclosed in plastic or metal cartridges so that they can be
store large files, such as movies, on a single disk. removed like floppy disks.
3. HARD DISK
Store the majority of information on today’s modern
computer. Standard Hard disk stores 30GB or more.
4. FLOPPY DISK/ DISKETTE
are used for moving information between computers,
laptops or other devices.
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 5
Midterms - Reporting
VIII. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT CPU
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the part of the Control Unit
computer where work gets done. ALU
Control Unit
o This is the part of the computer that control the MAIN MEMORY
Machine Cycle.
Arithmetic Logic Unit Operating System
o is a digital circuit that performs arithmetic and Applications
logical operations on input data or values. Input/output storage
Main Memory Working storage
o This is where the computer stores the data and Unused storage
commands that are currently being used.
PRIMARY STORAGE DEVICES
MACHINE CYCLE Is referred to as the main memory or internal memory which
is located in the motherboard of the CPU.
o ROM
o RAM
o Flash Memory
o Cache Memory
SECONDARY STORAGE DEVICES
works alongside the computer’s primary storage, RAM, and
cache memory.
o Hard Drive
o Solid State Drive
o Universal Serial Bus
o Optical Secondary Storage
IX. OPERATING SYSTEM
OPERATING SYSTEM
A computer's operating system is a robust and frequently DATA COMMUNICATION
large program that maintains and controls the hardware and Data communications (dc) is the process of transferring
other software on the device. data between participating parties or from one location to
Operating systems are necessary for every computer and another using computing and communication technology.
device that resembles a computer, including your laptop, Another way to talk about different types of data
tablet, desktop, smartphone, smartwatch, and router. communications is to refer to the functionality that is
available for a sender and a receiver to use. For example,
WORKING STORAGE a common example of data communications is a computer
The numbers and characters that are the intermediate connected to the Internet via a Wi-Fi connection, which
results of computer operations must be stored until the final uses a wireless medium to send and receive data from one
values are calculated. These values "in profress" are kept or more remote servers.
in temporary locations. TELECOMMUNICATION
Telecommunications, usually referred to as telecom, is the
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION electronic transfer of information over great distances,
It is the transmission of data and information over a including voice, data, and video.
communications channel between two computers, which TELEPROCESSING
can be several different things.
Teleprocessing describes a computer capable of
BASIC COMMUNICATION TYPES connecting to another computer or network device.
Data communication
Telecommunications
Teleprocessing
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 6
Midterms - Reporting
X. REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURY (RSI)
REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES ARE VERY COMMON Poor posture when sitting or standing.
AND USUALLY AFFECT YOUR: Working in the cold.
Finger and Thumb WHO GETS RSI?
Wrists Most common people affected include:
Elbows o Workers with physically demanding jobs.
Arms o Athletes.
Shoulders o Musicians.
Knees o People who sit at a desk or use a computer often
THE SYMPTOMS USUALLY START GRADUALLY HOW TO PREVENT RSI?
AND CAN INCLUDE: Adjust desk and pc area
pain Get up and move around
stiffness and weakness Stretch
tingling, pins-and-needles or numbness HOW ARE REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURIES
muscle cramps TREATED?
Swelling Rest
CAUSES OF REPETITIVE STRAIN INJURY (RSI) Ice
Working out too hard without warming up and cooling down Compression
Sports or other activities that require you to use the same Elevation
motion repeatedly.
CORRECT POSTURE IN USING THE COMPUTER
A.Y. 2022-2023 | BSN 2-B 7
You might also like
- Computer SoftwareDocument31 pagesComputer SoftwarellanzaannerizziNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument9 pagesComputer SoftwareNaitik SinghNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Operating System - For MergeDocument8 pages1 Intro To Operating System - For MergeProfessor 16No ratings yet
- Chapter 3. SoftwareDocument34 pagesChapter 3. Softwaresameerahmadkhan130No ratings yet
- Types of SoftwareDocument24 pagesTypes of Softwaredaras.kaur06No ratings yet
- CMP 215 - Module 1Document38 pagesCMP 215 - Module 1Clifford JamesNo ratings yet
- 04 Computer Systems Basic Software TRANSESDocument3 pages04 Computer Systems Basic Software TRANSESElyza DionisioNo ratings yet
- PSPC Computer FundamentalsDocument12 pagesPSPC Computer FundamentalsRinku tilluNo ratings yet
- ITE6102 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING MODULE 1 OVERVIEWDocument91 pagesITE6102 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING MODULE 1 OVERVIEWRyan Jule CruzNo ratings yet
- Computer Application PDFDocument16 pagesComputer Application PDFZohaib TariqNo ratings yet
- Software S2 2014 2015Document34 pagesSoftware S2 2014 2015bobolalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Software and PeoplewareDocument31 pagesLesson 5 Software and PeoplewareYenNo ratings yet
- Bab 1 Introductionl of OsDocument5 pagesBab 1 Introductionl of OsFarah HussinNo ratings yet
- Concept-of-Hardware-and-Software-Capabilities-and-Limitations-of-Computers-Data-Processing-Cycle-Intro-to-Internet-and-EmailingDocument18 pagesConcept-of-Hardware-and-Software-Capabilities-and-Limitations-of-Computers-Data-Processing-Cycle-Intro-to-Internet-and-EmailingEtta Fe AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument10 pagesComputerJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Software WorksheetDocument11 pagesSoftware WorksheetAlicia HaughtonNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Ii Computer SoftwareDocument5 pagesLecture-Ii Computer SoftwareSalman TahirNo ratings yet
- 03 Unit 3 (Software)Document24 pages03 Unit 3 (Software)Yassin Al-shoraihyNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument34 pagesSoftwareLois Nicole ClederaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ComputerDocument7 pagesBasic Concepts of ComputerAbdullah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Computer SystemDocument12 pagesUnit-3 Computer SystemKunal SahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Notes - SoftwareDocument10 pagesLesson 6 Notes - SoftwareMya-naomiNo ratings yet
- Type A Class Ix ch-3Document3 pagesType A Class Ix ch-3kjcoochbeharNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 01 Types and Components of A Computer System Part:1Document71 pagesChapter: 01 Types and Components of A Computer System Part:1Crimson PlanksNo ratings yet
- Grade 12: Tvl-Ict Install Operating System and Drivers For Peripheral / DevicesDocument10 pagesGrade 12: Tvl-Ict Install Operating System and Drivers For Peripheral / DevicesALBERT ALGONESNo ratings yet
- System Software: Important FeaturesDocument13 pagesSystem Software: Important Featuresvinay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Computer SoftwareDocument11 pagesComputer Softwaregeorgessenfuma813No ratings yet
- Os 1Document51 pagesOs 1api-19975941No ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1Document20 pagesLesson 3.1jarelleNo ratings yet
- Computer Software Phase One RevisedDocument32 pagesComputer Software Phase One RevisedFassou HabaNo ratings yet
- First Stage Koya University Software Engineering Department: Academic ComputingDocument16 pagesFirst Stage Koya University Software Engineering Department: Academic ComputingBawar Abid AbdallaNo ratings yet
- Oec TranslatorDocument22 pagesOec TranslatorAftab KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch.01 - Introduction - To - ComputersDocument10 pagesCh.01 - Introduction - To - ComputersTeklayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Computer SoftwareDocument40 pagesChapter 4. Computer SoftwareAhmadNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument18 pagesSoftwareFrancez LanoriaNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 3 - Software-Productivity Tool-Word PDFDocument5 pagesLesson - 3 - Software-Productivity Tool-Word PDFGheoff RicareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Operating SystemDocument27 pagesChapter 02 Operating SystemEshan HirushkaNo ratings yet
- Ch 5 System Software GuideDocument18 pagesCh 5 System Software GuideMuhammad Rizwan0% (1)
- Lecture 04Document24 pagesLecture 04Ayman PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Software: Set of Instructions That Tells The Computer How To Do Specific TaskDocument11 pagesSoftware: Set of Instructions That Tells The Computer How To Do Specific TaskRona EA SyNo ratings yet
- CH3 PresentationDocument14 pagesCH3 Presentationmuzammel mudathirNo ratings yet
- SoftwareDocument21 pagesSoftwareJoan Balmes ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5Document29 pagesChapter - 5shawonNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationDocument10 pagesComputer Applicationdiamonddiaries11No ratings yet
- Ntro OM: Duction PutingDocument17 pagesNtro OM: Duction PutingPaula Louise SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Software ConceptsDocument18 pagesChapter 2 - Software ConceptsKanor DalisayNo ratings yet
- Types of SoftwareDocument22 pagesTypes of SoftwarePriyankkaa BRNo ratings yet
- TEJADA The Software RevolutionDocument25 pagesTEJADA The Software RevolutionPad VeenzNo ratings yet
- 3 Software ConceptsDocument24 pages3 Software ConceptsM Shahid HanifNo ratings yet
- History of SoftwareDocument8 pagesHistory of SoftwareASHLEY SUSANA URBINANo ratings yet
- Different Types of Software With Examples BSCDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of Software With Examples BSCRajaTaimoorBagh100% (1)
- Basics of Computing Chapter 2 SoftwareDocument12 pagesBasics of Computing Chapter 2 SoftwareAdib AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 80 ReviewerDocument3 pages80 ReviewerRyanNo ratings yet
- EEC 112 Into To Computer SofwareDocument12 pagesEEC 112 Into To Computer SofwareorjimetitusterverNo ratings yet
- ICT Ch1 Notes - 1Document13 pagesICT Ch1 Notes - 1Ethar AzhariNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT CODE - (ASAI2101) 2 (1+1) : Agricultural InformaticsDocument71 pagesSUBJECT CODE - (ASAI2101) 2 (1+1) : Agricultural InformaticsSonu GreatNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Training ModuleDocument30 pagesBasic Computer Training Moduletemesgen fuliNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming Slide 2Document28 pagesComputer Programming Slide 2BLOOD xSeekerNo ratings yet
- An Easy Approach to Fundamentals of Computer SoftwareDocument8 pagesAn Easy Approach to Fundamentals of Computer SoftwareMusic MedNo ratings yet
- Free Antivirus And Antimalware Software For Ubuntu & Linux MintFrom EverandFree Antivirus And Antimalware Software For Ubuntu & Linux MintNo ratings yet
- Software Quality Assurance AnalystDocument3 pagesSoftware Quality Assurance Analystapi-121649886No ratings yet
- Linear Control Systems Lab 08 Block Diagram ReductionDocument13 pagesLinear Control Systems Lab 08 Block Diagram ReductionUmer EhsanNo ratings yet
- Designer PM Manual 2Document664 pagesDesigner PM Manual 2marceloayadNo ratings yet
- AC I DC ChokeDocument4 pagesAC I DC ChokeNedel LabileNo ratings yet
- Online Hostel Management SystemDocument47 pagesOnline Hostel Management SystemOgidiolu Temitope Ebenezer67% (3)
- DG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25Document43 pagesDG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25luisNo ratings yet
- Com Datasheet Supero412Document4 pagesCom Datasheet Supero412Erick PeimbertNo ratings yet
- VC SlopeDocument8 pagesVC SlopeEzKeezENo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions for Lecture 1 on Network SystemsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions for Lecture 1 on Network SystemsWadood QureshiNo ratings yet
- Telematics System (Diagnostics)Document77 pagesTelematics System (Diagnostics)rwNo ratings yet
- An 1382 - 6 Low Voltage Differential Signaling LVDS by AgilentDocument20 pagesAn 1382 - 6 Low Voltage Differential Signaling LVDS by AgilentJose Gonzalez100% (1)
- Ecd.2003.winter - Product ReviewDocument33 pagesEcd.2003.winter - Product ReviewWaleed MareeNo ratings yet
- Design of A Non-Overlapping Clock Generator For RFID Transponder EEPROMDocument4 pagesDesign of A Non-Overlapping Clock Generator For RFID Transponder EEPROM翁偉倫No ratings yet
- Agribot: An Agriculture Robot: Vol. 4, Issue 1, January 2015Document3 pagesAgribot: An Agriculture Robot: Vol. 4, Issue 1, January 2015Dreamer JayaNo ratings yet
- School Data Management System ReportDocument122 pagesSchool Data Management System ReportshekharyadawNo ratings yet
- Oracle8 On Rh7x HowtoDocument11 pagesOracle8 On Rh7x Howto4U6ogj8b9snylkslkn3nNo ratings yet
- XCELIUM BASIC Vs ADVANCED PROFILERDocument9 pagesXCELIUM BASIC Vs ADVANCED PROFILERPriya JeejoNo ratings yet
- A+ Guide To Managing & Maintaining Your PC PDFDocument45 pagesA+ Guide To Managing & Maintaining Your PC PDFJohn Paul AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Installing SolidWorks 2016 On Your PC Jan 2017 (Stand Alone)Document6 pagesInstalling SolidWorks 2016 On Your PC Jan 2017 (Stand Alone)Jignesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- madVR - Crash ReportDocument11 pagesmadVR - Crash ReportSampo RahikkalaNo ratings yet
- ReleaseNotes SEB MacOS 3.2.5Document32 pagesReleaseNotes SEB MacOS 3.2.5Hiền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Iclock 360 User Manual: About This Manual About This Manual A Ab Bo Ou Utt TTH Hiis SM Ma An Nu Ua AllDocument59 pagesIclock 360 User Manual: About This Manual About This Manual A Ab Bo Ou Utt TTH Hiis SM Ma An Nu Ua Alljufulimova100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Developing Device DriversDocument70 pagesChapter 6 - Developing Device DriversSunil PaiNo ratings yet
- FortiWeb Deployment Guide For VMwareDocument67 pagesFortiWeb Deployment Guide For VMwareCesar Augusto Jaramillo PossoNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems, Arduino & RTOS ModulesDocument2 pagesEmbedded Systems, Arduino & RTOS ModulesDr. Rajalakshmi MNo ratings yet
- ITT270 Group Project Develops Motion Detector for Deaf and BlindDocument13 pagesITT270 Group Project Develops Motion Detector for Deaf and BlindAdib AfhamNo ratings yet
- How To Get Best of Atmega88Document6 pagesHow To Get Best of Atmega88Nishmita D'AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Airbag Sensor Circuit DiagramDocument6 pagesAirbag Sensor Circuit DiagramSungkur NishanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Number SystemsDocument14 pages1.1 Number SystemsAgasthya JainNo ratings yet
- Fifo Controller PresentationDocument26 pagesFifo Controller PresentationthemikulNo ratings yet