Professional Documents
Culture Documents
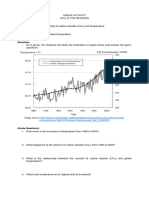
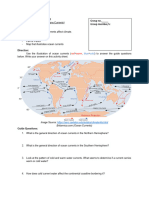
Waves and Optics
Uploaded by
BANAYO, ROYETH D.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views1 pageWaves and Optics
Uploaded by
BANAYO, ROYETH D.Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Reviewer in Modern Physics (Waves and Optics) Reviewer in Modern Physics C: A spaceship approaches the Moon, traveling at 0.
C: A spaceship approaches the Moon, traveling at 0.5c with respect to
➢ Three ways in which light can travel from a source to Einstein’s First Postulate: The first postulate upon which Einstein the Moon. Its crew shines a laser at the Moon. The beam strikes a lunar
based the theory of special relativity relates to inertial reference frames. mirror and is reflected back to the ship. The crew on the ship will
another location:
Inertial frame of reference: is a reference frame in which a body at rest measure the speed of the reflected beam to be
- come directly from the source through empty space; remains at rest and a body in motion moves at a constant speed in a Acceleration and velocity both change: In a uniform circular motion
- light can travel through various media; straight line unless acted on by an outside force. C: A spaceship, moving away from the Earth at a speed of 0.9c, fires a
- light can also arrive after being reflected, such as by a mirror. Einstein’s Second Postulate: The second postulate upon which Einstein light beam backward. An observer on Earth would see the light arriving
Ray: comes from mathematics and here means a straight line based his theory of special relativity deals with the speed of light. at a speed of
that originates at some point. Michelson-Morley experiment: demonstrated that the speed of light in Just the same: According to the special theory of relativity, what will
a vacuum is independent of the motion of the Earth about the Sun. you notice about your own pulse rate if you travel at a very high speed?
Geometric Optics: Part of optics, where the ray aspect of light
Time dilation: is the phenomenon of time passing slower for an observer 0.60 c: A train has a rest length of 100 m. Traveling at a very high
dominates. who is moving relative to another observer. velocity, it goes through a tunnel of length 80 m.
The Law of Reflection: The angle of reflection equals the angle of Proper time: is the time measured by an observer at rest relative to the Simple Harmonic Motion: The equation, x = a cos (ωt + f) represents
incidence. event being observed. Time and space are two closely-related concepts that are dependent
Refraction: The changing of a light ray’s direction (loosely called Proper length: is the distance between two points measured by an on each other: Which of the following statements is consistent with the
bending) when it passes through variations in matter is called observer who is at rest relative to both of the points. general theory of relativity?
Length contraction: is the shortening of the measured length of an When it interacts with matter: When does light behave as if it were a
refraction.
object moving relative to the observer’s frame. wave phenomenon?
may or may not be seen at the same time: Two meteorites are seen to Is converted to Energy: When two light atoms fuse together, mass
strike two distant locations at the same time. As seen from a different It will be shorter: While the spaceship is still at rest on earth, a woman
location, the two lightning bolts. on board finds that a wooden rod she is carrying is 1 meter long.
the same for all nuclei: The binding energy per nucleon is Remains the same: If you consider a blinking light source that is
The length of the rod remains the same: The length of a rod seems receding an observer, what happens to its speed?
shorter to an observer when it moves in a specific direction. What change Momentum: There is an upper limit on the speed of a particle. This
would he observe when the direction of rod changes by 180°? means that there is also an upper limit on its
Smaller: Relative to the sum of the masses of its constituents, the mass Iron: The element whose nuclei contain the most tightly bound nucleon
of nucleus is is
c but at a shorter wavelength: A spaceship, moving toward the Earth Zero: The decay of a sample of radioactive atoms is studied by observers
at a speed of 0.9c, shines a green laser at Earth. An observer on Earth moving in different ways. One moves at 0.8c, another at 0.5c, another at
would see the light arriving at a speed of 0.25c, and one at speed zero with respect to the sample.
remains the same: If you consider a blinking light source that Observed when speeds are near the speed of light: The term
approaches an observer, what happens to its speed? "relativistic" refers to effects that are
Increases: If you consider a blinking light source that approaches an Decreases: If you consider a blinking light source that is receding an
observer, what happens to its frequency? observer, what happens to its frequency?
Everyday Low Speeds: Under what conditions do relativity equations The same: How does the relativistic momentum of a fast-moving body
for length, mass, and time hold true? compare to the momentum (mv) of the same body according to classical
Increases: If you consider a blinking light source that approaches an physics?
observer, what happens to its wavelength? Move at a constant speed: According to the special theory of relativity,
The clock at the top: Which clock ticks faster, the clock at the bottom all laws of nature are the same in reference frames that:
of a skyscraper or another clock at the top? 6,000 m: Starship "Alpha" is traveling at 0.8c (γ = 5/3) with respect to
TIR: The incident angle θ1 is greater than the critical angle. The binding energy per nucleon is least for nuclei of intermediate the identical starship "Beta." Each starship has rest length 10,000 m.
Dispersion: is defined as the spreading of white light into its full size: Nuclear fission and fusion reactions give off energy because
spectrum of wavelengths.
You might also like
- Phy-3 Mod1Document28 pagesPhy-3 Mod1Fattah AbuNo ratings yet
- AST201 Midterm ReviewDocument4 pagesAST201 Midterm ReviewshaharyarNo ratings yet
- Review in Modern Physics (Waves and OpticsDocument2 pagesReview in Modern Physics (Waves and OpticsBANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Optics-1Document66 pagesLesson 7 Optics-1bloomNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 21 - Special Theory of RelativityDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 21 - Special Theory of RelativityGerry Lou QuilesNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument40 pagesObjectivesEunielyn SecretoNo ratings yet
- Relativity PPDocument17 pagesRelativity PPAlexandra AxînteiNo ratings yet
- Senior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsDocument8 pagesSenior High School A.Y 2020 - 2021 Modern Physics: RELATIVITY I. Modern PhysicsKyle Cedric MitalNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of LightDocument15 pagesDual Nature of LightUriahs Victor75% (4)
- Einstein's Theory of Relativity ExplainedDocument18 pagesEinstein's Theory of Relativity ExplainedKurt Romiel BalitaNo ratings yet
- Laser Cooling of Atoms ExplainedDocument13 pagesLaser Cooling of Atoms ExplainedHamdan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Relativity & Black Holes ExplainedDocument28 pagesRelativity & Black Holes Explainedramakrishna1121No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light and The Laws of Geometric OpticsDocument69 pagesThe Nature of Light and The Laws of Geometric OpticsultimuNo ratings yet
- 12th Class Chapter 19 NotesDocument25 pages12th Class Chapter 19 NotesMatham NarmadaNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics CHP 19Document25 pages12 Physics CHP 19Tahira YasminNo ratings yet
- Physics RelativityDocument26 pagesPhysics RelativityPriyanshu ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 10 - Relativity & Black HolesDocument28 pages10 - Relativity & Black HolesKarthik PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Physics II: Special Theory of RelativityDocument79 pagesPhysics II: Special Theory of RelativityStefan FizykNo ratings yet
- ASTRONOMY - Chapter 5 NotesDocument51 pagesASTRONOMY - Chapter 5 NotesJasser ZayyadNo ratings yet
- Let - Modern PhysDocument12 pagesLet - Modern PhysAna MarieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Newton, Einstein and GravityDocument53 pagesChapter 5 - Newton, Einstein and GravityGlobal Mandiri ComputerNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Relativity and ApplicationsDocument7 pagesThe Theory of Relativity and ApplicationsDelson SonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 37 RelativityDocument58 pagesChapter 37 RelativityAnisaNo ratings yet
- Relativity Key ConceptsDocument4 pagesRelativity Key ConceptsOey MirabuenoNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument3 pagesQuantum Physicsaashhs kechuoNo ratings yet
- GNR649_Lecture35_RelativityDocument25 pagesGNR649_Lecture35_RelativityR KumarNo ratings yet
- Institute of Life Long Learning, University of DelhiDocument31 pagesInstitute of Life Long Learning, University of DelhiAlok Kumar Tiwari100% (1)
- TR 15Document20 pagesTR 15tabilinNo ratings yet
- 1 Relativity - Student Copy NewDocument67 pages1 Relativity - Student Copy NewJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- P6Document9 pagesP6Godwin MañasNo ratings yet
- Unit-III: Dr. Vinod Ashokan, NIT JalandharDocument129 pagesUnit-III: Dr. Vinod Ashokan, NIT JalandharGurpreet MeeluNo ratings yet
- Glossary: 1 Physics For The Ib Diploma © Cambridge University Press 2014Document3 pagesGlossary: 1 Physics For The Ib Diploma © Cambridge University Press 2014KhushiNo ratings yet
- 37 RelativityDocument39 pages37 RelativityAdam100% (1)
- Length ContractionDocument6 pagesLength Contractionjagan005No ratings yet
- Special Theory of RelativityDocument19 pagesSpecial Theory of RelativityManchineellu PadmavathiNo ratings yet
- Handout No. 10 in Physical Science: MelcDocument11 pagesHandout No. 10 in Physical Science: MelcDulce J. LuatonNo ratings yet
- C Ru Z: Fourth Dimension Overview & Examples - What Is The FourthDocument8 pagesC Ru Z: Fourth Dimension Overview & Examples - What Is The Fourthmollycule.cutieNo ratings yet
- Nature and Propagation of LightDocument86 pagesNature and Propagation of LightMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument27 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsSachin100% (1)
- Unveiling Special RelativityDocument35 pagesUnveiling Special Relativityanon_573507030No ratings yet
- Modern Physics Chapter 3 6Document56 pagesModern Physics Chapter 3 6Khánh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Theories of LightDocument11 pagesTheories of LightMoa ArmyNo ratings yet
- Q4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 4Document4 pagesQ4 STEM General Physics 2 Week 4lamoks.gamingNo ratings yet
- New Theory of RelativityDocument20 pagesNew Theory of RelativitygkarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Reflection For OpticsDocument1 pageReflection For OpticsI N Z A N I T YNo ratings yet
- UNIT-II (Relativistic Mechanics)Document22 pagesUNIT-II (Relativistic Mechanics)varsha gatlaNo ratings yet
- Relativity Time DilationDocument10 pagesRelativity Time DilationMary Joy BernasolNo ratings yet
- AltEnergy 01Document49 pagesAltEnergy 01Drago MelovNo ratings yet
- Modern Physics ModuleDocument111 pagesModern Physics ModuleMichael EsmallaNo ratings yet
- EMERSON COY - PHD - THESISDocument23 pagesEMERSON COY - PHD - THESISAtifAwanNo ratings yet
- Core KnowledgeDocument20 pagesCore KnowledgeJason WolfeNo ratings yet
- Special Relativity Theory ExplainedDocument10 pagesSpecial Relativity Theory ExplainedManish GulatiNo ratings yet
- Lorentz TransformationDocument19 pagesLorentz TransformationSehrish MalikNo ratings yet
- Light EditedDocument41 pagesLight Editedmarc daniel ortizNo ratings yet
- Light Properties and Interactions in 40Document3 pagesLight Properties and Interactions in 40Rhonoelle Reevenujlah100% (1)
- NotesDocument65 pagesNotessureshmohanty.sailNo ratings yet
- Special RelativityDocument18 pagesSpecial RelativityNeil Venci Dale Gao-ayNo ratings yet
- Light and Optics Historical Background: Towards The Normal. (FAST)Document3 pagesLight and Optics Historical Background: Towards The Normal. (FAST)JefrilAmboy100% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 1C: Special Relativity and the Physics of LightFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 1C: Special Relativity and the Physics of LightNo ratings yet
- 5 - (CO2 Is The Reason!)Document1 page5 - (CO2 Is The Reason!)BANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- 10 - (Constellations Visible in The Northern Hemisphere)Document1 page10 - (Constellations Visible in The Northern Hemisphere)BANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- 9 - (Diff. Star Patterns Throughout The Year)Document1 page9 - (Diff. Star Patterns Throughout The Year)BANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- 4 - (Identifying Warm and Cold Ocean Currents)Document1 page4 - (Identifying Warm and Cold Ocean Currents)BANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- Banayo, R. - Perfromance Task 1 - Modern PhysicsDocument4 pagesBanayo, R. - Perfromance Task 1 - Modern PhysicsBANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- Reviewing the Teacher as a CurricularistDocument3 pagesReviewing the Teacher as a CurricularistBANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet
- Banayo, R. - Perfromance Task 1 - Modern PhysicsDocument4 pagesBanayo, R. - Perfromance Task 1 - Modern PhysicsBANAYO, ROYETH D.No ratings yet