Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adler & Jung Theories of Personality
Uploaded by
Patricia Nolan Lopez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesAdler's Individual Psychology focuses on how people's perceptions of past events shape their approach to life. Key concepts include the creative self, superiority and inferiority complexes, and social interest. Adler believed behavior is goal-oriented and purposeful. Critics argue Adler oversimplified causes of problems and that modifying behavior may not address severe illnesses. Individual Psychology aims to help clients identify counterproductive lifestyles and thoughts to develop more productive behaviors, which some critics say is the counselor inappropriately influencing clients.
Original Description:
Adler & Jung theories of personality
Original Title
Adler & Jung theories of personality
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAdler's Individual Psychology focuses on how people's perceptions of past events shape their approach to life. Key concepts include the creative self, superiority and inferiority complexes, and social interest. Adler believed behavior is goal-oriented and purposeful. Critics argue Adler oversimplified causes of problems and that modifying behavior may not address severe illnesses. Individual Psychology aims to help clients identify counterproductive lifestyles and thoughts to develop more productive behaviors, which some critics say is the counselor inappropriately influencing clients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesAdler & Jung Theories of Personality
Uploaded by
Patricia Nolan LopezAdler's Individual Psychology focuses on how people's perceptions of past events shape their approach to life. Key concepts include the creative self, superiority and inferiority complexes, and social interest. Adler believed behavior is goal-oriented and purposeful. Critics argue Adler oversimplified causes of problems and that modifying behavior may not address severe illnesses. Individual Psychology aims to help clients identify counterproductive lifestyles and thoughts to develop more productive behaviors, which some critics say is the counselor inappropriately influencing clients.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Instructions: Fill up the box below. You may add another row if needed.
This can be a part of your
reviewer in the future.
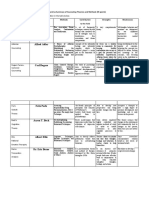
Alfred Adler: Individual Psychology
VIEW OF HUMAN KEY CONCEPTS OF COMPARE/CONTRAST CRITICISMS OF THE
NATURE INDIVIDUAL W/ PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY
PSYCHOLOGY THEORY
Adler abandoned The creative self Individual psychology, A major criticism of
Freud’s basic theories Superiority complex, Adler’s theory is about
because he believed Inferiority complex etc. the role of the
Freud was excessively counselor. From the
narrow in his stress Individual Psychology
on biological perspective, the
instinctual counselor exerts some
determination. influence on the
patient about their
behavioral change. This
criticism arises from
the fact that Adlerian
therapists aim to guide
the client to modify
his/her views and goals
(Engler, 2008).
Adler holds that the Behavior as goal Psychoanalysis, The counselor helps
individual begins to directed and purposeful including the theories of the client to identify
form an approach to id, ego and super-ego, counterproductive
life somewhere in Oedipus complex etc. lifestyles and thought.
their first six months. The client is then
assisted to change
these behaviors and
take up ones that are
more productive.
Critics argue that the
counselor’s job is to
assist the client in
attaining a healthy
mental frame and not
to influence them
directly to change
behavior.
Focuses on how the Social interest Striving for Success or Adler’s theory is also
person’s perception Superiority criticized due to its
of the past and his or The Final Goal – people tendency to
her interpretation of strive toward oversimplify the cause
each events has a a final goal of either of human problems.
continuing influence. personal According to Adler,
superiority or the goal inferiority feelings are
of success for the trigger for humans
all humankind. to take action. These
feelings are often the
result of mistaken
appraisals of self-worth
(Engler, 2008). In
addition to this, Adler
views the lack of
courage and
confidence by patients
as the cause of their
mental problems.
According to Adler, Striving for significance The Unconscious - is the Critics argue that such
humans are as a motivational force center of our mental life a simplistic outlook
motivated primarily which represses high cannot be used to
by social relatedness levels of anxiety created explain severe mental
rather than by sexual from our early illnesses that afflict
urges. childhood experiences patients. Adler’s theory
that is also criticized for
affects our words, suggesting that people
feelings and can overcome all the
actions. psychological problems
they face by modifying
their behavior.
Behavior is purposeful Understanding the The Striving Force as
and goal-oriented. family constellation Compensation –
People strive for
superiority or
success as a mean of
compensation
for feelings of inferiority
and
weakness.
Consciousness; more Unity and self- The Preconscious –
than consistency personality contains all those
unconsciousness, elements not are not
which is the focus of conscious but
therapy. can become conscious
either quite
readily or with some
difficulty.
Lifestyle is molded by Striving for superiority Striving for personality
people’s creative superiority –
power. Some people strive for
superiority
with little or no concern
with for
others.
The one dynamic The Conscious – which
force behind people’s plays a
behavior is the relatively minor role in
striving for success psychoanalytic
and superiority. theory, can defined as
those mental
elements in awareness
at any given
point in time.
Personality is unified
and self-consistent.
Each person must be
viewed as an
individual from a
holistic perspective.
Carl Jung: Analytical Psychology
VIEW OF HUMAN KEY CONCEPTS OF COMPARE/CONTRAST CRITICISMS OF THE
NATURE ANALYTICAL W/ PSYCHOANALYTIC THEORY
PSYCHOLOGY THEORY
Consciousness Is “I Amplification – Both Jung and Freud’s One important Jungian
Am” Elaboration and theory are concerned archetype is the
clarification of a dream- with the conscious and "shadow," a term he
image by means of unconscious mind of a borrowed from the
directed association and human. famous philosopher
of parallels from the Nietzsche and a
humane science reference to the
(symbology, mythology, deepest and darkest
mysticism, folklore, part of a person's
history of religion, personal unconscious.
ethnology, etc.). Jung decided that once
an individual
recognized the
presence of an evil side
within, impulse control
would become easier.
However,
contemporary critics
see mysticism and
occultism as irrational
and too much at work
in this part of Jung's
theory. Critics point
out that Jung seems to
have protected his
theory from scrutiny by
never settling on any
specific explanations
for evil.
Personality Isn’t Anima and Animus – Jung used to believe in Jung’s ideas have not
Permanent—It’s Personification of the religion, spiritual and been as popular as
Always Changing feminine nature of a cultural ideas. On the Freud’s. This might be
man’s unconscious and other hand, Freud used because he did not
masculine nature of a to be that psychology is write from the layman
woman’s. This an empirical science. and as such his ideas
psychological were not a greatly
bisexuality is a disseminated as
reflection of the Freud’s. It may also be
biological fact that it is because his ideas were
the larger number of a little more mystical
male (or female) genes and obscure, and less
which is the decisive clearly explained.
factor in the
determination of sex.
The Only Real Danger Association – The Jung has a positive On the whole modern
that Exists Is Man linking of ideas, impact on religion. His psychology has not
Himself perceptions, etc. theories tell that viewed Jung’s theory of
according to similarity, religion plays a key role archetypes kindly.
coexistence, opposition, in individual Ernest Jones (Freud’s
and causal dependence. development. On the biographer) tells that
Free association in other hand, Freud Jung “descended into a
Freudian dream rejected the idea of pseudo-philosophy out
interpretation: religion and spirituality. of which he never
spontaneous ideas He believes religion emerged” and to many
occurring to the should be separate his ideas look more like
dreamer, which need from the research and New Age mystical
not necessarily refer to the psychological. speculation than a
the dream situation. scientific contribution
to psychology.
Belief Follows Complex-indicators – Jung used to practice Jung’s research into
Evidence Prolonged reaction twice a week. On the ancient myths and
time, faults, or the other hand, Freud used legends, his interest in
idiosyncratic quality of to practice regularly. He astrology and
the answers when the sees his patient six fascination with
stimulus words touch sessions in a week. Eastern religion can be
on complexes which the seen in that light, it is
subject wishes to hide also worth
or is not conscious of. remembering that the
images he was writing
about have, as a matter
of historical fact,
exerted an enduring
hold on the human
mind.
Man Cannot Stand A Extraversion – Attitude- Jung used to believe in Jung himself argues
Meaningless Life type characterised by having the face to face that the constant
concentration of contact with the recurrence of symbols
interest on the external patient. On the other from mythology in
object. hand, Freud believes personal therapy and
that patients will be in the fantasies of
more comfortable psychotics support the
sharing emotions if they idea of an innate
are facing away from collective cultural
the psychologist and residue. In line with
lying comfortably. evolutionary theory it
may be that Jung’s
archetypes reflect
predispositions that
once had survival
value.
Conscious vs. God-image – A term Jung used to believe Jung’s work has also
unconscious derived from the that dreams can reflect contributed to
Church Fathers, many different aspects mainstream
according to whom the of human life. On the psychology in at least
imago Dei (image of other hand, Freud one significant respect.
God) is imprinted on the believed that dreams He was the first to
human soul. When such could be a distinguish the two
an image is manifestation of an major attitudes or
spontaneously innermost human orientations of
produced in dreams, desire. personality –
fantasies, visions, etc. it extroversion and
is, from the introversion. He also
psychological point of identified four basic
view, a symbol of the functions (thinking,
self, of psychic feeling, sensing, and
wholeness. intuiting) which in a
cross-classification
yield eight pure
personality types.
Determinism vs. free Mandala – Sanskrit for Jung believes that the Psychologists like Hans
will circle. Symbol of the conscious mind Eysenck and Raymond
centre goal, or of the constructively works on Cattell have
self as psychic totality; our emotions. On the subsequently built
self-representation of a other hand, Freud upon this. As well as
psychic process of believes that the being a cultural icon for
centering; production of conscious mind actively generations of
a new centre of crushes our emotions. psychology
personality. This is undergraduates Jung,
symbolically therefore, put forward
represented by the ideas which were
circle, the square, or the important to the
quaternity, by development of
symmetrical modern personality
arrangements of the theory.
number four and its
multiples.
You might also like
- WATKINSDocument12 pagesWATKINSNéstor GrandaNo ratings yet
- LarideDocument3 pagesLaridelouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- Model of Behaviourn 56Document17 pagesModel of Behaviourn 56expend finNo ratings yet
- Vanvliet2008 Backup BackupDocument13 pagesVanvliet2008 Backup Backupcem hocaNo ratings yet
- Wood 2002Document17 pagesWood 2002Meylana Wulandari P.HNo ratings yet
- Sigmund Freud: A Comparative Summary of Counseling Theories and Methods (35 Points)Document4 pagesSigmund Freud: A Comparative Summary of Counseling Theories and Methods (35 Points)John Erick DinerosNo ratings yet
- Managing Use of SelfDocument8 pagesManaging Use of SelfAnnamariaNo ratings yet
- Theories of Behavior ChangeDocument6 pagesTheories of Behavior ChangeadhisatiaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Disturbed Personal Identity Related To Lows Elf-EsteemDocument3 pagesRisk For Disturbed Personal Identity Related To Lows Elf-EsteemPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Attitude & Values: Prepared By: Mr. Sean G. Dimarunsing Ms. Angela D. SononDocument37 pagesAttitude & Values: Prepared By: Mr. Sean G. Dimarunsing Ms. Angela D. SononSean Dimar0% (1)
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12YZEL ALFECHENo ratings yet
- Her Old 2007Document10 pagesHer Old 2007Ivan FirmandaNo ratings yet
- Managing Use of Self For Masterful Professional PracticeDocument8 pagesManaging Use of Self For Masterful Professional PracticeIshhikaa ShhukllNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Document2 pagesFdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Grape Juice100% (1)
- Atencion y MotivaciónDocument9 pagesAtencion y MotivaciónNICKOLE PATRICIA MARIN DIAZNo ratings yet
- Anger Management A Holistic ApproachDocument8 pagesAnger Management A Holistic ApproachkaustubhniluNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument6 pagesOrganizational BehaviorRishi DubeyNo ratings yet
- Yerushalmi - WitnessDocument16 pagesYerushalmi - WitnessJennyNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento Estudiantes Ensiedad ACT o TCCDocument8 pagesTratamiento Estudiantes Ensiedad ACT o TCCtriple caliberNo ratings yet
- LESSON: The Discipline of Counseling ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLESSON: The Discipline of Counseling ObjectivesREYMARK PERALTANo ratings yet
- HUS 3304 Compare and ContrastDocument5 pagesHUS 3304 Compare and ContrastLydia newmanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Goal Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Goal Implementation Rationale EvaluationFatima C. Malik3181323No ratings yet
- Alzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesAlzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanMary Josette NavarraNo ratings yet
- Rehm1984self ManagmentDocument16 pagesRehm1984self ManagmentPNo ratings yet
- Efecto de Validación e Invalidación Emocional en Individuos Con Dificultades para La Regulación EmocionalDocument5 pagesEfecto de Validación e Invalidación Emocional en Individuos Con Dificultades para La Regulación EmocionalGibran VANo ratings yet
- Motivational and Affective Factors That Influence LearningDocument62 pagesMotivational and Affective Factors That Influence LearningLes Sirc50% (4)
- Directions For Research On Self-Disclosure and Immediacy: Moderation, Mediation, and The Inverted UDocument7 pagesDirections For Research On Self-Disclosure and Immediacy: Moderation, Mediation, and The Inverted UJulio César Cristancho GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Topic:-: Perception & Factors Influencing PerceptionDocument33 pagesTopic:-: Perception & Factors Influencing PerceptionSuraj JayNo ratings yet
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDocument4 pagesEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Hopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesHopelessness: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationJasmineNo ratings yet
- NCP Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesNCP Disturbed Body ImageGyle RaviloNo ratings yet
- AttitudeDocument15 pagesAttitudeAntas KumarNo ratings yet
- Implicit Bias Training ImageryDocument14 pagesImplicit Bias Training ImageryEstela MedinaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of PsychotherapyDocument9 pagesKinds of PsychotherapyMarielle Anne TuazonNo ratings yet
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDocument2 pagesNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Psychologists' Perceptions of Persons With Mental IllnessDocument6 pagesClinical Psychologists' Perceptions of Persons With Mental IllnessdsfasdfNo ratings yet
- Efectos Del Elogio en La Motivación Intrínseca de Los Niños. Revisión SistemáticaDocument22 pagesEfectos Del Elogio en La Motivación Intrínseca de Los Niños. Revisión SistemáticaGibran VANo ratings yet
- David Son Empirical EmotionDocument4 pagesDavid Son Empirical EmotionLeocadio Martin BorgesNo ratings yet
- Adlerian Theory in Group Counseling PDFDocument11 pagesAdlerian Theory in Group Counseling PDFclaudia ruizNo ratings yet
- Attitude Content Structure and Function, How Attitude Influence Behaviour, Attitude Component ModelsDocument10 pagesAttitude Content Structure and Function, How Attitude Influence Behaviour, Attitude Component ModelsGodha KiranaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Risk For Falls (Antepartum)Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Risk For Falls (Antepartum)kaimimiyaNo ratings yet
- A RecapDocument3 pagesA Recapjomelleann.pasolNo ratings yet
- CBT View of Human NatureDocument6 pagesCBT View of Human NatureAliya MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6axcelrosemendozaNo ratings yet
- Midterm ReviewDocument18 pagesMidterm Reviewjms7278No ratings yet
- Methodology and Meaning: Improving Relationship Intelligence With The Strength Deployment InventoryDocument20 pagesMethodology and Meaning: Improving Relationship Intelligence With The Strength Deployment InventorykarimhishamNo ratings yet
- CounselingDocument5 pagesCounselingCathy SabladaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document1 pageLesson 8Rose Ann AlipongaNo ratings yet
- Diss 11 - Discipline of CounselingDocument7 pagesDiss 11 - Discipline of CounselingRochelle Acala Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion Model - Nola JDocument35 pagesHealth Promotion Model - Nola JmajoodhNo ratings yet
- Discipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences - NotesDocument6 pagesDiscipline and Ideas in Applied Social Sciences - NotesSAMANTHA ANN GUINTONo ratings yet
- From Client Process To Therapeutic RelatingDocument15 pagesFrom Client Process To Therapeutic RelatingjeanNo ratings yet
- Attitude Change: Main ArticleDocument12 pagesAttitude Change: Main ArticledakshdeepakNo ratings yet
- The Presented List of Counseling GoalsDocument9 pagesThe Presented List of Counseling GoalsHAKDOGNo ratings yet
- DiassDocument11 pagesDiassPileo Ericha LlaneraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Discipline of CounselingDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Discipline of Counselingryanzeta19No ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCharles Mallari Valdez100% (1)
- Social Work Practice With IndividualsDocument37 pagesSocial Work Practice With Individualsnorjanah arumpacNo ratings yet
- UNDSDocument2 pagesUNDSskyNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence: The Ultimate Guide to Build Healthy Relationships. Learn How to Master your Emotions to Finally improve Your EQ and Social Skills.From EverandEmotional Intelligence: The Ultimate Guide to Build Healthy Relationships. Learn How to Master your Emotions to Finally improve Your EQ and Social Skills.No ratings yet
- Who Is Santiago Alvarez How Come His Writing Is A Primary SourceDocument2 pagesWho Is Santiago Alvarez How Come His Writing Is A Primary SourcePatricia Nolan LopezNo ratings yet
- Strategies To Increase Comprehension and Improve Note-TakingDocument3 pagesStrategies To Increase Comprehension and Improve Note-TakingPatricia Nolan LopezNo ratings yet
- Skinner-Behavioral Analysis Related Research - ReportDocument3 pagesSkinner-Behavioral Analysis Related Research - ReportPatricia Nolan LopezNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis of The Important Historical Information Found in Antonio Pigafetta's First Voyage Around The World.Document3 pagesCritical Analysis of The Important Historical Information Found in Antonio Pigafetta's First Voyage Around The World.Patricia Nolan LopezNo ratings yet