Professional Documents
Culture Documents
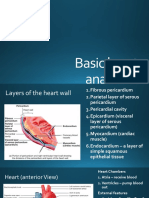
ECG Basics: Wave/Segments Time (Sec.) /form
Uploaded by
Jaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECG Basics: Wave/Segments Time (Sec.) /form
Uploaded by
Jaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleCopyright:
Available Formats
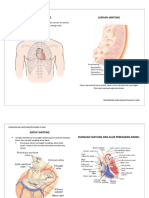
ECGs Made Easy!
ECG Basics
-A recording of the electrical signals created by
actions potentials traveling through the heart.
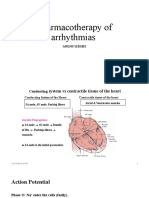
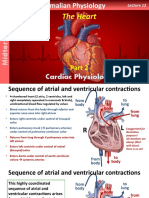
1) P wave—atrial depolarization.
1) Atrial depolarization, initiated by the
SA node, causes the P wave. -PR interval—impulse through atria,
AV node, bundle of His, right/left
bundle branches.
2) PR segment—AV nodal delay. 1
3) QRS complex—ventricular depolarization 2
& atrial repolarization.
2) With atrial depolarization complete, 4) ST segment—Time ventricles contracting 3
the impulse is delayed at the AV node.
and emptying.
5) T wave—ventricular repolarization.
-QT interval-time for ventricular 4
depolarization and repolarization.
6) TP segment—Ventricles relaxing &
3) Ventricular depolarization begins at filling.
apex, causing the QRS complex. Atrial
Systemic Approach repolarization occurs.
1) Determine rhythm and rate.
5
2) Look at P wave. QRS
Complex
3) PR interval duration.
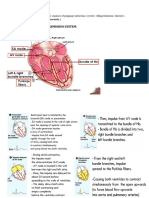
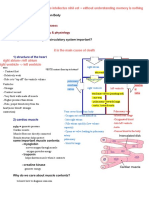
4) QRS interval duration. Conduction System of the Heart
5) QT interval duration. 1) SA node in right atrium repeatedly depolarizes
6) Changes in ST segment & T wave? 4) Ventricular depolarization is complete. to threshold spontaneously triggering action
7) Interpret rhythm (ie A. fib). potentials. Action potential propagates through
PR Interval both atria allowing simultaneous atrial contraction.
Pacemaker Rates ST
2) Action potentials slow considerably passing
-Main pacemaker is the SA node at Segment through the AV node (in the intertribal septum).
0-100 BPM. 3) Atrioventricular (AV) bundle or bundle of His
5) Ventricular repolarization begins at
Secondary pacemaker is the AV apex, causing the T-wave. conduct action potential from atria to ventricle.
junction at 40-60 BPM. PR 4) Right and left bundle branches carry signal
through interventricualr septum to apex.
Segment
Last intrinsic pacemaker are the
Purkinje fibres—20-40 BMP. QT Interval
5) Purkinje fibres conduct potentials from apex
upward. Plateau (maintained depolarization) due to Ca inflow
2+
when voltage-gated slow Ca channels open and K
2+
+
QRS Configuration outflow when some K+ channels open.
Wave Intervals 6) Ventricular repolarization is -Q wave—first negative deflection after P wave.
complete. Repolarization due to
-R wave—first positive deflection after P/Q wave.
Wave/Segments Time (sec.)/Form closure of Ca2+ channels
and K+ outflow when
-S wave—first negative deflection after R wave.
P Wave 0.06-0.12 Rapid depolarization due to additional K+ channels
Na+ inflow when voltage- open.
PR Interval 0.12-0.20 -During the plateau period of steady gated fast Na+ channels
open.
QRS Complex 0.06-0.10 depolarization, the ECG tracing is flat. Remember!
ST Segment Isoelectric -Depolarization towards lead QRS=intraventricular conduction time. QRS
without a P wave means impulse may have
T Wave Upright =positive deflection originated in the ventricles, hints
QT Interval 0.35-0.45 -Depolarization away from lead ventricular arrhythmia.
=negative deflection
You might also like
- A234 ElectrocardiogramsDocument4 pagesA234 Electrocardiogramsramloghun veerNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument15 pagesCardiovascular PhysiologyParker KapembwaNo ratings yet
- Phys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalDocument10 pagesPhys 4.1 CV Heart ElectricalBeverly DatuNo ratings yet
- Sistema de Conduccion Karen Daniela VelascoDocument3 pagesSistema de Conduccion Karen Daniela Velascoapi-540316757No ratings yet
- I. Systematic Approach To ECG InterpretationDocument11 pagesI. Systematic Approach To ECG Interpretationkilladim992No ratings yet
- Ecg TeachingDocument44 pagesEcg TeachingarvindkanagaratnamNo ratings yet
- What Is An ECG?Document23 pagesWhat Is An ECG?Karan PrabaNo ratings yet
- ECG and Einthoven's Triangle Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesECG and Einthoven's Triangle Flashcards - QuizletMr. DybalaNo ratings yet
- Buku Saku Pemeriksaan EkgDocument21 pagesBuku Saku Pemeriksaan Ekgpaskah dhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document29 pagesUnit 1SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding The 12 - Lead ECG, Part 1Document9 pagesUnderstanding The 12 - Lead ECG, Part 1j.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- 4 07introtoecg PDFDocument16 pages4 07introtoecg PDFPatricia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Jantung Lapisan JantungDocument21 pagesAnatomi Jantung Lapisan JantungirineNo ratings yet
- Initiation of Hearbeat Notes STPM TERM 2Document8 pagesInitiation of Hearbeat Notes STPM TERM 2eryna sofeaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction System Power Point PresentationDocument30 pagesCardiac Conduction System Power Point PresentationAaya AdelNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodDocument16 pagesKami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodJada NovakNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias: Thursday, January 17, 2019 1:04 PMDocument3 pagesArrhythmias: Thursday, January 17, 2019 1:04 PMaminath2288No ratings yet
- PharmD 2 Year CVS IntroductionDocument13 pagesPharmD 2 Year CVS IntroductionvarishNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Basic Ecg Interpretation & Procedure: BY: Ahmad Hafiz Bin Alias Universuty Lecturer UniszaDocument26 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation & Procedure: BY: Ahmad Hafiz Bin Alias Universuty Lecturer UniszaLogadarshini VeerasamyNo ratings yet
- Ecg & Arrhythmia Recognition: Dr. Arief Fadhilah, SPJP (K), FihaDocument52 pagesEcg & Arrhythmia Recognition: Dr. Arief Fadhilah, SPJP (K), Fihaalfian zulhakimNo ratings yet
- QuizletDocument7 pagesQuizletSarath kumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding ECG's KingsholmDocument53 pagesUnderstanding ECG's KingsholmBen HarperNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ECGs DoctorialsDocument36 pagesIntroduction To ECGs DoctorialsJaimie Charlotte Marie LangilleNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document106 pagesEcg 2hammad992No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of ArrythmiasDocument68 pagesPharmacotherapy of ArrythmiasABREHAM BUKULONo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias GeneralDocument131 pagesArrhythmias GeneralAnonymous IRl5fn6No ratings yet
- Basic ECG InterpretationDocument62 pagesBasic ECG Interpretationmohannadalkwiese3No ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonDocument41 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonElgeene DizonNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological Properties of Cardiac MyocytesDocument39 pagesElectrophysiological Properties of Cardiac Myocytesapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Elektro Kardio Grafi - Dasar - : DR Eka Ginanjar, SPPDDocument105 pagesElektro Kardio Grafi - Dasar - : DR Eka Ginanjar, SPPDalmiraerickaiNo ratings yet
- Basic ECGDocument14 pagesBasic ECGDexter TurlaNo ratings yet
- ARRHYTHMIADocument8 pagesARRHYTHMIAJan Aerielle AzulNo ratings yet
- Slides Step 1b Assessing The Heart Rhythm NursingDocument7 pagesSlides Step 1b Assessing The Heart Rhythm Nursinggardenstate85No ratings yet
- 191 201 PDFDocument11 pages191 201 PDFDanyal ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Nelec 2: Acute and Critical Care Nursing: Unit Learning OutcomeDocument4 pagesNelec 2: Acute and Critical Care Nursing: Unit Learning Outcomeyas minNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Document5 pagesCardiac Electrophysiology Basics (RL-204-Tn)Navojit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Nclex RN Review Notes 2018 Triple eDocument30 pagesNclex RN Review Notes 2018 Triple eEndla SriniNo ratings yet
- Green Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility PresentationDocument31 pagesGreen Orange Blue Creative Healthcare Facility Presentationshreyamukherjee3009No ratings yet
- Week3-6pptcaridac MuscleDocument7 pagesWeek3-6pptcaridac MuscleSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument17 pagesIlovepdf MergedAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Bagliani G. Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Disease. Javier Antico Gonzalez LopezDocument13 pagesBagliani G. Atrioventricular Nodal Conduction Disease. Javier Antico Gonzalez Lopezsonia isanamiNo ratings yet
- 4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument8 pages4.03 Anti-Arrhythmic Drugs PDFKarl ChavezNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Cardiac PhysiologyDocument37 pagesThe Heart: Cardiac PhysiologyRevanth VejjuNo ratings yet
- MED II 1.01-ECG-and-Arrythmia-RecognitionDocument40 pagesMED II 1.01-ECG-and-Arrythmia-RecognitionCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- CCN Lab (Feu)Document37 pagesCCN Lab (Feu)Ashley Nicole LimNo ratings yet
- SPDX Electrocardiography-EcgDocument6 pagesSPDX Electrocardiography-Ecgdumppotato24No ratings yet
- C9Document15 pagesC9SLKNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceDocument25 pagesBasic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceSoySauceNo ratings yet
- 35 7-PDF EcDocument1 page35 7-PDF EcLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- Criterii EKG Mayo ClinicDocument45 pagesCriterii EKG Mayo ClinicAnca LunguNo ratings yet
- ECG MorphologyDocument36 pagesECG MorphologyMr Joko100% (2)
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Physiological Properties of Cardiac Muscle 2Document12 pagesPhysiological Properties of Cardiac Muscle 2deput_rprNo ratings yet
- Conduction of The HeartDocument1 pageConduction of The HeartPearlyn John BrittoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Types: - Skeletal (Striated) Muscle - Smooth Muscle (Intestines, Blood Vessels, Uterus) - Cardiac Muscle (Exclusively Heart)Document11 pagesMuscle Types: - Skeletal (Striated) Muscle - Smooth Muscle (Intestines, Blood Vessels, Uterus) - Cardiac Muscle (Exclusively Heart)m_sabryNo ratings yet
- Ablation Above The Semilunar Valves: When, Why, and How?: Mahmoud Suleiman, MD, Samuel J. Asirvatham, MDDocument6 pagesAblation Above The Semilunar Valves: When, Why, and How?: Mahmoud Suleiman, MD, Samuel J. Asirvatham, MDkaushikNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrhythmias II: TachyarrhythmiasDocument83 pagesCardiac Arrhythmias II: Tachyarrhythmiasmargareth hoyan SilabanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Ion ChannelsDocument10 pagesCardiac Ion ChannelsDiana GordilloNo ratings yet
- Ghid de Resuscitare Dupa Chirurgia Cardiaca EACTS 2009Document24 pagesGhid de Resuscitare Dupa Chirurgia Cardiaca EACTS 2009Raluca L100% (1)
- History and Background of Quality Measurement: Jonathan Chun, MD Andrea Chao Bafford, MD, FACSDocument5 pagesHistory and Background of Quality Measurement: Jonathan Chun, MD Andrea Chao Bafford, MD, FACSSara MezianeNo ratings yet
- Collagen Film DressingDocument2 pagesCollagen Film DressingRadiika BalamuruganNo ratings yet
- GI Visuals From Emergency Medicine Board Review For Visual LearnersDocument40 pagesGI Visuals From Emergency Medicine Board Review For Visual LearnersIanNo ratings yet
- Gingival Tissue ManagementDocument144 pagesGingival Tissue ManagementMakkapati AmaniNo ratings yet
- Undetectable Hair Transplants by Dr. Ch. Krishna PriyaDocument155 pagesUndetectable Hair Transplants by Dr. Ch. Krishna PriyaKrishna RayaluNo ratings yet
- Four Flower PointsDocument4 pagesFour Flower Pointsgaetanscribd100% (1)
- Coachman Pink QDT 2010 PDFDocument15 pagesCoachman Pink QDT 2010 PDFLunna FariasNo ratings yet
- Information Text by DR Ali EvliceDocument5 pagesInformation Text by DR Ali Evlicehitler88No ratings yet
- Neurocritical Care Review: Practice QuestionsDocument52 pagesNeurocritical Care Review: Practice QuestionsAmitShettyNo ratings yet
- Thromborel SDocument8 pagesThromborel SJoseline Alejandra Bravo Bravo100% (2)
- JOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareDocument3 pagesJOHN CARLO APATAN - Checklist On Tracheostomy CareJOHN CARLO APATANNo ratings yet
- Care - Maintenance of Endoscopy EquipmentDocument109 pagesCare - Maintenance of Endoscopy EquipmentSyed Mohamad FaridNo ratings yet
- 2nd Announcement Pito Xi Makassar 1Document4 pages2nd Announcement Pito Xi Makassar 1Peter SalimNo ratings yet
- Procedure TextDocument3 pagesProcedure Textichakhair100% (1)
- Basic Life Support: Elements of The Survey The SceneDocument5 pagesBasic Life Support: Elements of The Survey The SceneMarrianne MortaNo ratings yet
- What To Do About Extracranial and Intracranial Stenosis: Home About Issues Categories Back Issues Case Reports ContactDocument13 pagesWhat To Do About Extracranial and Intracranial Stenosis: Home About Issues Categories Back Issues Case Reports ContactpramitaListyNo ratings yet
- VenkateshDocument127 pagesVenkateshpriya selvarajNo ratings yet
- Shock 2022 SeminarDocument17 pagesShock 2022 Seminarrosie100% (2)
- Assem Draz: Neurological DisordersDocument26 pagesAssem Draz: Neurological DisordersxuexueNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Obstructive Jaundice by Ultrasonography With MRCP CorrelationDocument32 pagesEvaluation of Obstructive Jaundice by Ultrasonography With MRCP CorrelationSarbesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Scaphoid Fracture (YHT)Document100 pagesScaphoid Fracture (YHT)Mis StromNo ratings yet
- Subcapsular Hematoma of The Liver After Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument3 pagesSubcapsular Hematoma of The Liver After Laparoscopic CholecystectomyCeci M RNo ratings yet
- AA 09.2019 - Perioperative Dextrose Infusion and Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting A Meta-Analysis of Randomized TrialsDocument8 pagesAA 09.2019 - Perioperative Dextrose Infusion and Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting A Meta-Analysis of Randomized TrialsMILTON HALYSONNo ratings yet
- Special Circumstances GuidelinesDocument19 pagesSpecial Circumstances GuidelinesRayNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardDocument5 pagesHemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardFitz JaminitNo ratings yet
- Ref Des Medicaments Cnops 2014Document770 pagesRef Des Medicaments Cnops 2014doxydnitro67% (6)
- Diagnostic Exam Funda ReviewDocument13 pagesDiagnostic Exam Funda Reviewmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Regional Anesthetic Blocks - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesRegional Anesthetic Blocks - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfCarolina SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 5th Edition Scanlon ch01Document28 pagesEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 5th Edition Scanlon ch01ellieNo ratings yet