Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Historical Foundations - Ancient Period-1 PDF
Uploaded by
BERNALIN MIRANDA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesThis document summarizes the historical foundations of education in four ancient periods - Primitive, Oriental, Greek, and Roman education. Primitive education aimed to conform individuals to their tribes and ensure survival through practical and theoretical training. Oriental education focused on preserving social stability through moral and theoretical training. Greek education promoted individuality and development through liberal education. Roman education emphasized utilitarianism and trained youth to be good soldiers, workers and citizens through physical, cultural and professional education.
Original Description:
Original Title
Historical Foundations_Ancient Period-1.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the historical foundations of education in four ancient periods - Primitive, Oriental, Greek, and Roman education. Primitive education aimed to conform individuals to their tribes and ensure survival through practical and theoretical training. Oriental education focused on preserving social stability through moral and theoretical training. Greek education promoted individuality and development through liberal education. Roman education emphasized utilitarianism and trained youth to be good soldiers, workers and citizens through physical, cultural and professional education.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesHistorical Foundations - Ancient Period-1 PDF
Uploaded by
BERNALIN MIRANDAThis document summarizes the historical foundations of education in four ancient periods - Primitive, Oriental, Greek, and Roman education. Primitive education aimed to conform individuals to their tribes and ensure survival through practical and theoretical training. Oriental education focused on preserving social stability through moral and theoretical training. Greek education promoted individuality and development through liberal education. Roman education emphasized utilitarianism and trained youth to be good soldiers, workers and citizens through physical, cultural and professional education.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
PHILIPPINE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
The National Center for Teacher Education
College of Flexible Learning and ePNU
Taft Avenue cor. Ayala Blvd., Ermita, Manila
cflex@pnu.edu.ph317-1768 local 776
The FUTURE is NOW.
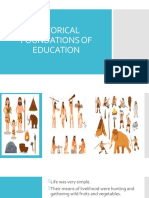
HISTORICAL FOUNDATIONS OF EDUCATION
Ancient Period
I. Education for Conformity / Primitive Education
Features Descriptions
Aims 1. To survive
2. To conform to the tribe to which they belong
Types 1. Practical Education – work activities necessary to stay alive a.k.a
vocational education and domestic training
2. Theoretical Education – spiritual and worship activities, social
knowledge on customs, rites of his social groups a.k.a. intellectual
education and religious training
Contents • Ritualistic and prescriptive
Agencies 1. The family was the center for practical training.
2. Father taught the boys duties of securing life.
3. Mother instructed the girls the duties of household management.
Organization • No levels of instruction
Methods 1. Tell me and show me (observation and imitation)
2. Organic
3. Trial and error
4. Enculturation
5. Indoctrination
Effects 1. Culture was passed on and preserved for generation.
2. People were able to adjust and adapt to political and social life.
3. Tribes were able to meet their economic needs and were able to
survive.
Proponent • Primitives
II. Education for the Preservation of Social Stability / Oriental Education
Aims • To impress traditional ideas and customs in order to maintain and
perpetuate the long established social order (based on the theories of
recapitulation and complacency)
China: To preserve and perpetuate ancestral tradition
India: To preserve the caste system
Egypt: To preserve religious tradition
Persia: To strengthen military tradition
Prepared for E-EDUC1 CTP ONLINE Students_Term1_SY 2021-2022
PHILIPPINE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
The National Center for Teacher Education
College of Flexible Learning and ePNU
Taft Avenue cor. Ayala Blvd., Ermita, Manila
cflex@pnu.edu.ph317-1768 local 776
The FUTURE is NOW.
Types 1. Moral Training – training in customs, duties and polite behavior
(ethical aspect of discipline)
2. Theoretical Training – language and literature
Contents • Reading, writing, arithmetic, and religion
Agencies 1. Home as center for most ethical and social training.
2. Others are pagoda, temple, covered sheds
Organization • Elementary and high school levels
Methods • imitation, memorization
Effects 1. Development of static and highly formal educational system.
2. Learning is mechanical.
3. Individual development becomes impossible
4. Produced individuals who are patient, obedient, gentle, polite,
submissive and respectful but lacking in ambition, self-confidence,
responsibility, initiativeness and resourcefulness.
5. Ideal for those who oppose change.
6. Traditions were perpetuated.
7. Citizens were easily integrated to social life.
Proponents • Orientals
III. Education for the Development of Individuality / Greek Education
Aims • To promote individual success and welfare through the harmonious
development of the various aspects of human personality
Spartan: To develop a good soldier in each citizen
Athenian: To perfect man (body and mind) for individual excellence
needed for public usefulness
Greek educational theorists: Socrates – truth
Plato – justice
Aristotle – happiness
Types 1. Spartan - Military and physical training
2. Athenian - Liberal education
Contents 1. Spartan - Military activities and practices
2. Athenian - Music, lyre, and flute playing; physical education; military
exercises
Agencies State
Organization A. Spartan
Birth to 7 yrs old – training at home
7 to 18 yrs old – military training
Prepared for E-EDUC1 CTP ONLINE Students_Term1_SY 2021-2022
PHILIPPINE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
The National Center for Teacher Education
College of Flexible Learning and ePNU
Taft Avenue cor. Ayala Blvd., Ermita, Manila
cflex@pnu.edu.ph317-1768 local 776
The FUTURE is NOW.
18 to 20 yrs old – warfare training; receives oath of allegiance
30 yrs old –becomes full-fledged citizen; is required to marry
B. Athenian
1.Home (G); Private schools (B)
2. State
Methods 1. Spartan - Competition and rivalry
2. Athenian - Principle of individuality
Effect • Emphasized the complimentary development of the human
personality for his cultural improvement and for social
transformation of the State
Proponents • Greeks
IV. Education for Utilitarianism / Roman Education
Aims • To educate the Roman youth for realizing national ideals
Early Romans: Vir bonus (good soldier, good worker, good citizen)
Later Romans: Linguistic facility (oratory)
Types • Physical training (martial arts, use of war weapons)
Contents 1. Cultural – liberal arts, rhetoric, dialectic, geometry, music
2. Professional – law, medicine, architecture
Agency • Military camps (emphasizes courage, bravery, manliness, honesty,
reverence,
obedience)
Organization/Methods 1. Elementary – memorization, imitation
2. Secondary – literary exercises, intensive drill on speech, grammar
Effects 1. Introduced the concept of educational ladder
2. Produced a nation of doers
Proponents • Romans
Prepared for E-EDUC1 CTP ONLINE Students_Term1_SY 2021-2022
You might also like
- Education During The Ancient Period PDFDocument3 pagesEducation During The Ancient Period PDFBERNALIN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Handbook of Intercultural Training: Area Studies in Intercultural TrainingFrom EverandHandbook of Intercultural Training: Area Studies in Intercultural TrainingNo ratings yet
- 2 - History of EducationDocument114 pages2 - History of Educationjade tagabNo ratings yet
- Foundation of EducationDocument68 pagesFoundation of EducationIvy Hjelca Sanoria SelencioNo ratings yet
- Ed 112 Unit 2 Lesson 1Document6 pagesEd 112 Unit 2 Lesson 1Arlene Culagbang GuitguitinNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Education: CompetenciesDocument23 pagesFoundations of Education: CompetenciesInvincibleReineNo ratings yet
- Comparative of Education: Laconsolacion University PhilippinesDocument50 pagesComparative of Education: Laconsolacion University PhilippinesHajjieCortezNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation in EducationDocument6 pagesHistorical Foundation in EducationCarmina PateniaNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document7 pagesGroup 1qfeedtbzNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer Combined 136pages 3mbDocument172 pagesLET Reviewer Combined 136pages 3mbjade tagab100% (1)
- NotesDocument6 pagesNotesdelacruz.jghNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument9 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationNelson Santillan100% (1)
- LET Reviewer Combined 136pages 3mbDocument136 pagesLET Reviewer Combined 136pages 3mbEngineerEducator100% (24)
- Buhawe JennicelDocument40 pagesBuhawe Jennicelfrank vergNo ratings yet
- Foundation of EducationDocument198 pagesFoundation of EducationNiel Vincent Catapang100% (2)
- Guess The PictureDocument39 pagesGuess The Picturefrank vergNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education (: Primitive, Sumerian and Early Egyptian Education)Document111 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education (: Primitive, Sumerian and Early Egyptian Education)Angelica SantiagoNo ratings yet
- The Historical Foundation of EducationDocument54 pagesThe Historical Foundation of EducationEstela Marie Damian DiuyanNo ratings yet
- History of Education Topic 2 and 4Document33 pagesHistory of Education Topic 2 and 4Mejah GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Primitive EducationDocument7 pagesPrimitive EducationAn Jannette Almodiel83% (6)
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument7 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationRamie Arana Bag-ao IIINo ratings yet
- FOUNDATIONS-OF-EDUCATION - AnsweredDocument18 pagesFOUNDATIONS-OF-EDUCATION - Answeredmichelle dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Presenter: Darlene D. DavidDocument27 pagesPresenter: Darlene D. DavidDarlene Dacanay DavidNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument26 pagesFoundations of EducationDom Martinez100% (1)
- PNU Professional Education ReviewerDocument42 pagesPNU Professional Education ReviewerMhar Ariz Marino100% (2)
- PNU LET Reviewer For Professional EducationDocument382 pagesPNU LET Reviewer For Professional EducationMae FuntanarNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Education Chapter 1Document94 pagesFoundations of Education Chapter 1Sheilla Mae Baclor Bacudo100% (4)
- Ancient To Roman EducationDocument5 pagesAncient To Roman EducationJonie Abilar100% (1)
- Foundations of Education - Content OnlyDocument22 pagesFoundations of Education - Content Onlymarvin moscaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Historical Foundations of EducationDocument34 pagesModule 1 Historical Foundations of EducationKim GallegoNo ratings yet
- HOMBRE Early Egyptian EducationDocument34 pagesHOMBRE Early Egyptian EducationEn Cy100% (1)
- Prof. Ed PDFDocument194 pagesProf. Ed PDFJay BautistaNo ratings yet
- Educ198 ReviewerDocument5 pagesEduc198 ReviewerJoyce MacerianoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument8 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationAlvin PatiñoNo ratings yet
- 2009 Let-Prof Ed.Document83 pages2009 Let-Prof Ed.Jealyn FloresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3. Historical FoundationDocument10 pagesChapter 3. Historical FoundationJohna BelardoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of EducationDocument82 pagesHistorical Foundations of EducationDulnuan CrizamaeNo ratings yet
- Historical Matrix: SANTOS, Rocel Angela B. (OBTEC) I-20 Mr. Jerick C. FerrerDocument16 pagesHistorical Matrix: SANTOS, Rocel Angela B. (OBTEC) I-20 Mr. Jerick C. FerrerJuan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PROF. ED. 103 Handout 2Document2 pagesPROF. ED. 103 Handout 2Franchesca Ashley Marie BasilioNo ratings yet
- Moncast: The Teacher and The CurriculumDocument21 pagesMoncast: The Teacher and The CurriculumElay SabordoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Philippine Popular CultureDocument18 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Philippine Popular CultureLemhar DayaoenNo ratings yet
- DPE 101 Foundation of Education 2 DoneDocument14 pagesDPE 101 Foundation of Education 2 DoneWilmer UnabiaNo ratings yet
- BeginningsAndHistoricalFoundationsOfEducation AQUINO EDC201Document96 pagesBeginningsAndHistoricalFoundationsOfEducation AQUINO EDC201Eugene Jay AquinoNo ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument96 pagesFoundations of EducationJhazzy Jay ReyesNo ratings yet
- 4-Historical Foundations of Education: Edit 0 3Document10 pages4-Historical Foundations of Education: Edit 0 3Dyanne de JesusNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundations of Education: Laguna State Polytechnic University Los Ba Os CampusDocument15 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education: Laguna State Polytechnic University Los Ba Os CampusMarvin Marco100% (1)
- Historical Foundations of Education PandanDocument40 pagesHistorical Foundations of Education Pandanpaulinmae888No ratings yet
- Christ The King College: Graduate SchoolDocument6 pagesChrist The King College: Graduate SchoolRyan Barrel ZubiagaNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Document13 pagesHistorical Foundation of Education: Unit 2Marilyn BersolaNo ratings yet
- Articles On Comparative EducationDocument8 pagesArticles On Comparative EducationRobert TerradoNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of Education Lecture No. 2Document29 pagesHistorical Foundation of Education Lecture No. 2Abigail PanesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Two Education in Ancient TimeDocument10 pagesLesson Two Education in Ancient TimeIan OjiwahNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Foundation of Education 2Document47 pagesTerm Paper - Foundation of Education 2bernadeth felizarteNo ratings yet
- Primitive EducationDocument5 pagesPrimitive EducationJesus Valenzona Jr.No ratings yet
- Foundations of EducationDocument24 pagesFoundations of EducationRaizyl Duque100% (2)
- Major in EnglishDocument137 pagesMajor in EnglishGerry BunaoNo ratings yet
- SG 1 Assignment 1 2 3Document10 pagesSG 1 Assignment 1 2 3Allen Kurt RamosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For History of Philippine EducationDocument7 pagesReviewer For History of Philippine EducationEllamae AlamoNo ratings yet
- Teaorg ReviewerDocument5 pagesTeaorg ReviewerAlfonso Jr QuindozaNo ratings yet
- SwahiliDocument7 pagesSwahiliMohammedNo ratings yet
- This I BeleiveDocument3 pagesThis I Beleiveapi-708902979No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document38 pagesChapter 1Kurt dela Torre100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 4Document6 pagesLesson Plan 4Lilay Barambangan100% (3)
- 20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoDocument3 pages20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoJerome LeañoNo ratings yet
- US of GIT of CattleDocument13 pagesUS of GIT of CattlesangeetsamratNo ratings yet
- Clause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseDocument1 pageClause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseTieng HuangNo ratings yet
- GnatusDocument36 pagesGnatusNacer Mezghiche100% (1)
- Internship Proposal FormDocument3 pagesInternship Proposal FormMuhammad FidaNo ratings yet
- Enga10 Speaking Test3Document2 pagesEnga10 Speaking Test3luana serraNo ratings yet
- Content Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)Document6 pagesContent Kartilya NG Katipunan: Kataastaasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan NG Mga Anak NG Bayan)AngelaNo ratings yet
- Learning Module 4 - BARTENDINGDocument34 pagesLearning Module 4 - BARTENDINGivy mae flores67% (3)
- PEOPLE v. ROBERTO QUIACHON Y BAYONADocument11 pagesPEOPLE v. ROBERTO QUIACHON Y BAYONAMarkNo ratings yet
- Sample Invoice PDFDocument3 pagesSample Invoice PDFMarcus OlivieraaNo ratings yet
- Checklist-Telephone - Mobile ExpenseDocument2 pagesChecklist-Telephone - Mobile ExpenseMichelle Domanacal UrsabiaNo ratings yet
- (Bible in History - La Bible Dans L'histoire 8) John T. Willis - Yahweh and Moses in Conflict - The Role of Exodus 4-24-26 in The Book of Exodus-Peter Lang International Academic Publishers (2010)Document244 pages(Bible in History - La Bible Dans L'histoire 8) John T. Willis - Yahweh and Moses in Conflict - The Role of Exodus 4-24-26 in The Book of Exodus-Peter Lang International Academic Publishers (2010)Anonymous s3LTiHpc8100% (2)
- Engineering Discourse Communities RMDocument4 pagesEngineering Discourse Communities RMapi-336463296No ratings yet
- Entrep Module 4 Q1 Week 4 1Document14 pagesEntrep Module 4 Q1 Week 4 1VirplerryNo ratings yet
- WearebecausewebelongDocument3 pagesWearebecausewebelongapi-269453634No ratings yet
- Region XiDocument2 pagesRegion XiGarcia, Rafael Rico O.No ratings yet
- 1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionDocument32 pages1 SAP HCM Overview - IntroductionashwiniNo ratings yet
- Soil MechDocument21 pagesSoil MechAhsan AbbasNo ratings yet
- Celebrations Around The WorldDocument3 pagesCelebrations Around The WorldpaolaNo ratings yet
- Rawson Homes Duplex DesignsDocument16 pagesRawson Homes Duplex DesignsJhondy TibubosNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2019 (Online) Phase-2Document22 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For JEE (MAIN) - 2019 (Online) Phase-2Manila NandaNo ratings yet
- R Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35Document232 pagesR Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35gonzalo_barandiarán83% (6)
- Sen Çal KapımıDocument9 pagesSen Çal KapımıMa Gabriela Ojeda CasellaNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Timein AmericaDocument335 pagesOnce Upon A Timein Americaqwerty-keysNo ratings yet
- Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument16 pagesCase Study of AmoebiasisGlorielle ElvambuenaNo ratings yet
- Thesis TopicsDocument9 pagesThesis TopicsInayath AliNo ratings yet