Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etudes Facile EXP - Copie PDF
Uploaded by
Ritaj NadifeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Etudes Facile EXP - Copie PDF
Uploaded by
Ritaj NadifeCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Bac PC-SVT Prof : Moussaoui Chafik
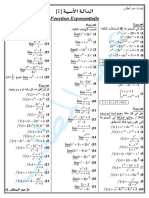
2021-2020 الدوال األسية YouTube : Etudes facile
Exercice 1.: Simplifier : Exercice 6.: Calculer la limite de f en +
−x x+2 1− x x ²+2 x −2 x − x ²
A = e e 2x
; B=e e ; C =e e et −
e 3x
e e 1− x 3x+4
f ( x) = e x +1 ; f ( x) = e − x ; f ( x) = e x ² + x −1
E = 2 x ; F = − x ; G = 2 x+4
e e e x +1 1
2+
x ² −2 x+2
1 2 2 f ( x) = e x²
; f ( x) = e ; f ( x) = e x
I= ; J = −x ; K = x
e 2x
e e Exercice 7.: Calculer les limites :
1
; lim ( x ² − e ) e x
3
13 + x lim e x + 3 x + 2e ; lim 2 − e x +
L = (e )
2 x 10
; M = (e 2+ x 2
) ; N = e x →+ x →−
x x →+
1 ex x xe x − 2
e 2 x e3 x lim 1 − e x ; lim ; lim x ; lim x
O = ( e 2 − x ) e3 x − 4 ; P = e 2 x e − x ; Q =
x →− e + 1
x
2 x →− x →− x x →+ e
(e ) x 4
lim x + + e x ( e x + 1) ; lim
1 x−2 x
.e ; lim
x +1 x
.e
R = ( e x + 1) ; S = ( e x + e − x ) ; T = (e − e )
2 2 x →− 2 x →+ x x →− 2x
2x −x 2
lim x − x + x + 1 ; lim x ( e x − 1) ; lim 2 x ( e x − 1)
x² x 2 2
Exercice 2.: Montrer que : x →+ e e x →+ x →−
e − x (1 + e x ) 1
= 1 ; ( e x + e − x ) − e − x ( e3 x + e − x ) = 2 lim x + e − x ; lim e x + e − x ; lim e x + e − x + 3
2
e (e
x −2 x
+e −x
) x →+ e + 2 x →+ x →−
lim e x + e − x ; lim e x + e− x ;
e ( e x + e − x ) + (e ) = 2e 4 x + 2
2 −x 2
2x x
−e
x →+ x →−
Exercice 8.: Calculer les limites
( e + 1) − ( e − 1) = 1 lim ( x3 − 2 x + 1) e x ; lim ( x ² − e x ) e x ; lim ( x ² − 1) e x
x 2 x 2
e + 2e + 1
2x x
−x
= 1 + e ; x →− x →− x →−
e2 x + e x 4e x
lim x ² − 2 x − e ; lim e − e + 2 ; lim x ² − e 2 x + e x
x 2x x
e x − 1 1 − e− x 2 e x − e− x e2 x − 1 x →+ x →+ x →+
= = 1 − ; = e +1x
xe + 2 x
e + ex −1 2x
e x + 1 1 + e− x e x + 1 e x + e− x e2 x + 1 lim ; lim ; lim
x →+ e x − 1 x →+ e x − 1 x →+ e2 x − 1
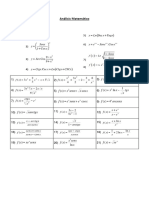
Exercice 3.: Résoudre les équations
e x = e 2 ; e 2 x − e3 = 0 ; e x −1 = e 2 x +3 ; e x ² +1 = e 2 x² + 2 x − 4 xe x + 2 x − 1 e2 x
lim ; lim ; lim
x →+ ex x →+ x² x →− x 3 + x + 1
e x = 3 ; e5 x = −2 ; e x + 2 − 4 = 0 ; e x ² + 3 = 0
ex −1 e x −1 − 1 e2 x + e x − 2
2 x+2 lim ; lim ; lim
e x + 1 1 e 2 x +1 x →0 x x →1 x − 1 x →0 x
= ; = e ; e x −1
=e
ex −1 2 e x −3 ex −1 e x −1 − 1 e2 x + e x − 2 2e x − 1 − 1
3 lim ; lim ; lim ; lim
x →1 x − 1
t 2 − 2t − 3 = 0 ; e 2 x − 2e x − 3 = 0 ; e x − −2 =0 x →0 x x →0 x x →0 x
ex Exercice 9.: Calculer les limites :
Exercice 4.: Résoudre les inéquations e2 x e3 x e4 x e2 x e3 x
lim ; lim 4 ; lim 3 ; lim ; lim
e x e2 ; e2 x − e3 0 ; e x −1 e 2 x +3 ; e x ² +1 e 2 x →+ x ² x →+ x x →+ x x →+ x x→+ x
e x 3 ; e5 x −2 ; e x + 2 − 4 0 ; e x ² + 3 0 lim xe2 x ; lim x 4e3 x ;
x →− x →−
; lim
x →−
− xe 2 x ; lim
x →−
− xe 2 x
Exercice 5.: Etudier le signe des Exercice 10.: Calculer la dérivée de f
expressions suivants dans chaque cas :
e x − 2 ; 2e x − 4 ; 1 − e x ; e x −4 − 1 1
x
x
e 3x
; e 2x
; e 2
; e ; e − x ; e −2 x
3
x ² −4
e−e 2x
; e −1 ;
x
e −2 ; e
x
+ 2 1
−2 x e3 x + e3 x − 2 ; e3 x − e3 x + x ; e3 x − x ² + 1 −
e +1
(e x
+ 1)( e x − 1) ; (e −x
+ 1)( e 2 x − 1) ;
e2 x − 1
x
xe x ; x ²e x ; xe 2 x ; xe x ; xe 2 x
e − 2e
2x x
; ; ;
x −1 x
( x + 2) ex ; ( x ² − 1) e x ; e ; x − 1.e x
x
2 Bac PC-SVT Prof : Moussaoui Chafik
2021-2020 الدوال األسية YouTube : Etudes facile
(e − 2 ) e x ; ( e x − 1) ; ( e 2 x − x ) ; Cas 1 : f ( x) = e x + 2 − 1 ; I = ; f (−2) = 0
2 3
x
ex −1
e −1
x
ex ex e2 x ex 1 x Cas2 : f ( x) = ; I= ; f (0) = 0
; ; ; ; x ; x ex + 1
x x² x x e e
Exercice 16.: Montrer que :
1 e −1
x
x xe − 1
x
−x
; ; x ; 1. f ( x) = e + e est paire
x
e +1
x
e +1 ex
2. f ( x) = x ( e x + e− x ) est impaire
x
Exercice 11.: Etudie les variations de
f et en déduire le signe de f dans chaque 3. x = −1 Est un axe de symétrie pour ( C f )
x +1 − x −1
cas :
, f ( x ) = e + e .
f ( x) = e x − x ; f ( x) = x − e x + 1
4. I (−1;0) Est un centre de symétrie pour
f ( x) = 2e x + x − 2 ; f (0) = 0
f ( x) = e −2 x − x − 1 ; f (0) = 0
( C f ) , f ( x) = ( x + 1) ( ex +1 + e− x −1 )
Exercice 17.: Etudier la continuité de
f ( x) = (1 − x)e x ; f (1) = 0
f en a
Exercice 12.: Etudier la position ex −1
relative de ( C f ) et ( D ) dans chaque cas : • f ( x) =
x
; x0
; a=0
x −1 f (0) = 1
f ( x) = x + ; ( D) : y = x
ex f ( x) = x ² + x − 1 ; x 0
• ; a=0
x f ( x) = xe + 1 ; x 0
x
f ( x) = 1 − x − x ; ( D) : y = 1− x
e −1
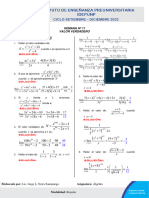
Exercice 18.: Etudier la dérivabilité
1 2e x 1
f ( x) = x − − x ; ( D) : y = x − de à droite de 0 :
2 e +3 2
✓ f ( x) = e x − 1 ; x 0
Exercice 13.: Etudie la convexité de
f (0) = 0
( C f ) dans chaque cas : Exercice 19.: Déterminer le domaine
f ( x) = 1 + x ( e x + 1) ; f ( x) = ( x + 1) e − x + x de définition de f dans chaque cas :
f ( x) = e x ( e x − 4 ) ; x ex ex −1
f ( x) = ; f ( x ) = ; f ( x ) = ln x
Exercice 14.: ex −1 e2 x − 3 e +1
Montrer que l’équation admet une solution f ( x) = ln ( e − 4 ) ; f ( x) = 1 − e ; f ( x) = e 1− x
x x
unique dans I : Exercice 20.: Déterminer les
f ( x) = 2e + x − 3 ; I = 0,1
x
primitives des fonctions suivantes :
f ( x) = ( x − 1)e x − 1 ; I = 1, 2 2e 3 x − e − x 2e x − 4e5 x e x ( e x − 1)
2 ex
(e − 1)
x 2
Exercice 15.:
Répondre aux questions suivantes dans e2 x 2e x ex e x + x²
(e + 1)
chaque cas : 2
ex + 2 3e x + x3
2x
2e x + 1
1. Etudier les variations de f
2. Montrer que la fonction f admet une
fonction réciproque f −1 définie sur un
intervalle J à déterminer
3. Montrer que f −1 est dérivable en 0 et
calculer ( f −1 ) (0)
4. Déterminer l’expression de f −1
You might also like
- Wykres I Wlasnosci Funkcji HomograficznejDocument16 pagesWykres I Wlasnosci Funkcji HomograficznejWikaNo ratings yet
- الدالة الأسية1 PDFDocument1 pageالدالة الأسية1 PDFIslem AklilNo ratings yet
- Ilustracion Fracciones Parciales 2009 1Document6 pagesIlustracion Fracciones Parciales 2009 1Jorge Enrique Zapata AriasNo ratings yet
- Cwiczenia 5Document2 pagesCwiczenia 5HermannNo ratings yet
- Cam A12 Tema2Document45 pagesCam A12 Tema2duduNo ratings yet
- 3 3Document7 pages3 3蔡欣倢No ratings yet
- Cálculoi Ejercicios Dominio LimitesDocument1 pageCálculoi Ejercicios Dominio LimitesRoberto FernandezNo ratings yet
- Granica I Ciągłość Funkcji. Asymptoty Wykresu Funkcji, Ćw. 6,7,8Document3 pagesGranica I Ciągłość Funkcji. Asymptoty Wykresu Funkcji, Ćw. 6,7,8wladyslawNo ratings yet
- 08-Sistemas InecuacionesDocument4 pages08-Sistemas InecuacionesAliciaNo ratings yet
- Ciągi I Funkcje 2022Document1 pageCiągi I Funkcje 2022karolinakucala1985No ratings yet
- EP (C-3) - SolucionarioDocument3 pagesEP (C-3) - Solucionarioalvarojch123No ratings yet
- دالة عددية مع القيمة المطلقةDocument11 pagesدالة عددية مع القيمة المطلقةMohammed DrahmouneNo ratings yet
- Temat 13Document1 pageTemat 13Облік і аудит КНЕУNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Mohamed JaawaneNo ratings yet
- Математика 3 задачи за вежбање-прв дел PDFDocument10 pagesМатематика 3 задачи за вежбање-прв дел PDFTralalaNo ratings yet
- Funkcja Homograficzna - Rozwiązania ZadanDocument14 pagesFunkcja Homograficzna - Rozwiązania Zadanpiotr.game3443No ratings yet
- Zad 09Document1 pageZad 09karolNo ratings yet
- Układy Równań Z OdpDocument2 pagesUkłady Równań Z OdpAdam Jankowski0% (2)
- Listupow TorkaDocument18 pagesListupow TorkaSofía DazaNo ratings yet
- 04programacionlineal PDFDocument44 pages04programacionlineal PDFJUAN AGUSTÍN FRAILE SAN TEODORONo ratings yet
- Tema 4 Programacion LinealDocument44 pagesTema 4 Programacion LineallailaNo ratings yet
- Corrigé Série InéquationsDocument5 pagesCorrigé Série Inéquationsy.baelli05No ratings yet
- Jak Obliczyc Granice Funkcji W PDocument18 pagesJak Obliczyc Granice Funkcji W PWiktoria GiermasińskaNo ratings yet
- TheoriespdfDocument5 pagesTheoriespdfSwam PyaeNo ratings yet
- Podrecznik Nauczyciela Matematyka Zpir Klasa 3 Rozdzial 4Document72 pagesPodrecznik Nauczyciela Matematyka Zpir Klasa 3 Rozdzial 4hannaNo ratings yet
- Examen Calculo IntegralDocument5 pagesExamen Calculo IntegralAnonymous 9QGOeYNo ratings yet
- Inf ME Egzamin Pop 2019-20Document2 pagesInf ME Egzamin Pop 2019-20filipfilxmNo ratings yet
- MAT103 Tws 7Document5 pagesMAT103 Tws 7aheyahNo ratings yet
- Jak Obliczyc Granice Funkcji W PunkcieDocument14 pagesJak Obliczyc Granice Funkcji W PunkcieВалерия ЗаболотнаяNo ratings yet
- رحماني عماد - الموضوع الأسبوعي 03Document6 pagesرحماني عماد - الموضوع الأسبوعي 03نجاري شيماءNo ratings yet
- دﺪﺣ 3 2 lim ; lim 2 6 1 2 − − − + 3 12 lim ; lim 3 2 − − + 2 3 lim ; lim 2 3 2 3 + − − + 1 2 4 2 lim ; lim 2 1 + − + − − −Document2 pagesدﺪﺣ 3 2 lim ; lim 2 6 1 2 − − − + 3 12 lim ; lim 3 2 − − + 2 3 lim ; lim 2 3 2 3 + − − + 1 2 4 2 lim ; lim 2 1 + − + − − −Ismail El MajdoubiNo ratings yet
- Matematyka - ZadaniaDocument6 pagesMatematyka - Zadaniafranchuksofia2005No ratings yet
- LZ Am2aDocument10 pagesLZ Am2aGieniuNo ratings yet
- Guia 1 Integrales Indefinidas 12-3-24Document2 pagesGuia 1 Integrales Indefinidas 12-3-24maricel pozoNo ratings yet
- Cwiczenia 4Document2 pagesCwiczenia 4HermannNo ratings yet
- Inf Nstac AM CW WielFunWymDocument1 pageInf Nstac AM CW WielFunWymMichał DregerNo ratings yet
- 2 Limite de Una Funcion Real de Variable Real Practicas PropuestasDocument5 pages2 Limite de Una Funcion Real de Variable Real Practicas PropuestasmaicolalejandroleyvasandovalNo ratings yet
- Algebra - S11 - Set - Dic 20222Document3 pagesAlgebra - S11 - Set - Dic 20222Gerardo Joel Cahuana GomezNo ratings yet
- Polinomios IIDocument1 pagePolinomios IIEsterNo ratings yet
- Jak Wyznaczyc Rownanie AsymptotyDocument19 pagesJak Wyznaczyc Rownanie AsymptotykacperNo ratings yet
- Guía de Práctica 4Document1 pageGuía de Práctica 4Yhayr UraccahuaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Racionalni Algebarski Izrazi - RješenjaDocument3 pages1.1 Racionalni Algebarski Izrazi - RješenjacyberhoodNo ratings yet
- SIMR AN1 EGZ 2016 02 02a RozwDocument6 pagesSIMR AN1 EGZ 2016 02 02a RozwІрина БіланикNo ratings yet
- CalkiDocument2 pagesCalkiMilkaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de Productos Notables-Ecuaciones-Sistemas de Ecuaciones 1.Document3 pagesEjercicios de Productos Notables-Ecuaciones-Sistemas de Ecuaciones 1.ISABEL67% (3)
- Worksheet - LimitsDocument1 pageWorksheet - LimitsLavanya JindalNo ratings yet
- StrigoDocument3 pagesStrigoabderrahimNo ratings yet
- Derivada de Seno y Coseno Hiperbólico Por La Definición de LimitesDocument2 pagesDerivada de Seno y Coseno Hiperbólico Por La Definición de Limitespachequito162007No ratings yet
- 06b. The Quotient Rule - AnswersDocument3 pages06b. The Quotient Rule - AnswersAmy KambwanjiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Exercises 2Document3 pagesCalculus Exercises 2MikeNo ratings yet
- (3651) Asymptoty I Pochodna Z DefinicjiDocument2 pages(3651) Asymptoty I Pochodna Z DefinicjiradoszczakNo ratings yet
- SIMR AN1 EGZ 2009 02 02b RozwDocument6 pagesSIMR AN1 EGZ 2009 02 02b RozwІрина БіланикNo ratings yet
- Pochodne Funkcji, Ćw. 9,10,11,12,13,14Document6 pagesPochodne Funkcji, Ćw. 9,10,11,12,13,14wladyslawNo ratings yet
- Derivadas CadenaDocument2 pagesDerivadas CadenaPatrik SanchezNo ratings yet
- 6 Uklady RownanDocument3 pages6 Uklady RownanN NNo ratings yet
- Practica PPDocument3 pagesPractica PPCami xdNo ratings yet
- Wda 1 PolyDocument2 pagesWda 1 Polymichal.lompart1No ratings yet
- Solucionario 05 PDFDocument8 pagesSolucionario 05 PDFMarioMaximilianoMaldonadoNo ratings yet